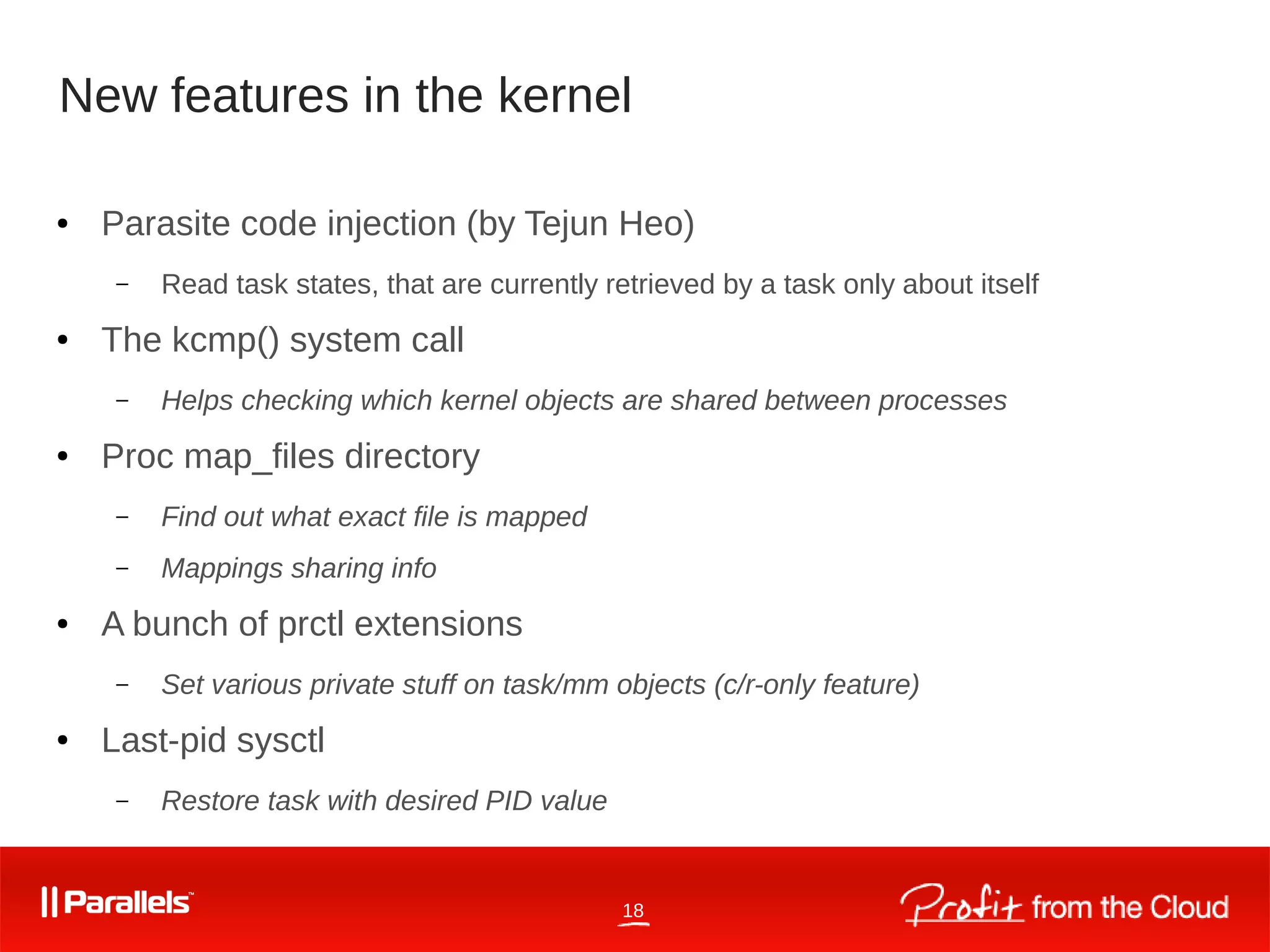
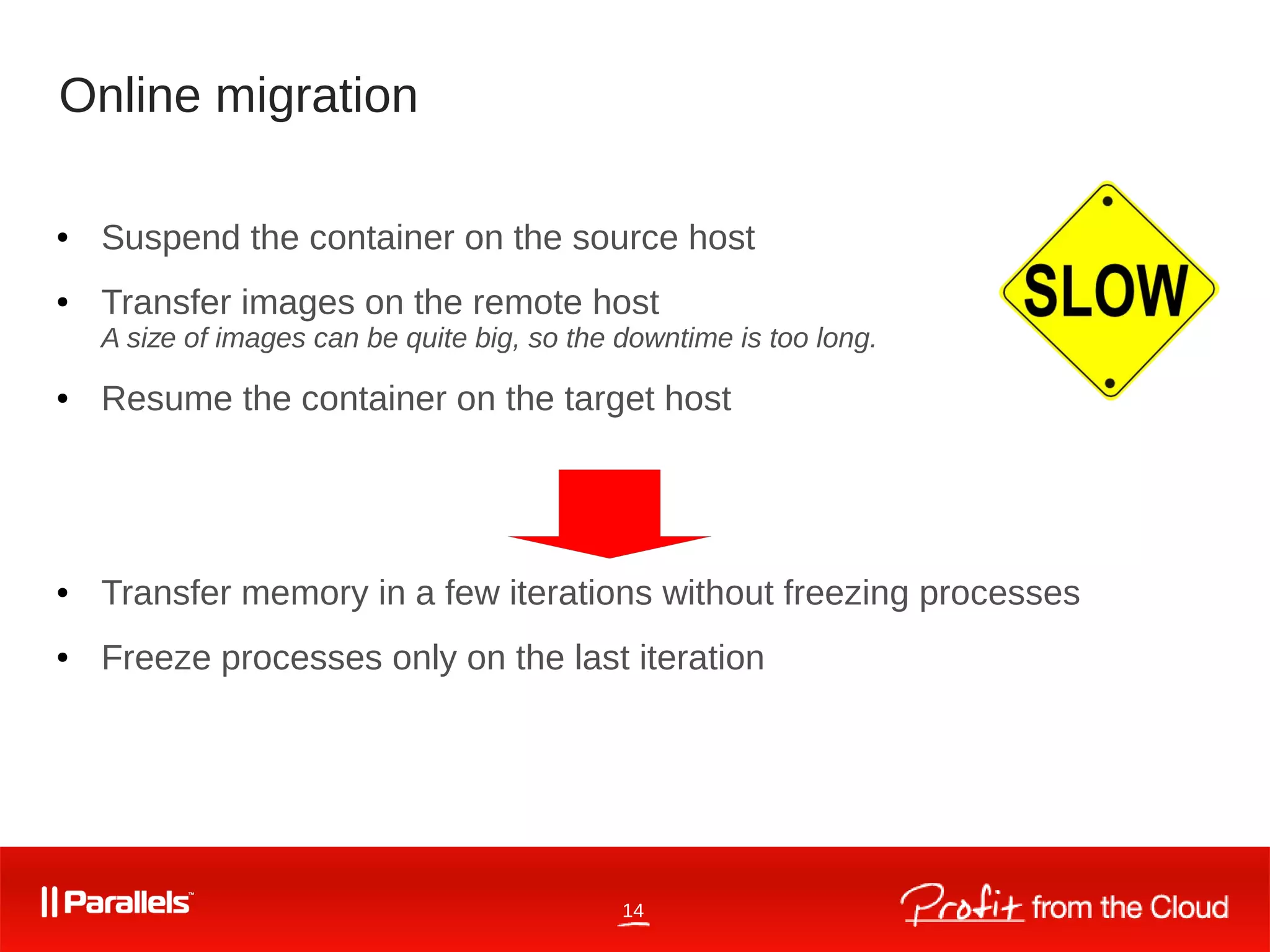
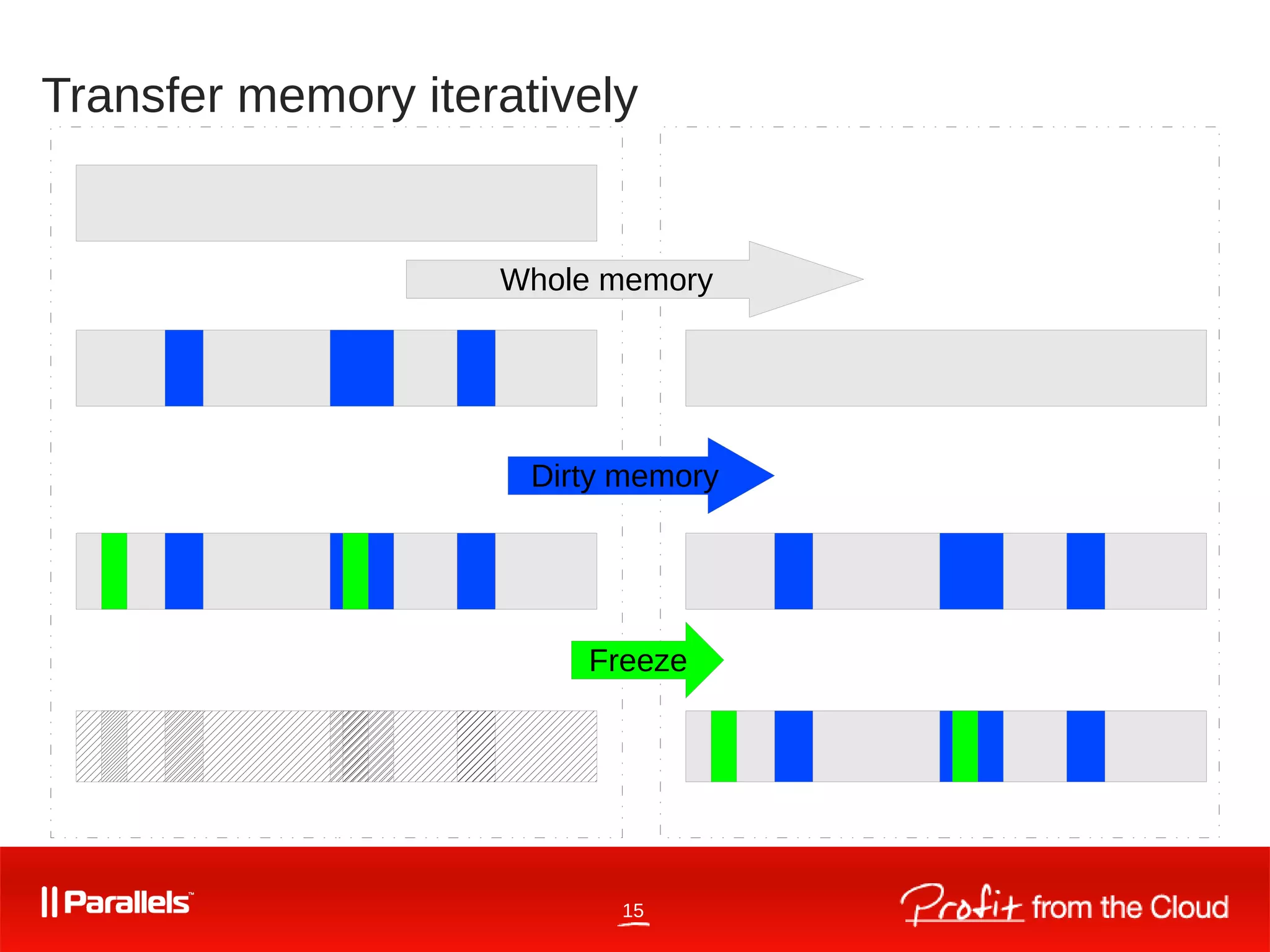
CRIU is a tool for checkpointing and restoring running Linux containers and processes. It began as an OpenVZ kernel module in 2005 and became its own open source project in 2011. CRIU works by dumping the memory, filesystem, and kernel state of running processes and restoring them elsewhere. It supports live migration through iterative dumping of memory without freezing processes. New features in CRIU and the Linux kernel continue to improve its capabilities for tasks like online migration and restoring processes with custom PIDs. CRIU is developed and maintained by a large open source community.



