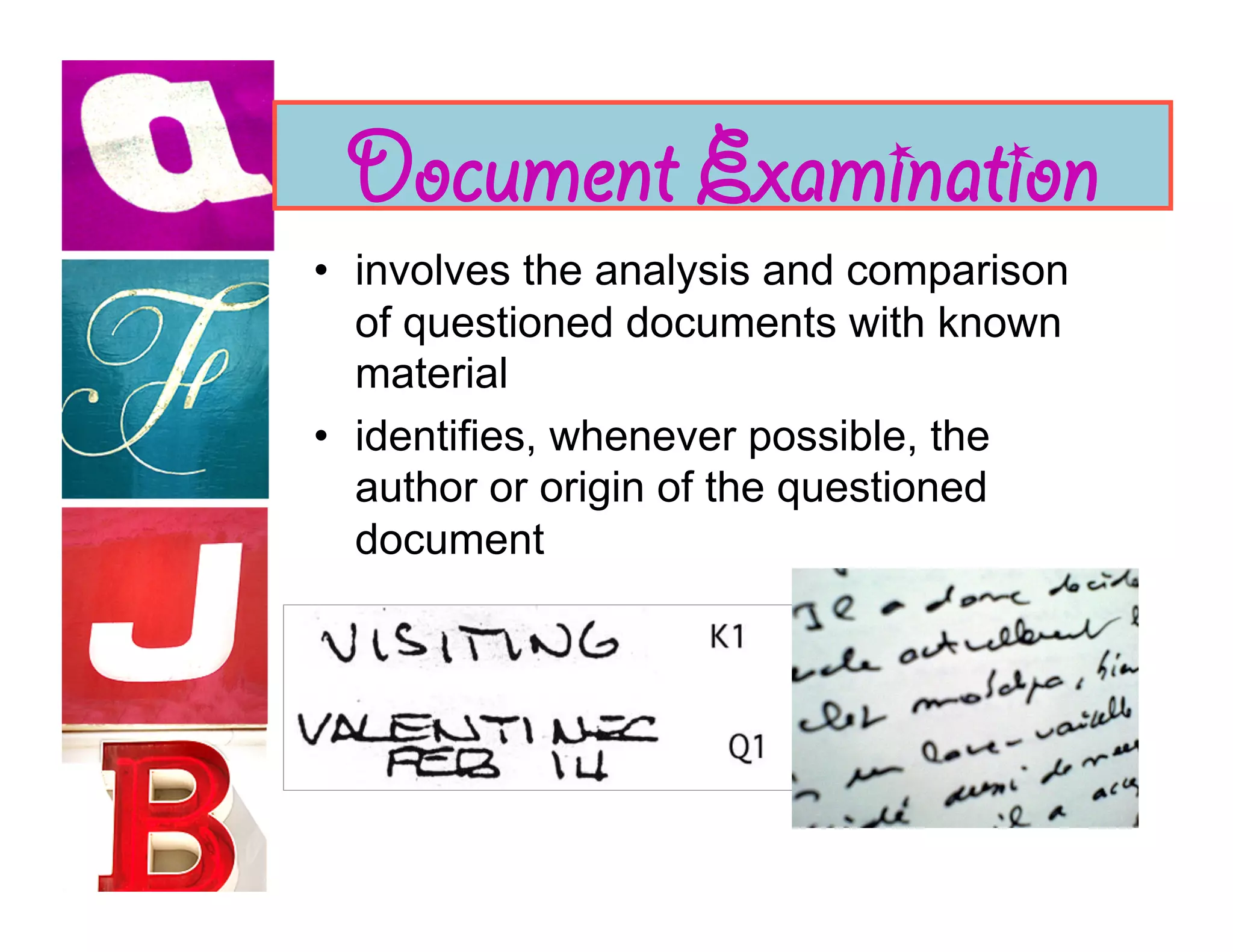
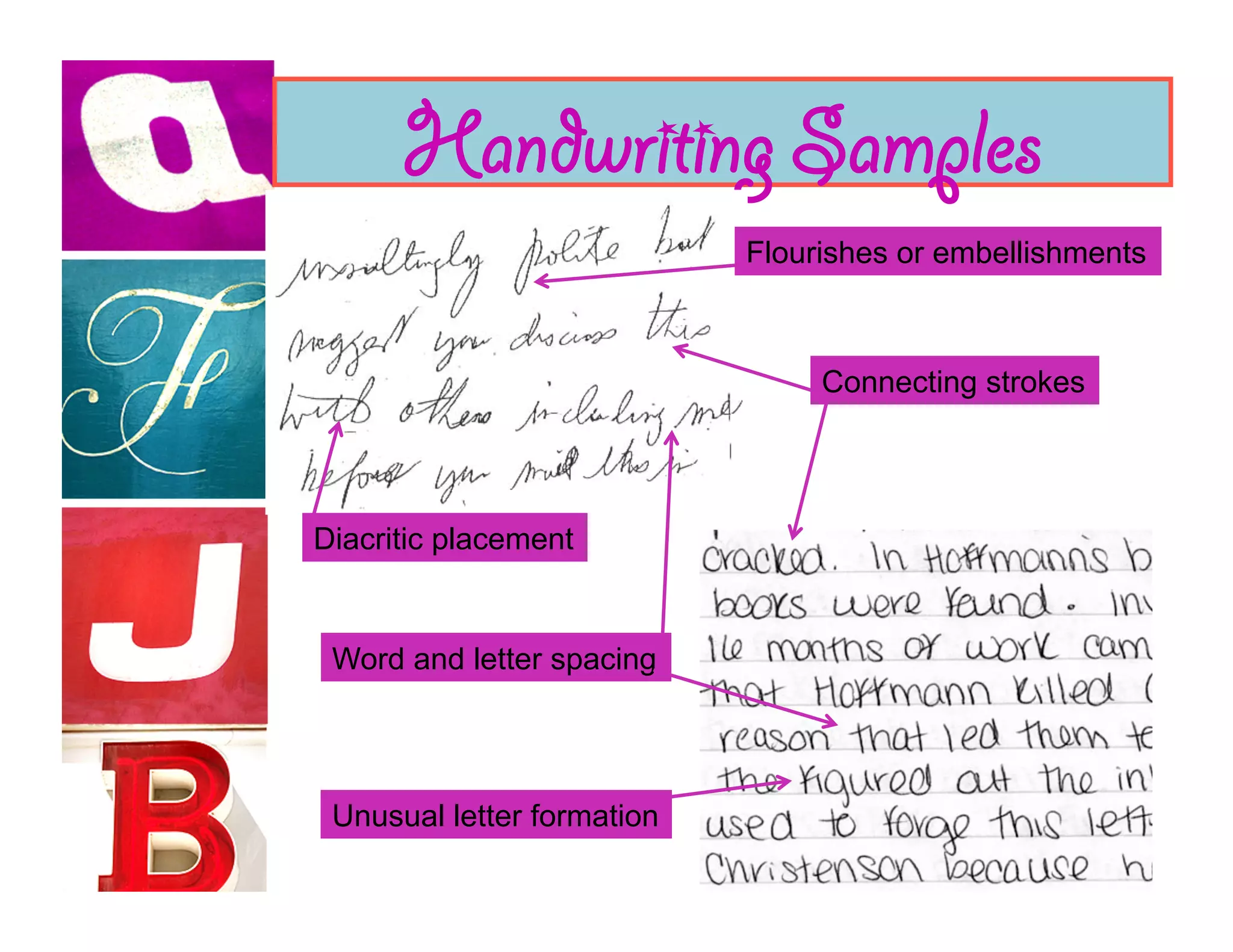
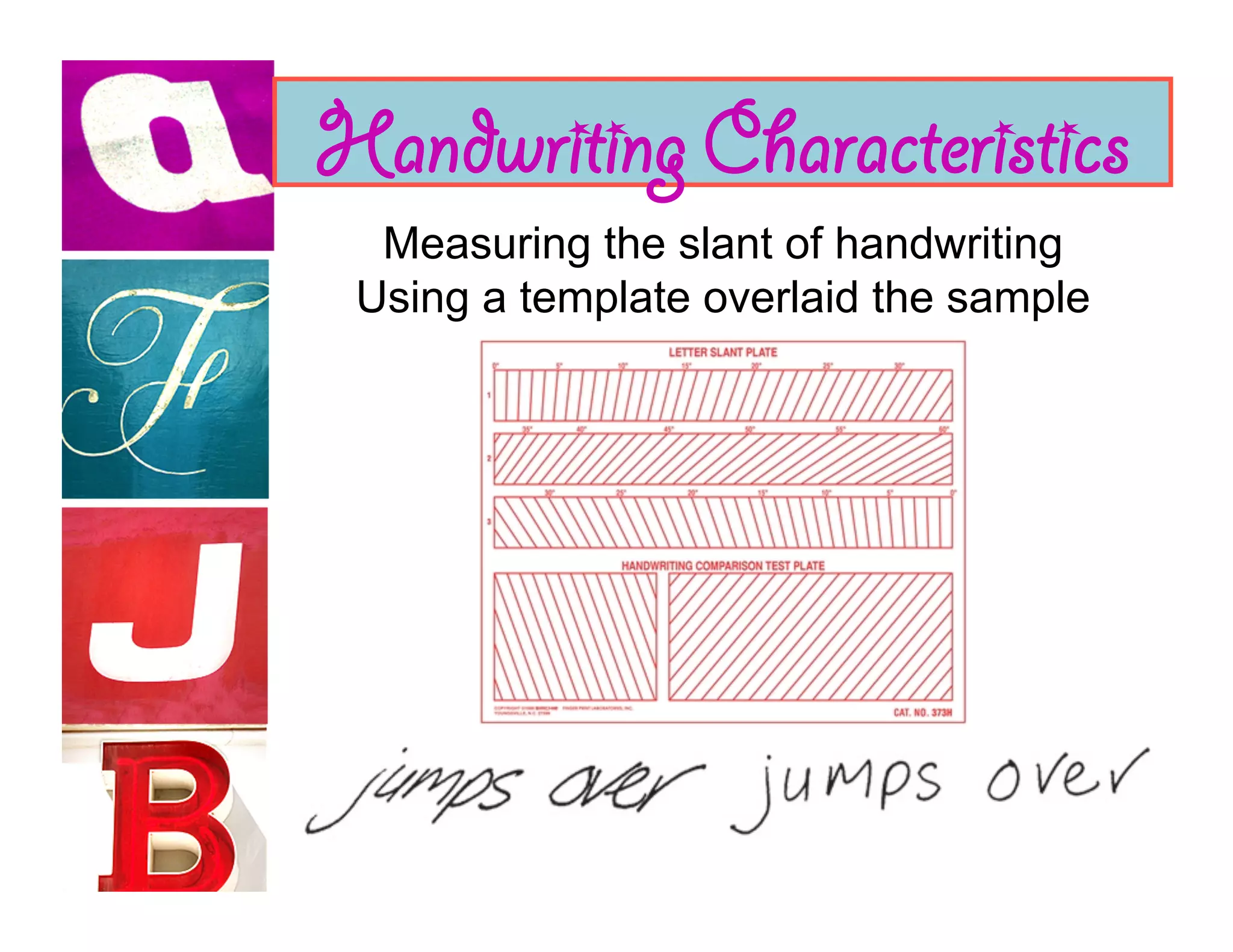
