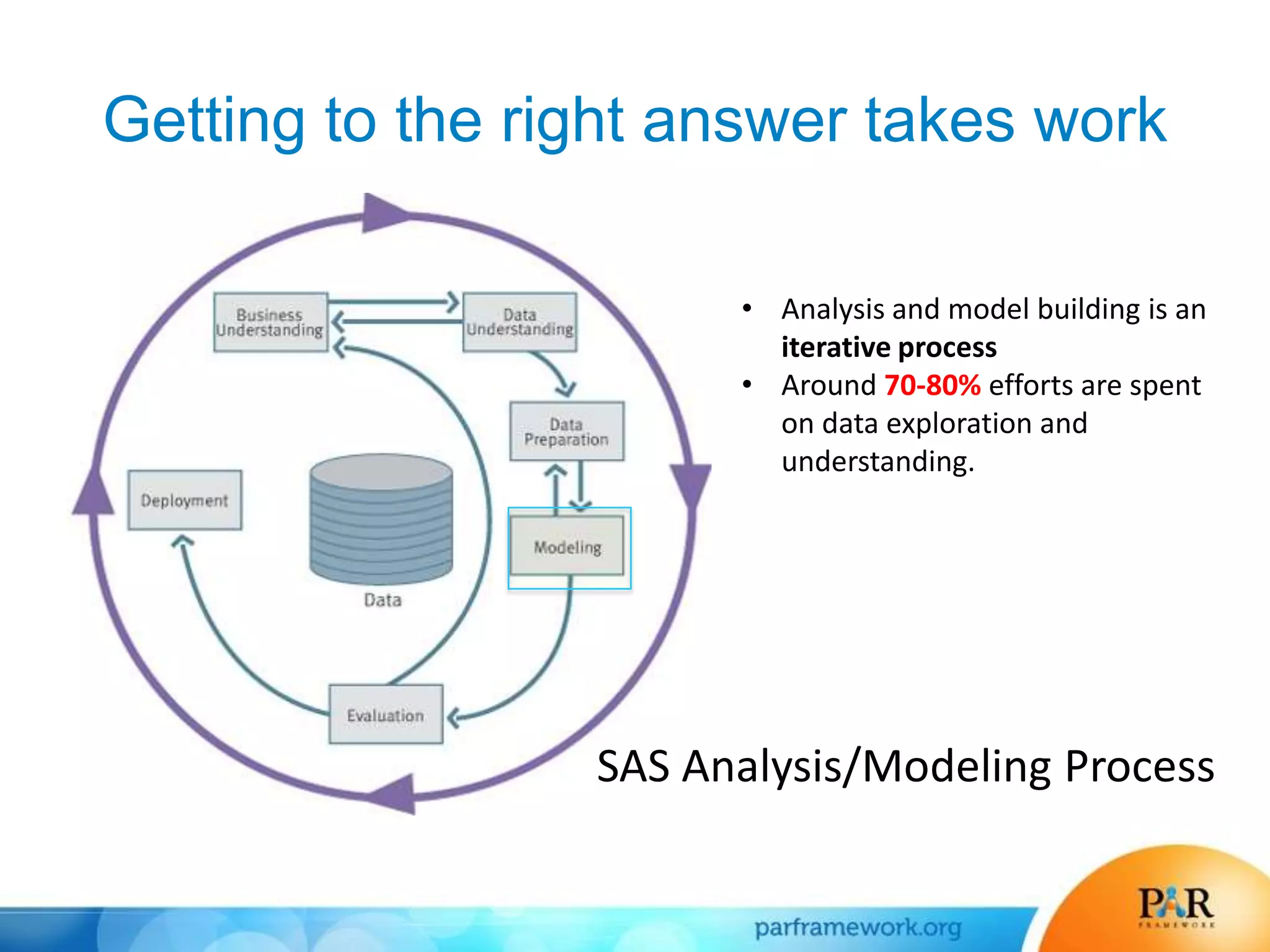
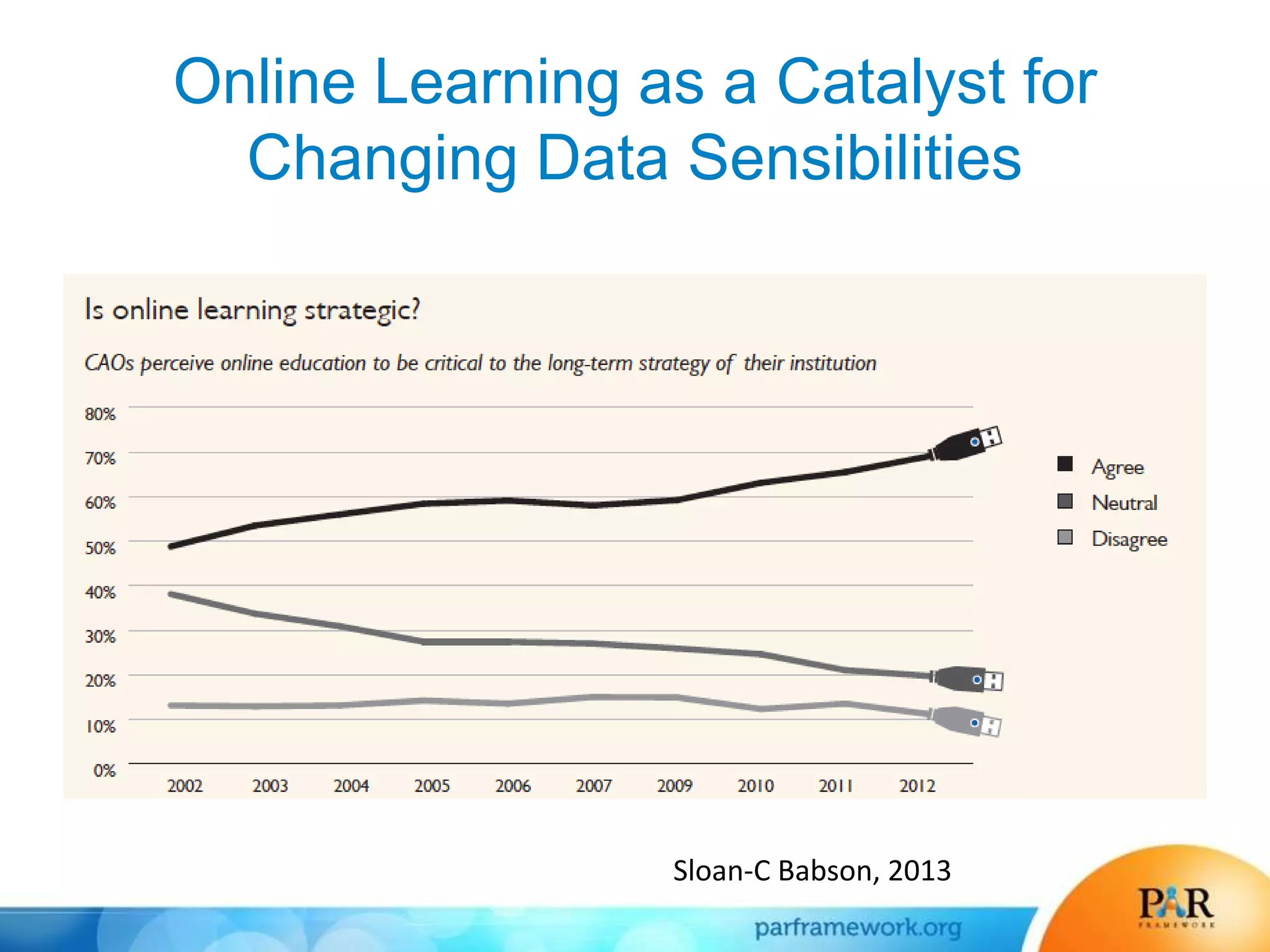
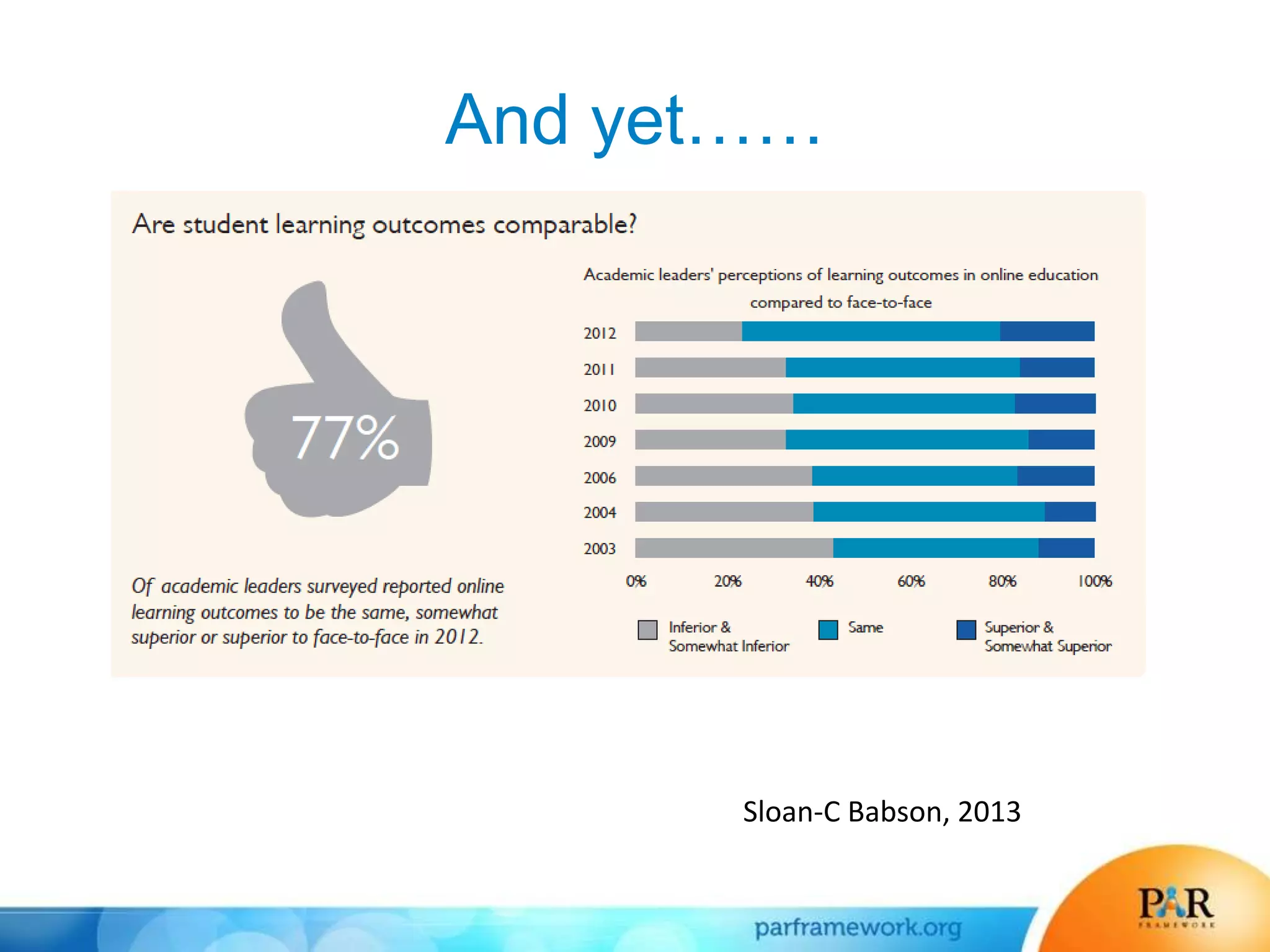
