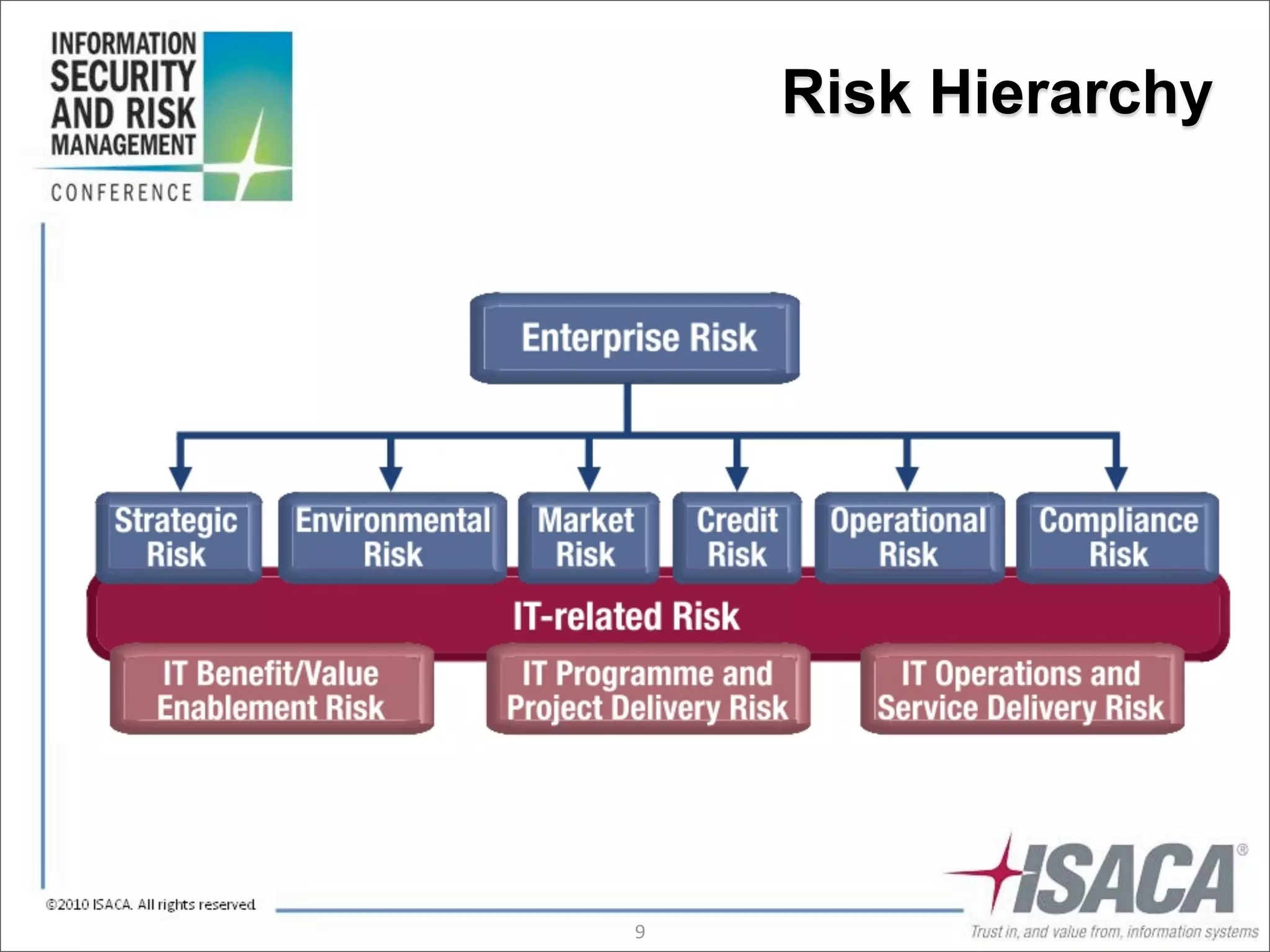
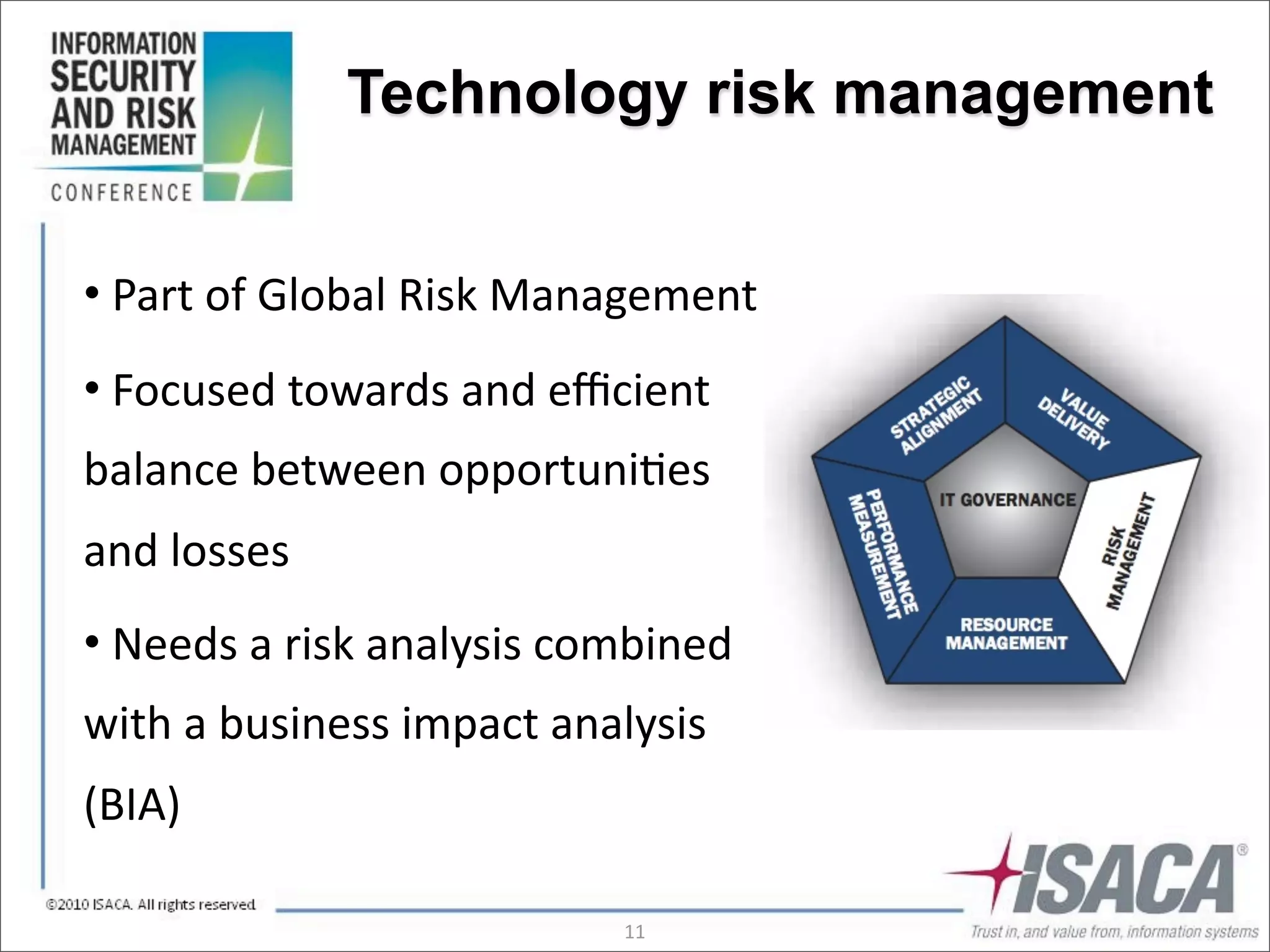
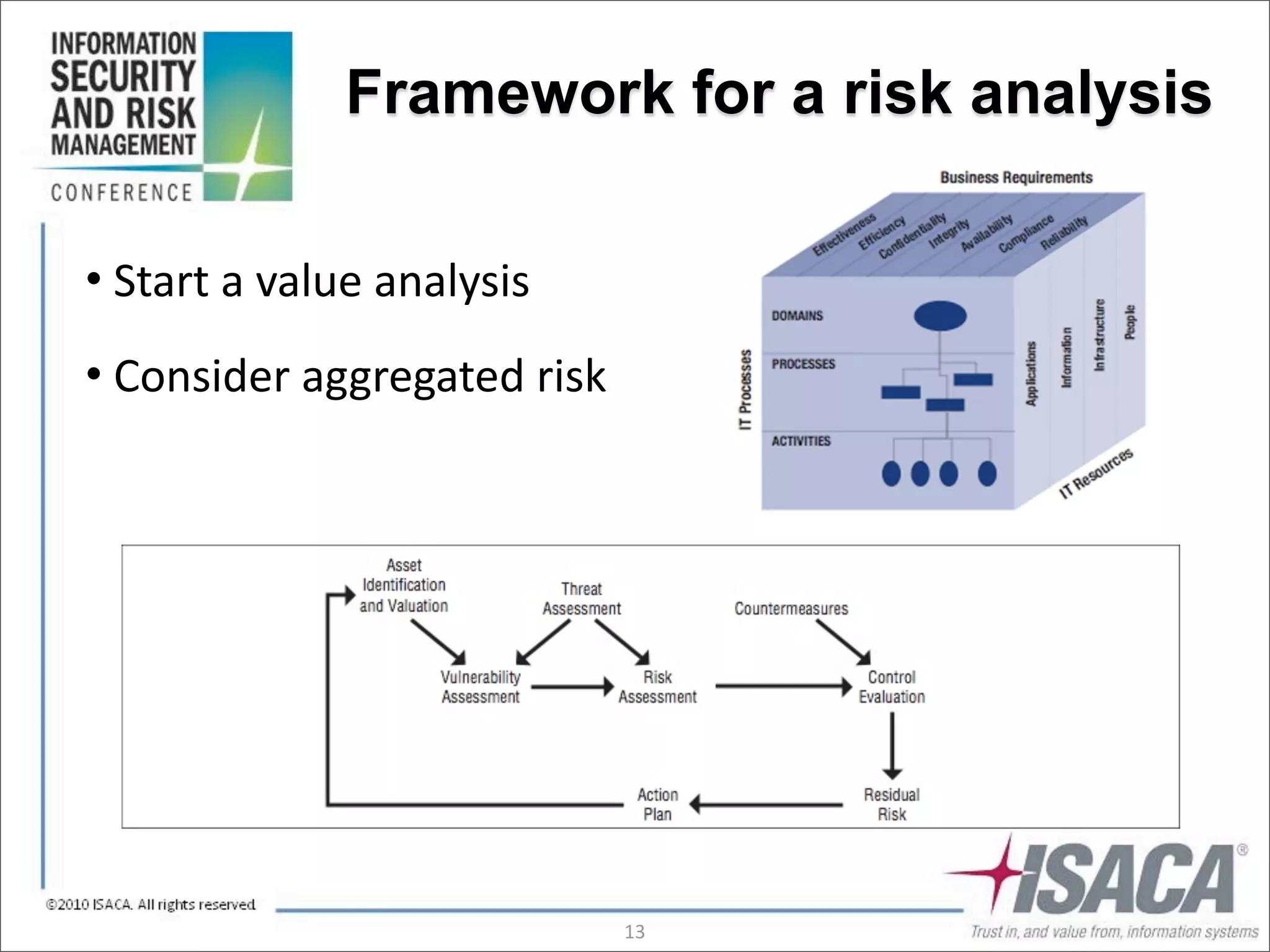
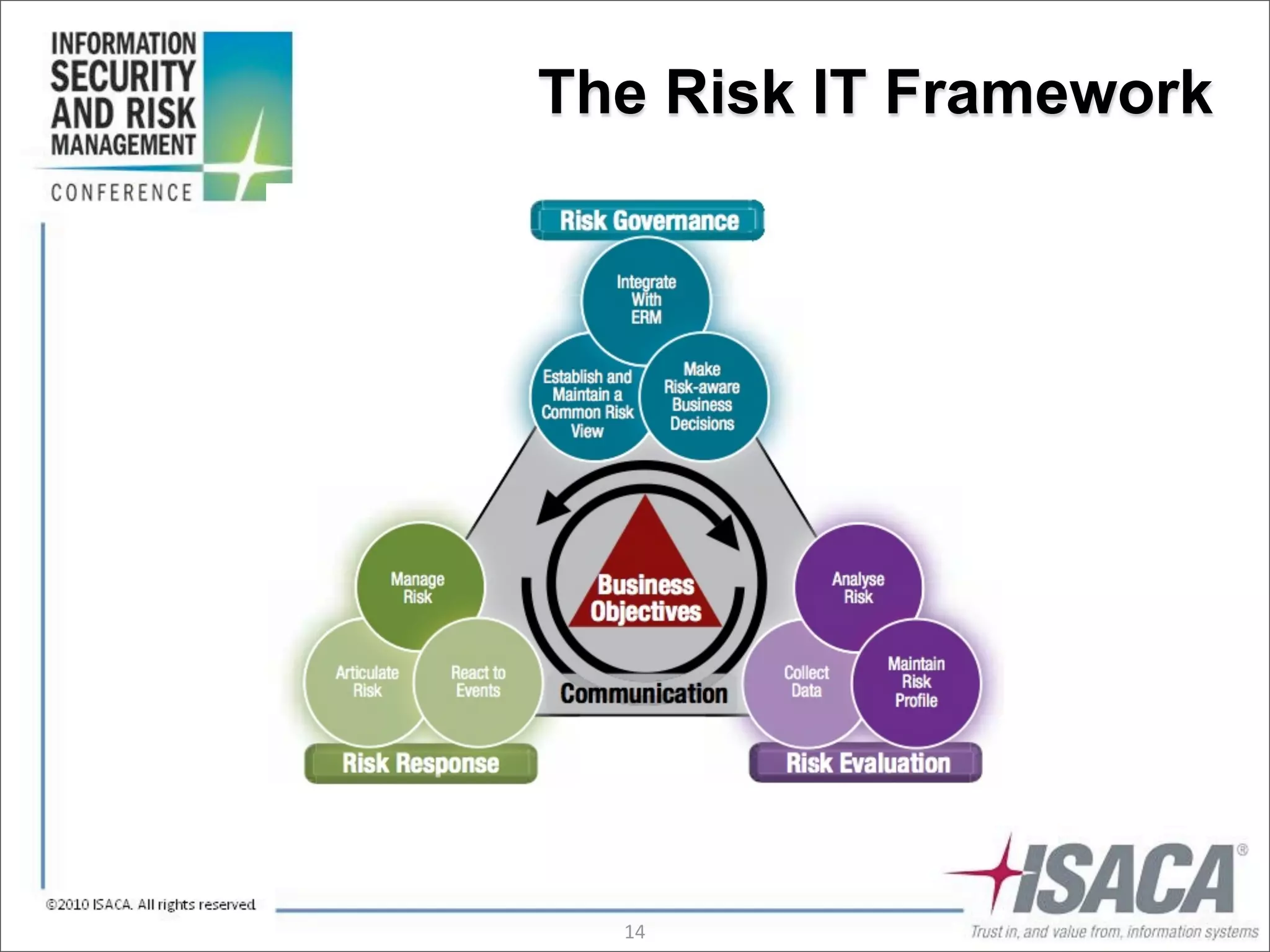
