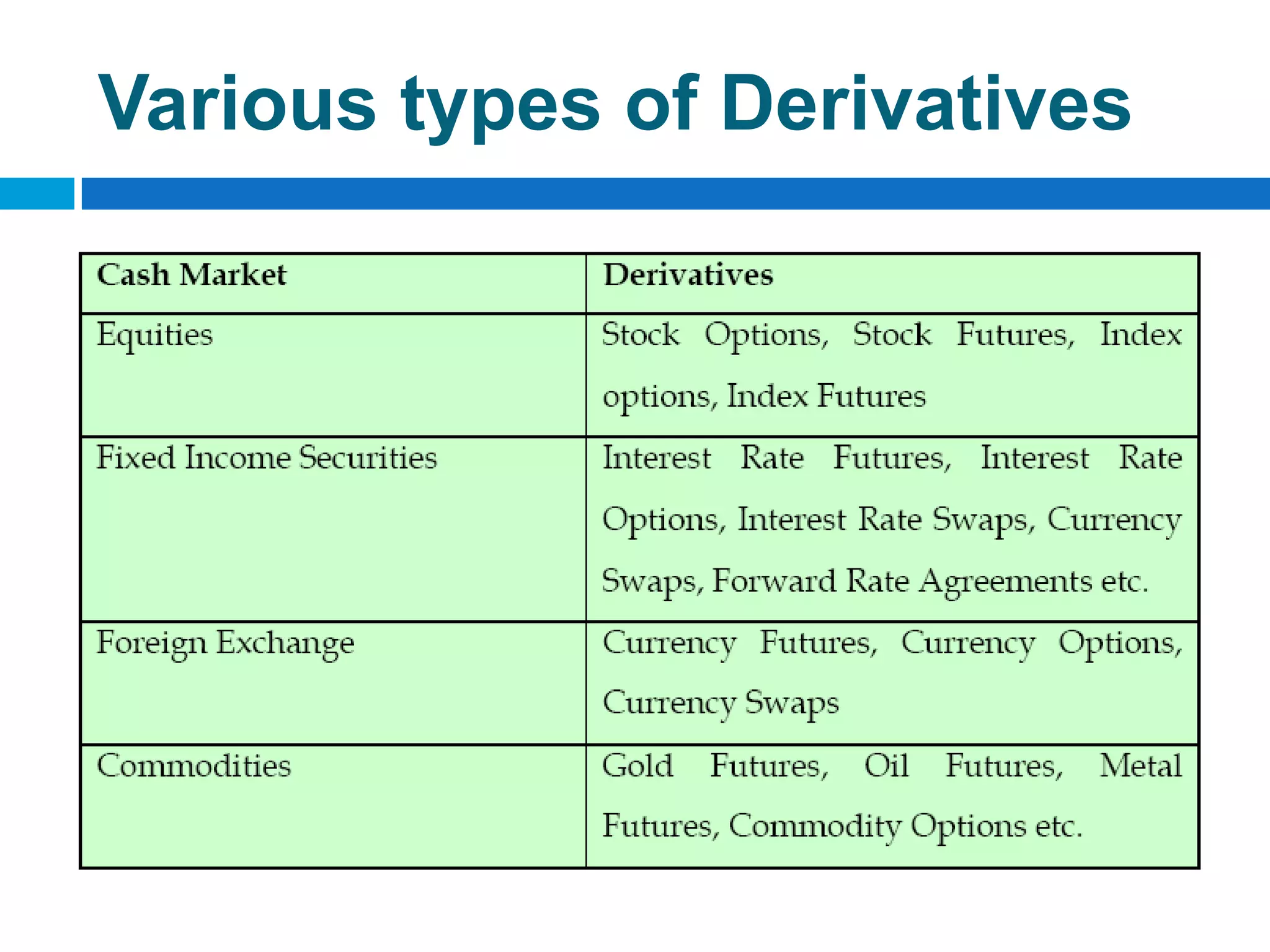
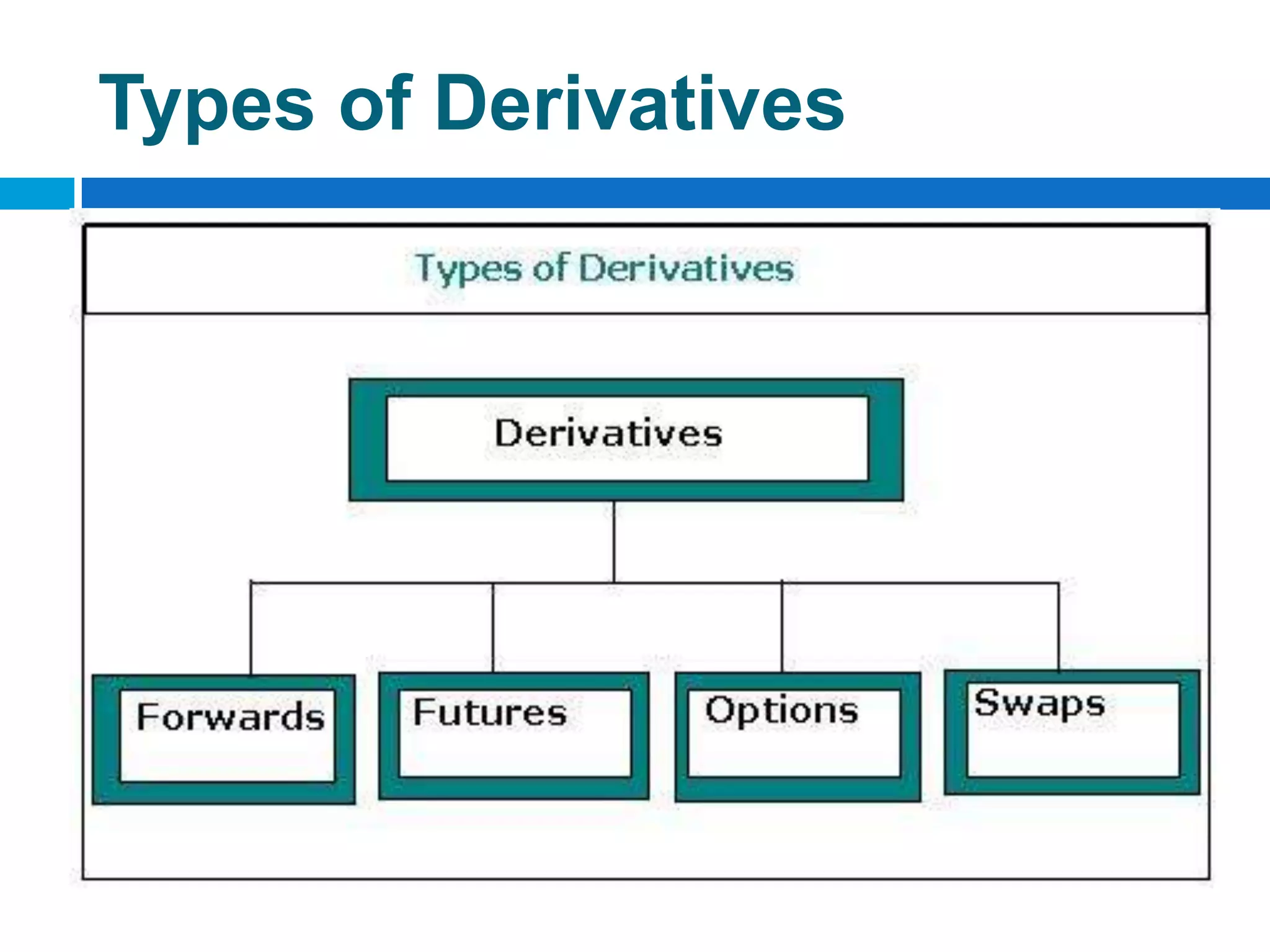
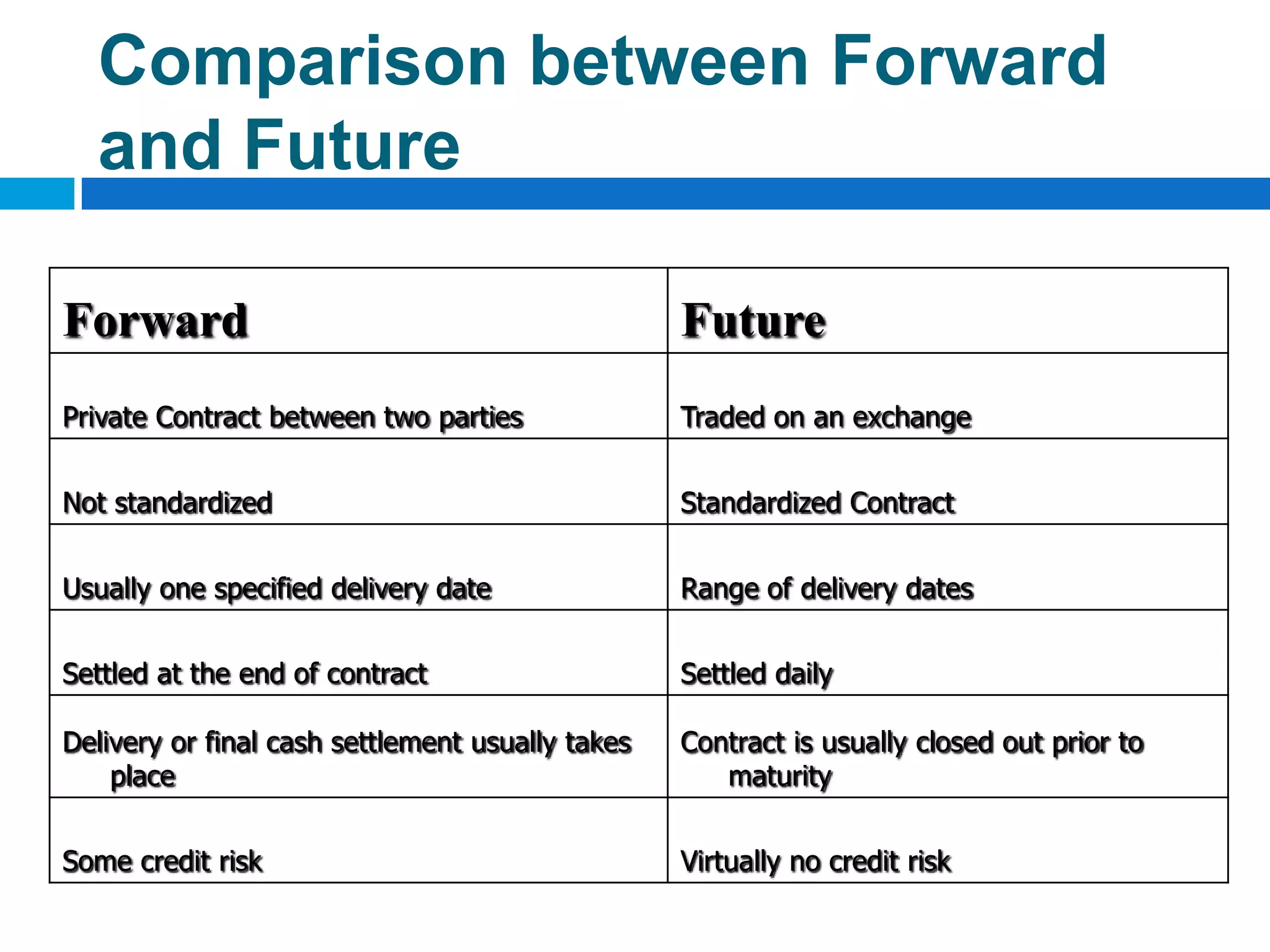