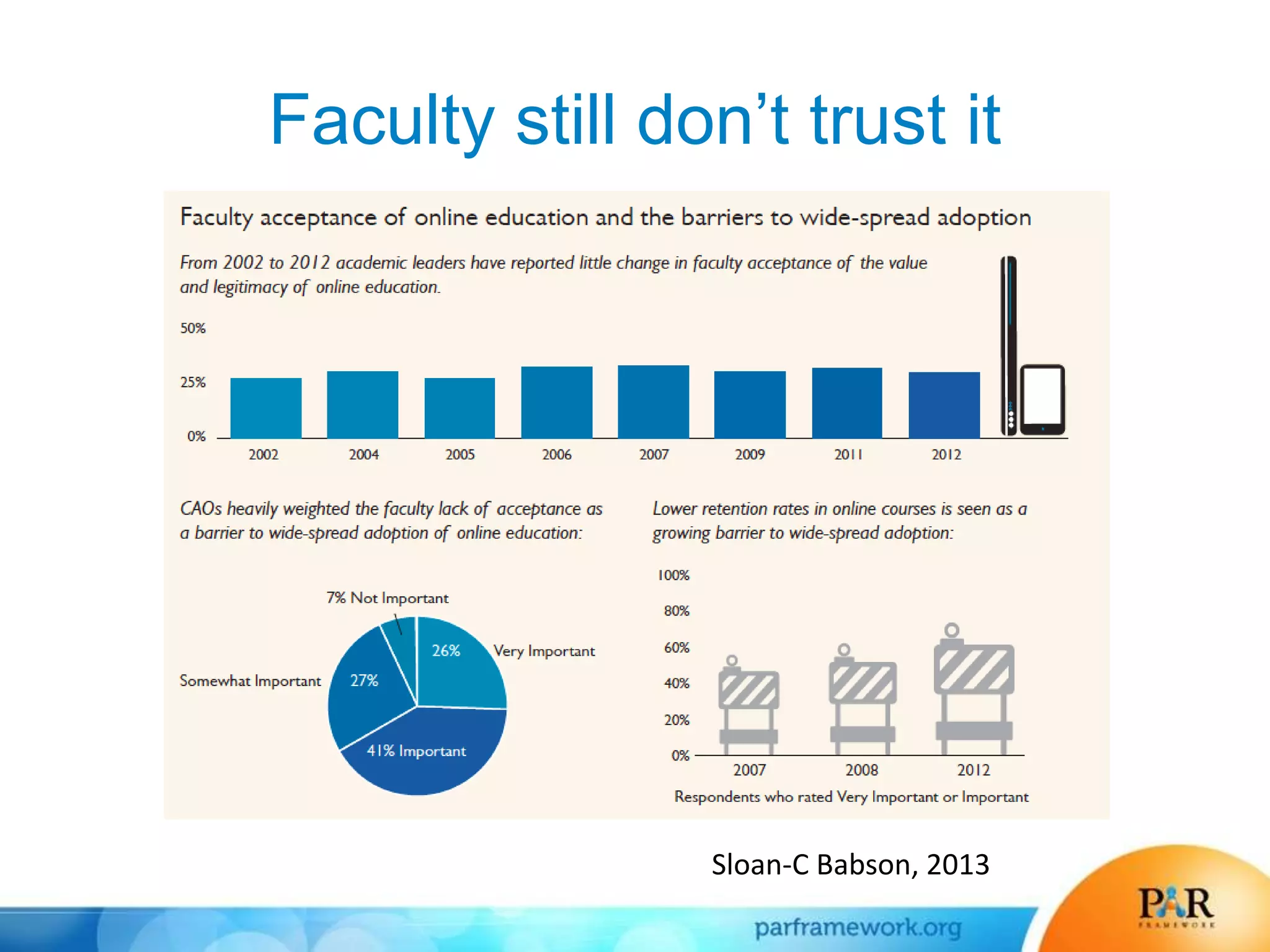
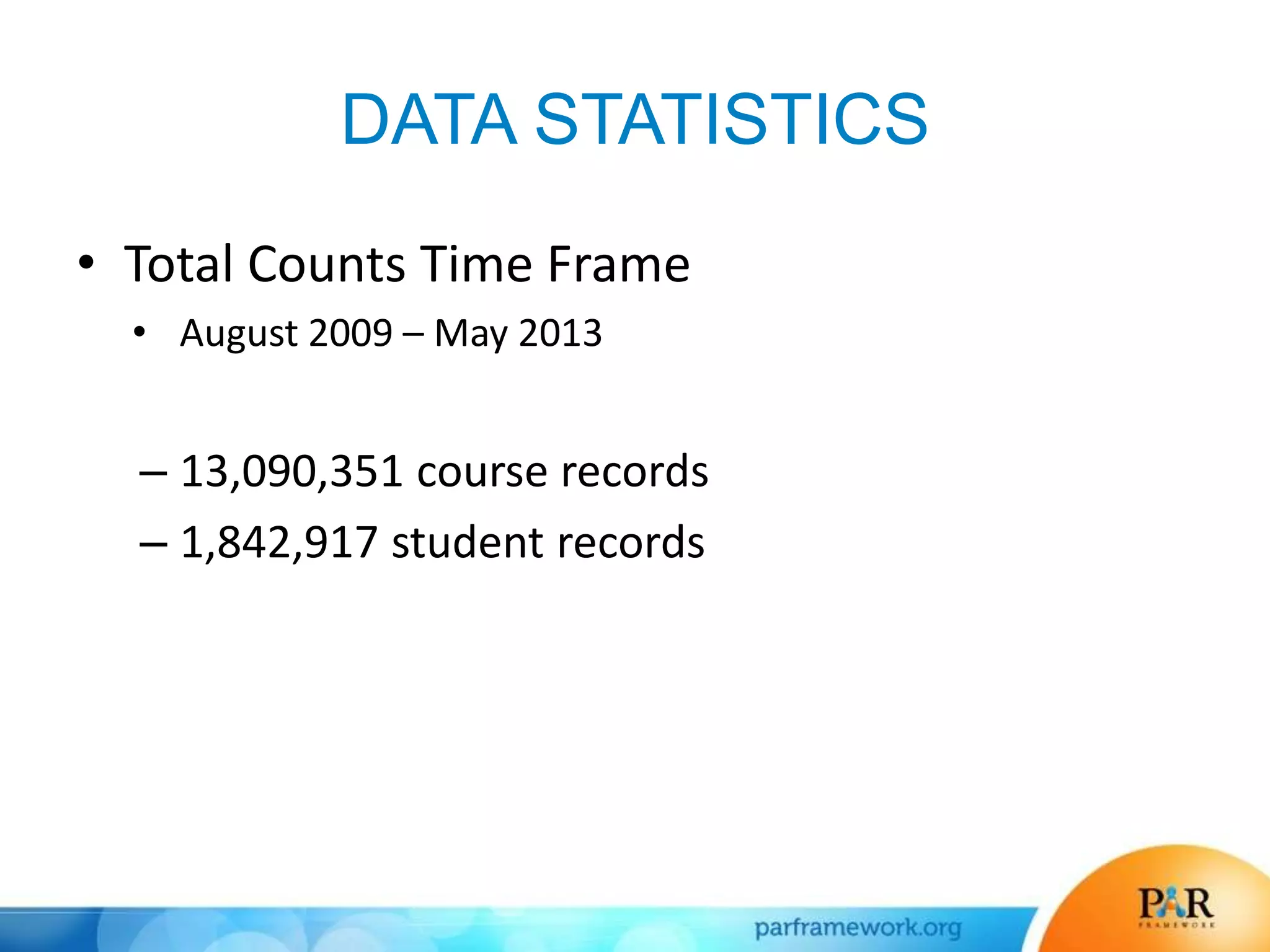
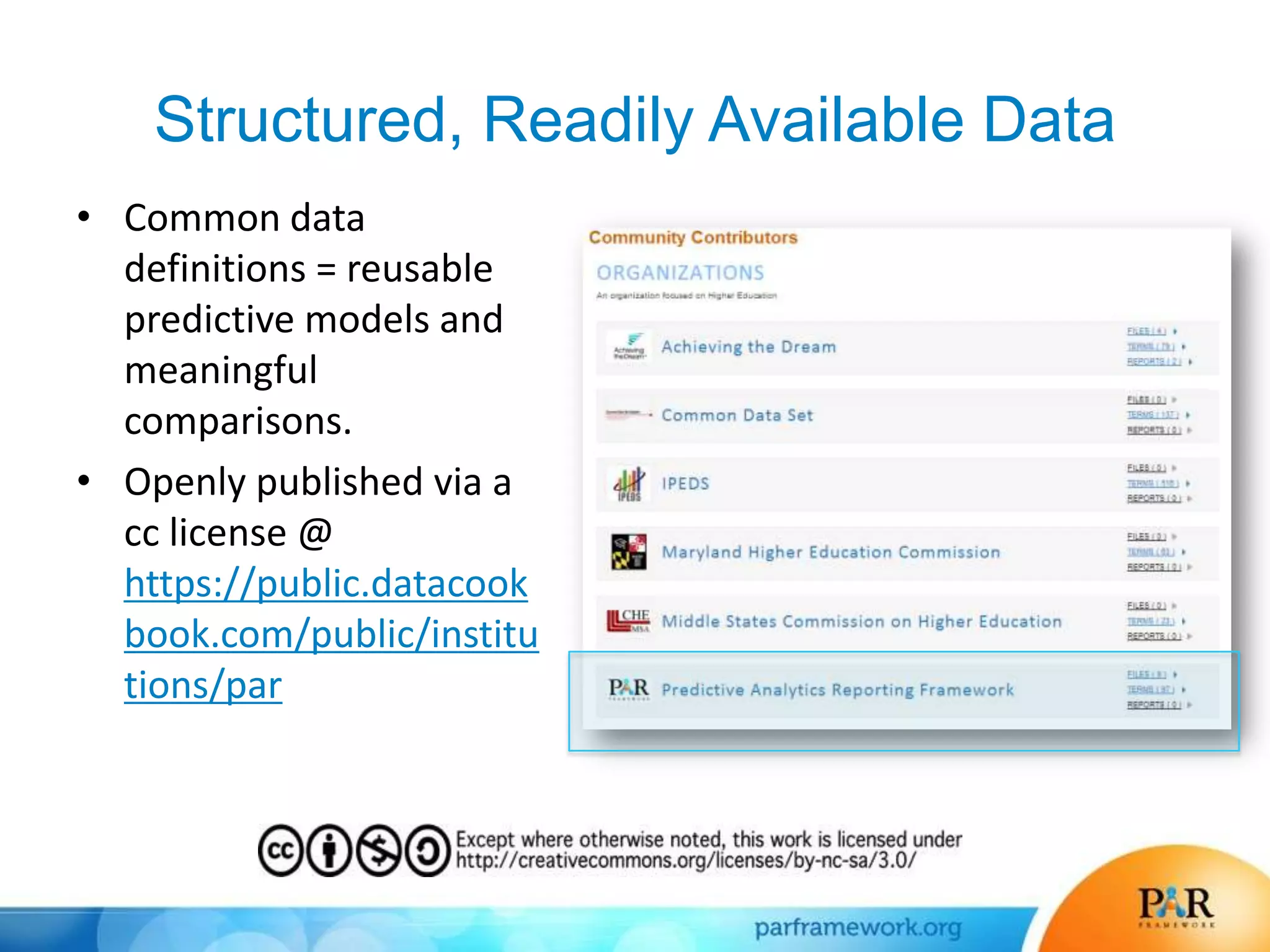
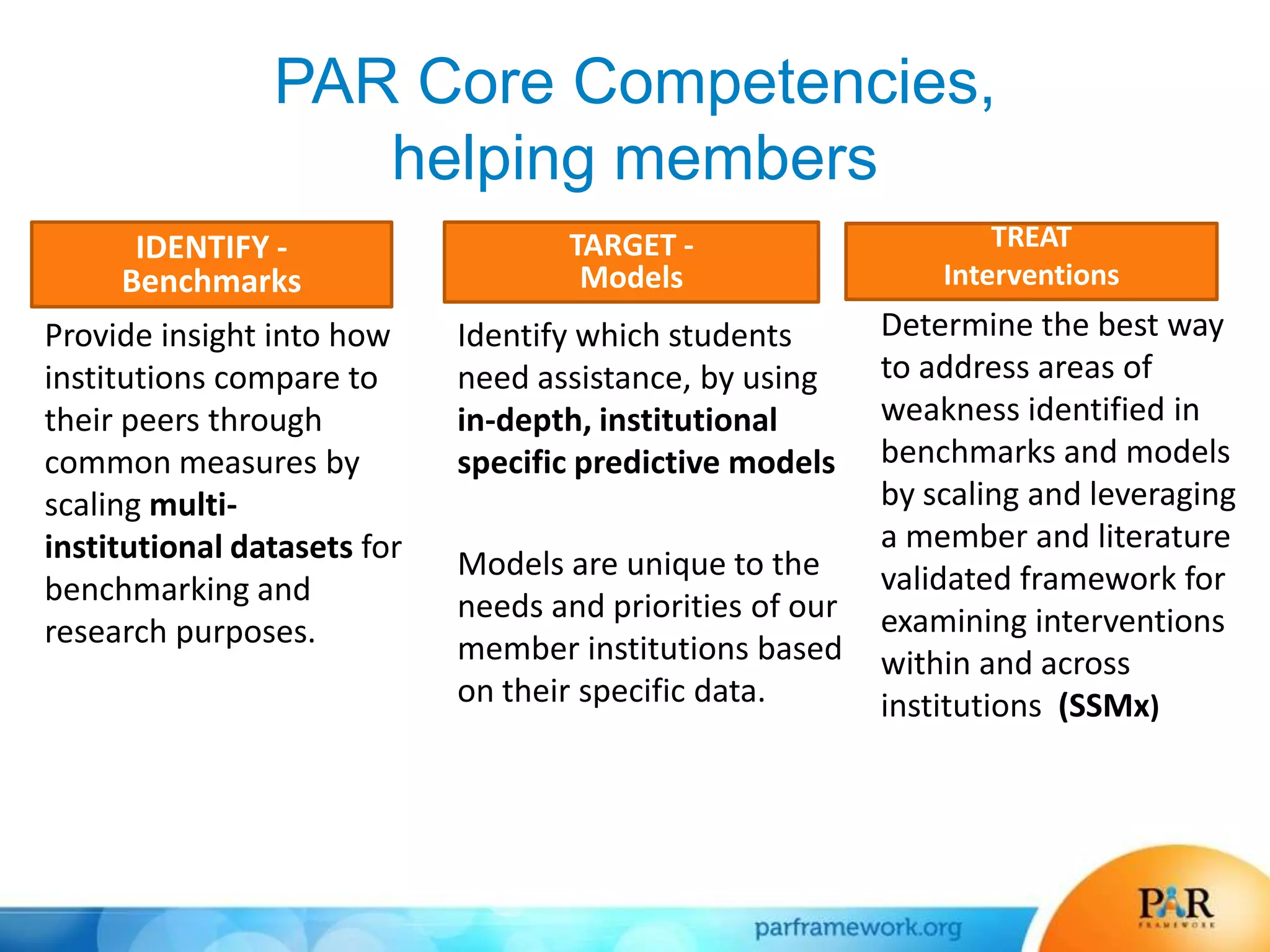