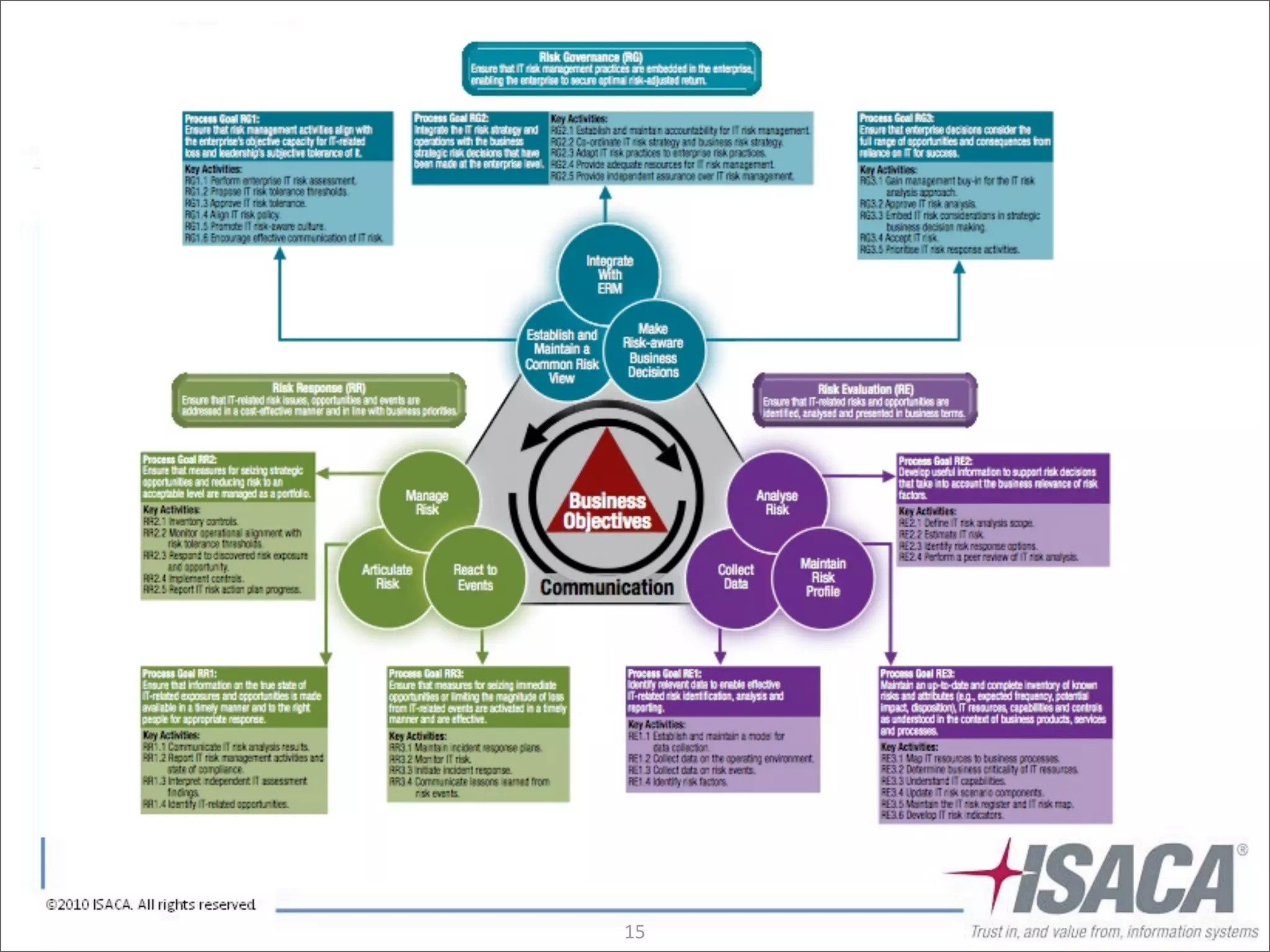
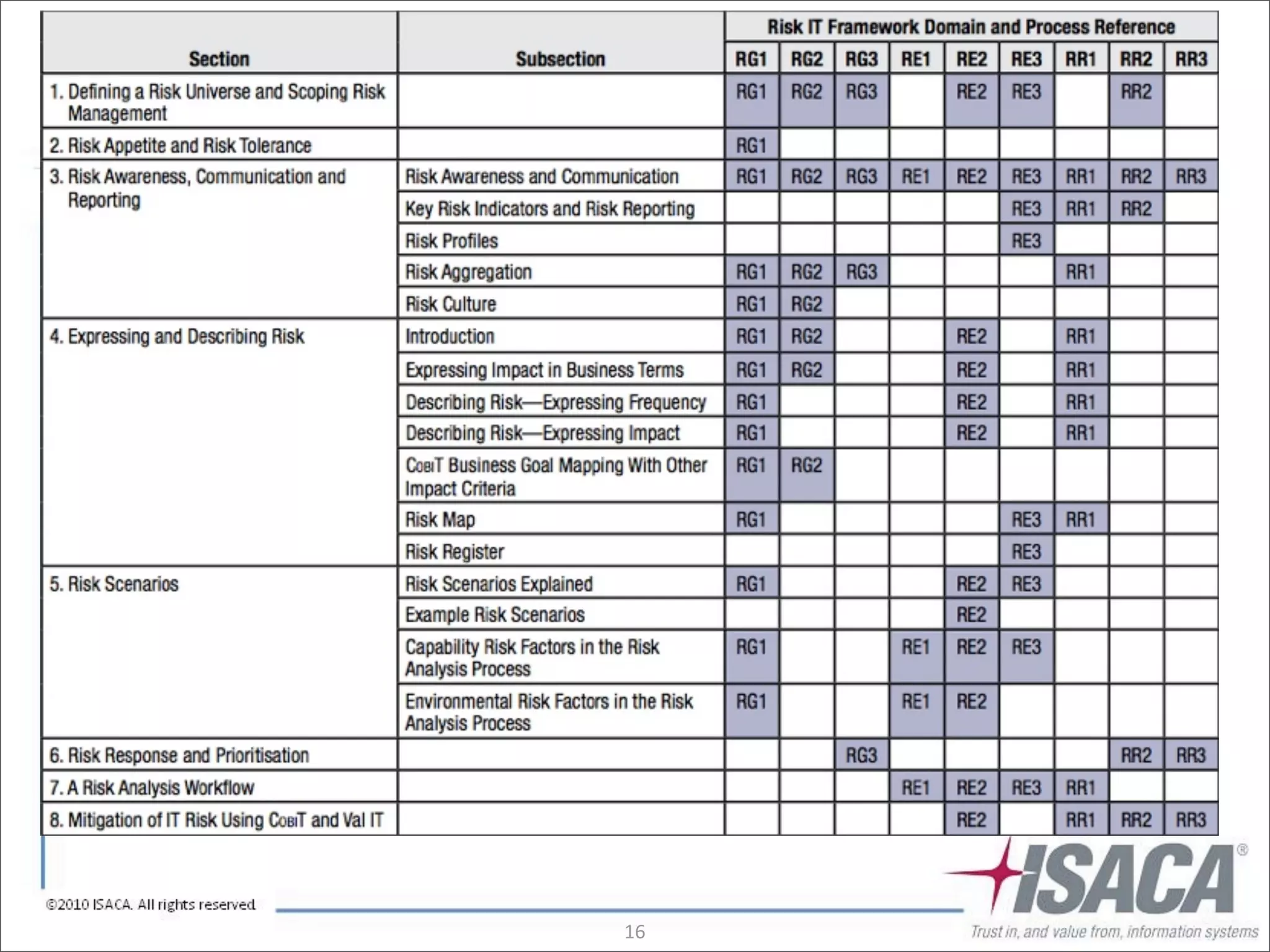
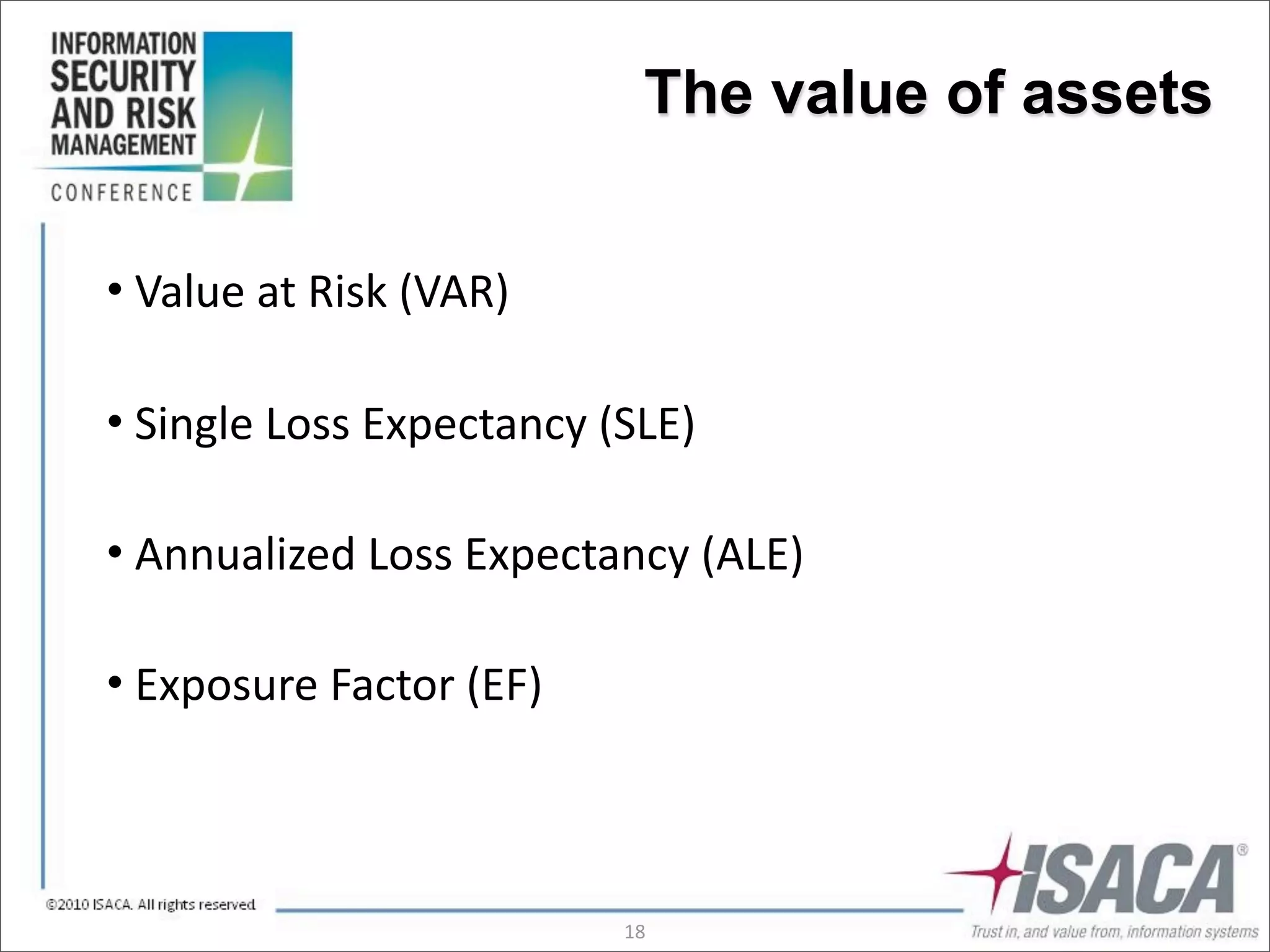
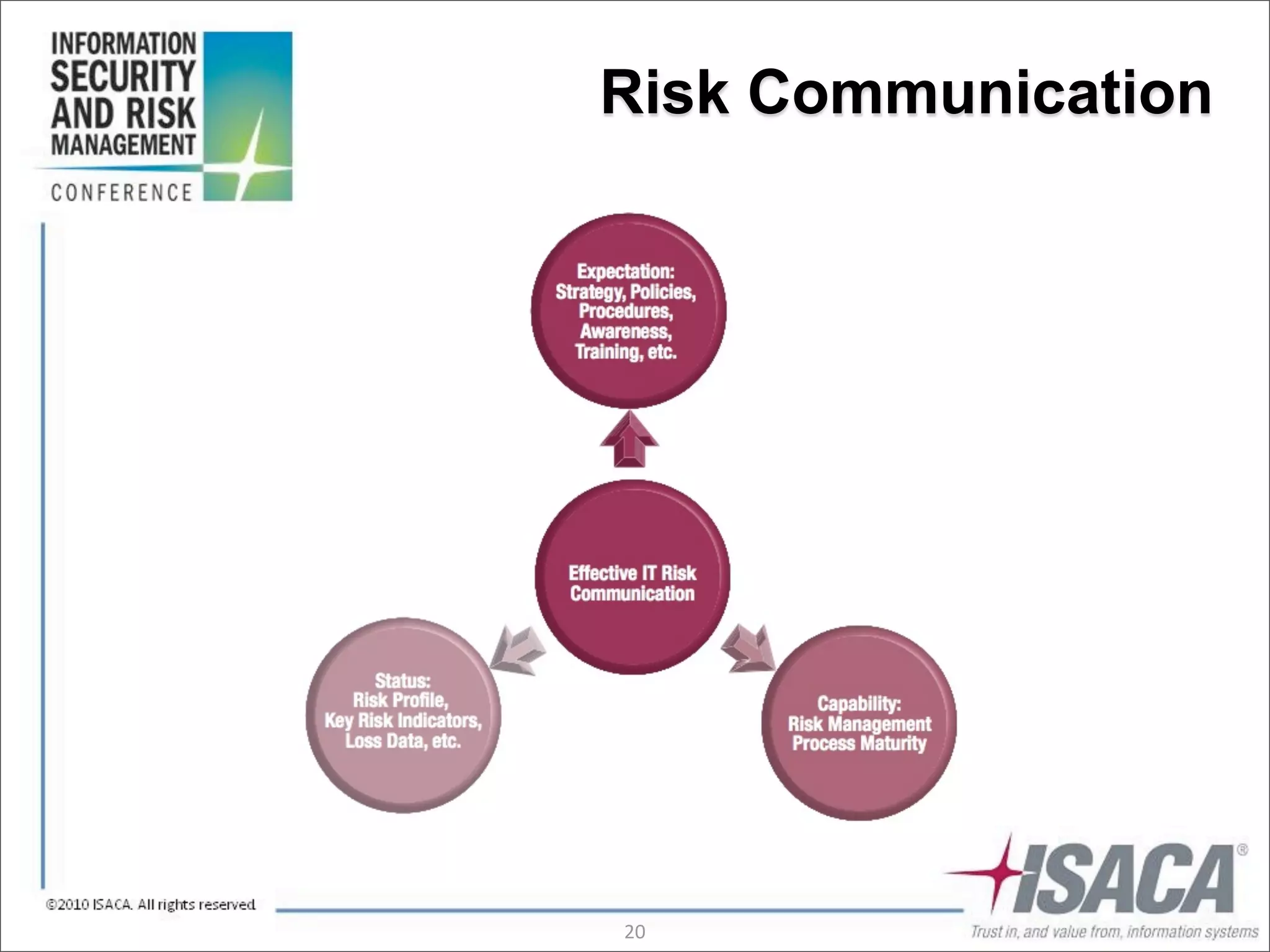
