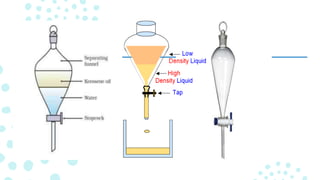
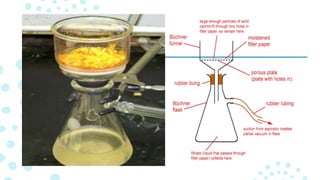
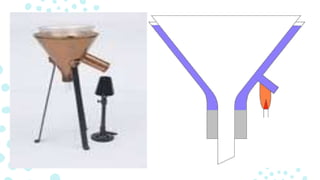
A funnel is a tube or pipe that is wide at the top and narrow at the bottom, used to guide liquids or powders into small openings. Funnels are commonly made of stainless steel, aluminum, glass, or plastic. There are several types of specialized funnels including filter funnels for separating solids from liquids, powder funnels for transferring powders, and separatory funnels for separating mixtures into immiscible solvent phases. Other types include Büchner funnels for vacuum filtration, dropping funnels for slow reagent addition, and eco funnels designed to reduce chemical contamination.