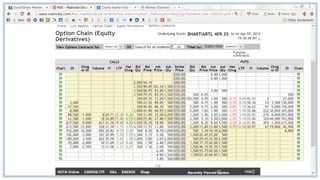
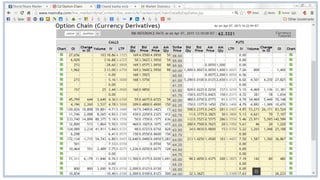
This document discusses futures, options, and derivatives. It defines futures as contracts to buy or sell assets at a specified price and time. Options give the holder the right but not obligation to buy or sell and exist in different types like real, traded, vanilla, and exotic. There are European, American, and Bermuda option models depending on when the contract can be exercised. Options have call and put types. Derivatives are speculative instruments that allow risk management but can also concentrate risk if not used properly.