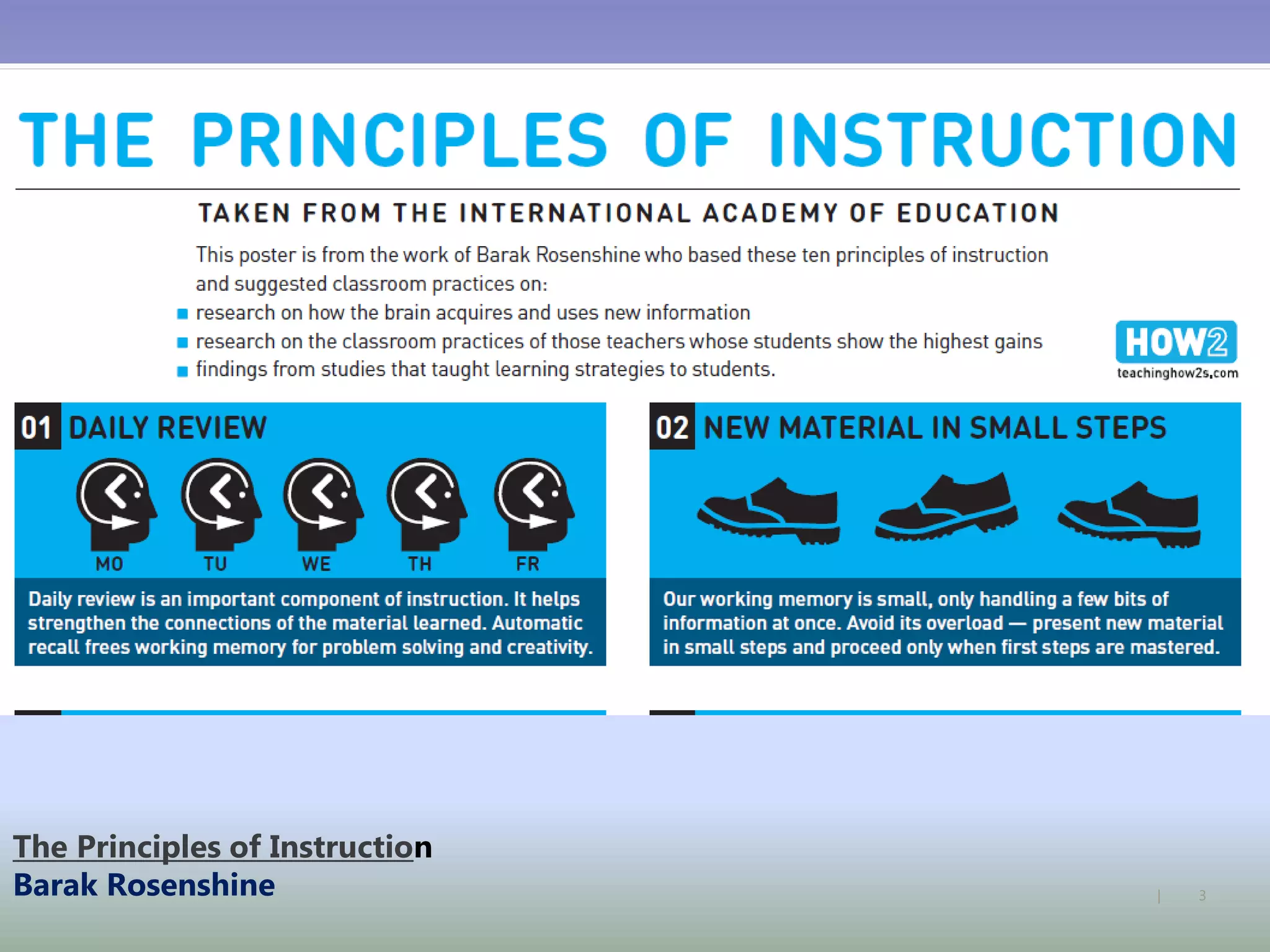
