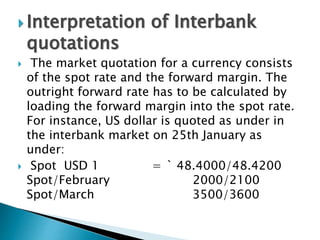
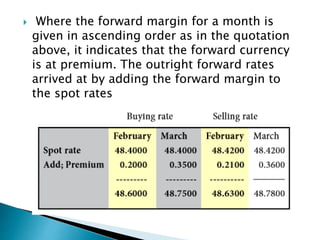
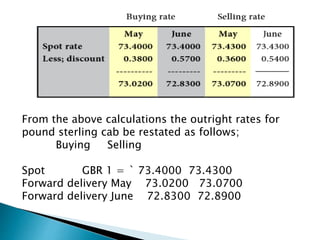
The document discusses forward rates, forward margins, and how to calculate them. Some key points:
- The forward margin is the difference between the forward rate and spot rate, and can be at a premium or discount.
- If at a premium, the foreign currency is more expensive forward than spot. If at a discount, it is cheaper forward than spot.
- To get the forward rate from the spot rate, you either add the premium or subtract the discount.
- An example calculation of a forward margin using interest rate differentials and time periods is provided.