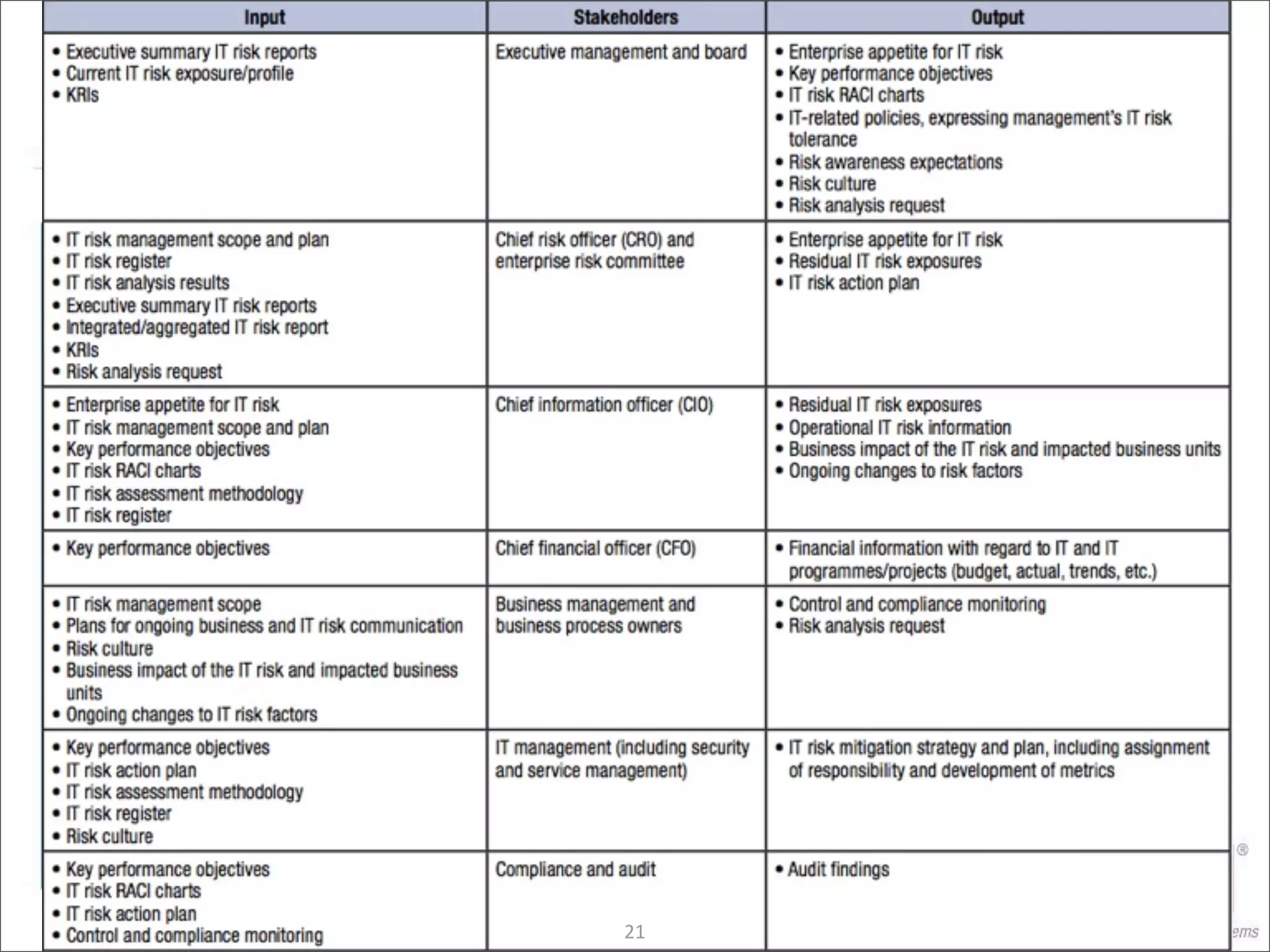
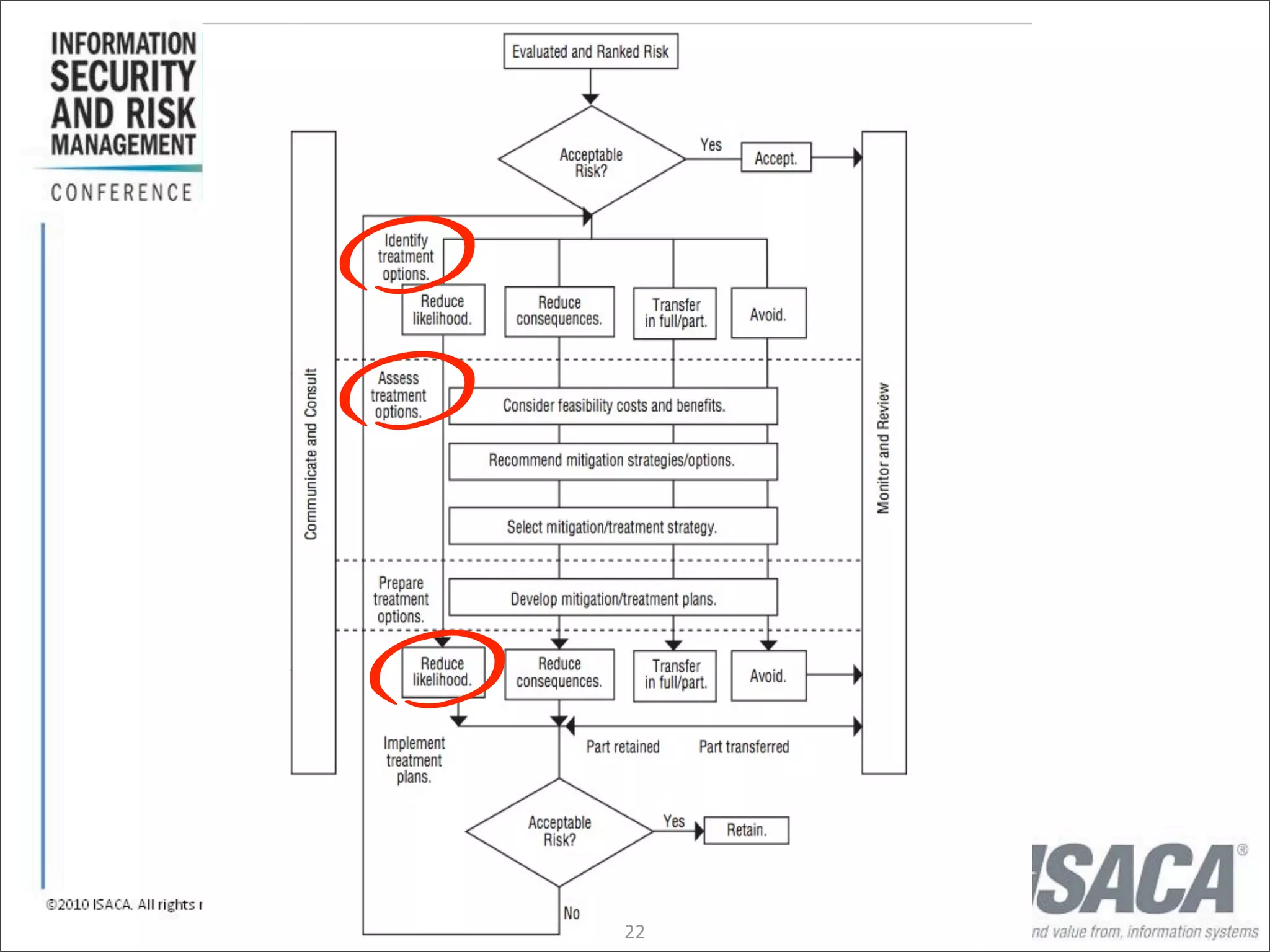
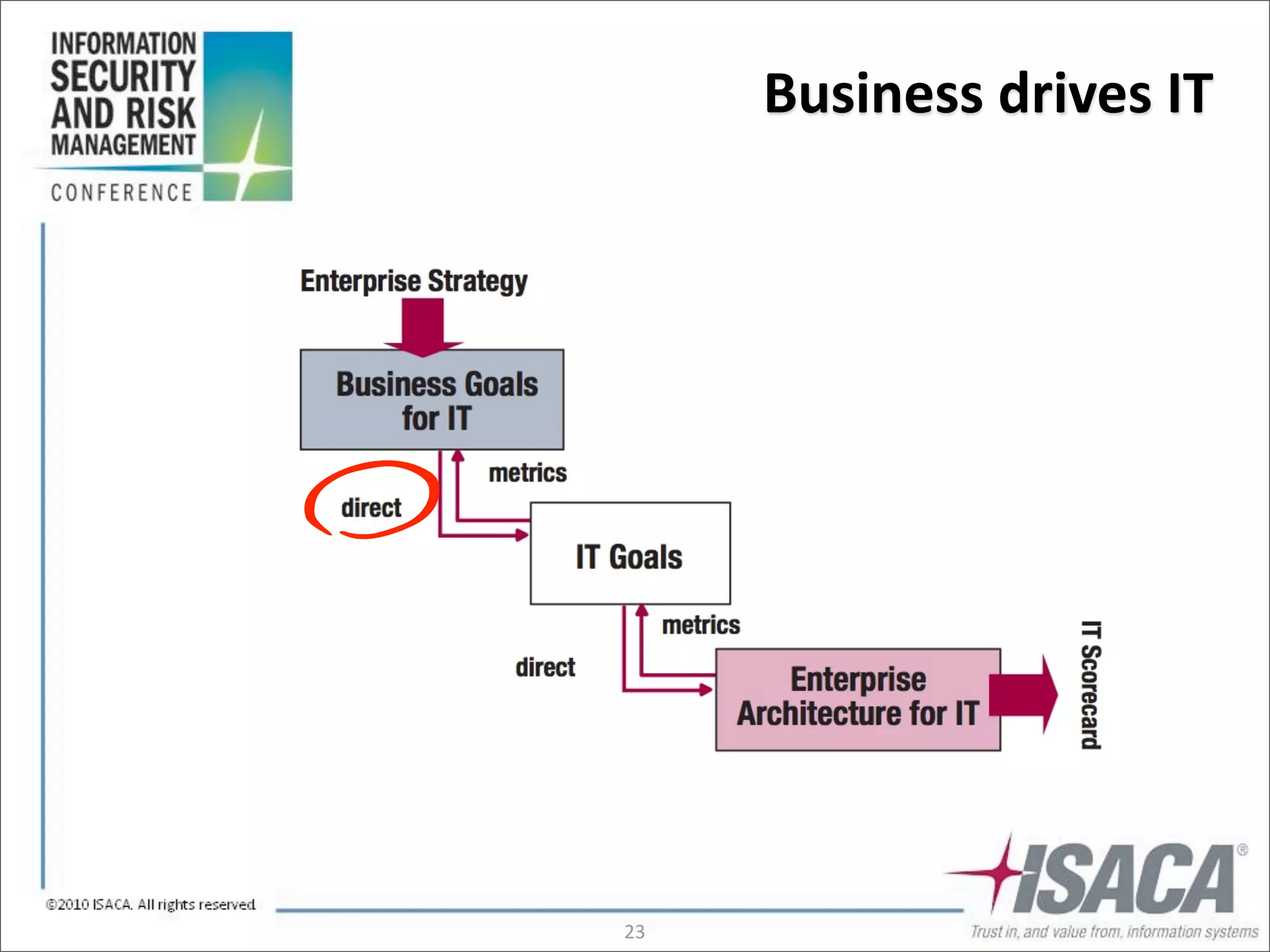
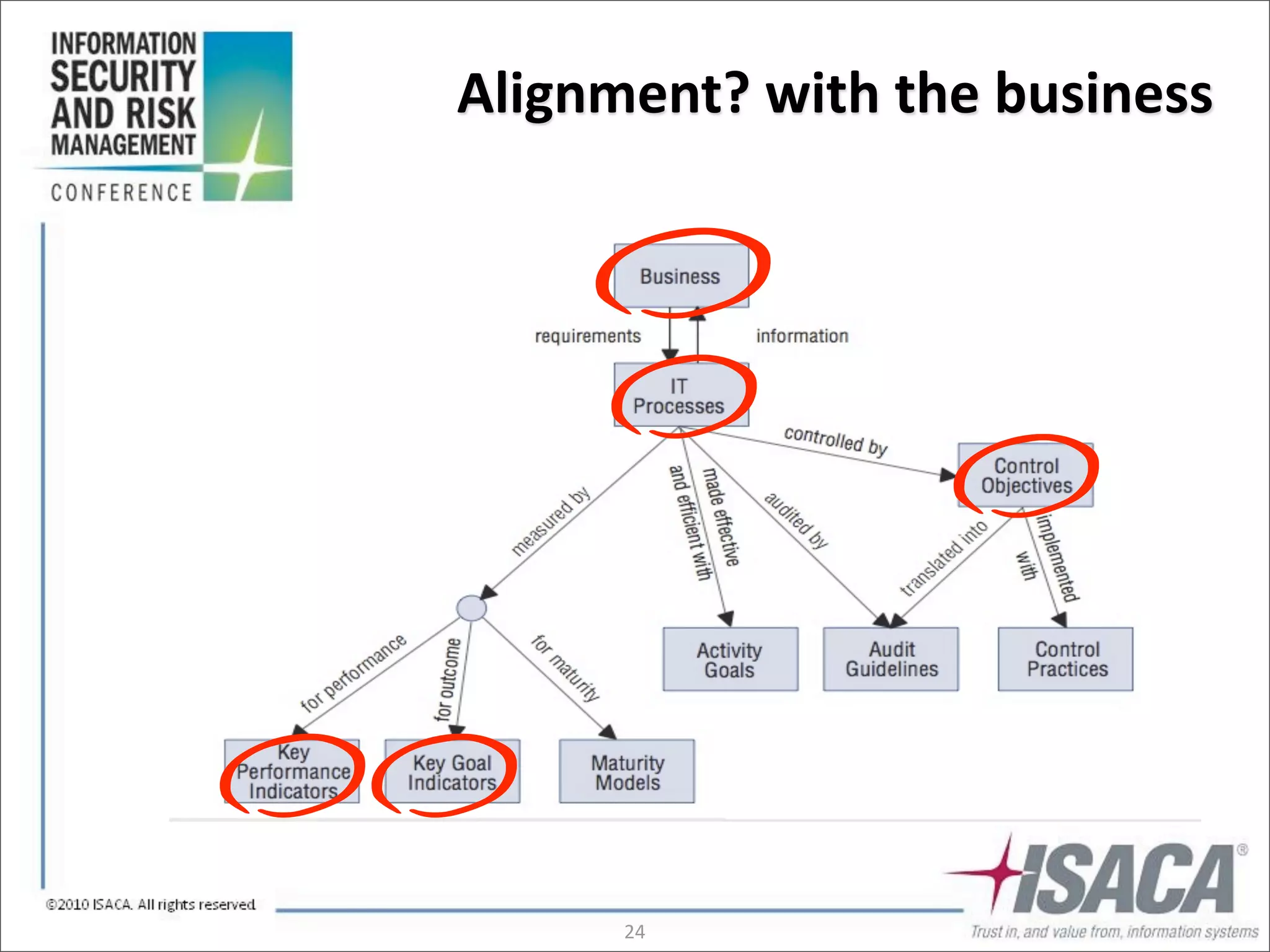