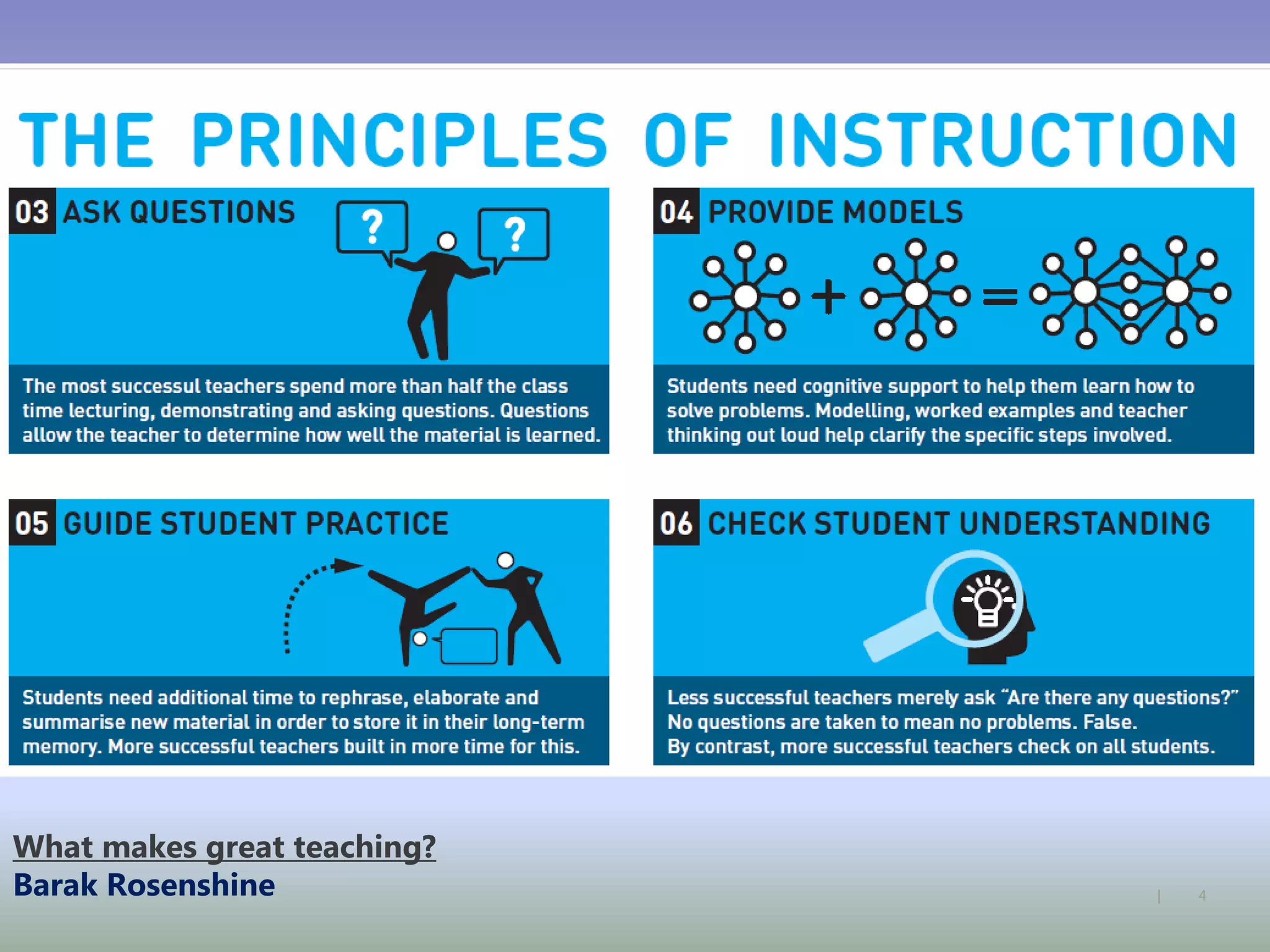
