1) Current risk management approaches are problematic because they are either too notional and abstract or too focused on tangible metrics.
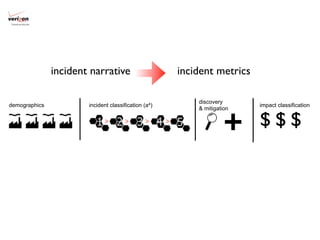
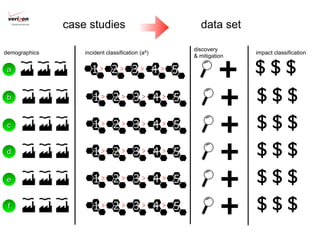
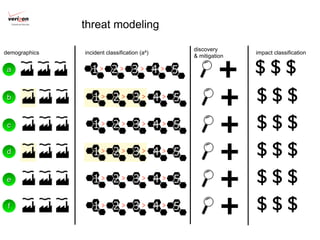
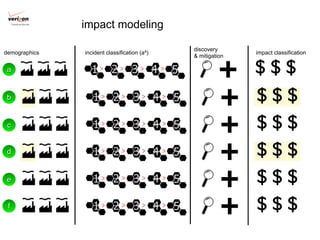
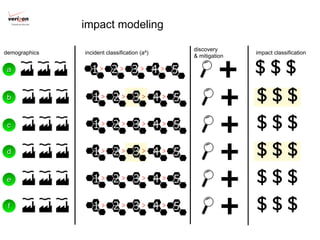
2) A new evidence-based approach is proposed that uses incident data frameworks to extract metrics that can be used to build models of threats, impacts, and management capabilities.
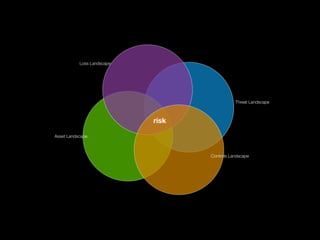
3) By analyzing patterns in incident data, more accurate assessments of risk can be made based on an organization's unique loss landscape, threat landscape, controls landscape, and how these change over time. This moves risk management from superstition to a measurable science.