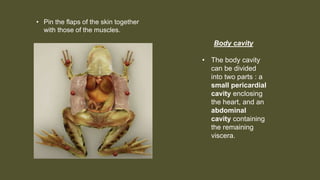
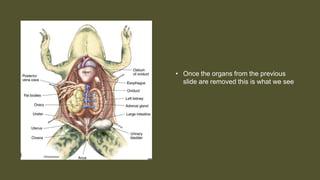
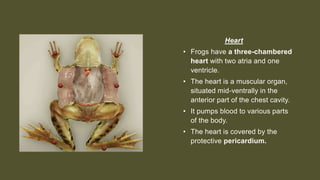
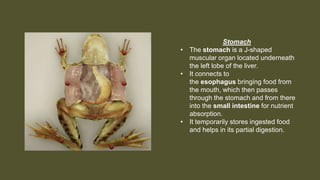
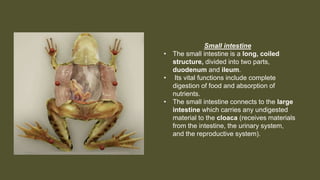
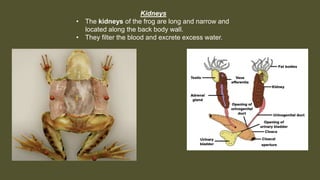
This document provides an overview of the internal anatomy of a female leopard frog. It details the major internal organs like the heart, lungs, liver, stomach, intestines, kidneys, and reproductive system. Descriptions include the location and basic functions of each organ. For example, it notes that the frog heart has three chambers and is located in the chest cavity, while the lungs are small pouches on either side of the midline that facilitate gas exchange. The document provides guidance on dissection techniques to view these internal structures.