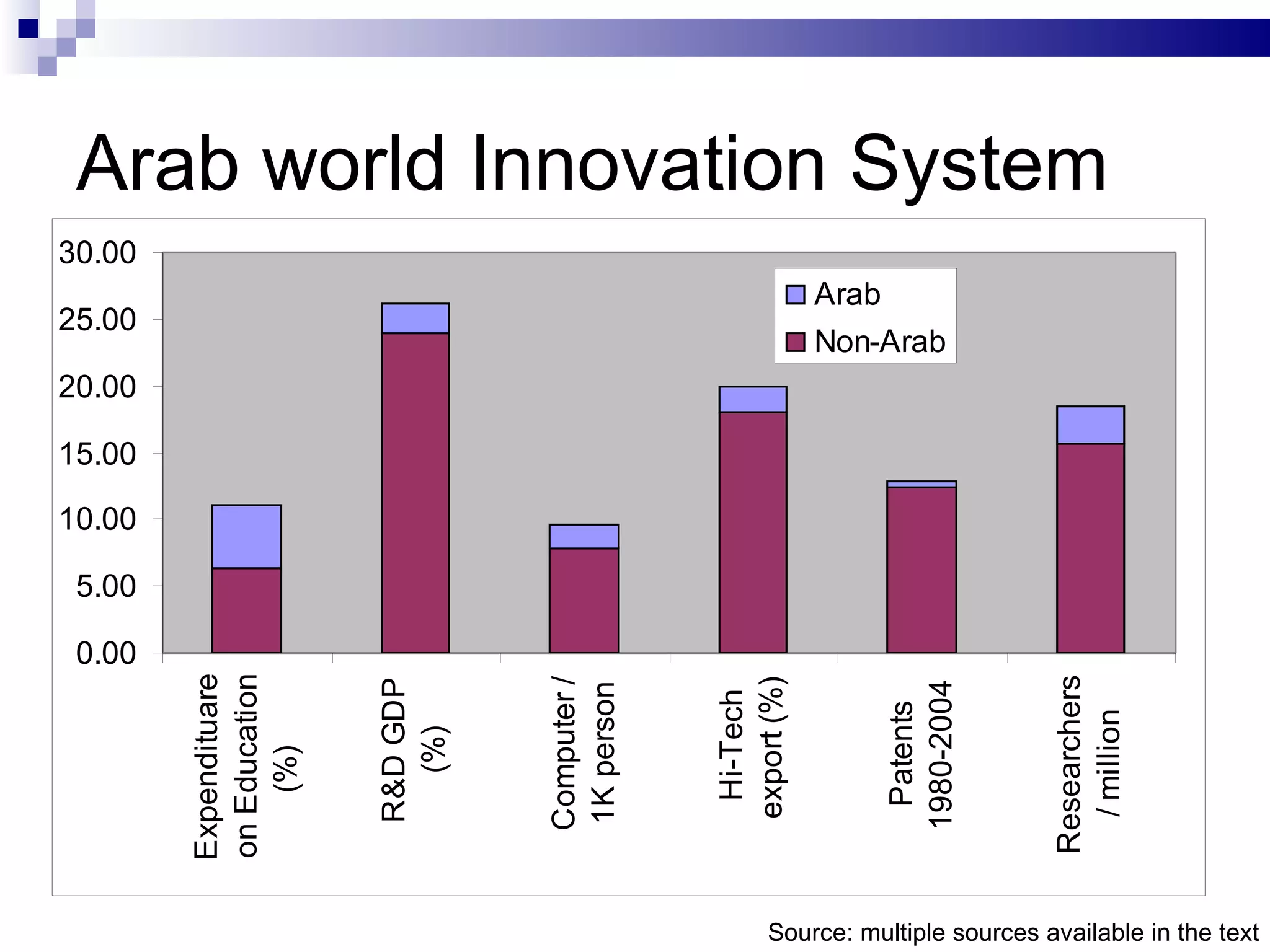
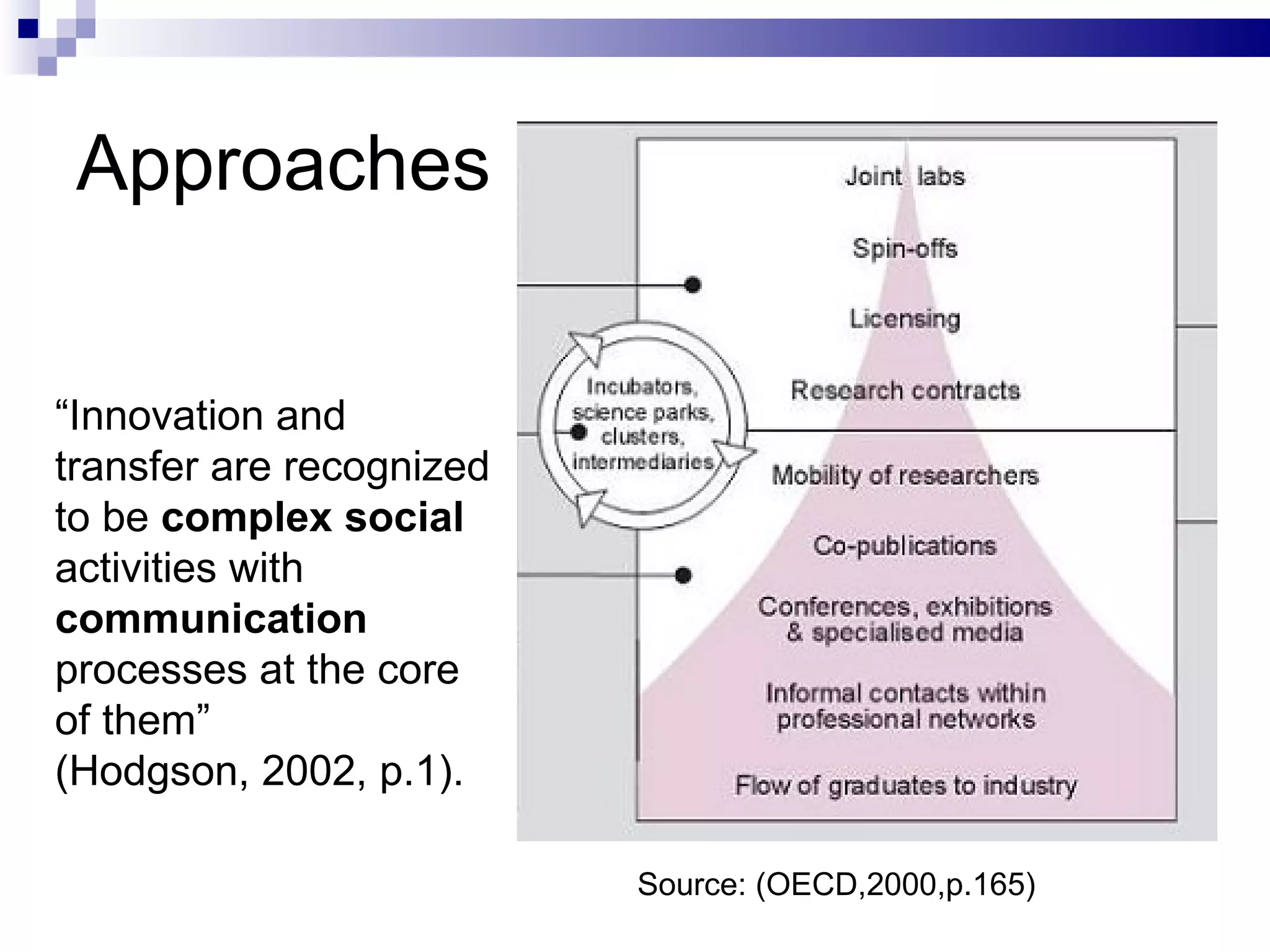
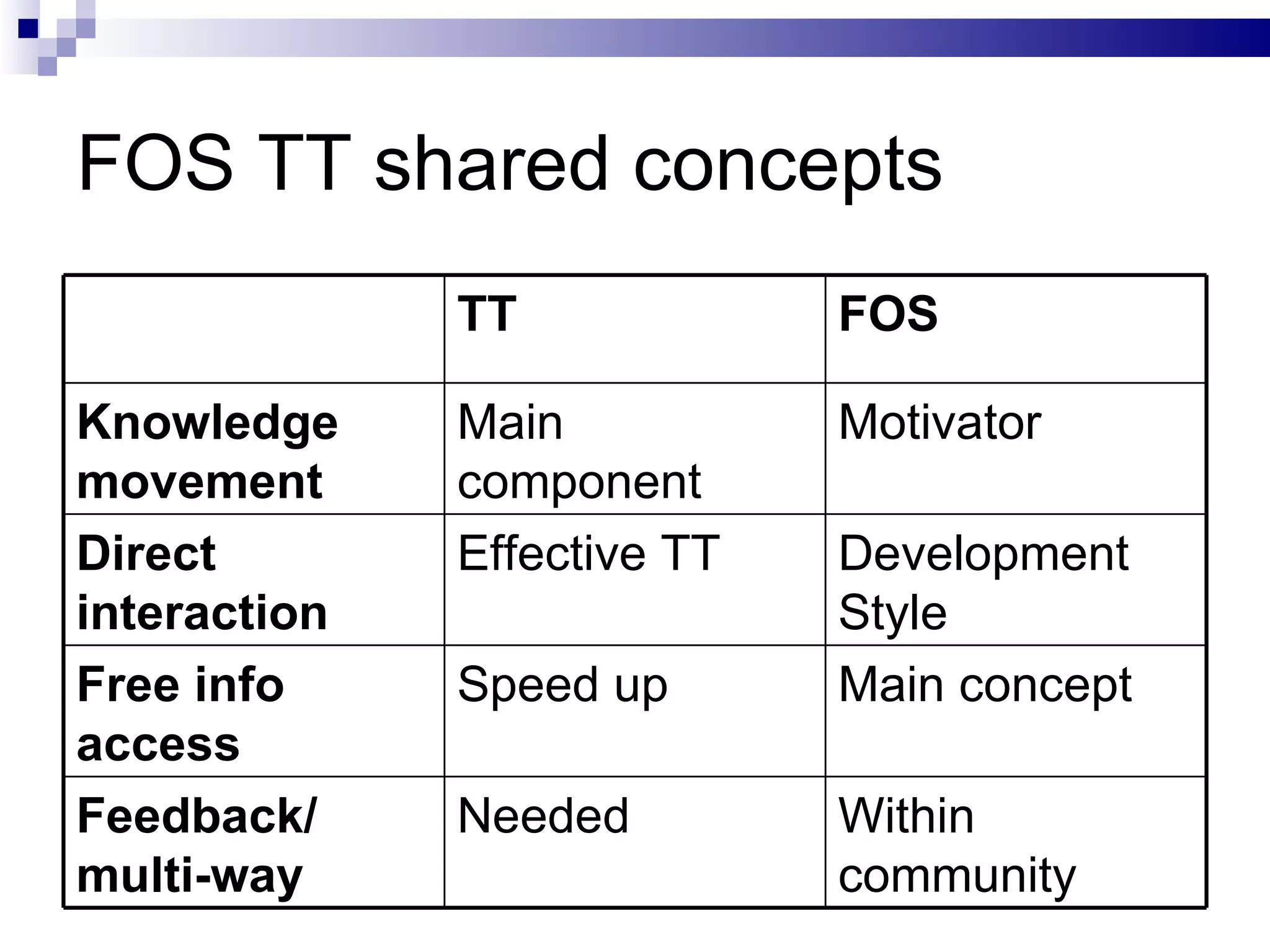
The document discusses using free and open source (FOS) as a technology transfer (TT) tool in the Arab world. It outlines some key issues with innovation and TT in the region like lack of funding and links between research and industry. It then presents FOS as a potential low-cost TT model that could help by facilitating cooperation and knowledge sharing between different actors. Some benefits identified are minimizing costs, risks and brain drain while expanding access to knowledge resources. However, the document also notes there are still challenges to adopting FOS in the Arab world like weak ICT infrastructure and lack of FOS expertise and community. It concludes that strategic plans, social values of sharing and rewarding participation will be important to leverage FOS for