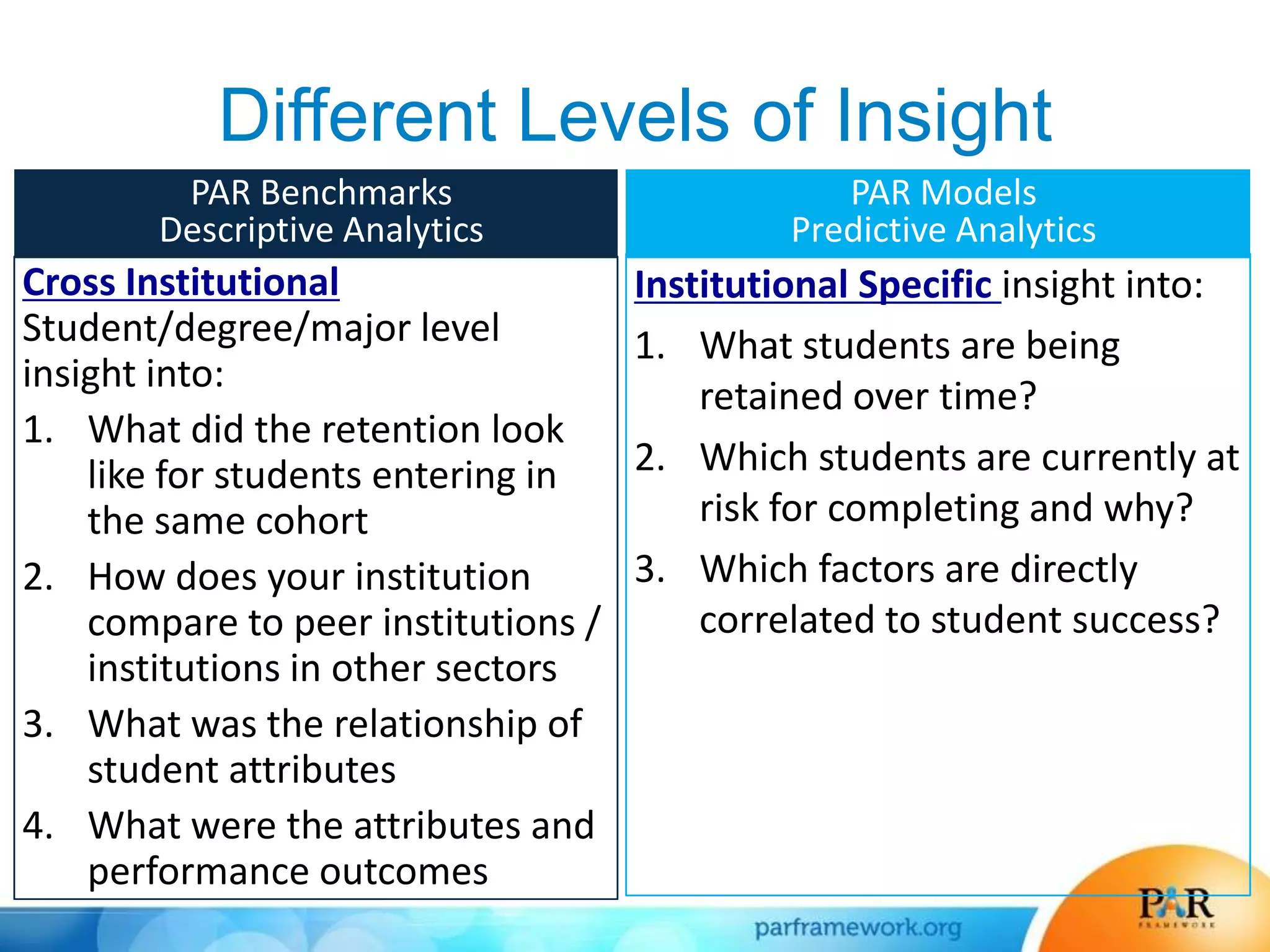
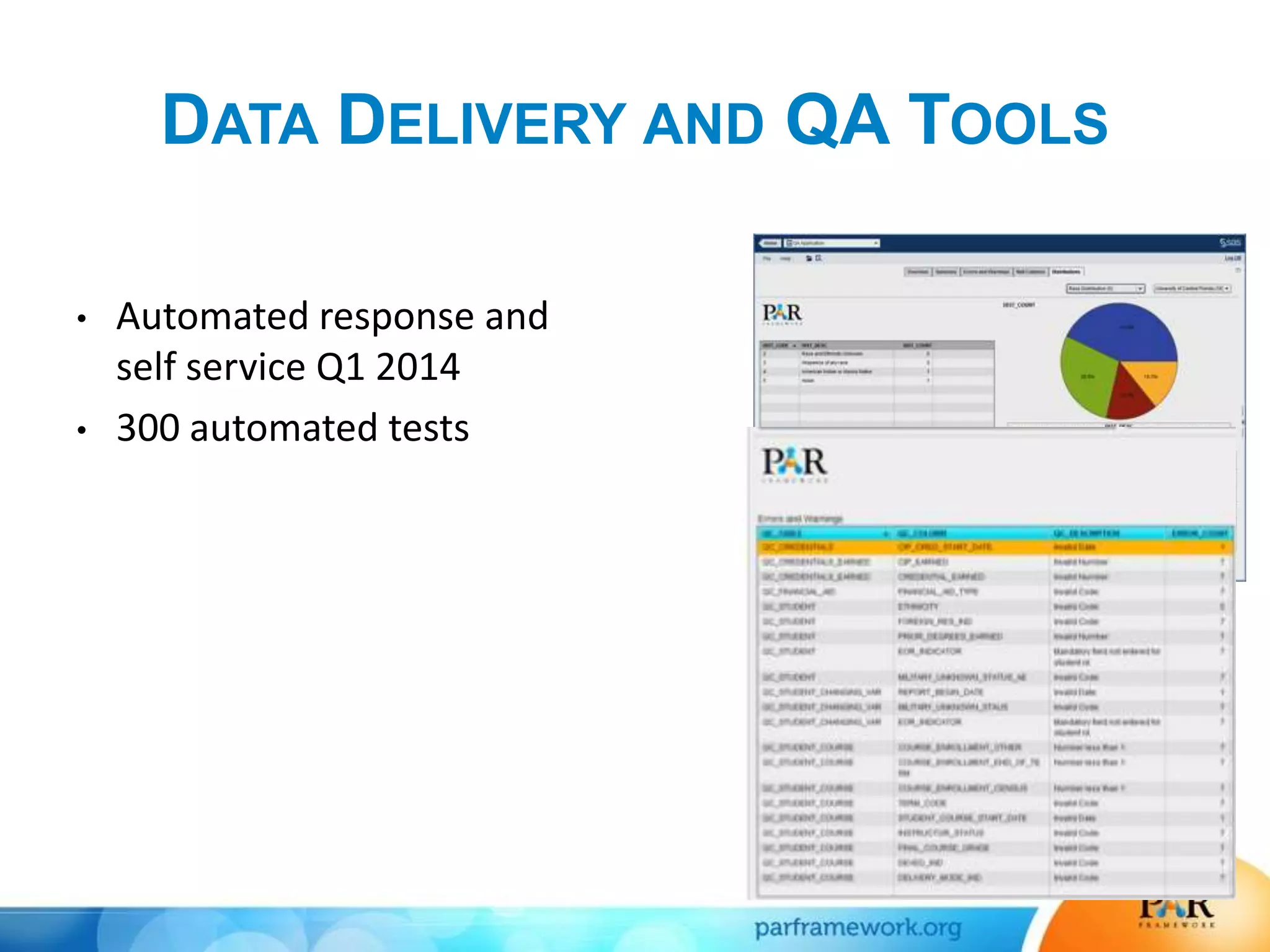
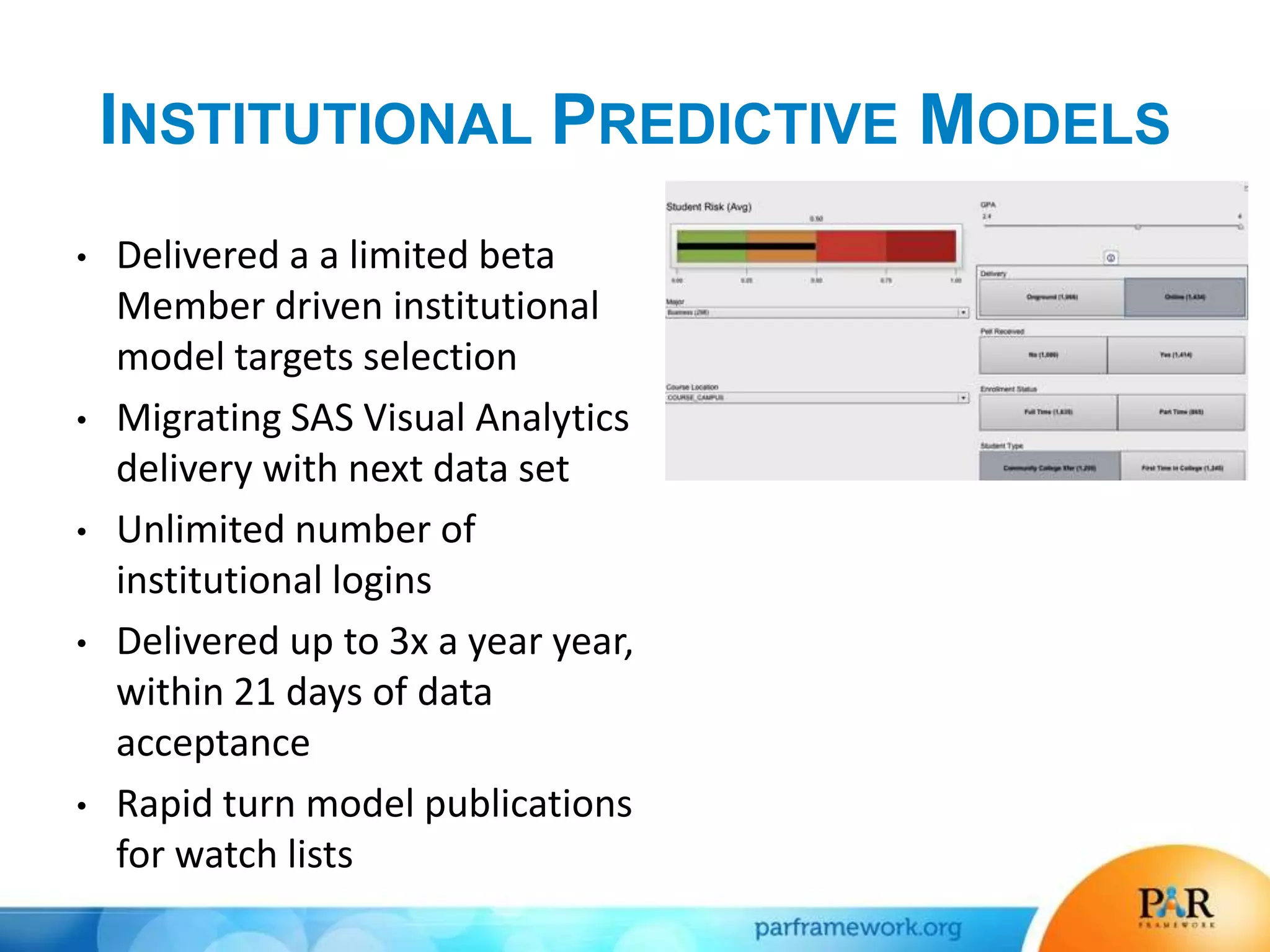
