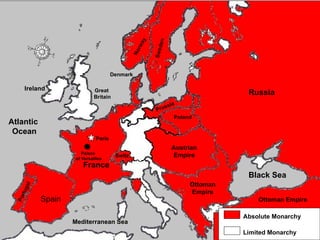
The document provides an overview of the causes and events of the French Revolution from 1789-1799. It discusses how the ideas of the Enlightenment and inequalities between the three estates led to unrest. Key events included the formation of the National Assembly, the storming of the Bastille, bread riots, and the declaration of the Rights of Man which established new freedoms and moved France from an absolute to constitutional monarchy.