![16
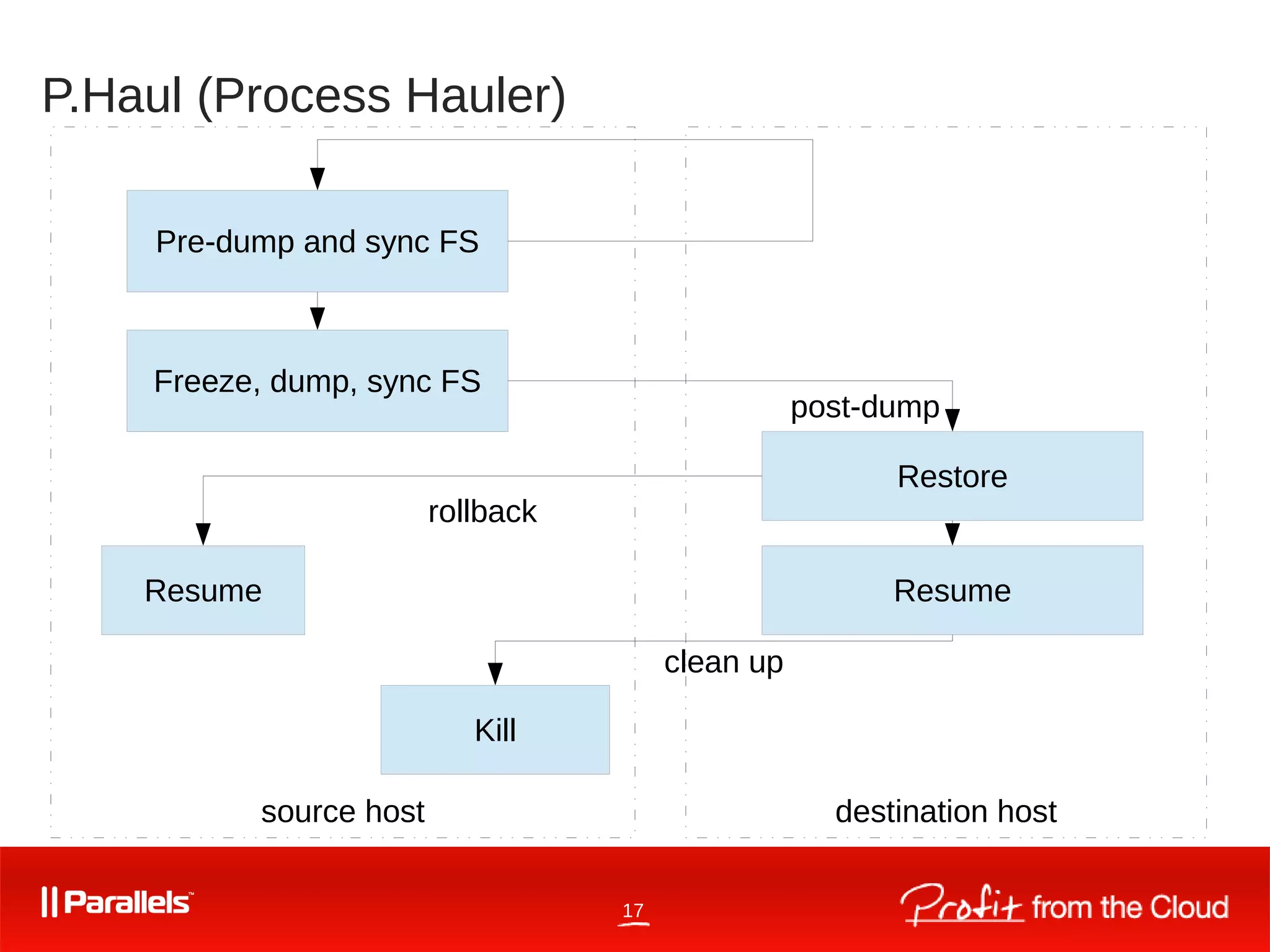
P.Haul (process hauler) - Live migration using CRIU
Live migration using CRIU
● Iterative
● Optimal
● Customizable
#./p.haul ovz 100 10.30.25.213
Migration succeeded
total time is ~2.86 sec
frozen time is ~1.99 sec
( ['0.27', '0.18', '1.55'] )
restore time is ~0.86 sec
img sync time is ~0.32 sec](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/criu-fosdem-2015-150201044716-conversion-gate02-150521101800-lva1-app6891/75/FOSDEM-2015-Live-migration-for-containers-is-around-the-corner-12-2048.jpg)