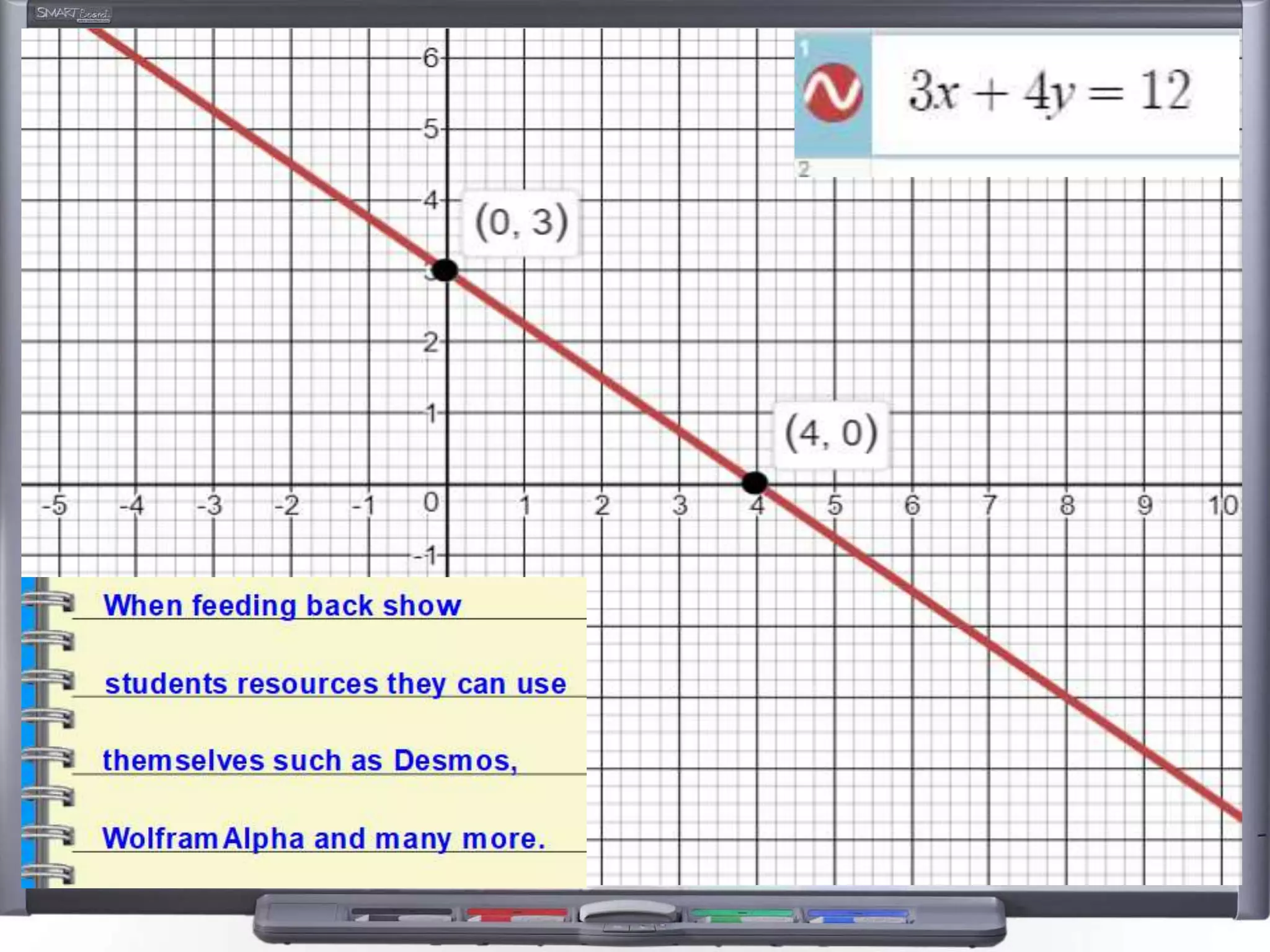
