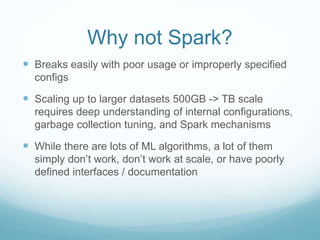
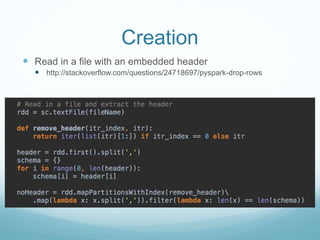
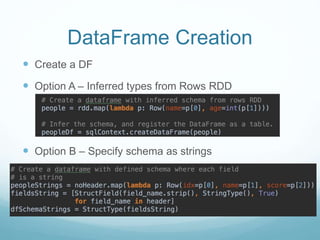
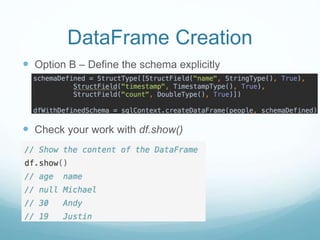
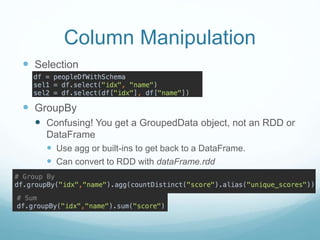
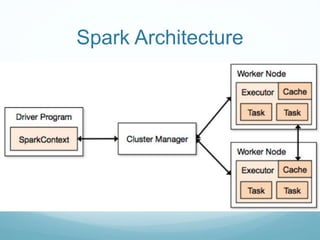
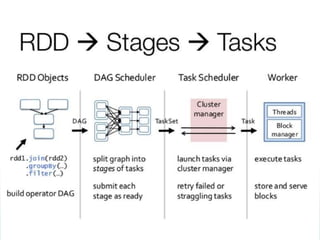
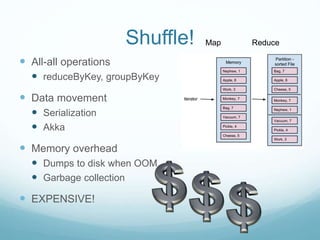
The document discusses utilizing Spark and DataFrames for efficient data engineering, emphasizing ease of use in batch ETL processes while highlighting potential pitfalls such as scaling issues and the need for proper configuration. It presents detailed instructions on DataFrame creation, column and row manipulation, and error handling, alongside recommendations for model building and feature extraction. The document also addresses Spark's architecture, performance tuning, and provides links to additional resources for further learning.