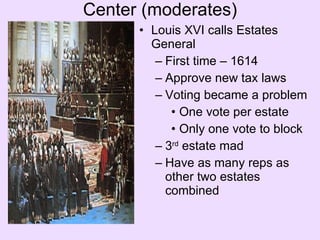
The French Revolution began in 1789 and ended in 1799. It was caused by economic, political, and social factors including a bankrupt government, an absolute monarchy, and unequal rights and taxation that disadvantaged the third estate. The revolution removed the monarchy and established a republic, but this period was marked by instability and violence including the Reign of Terror led by Robespierre that resulted in thousands of deaths by guillotine. The revolution dramatically transformed French government and society and had widespread impact on other European countries.