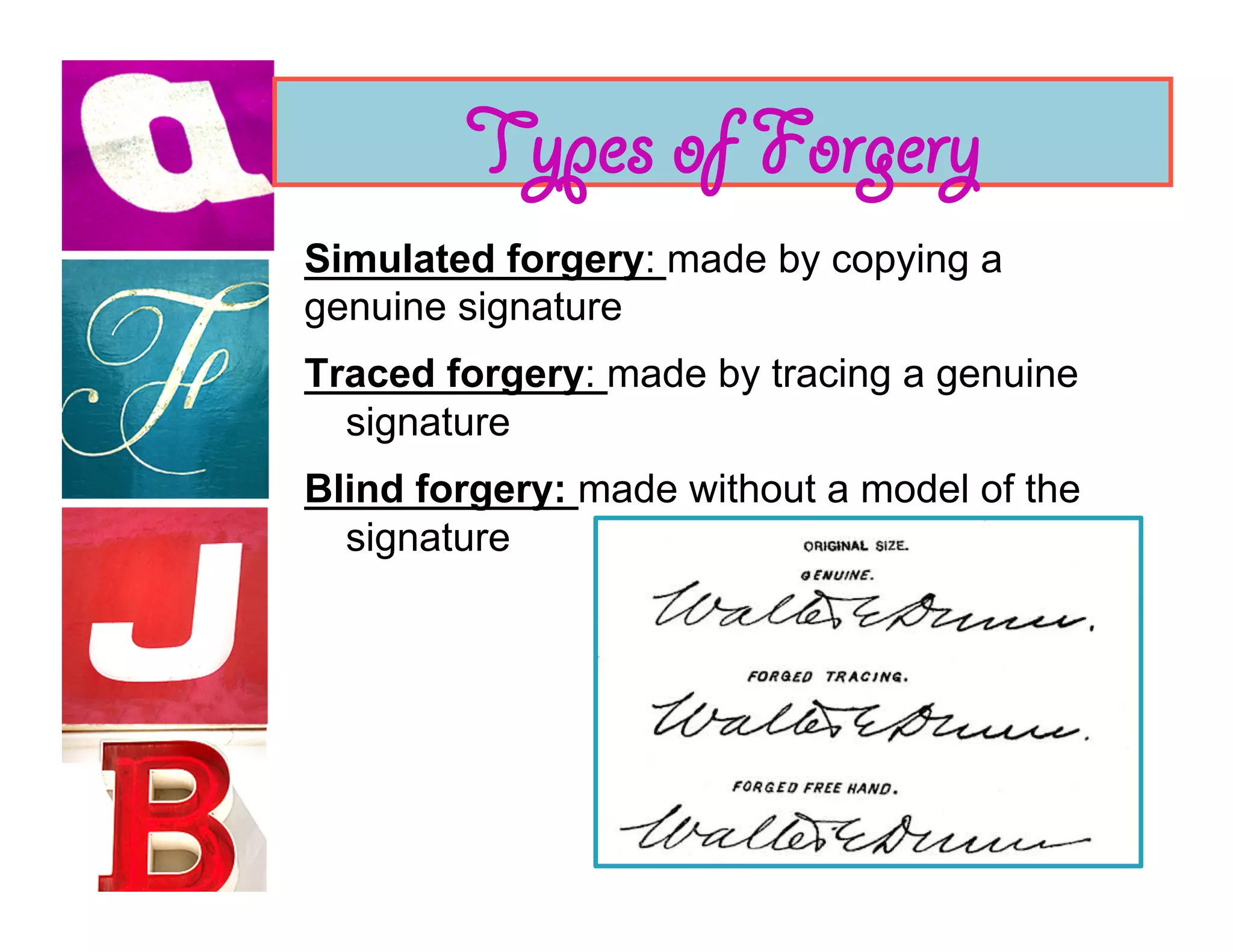
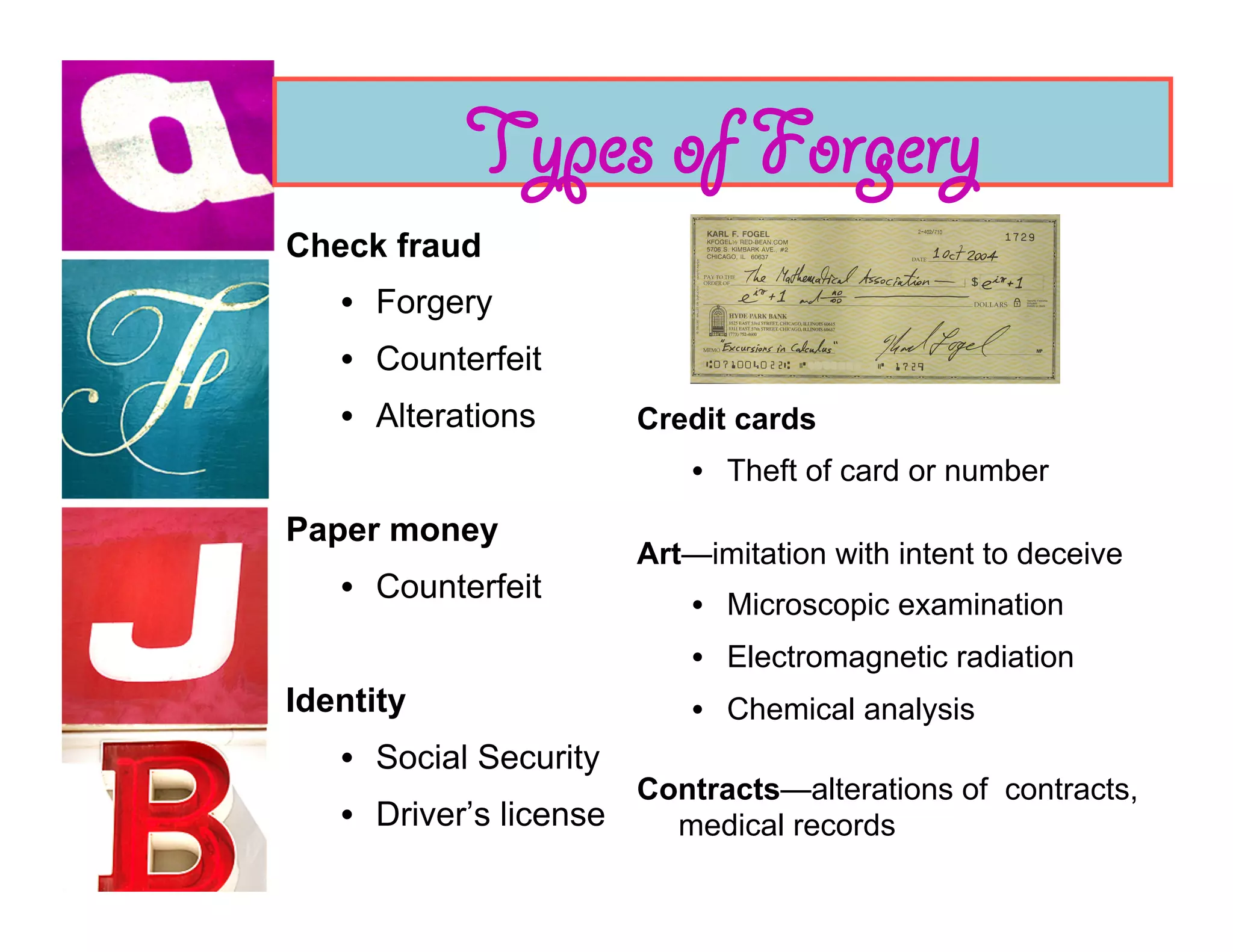