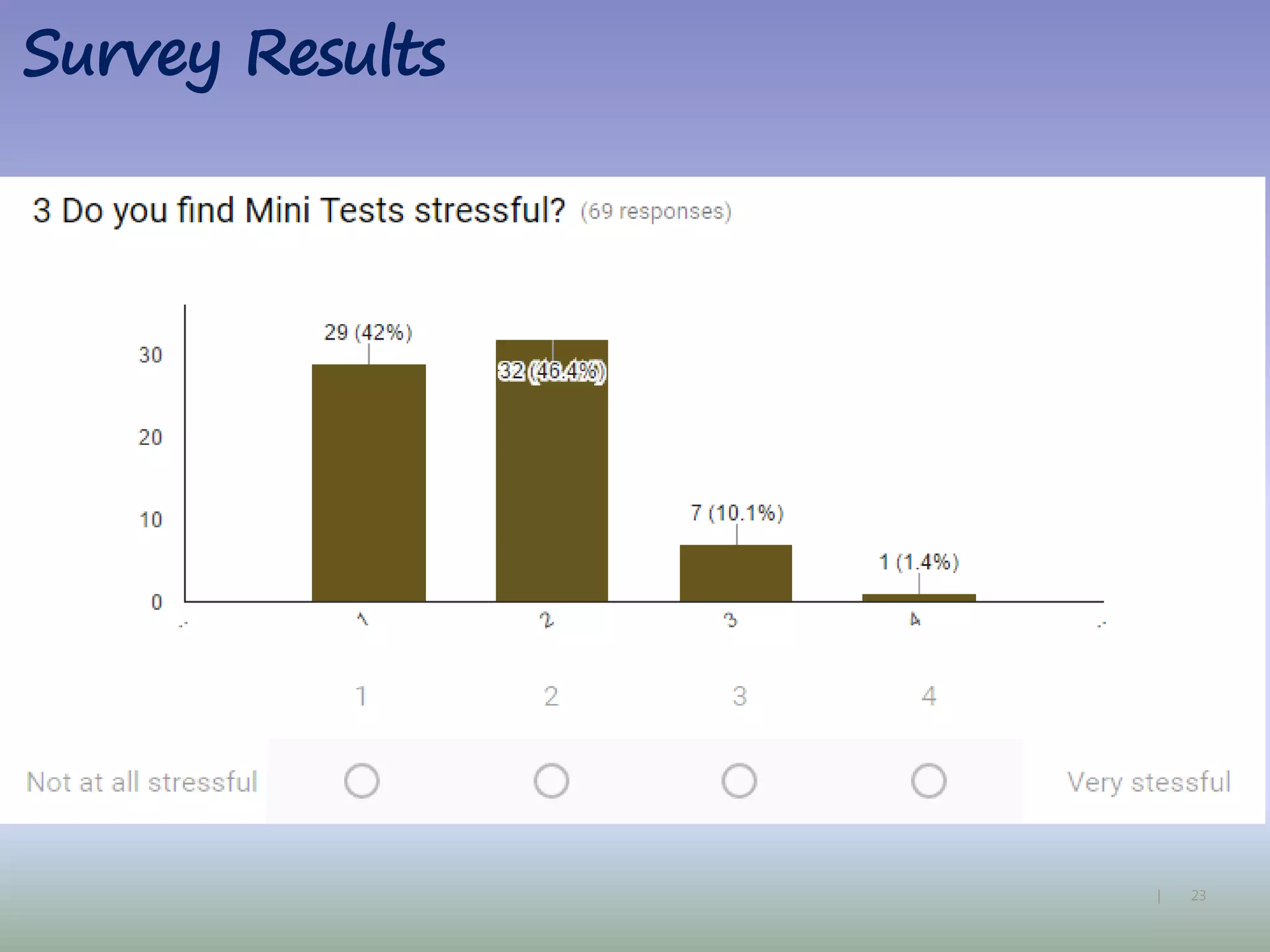