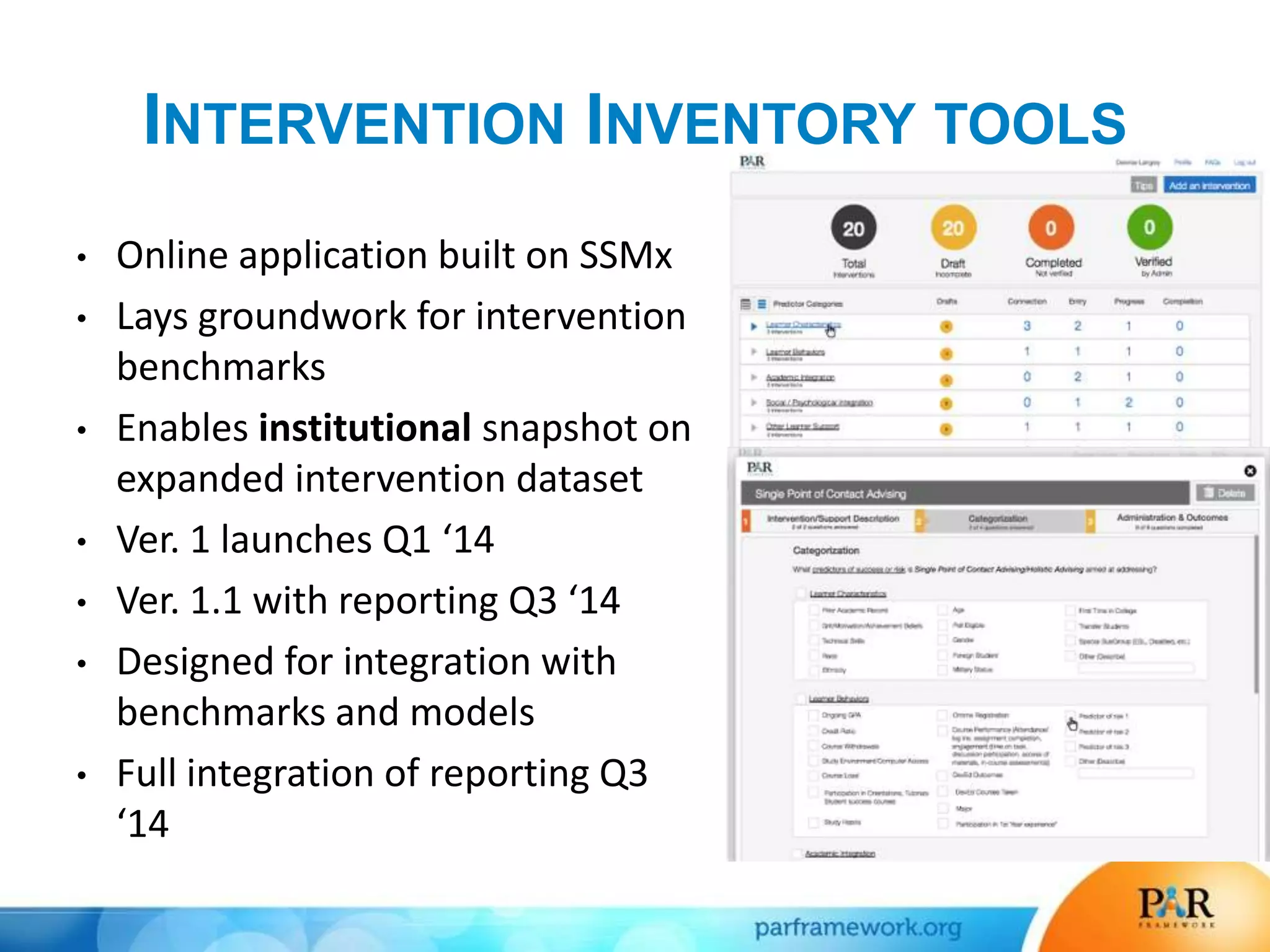
This document summarizes a presentation about how data and predictive analytics are changing expectations around accountability and student success in post-secondary education. It discusses how predictive modeling can identify at-risk students, but predicting risk is not enough - institutions must also link predictions to interventions. The presentation also explores opportunities to generate new insights from data and leverage online learning to fulfill its promise by embracing analytics. The PAR Framework collaborative aims to help institutions improve effectiveness and outcomes through common data definitions, benchmarks, predictive models, and an intervention inventory tool.