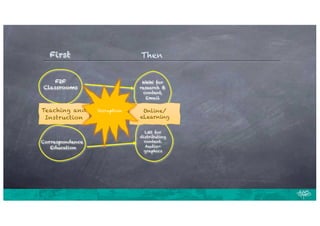
The document discusses the evolution and future of education, emphasizing the shift towards flexible, boundary-less learning environments facilitated by technology. It highlights the importance of self-directed learning, connectedness, and agency among students, while also acknowledging challenges faced during transitions to online learning. Key principles include ubiquity, connectedness, and the need for personalized educational experiences that resonate with individual learner interests.