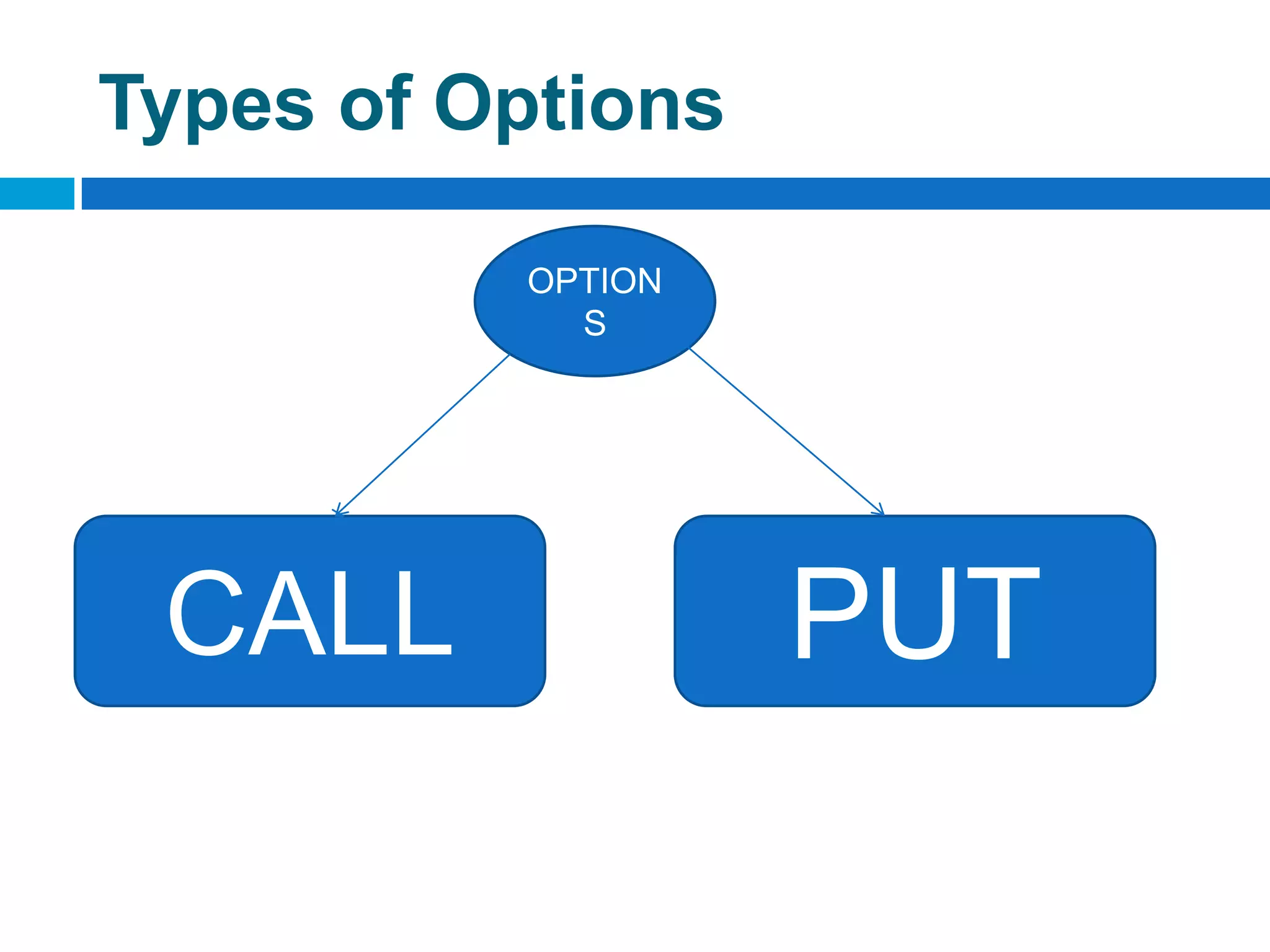
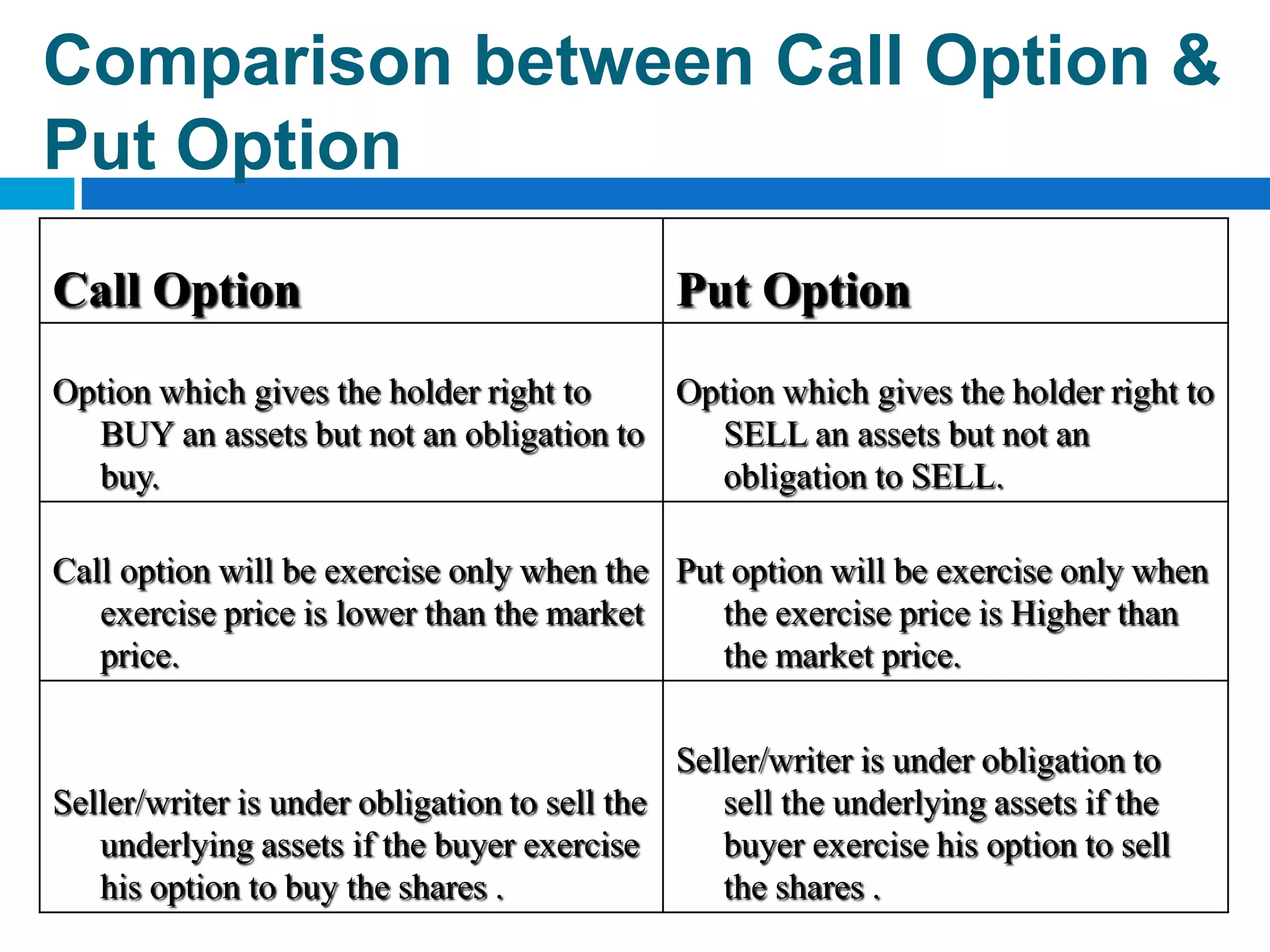
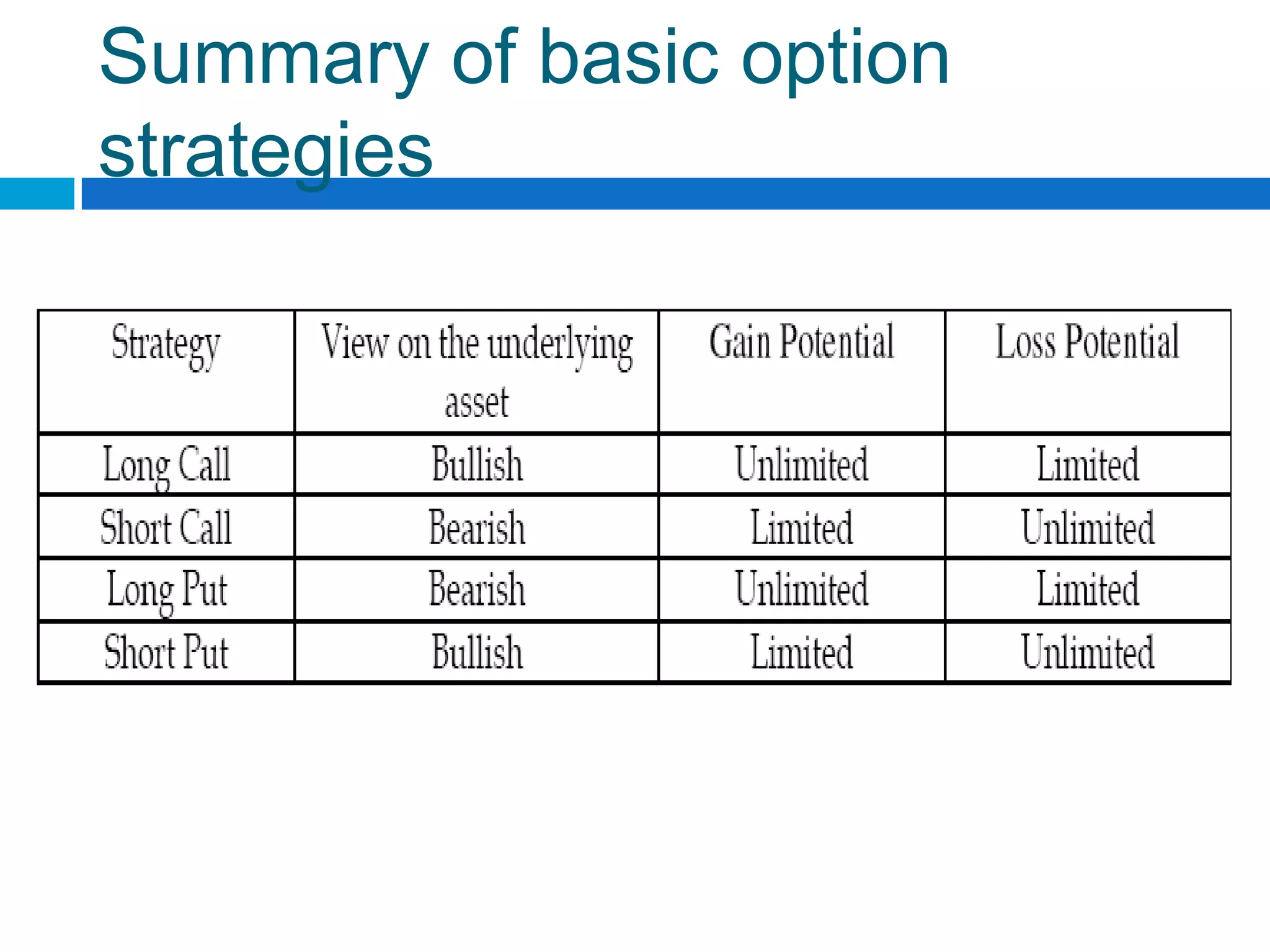
The document discusses derivatives, which are financial instruments whose value is based on an underlying asset. It covers various types of derivatives like futures, forwards, swaps, and options. Futures are standardized contracts to buy or sell an asset at a future date, while forwards involve customized non-standardized contracts. Swaps involve exchanging cash flows between two parties. Options give the holder the right but not obligation to buy or sell the underlying asset.