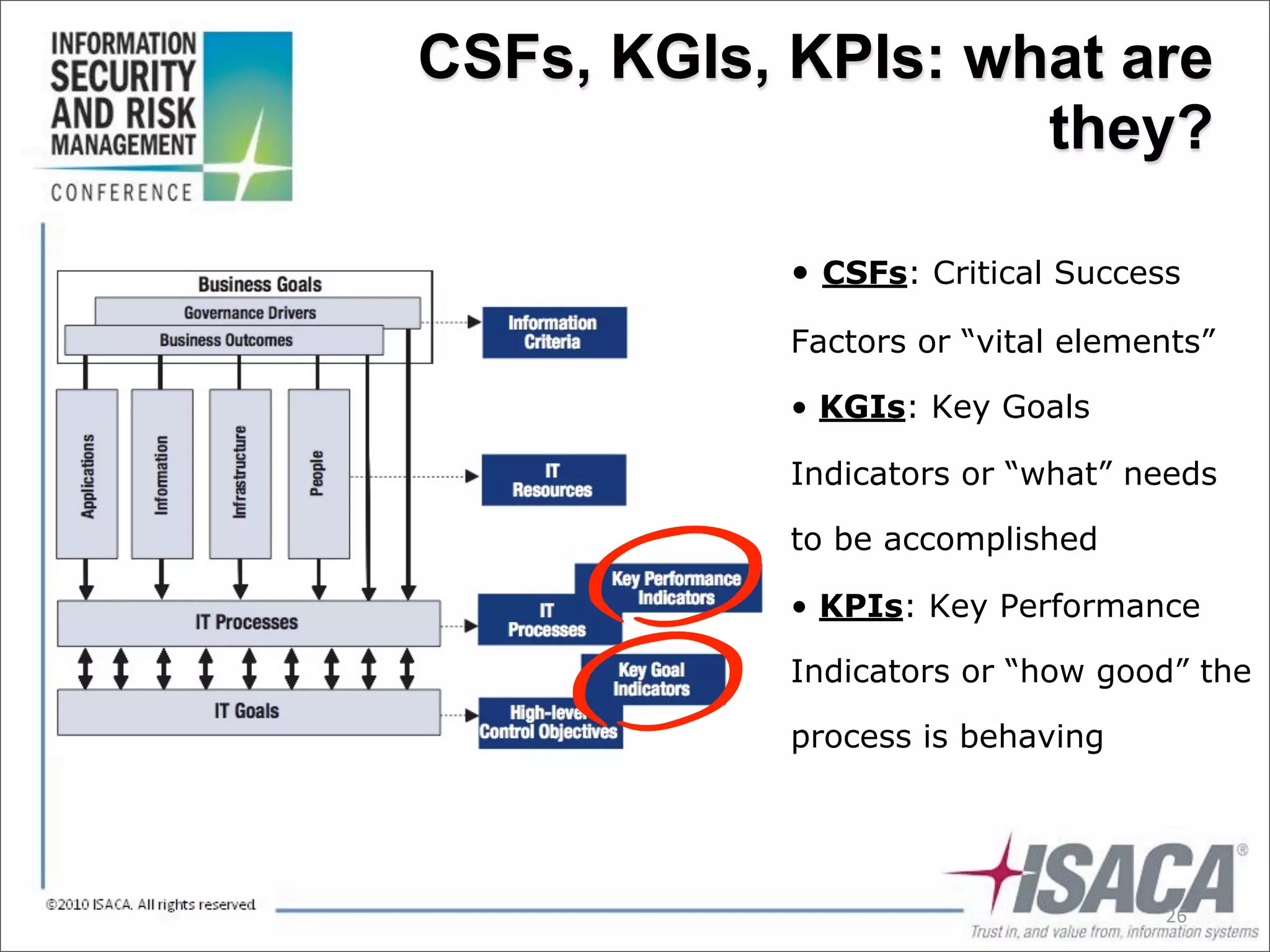
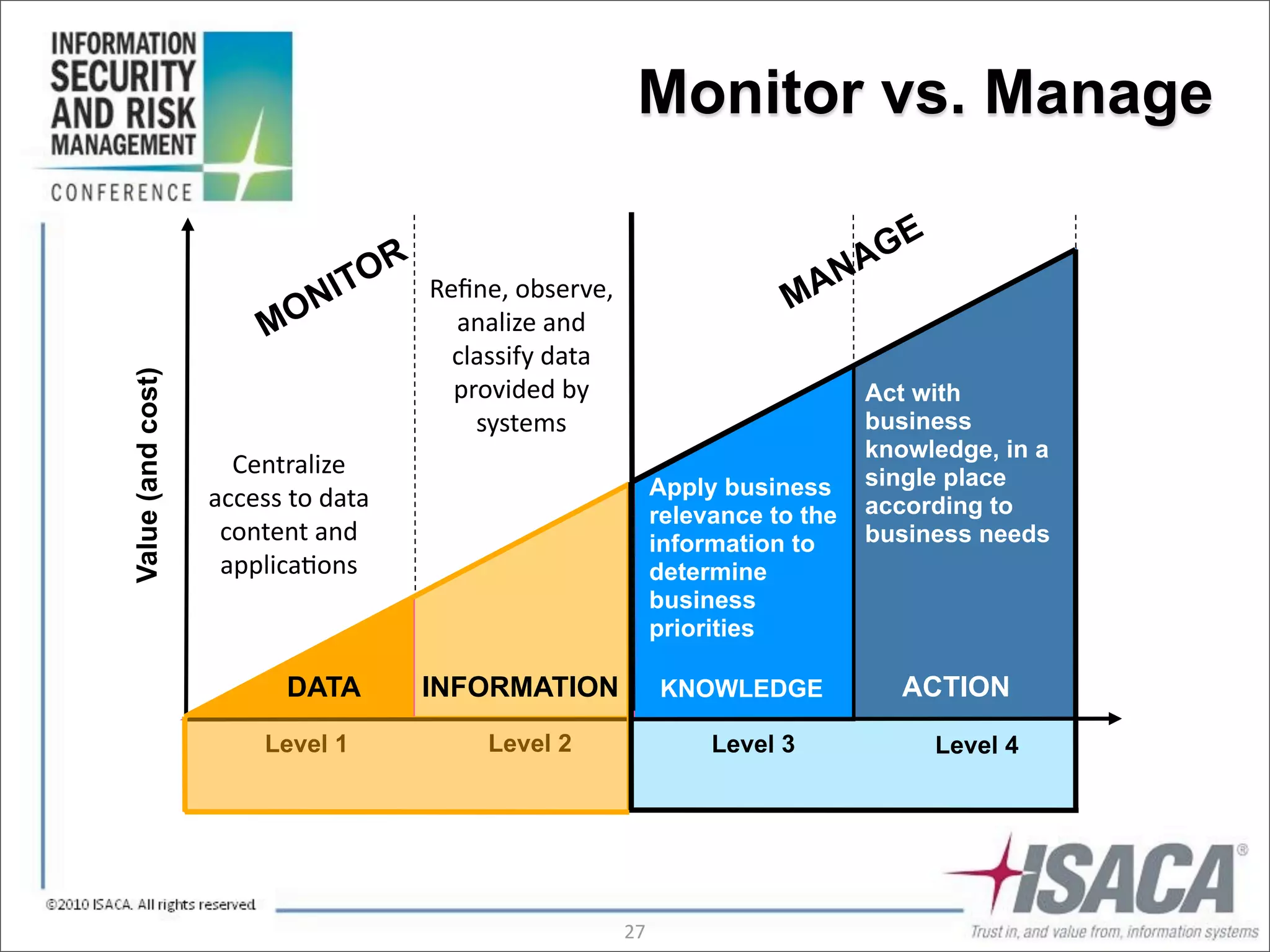
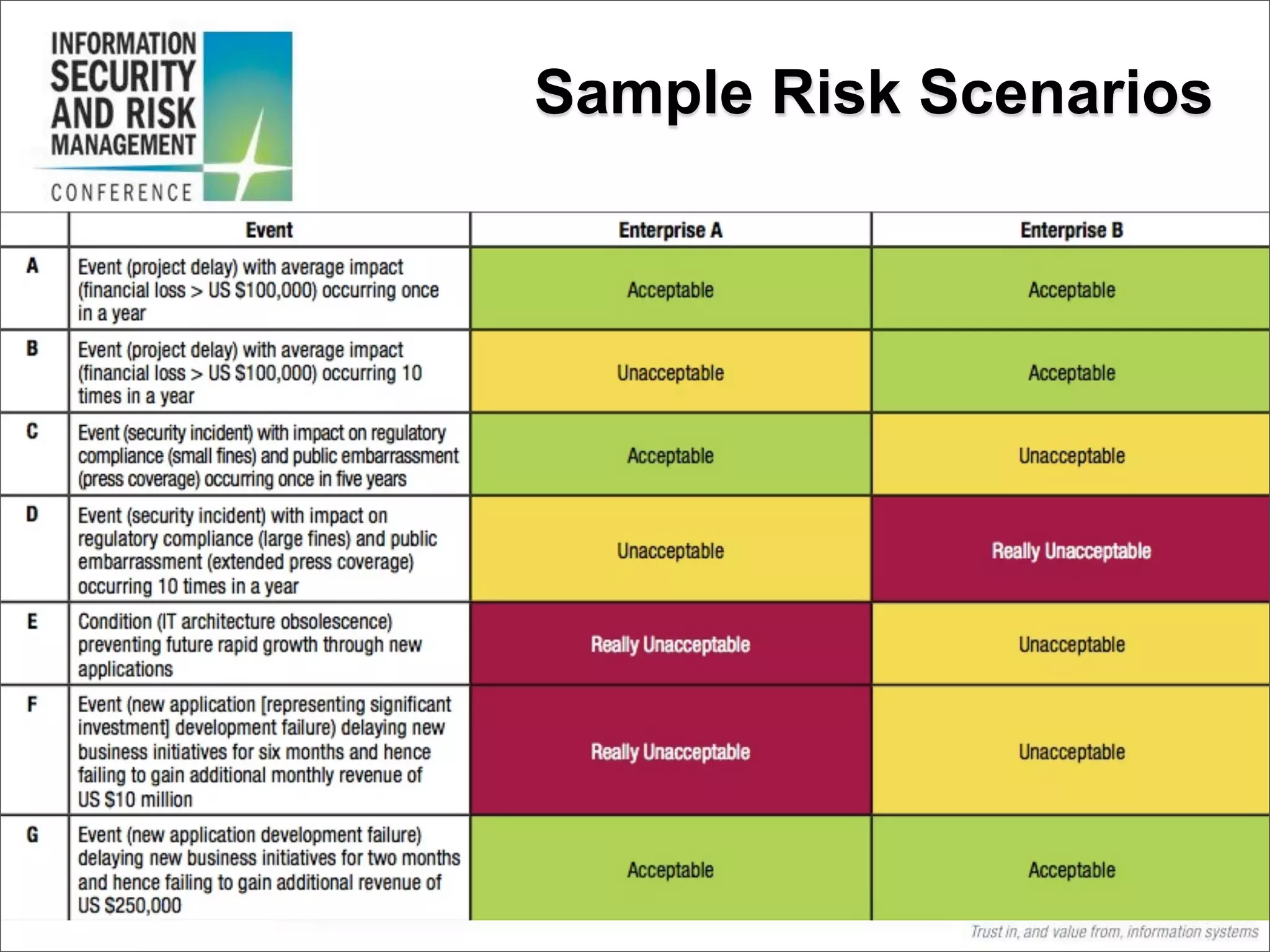
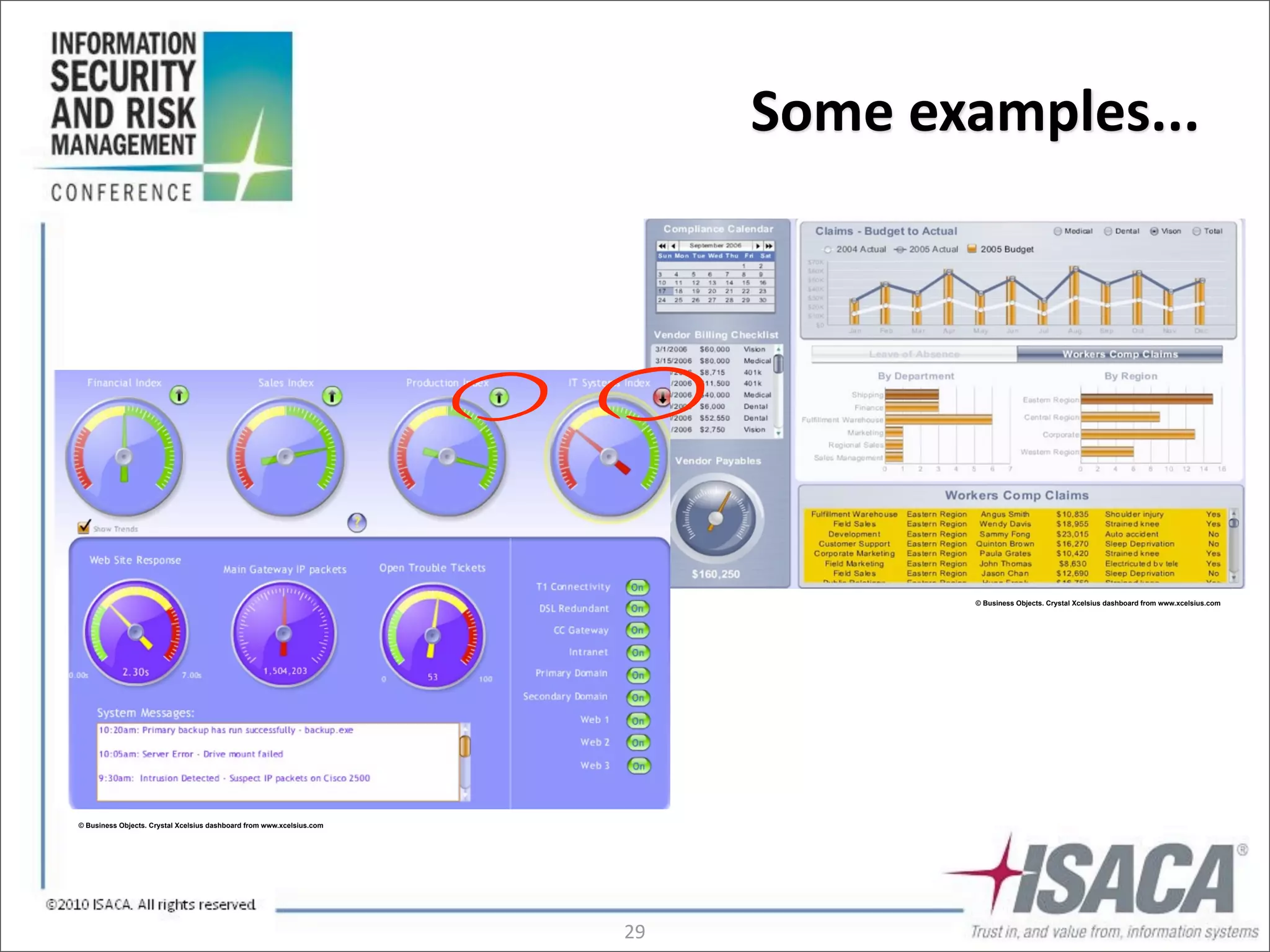