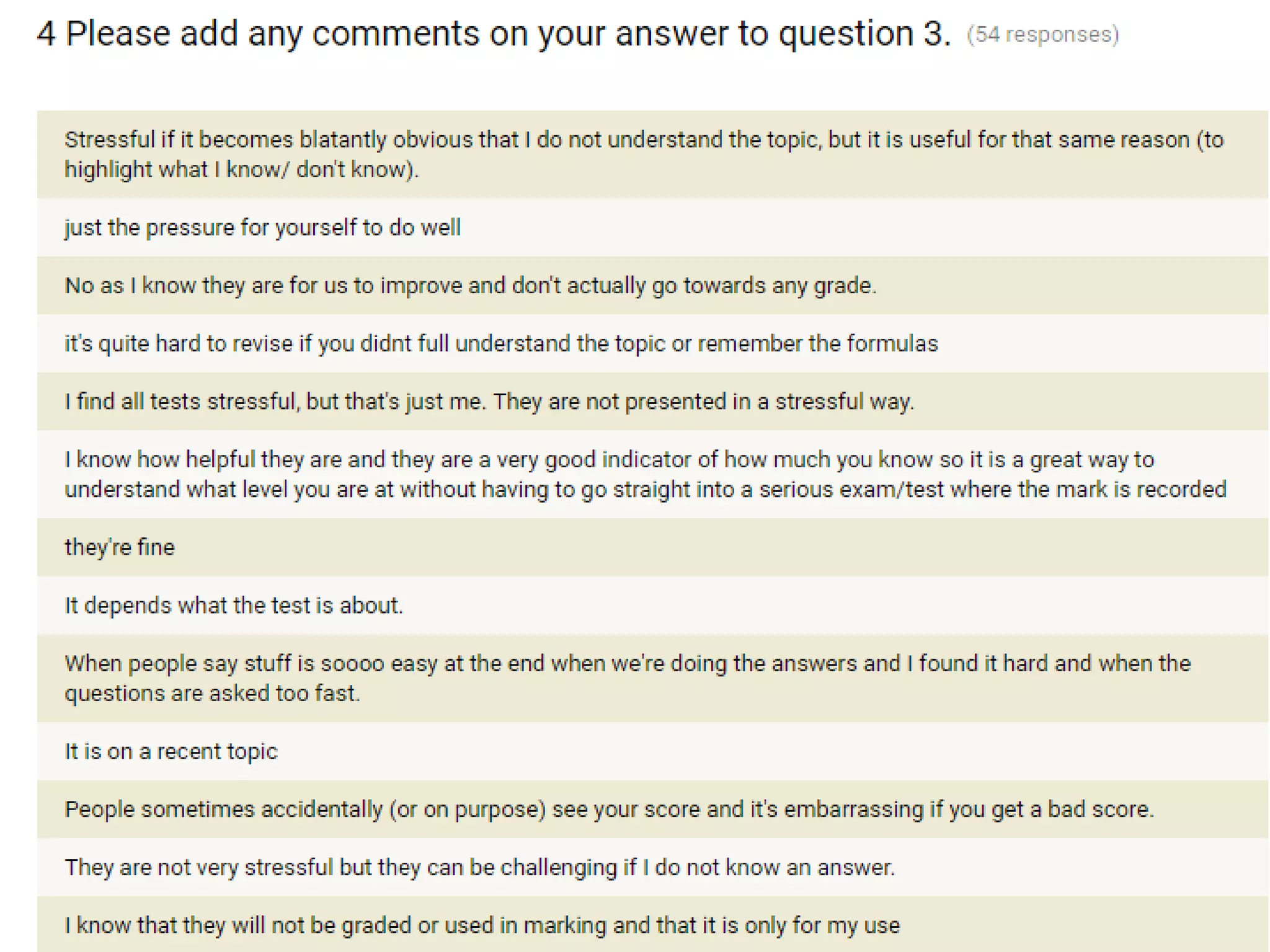
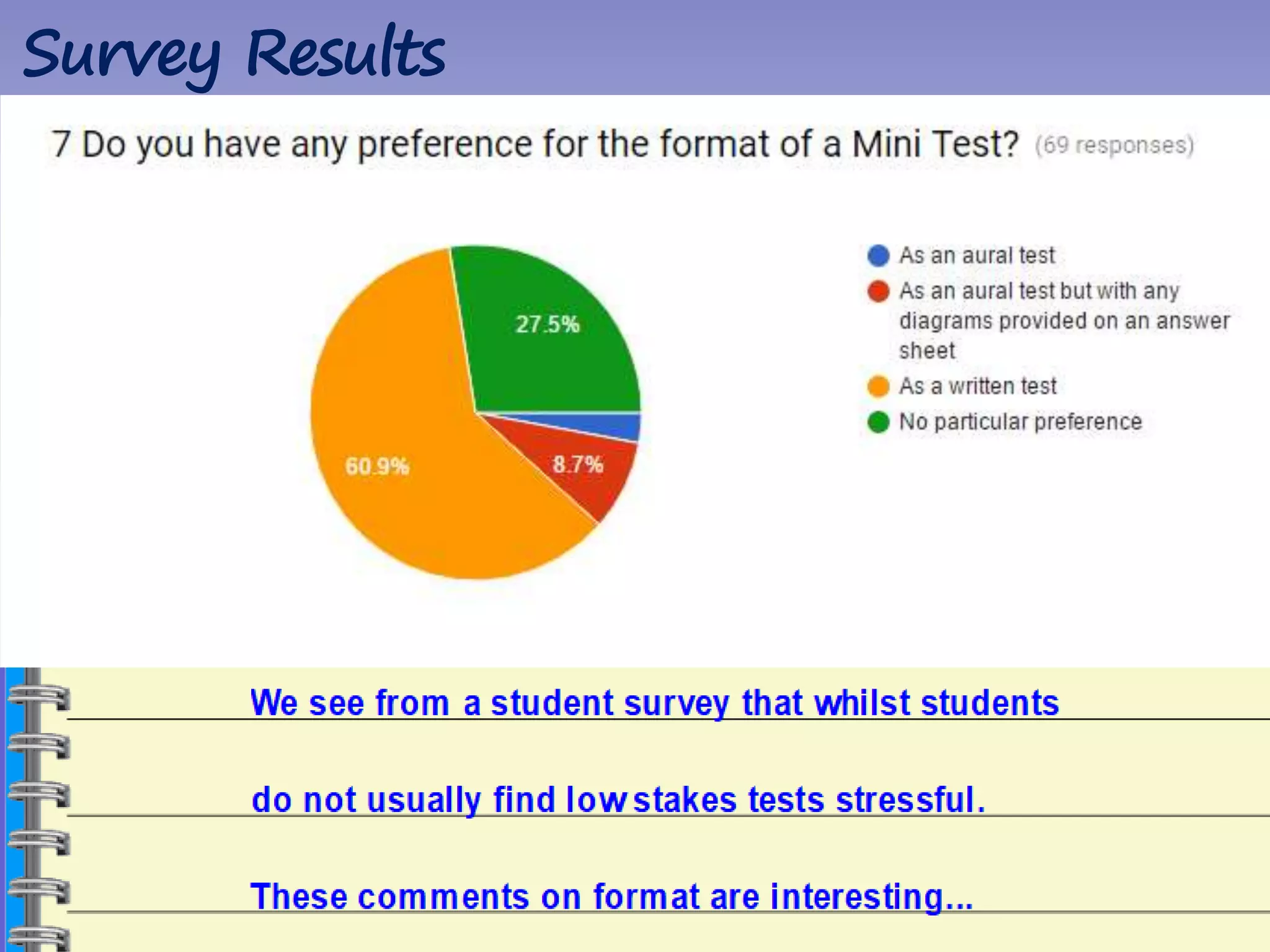