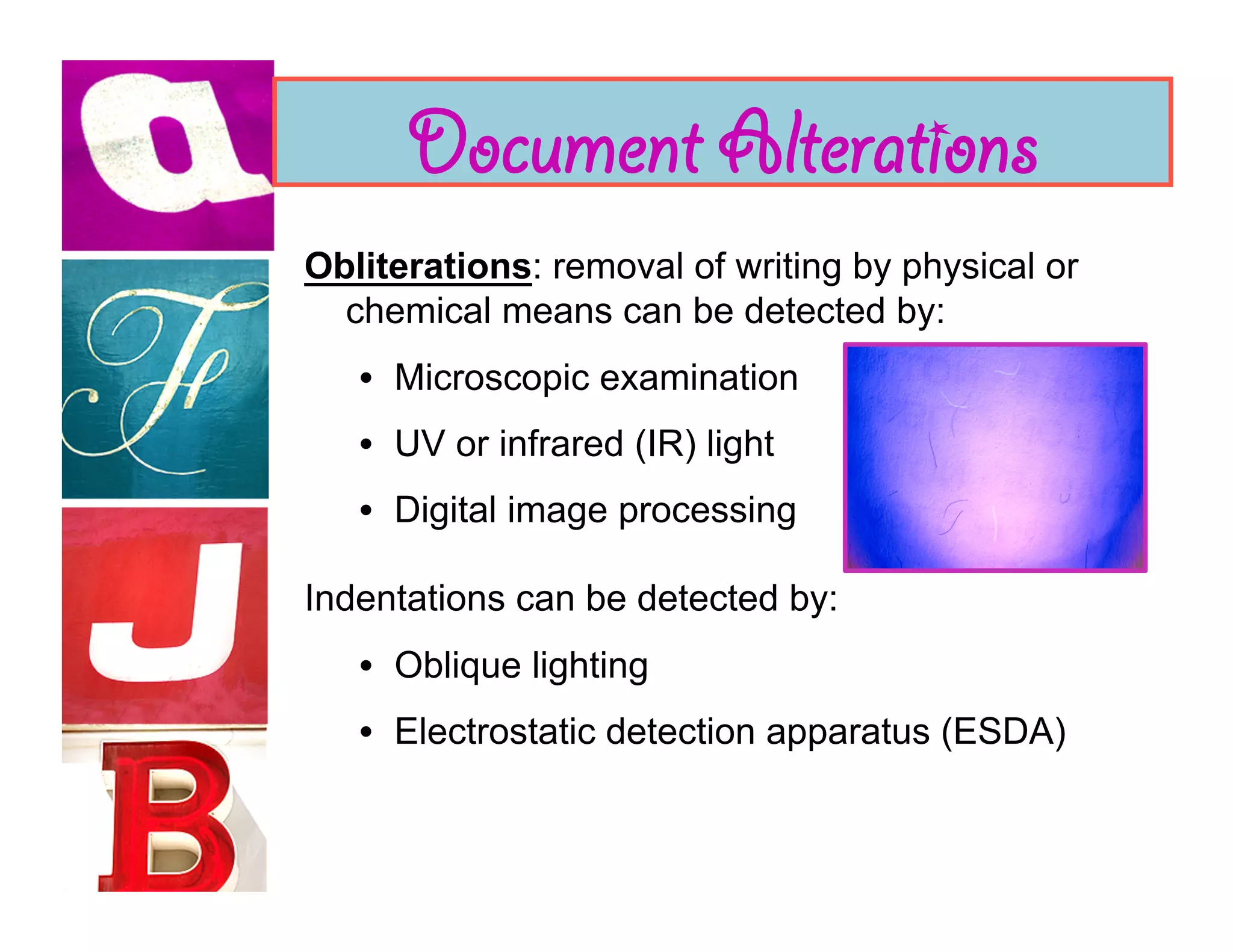
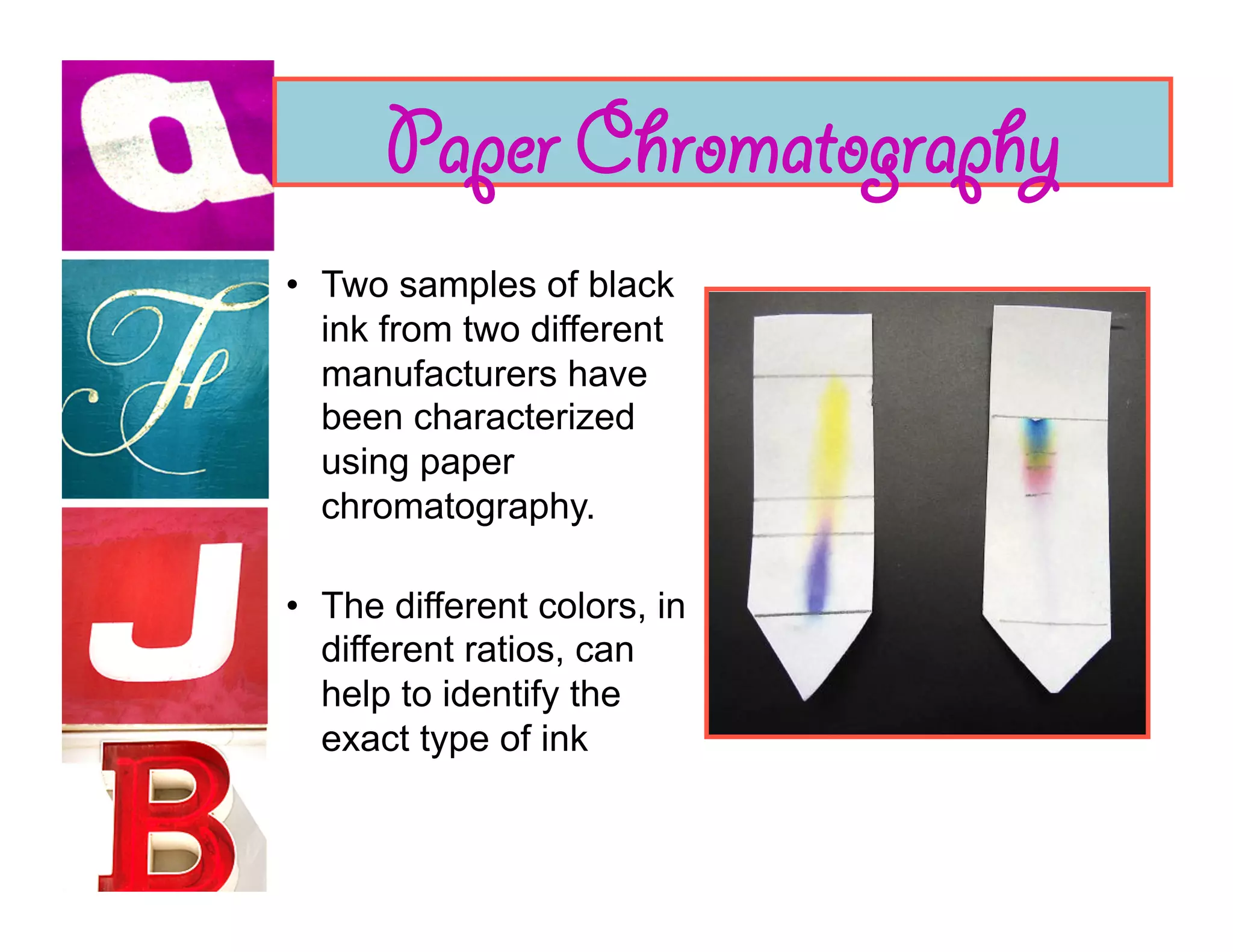
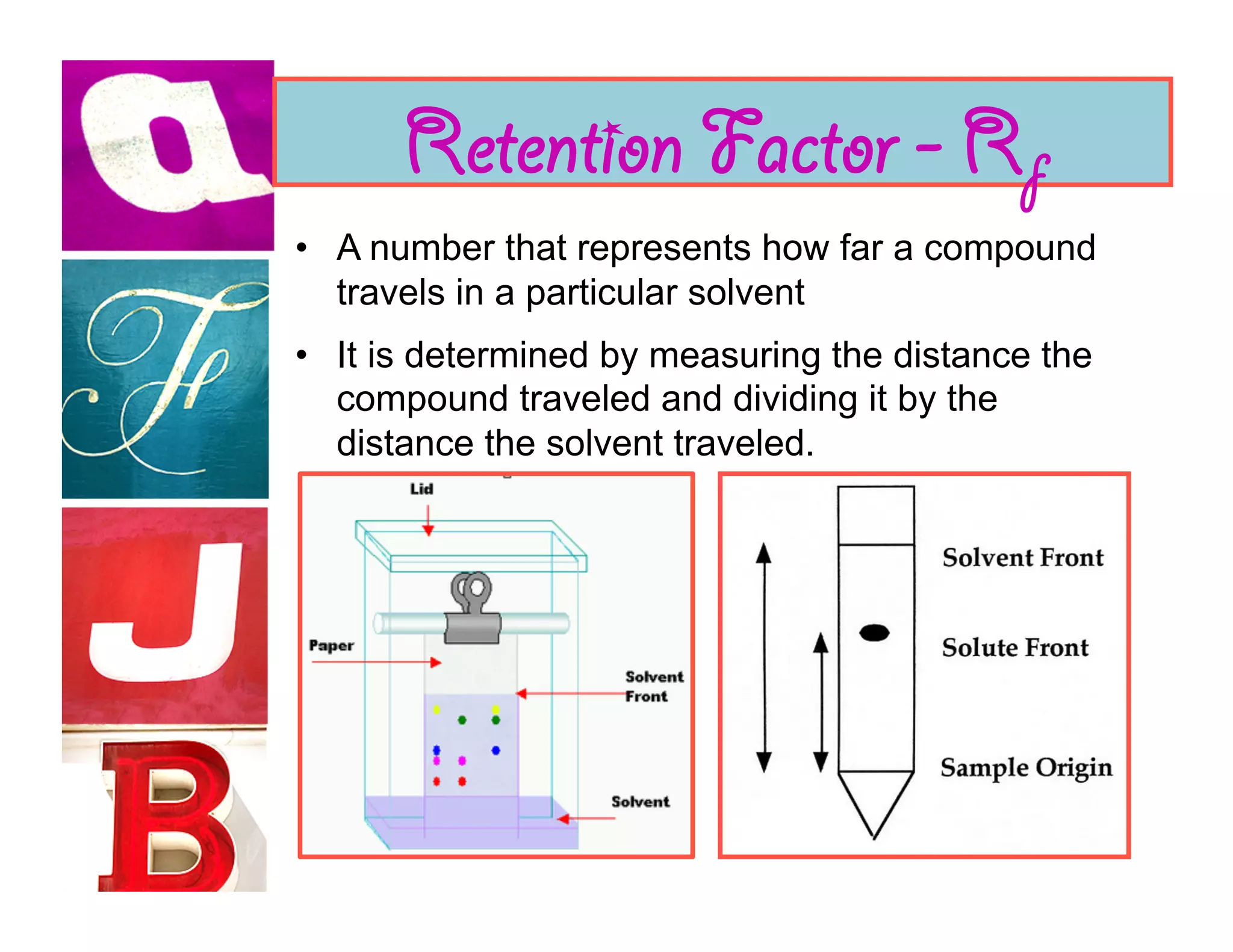
