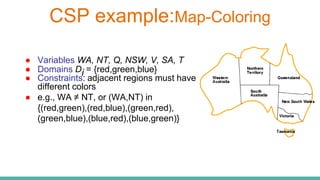
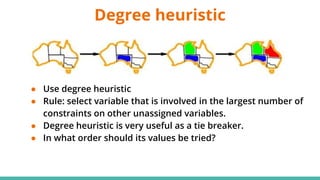
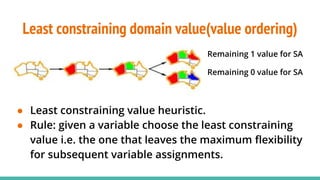
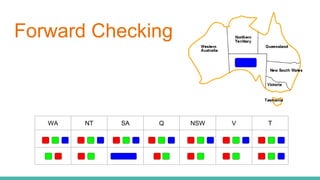
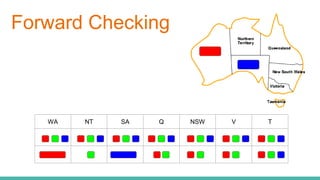
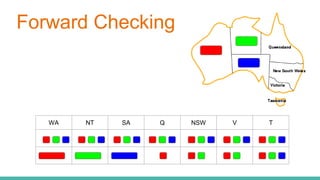
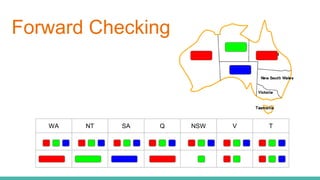
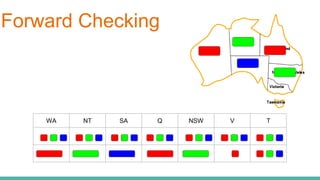
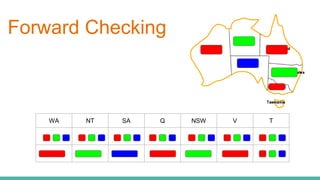
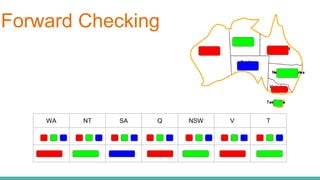
This document discusses constraint satisfaction problems (CSP) and the CSP solving technique called forward checking. It provides an example of a map coloring CSP problem and then explains forward checking, which tracks remaining legal values for unassigned variables and terminates the search when a variable has no legal values left. It also discusses using heuristics like the degree heuristic, minimum remaining values heuristic, and least constraining value heuristic to guide the search order during forward checking.