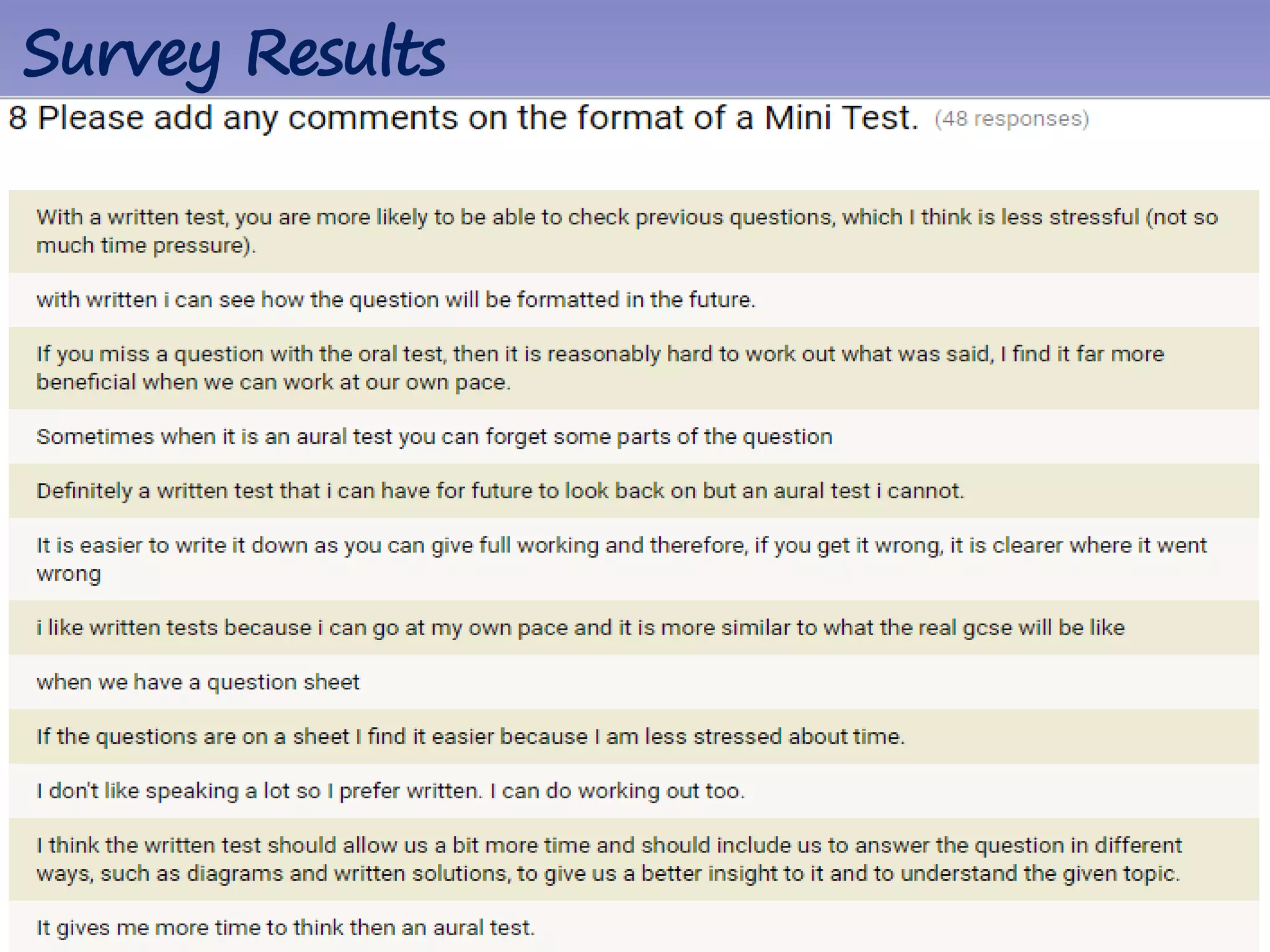
