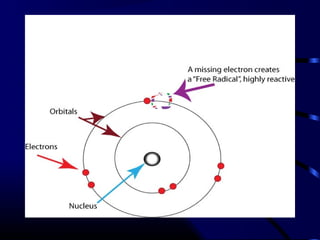
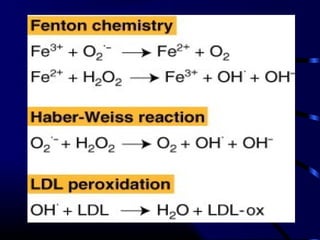
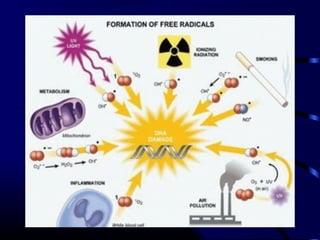
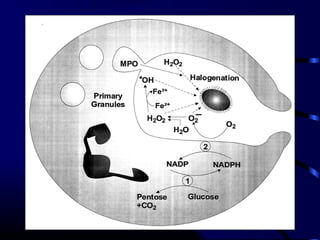
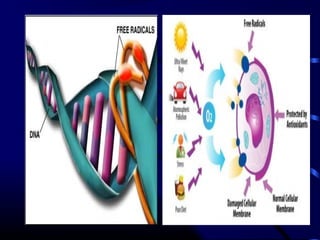
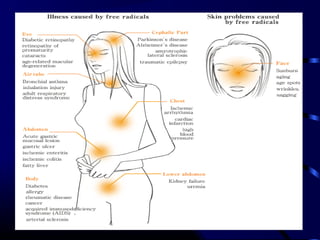
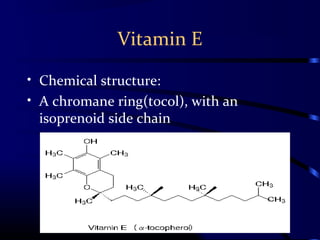
Free radicals are molecules with unpaired electrons that can damage cells. Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from free radical damage. The document defines free radicals and describes how they are normally produced and how they can damage lipids, proteins, and DNA. It then explains the systems cells use to prevent and intercept free radicals, including enzymes like superoxide dismutase and antioxidants like vitamin E. Vitamin E acts as a chain-breaking antioxidant that stops the chain reactions of lipid peroxidation caused by free radicals. A deficiency of vitamin E can occur if one cannot absorb dietary fat or in premature infants, but it is generally uncommon as it is found in many foods.