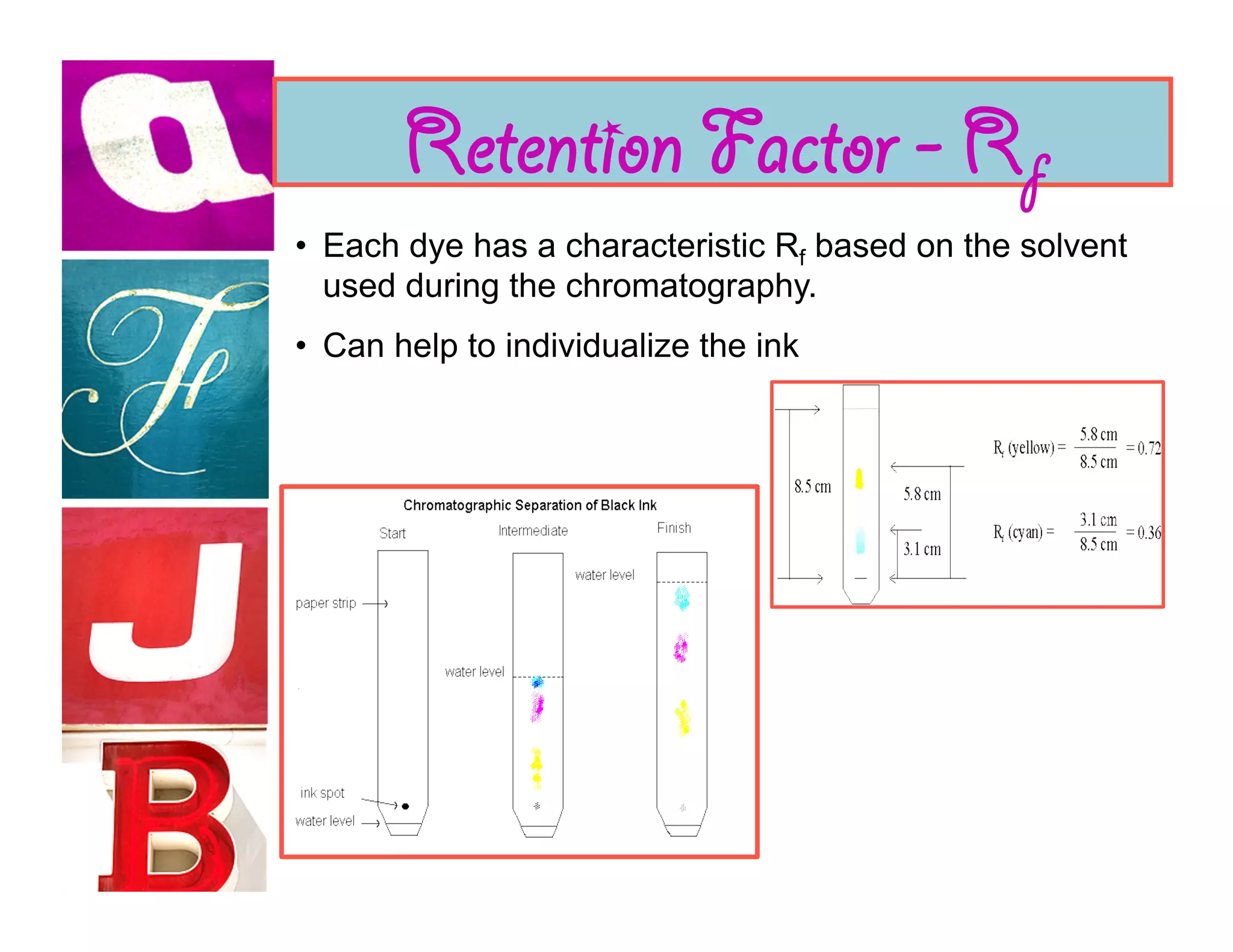
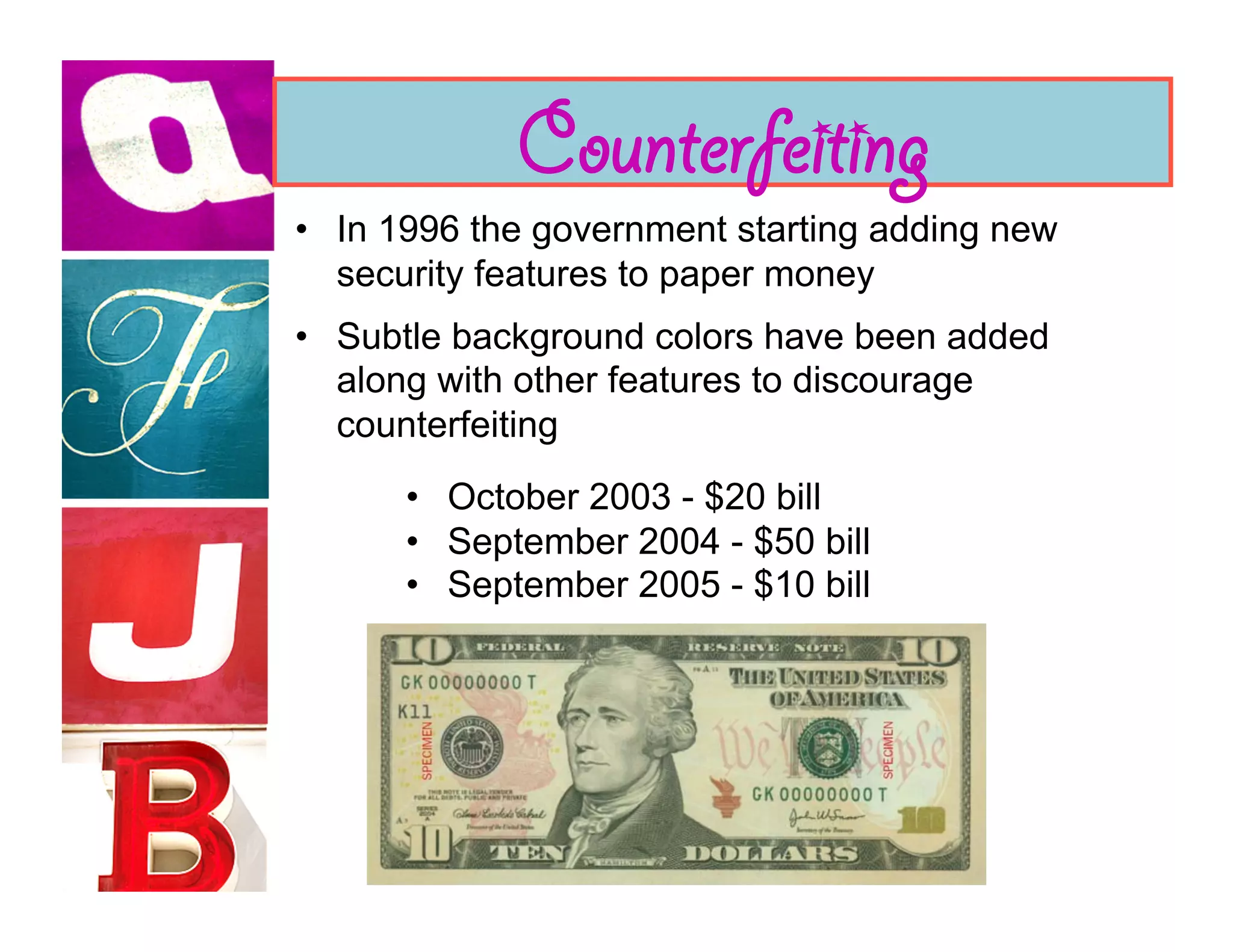
Document analysis involves examining handwriting, ink, and paper to determine the source or authenticity of documents. Various techniques are used to analyze these elements, including chromatography to analyze ink composition and compare it between samples. Characteristics of handwriting such as letter formation, word spacing, and embellishments can provide clues to identify or eliminate a person as the author of a questioned document.