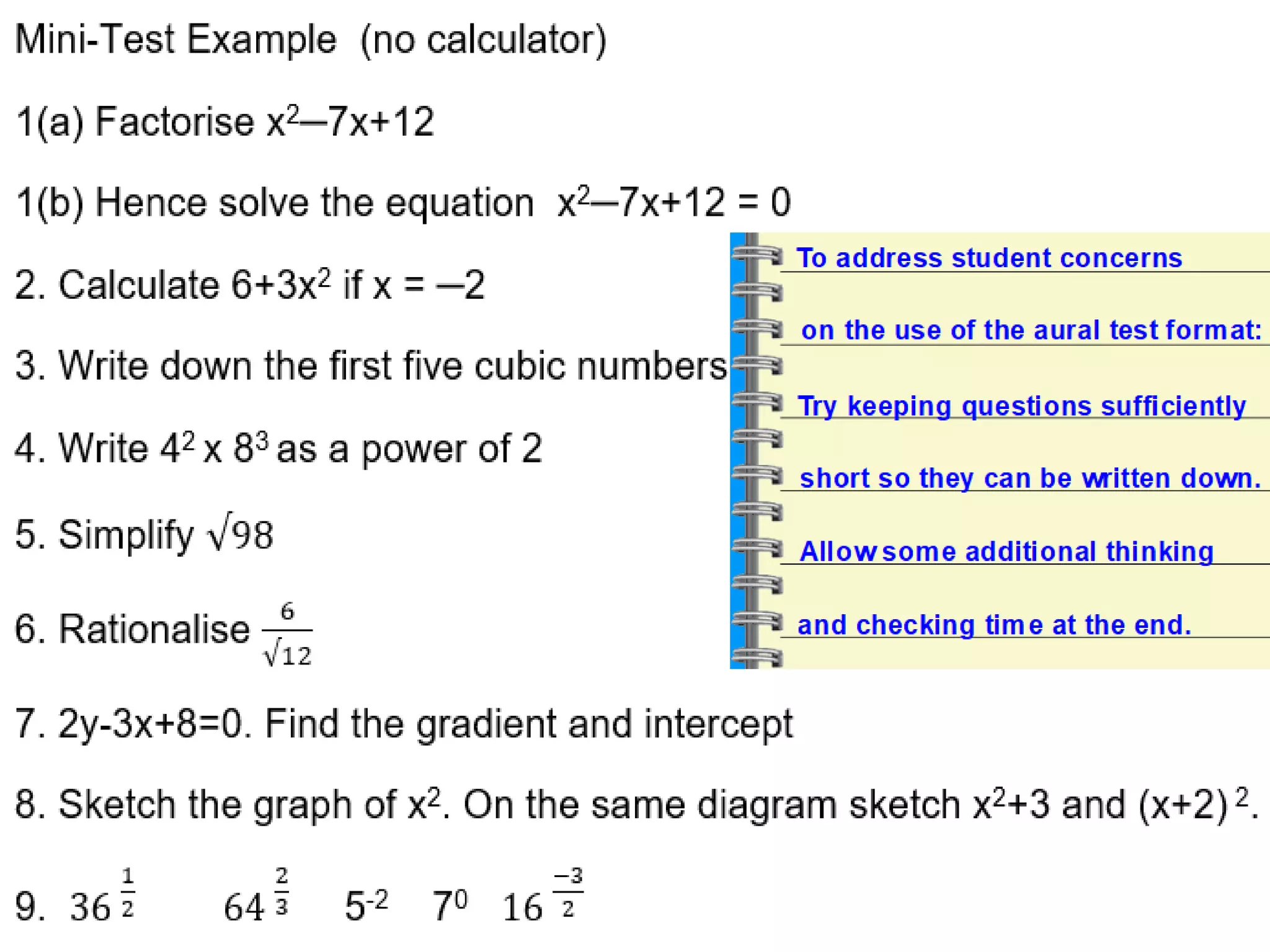