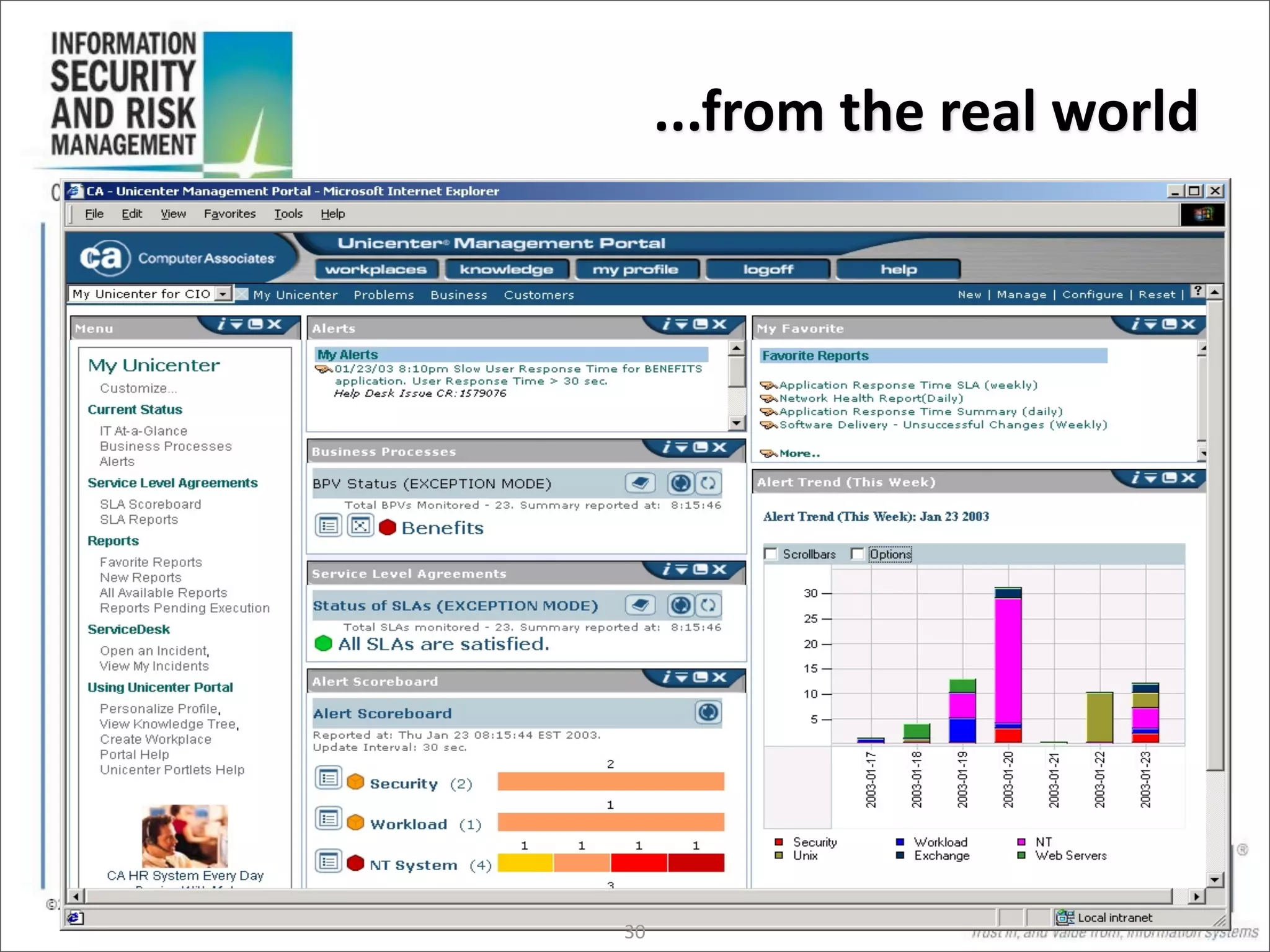
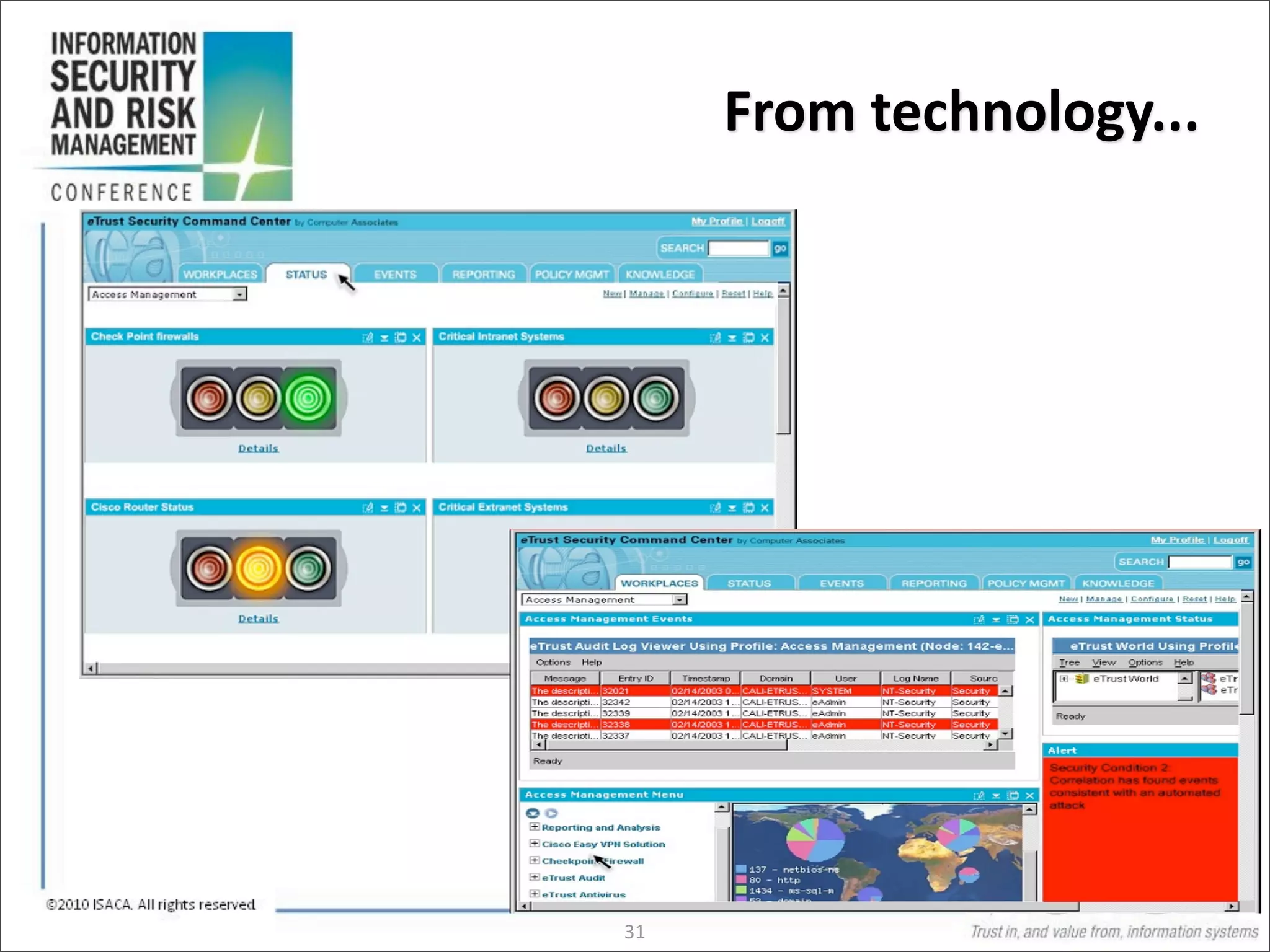
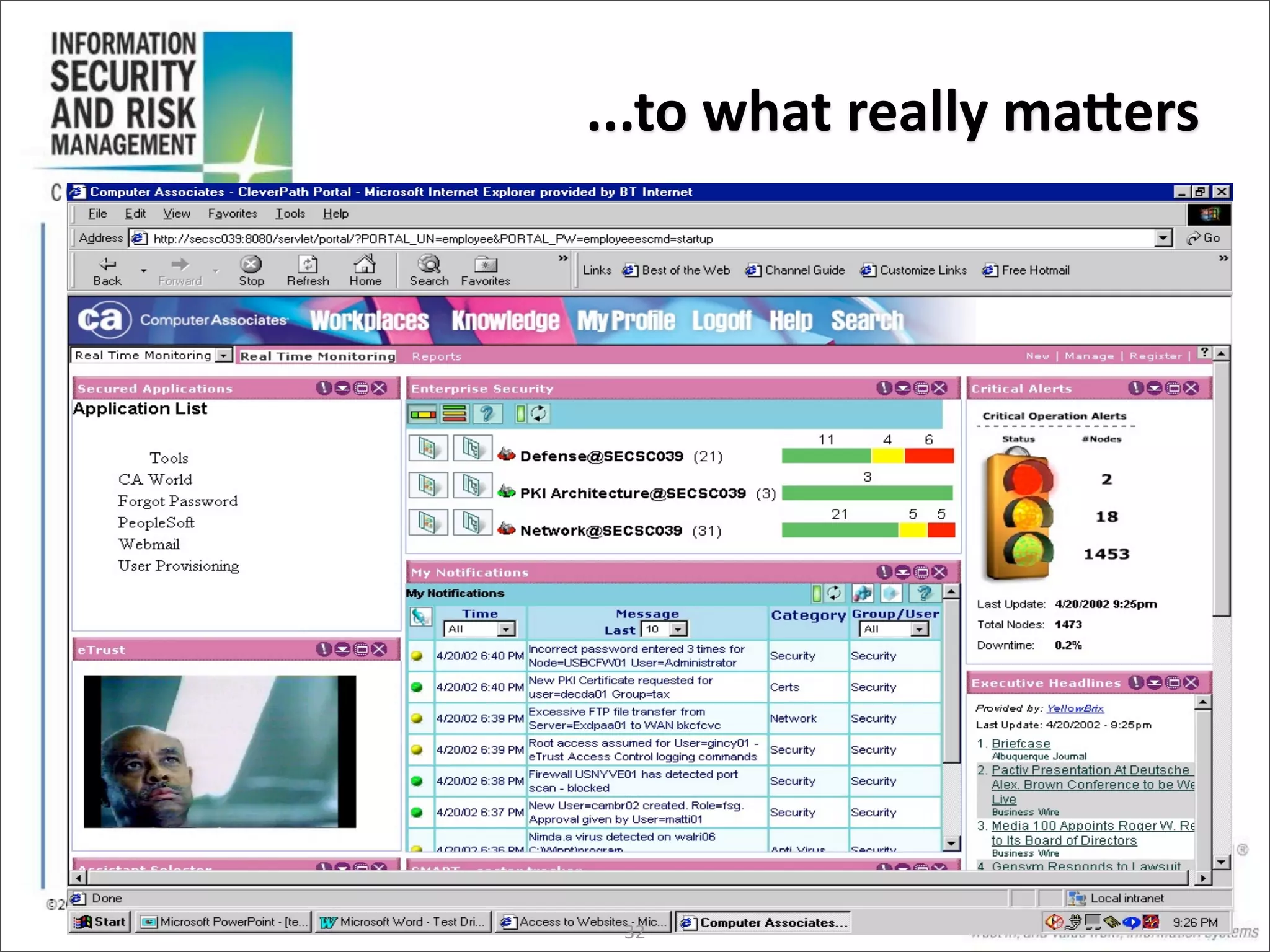
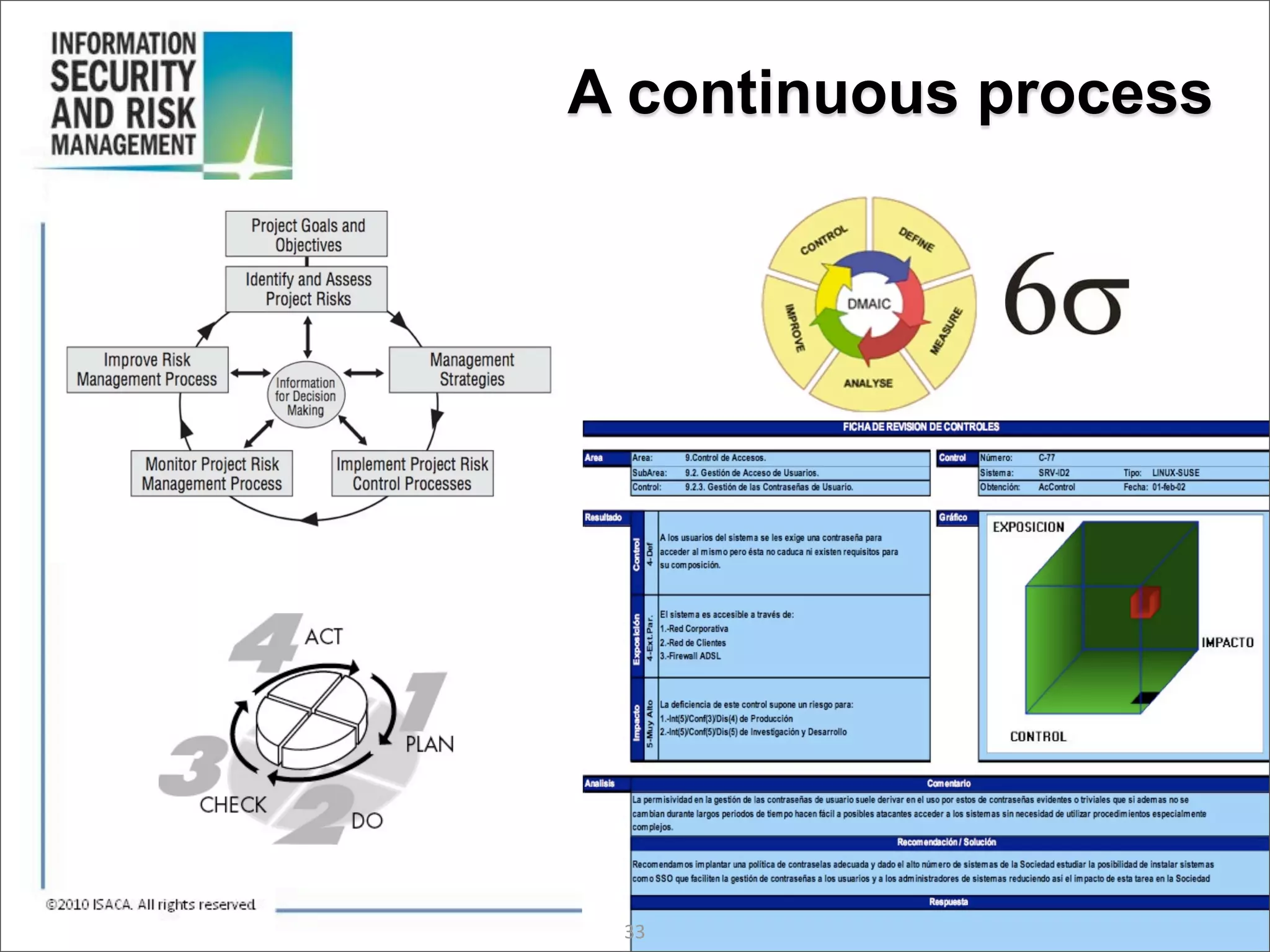
