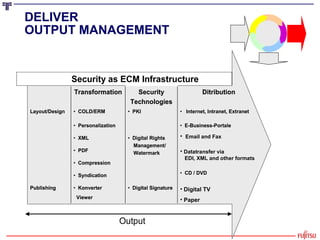
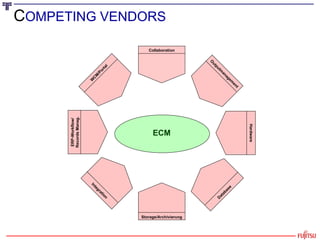
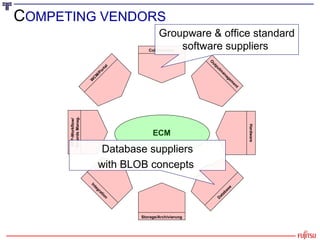
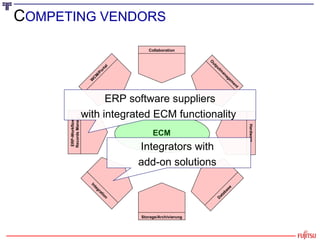
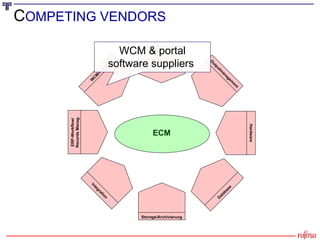
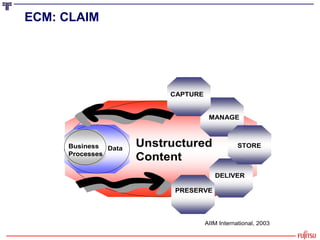
The document presents an overview of the transition from Enterprise Content Management (ECM) to Enterprise Information Management (EIM), emphasizing the importance of effectively managing the ever-growing volumes of unstructured data. It highlights the market drivers behind ECM, discusses strategies for utilizing content as an economic resource, and outlines the essential components and approaches to enhance information management. Key themes include the significance of compliance, collaboration, simplicity in user interfaces, and the integration of various information technologies.





























































































![Dr. Ulrich Kampffmeyer PROJECT CONSULT Unternehmensberatung GmbH Breitenfelder Str. 17 20251 Hamburg Germany Phone: +49-40-46076220 E-Mail: [email_address] Powerpoint version of the presentation (automated animation) http://www.PROJECT-CONSULT.net/files/20090212_ECM_to_EIM_Fujitsu_Marrakech_3_Kff_Show.pps Company information http://www.PROJECT-CONSULT.com ECM article on Wikipedia http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enterprise_content_management ECM Enterprise Content Management (Book in English, French and German) http://www.project-consult.net/Files/ECM_White%20Paper_kff_2006.pdf PROJECT CONSULT Newsletter (Archive) http://pcnewsletter.coextant.info/ Information](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20090212ecmtoeimfujitsumarrakech3kffhandout-090306090559-phpapp01/85/EN-From-ECM-Enterprise-Content-Management-to-EIM-Enterprise-Information-Management-Ulrich-Kampffmeyer-Marrakech-2009-108-320.jpg)