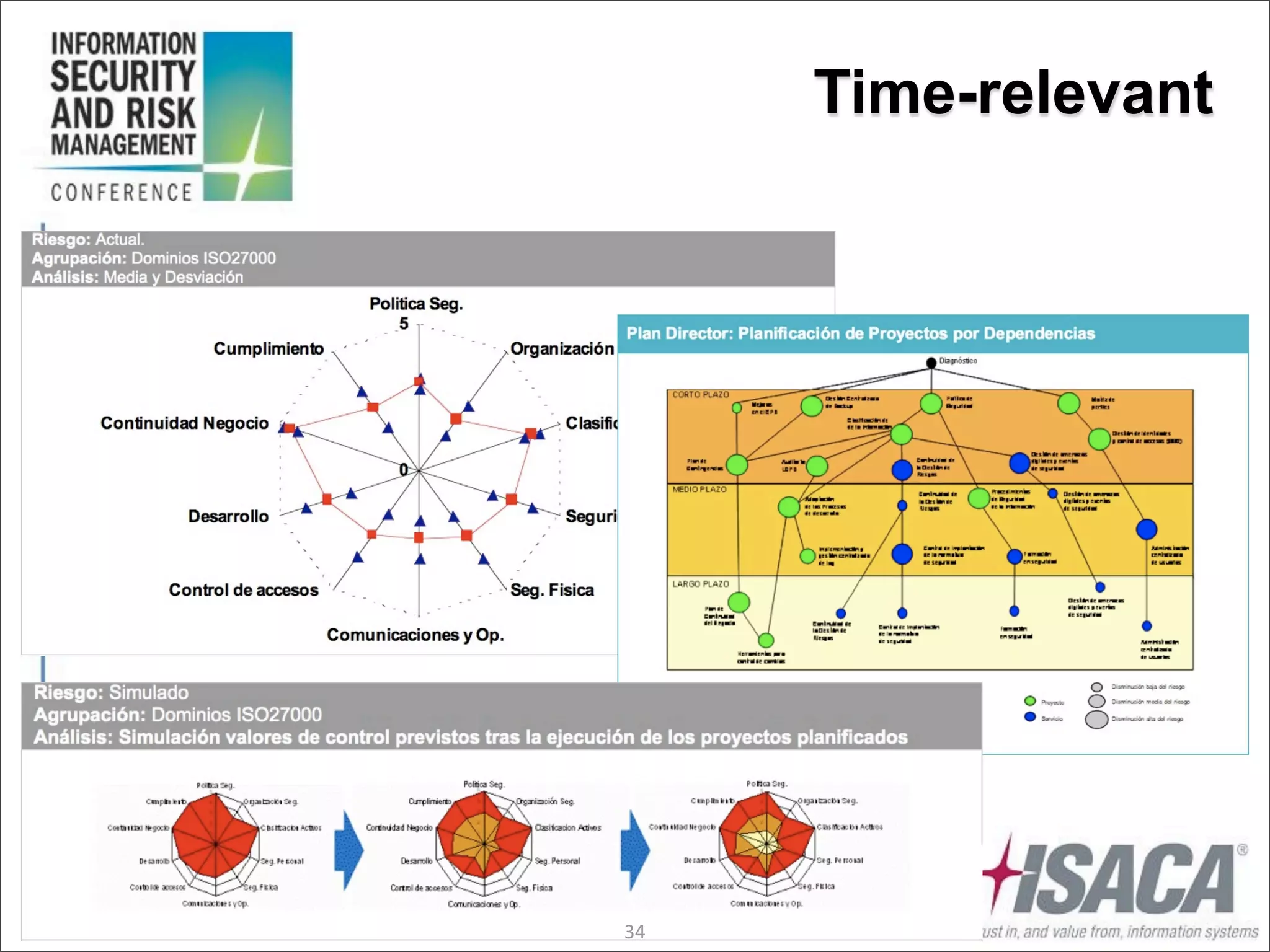
The document discusses the evolution of risk management from focusing on technology risks to encompassing broader enterprise risks. It emphasizes the importance of understanding different types of risks, conducting risk analysis, and implementing a structured approach to risk management through defined processes. Key elements include risk transfer, tolerance, termination, treatment, and communication to align risk management with business objectives.