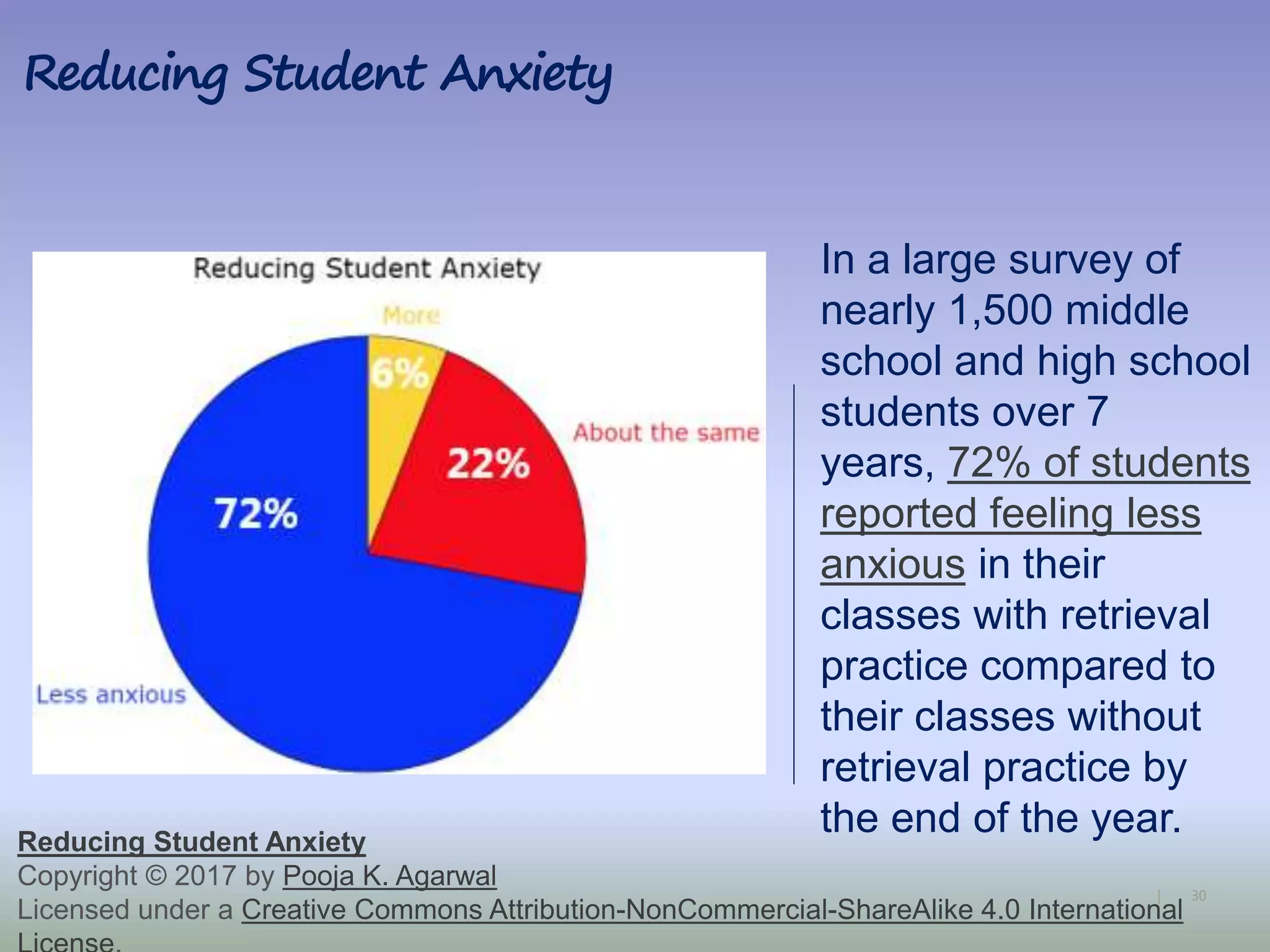
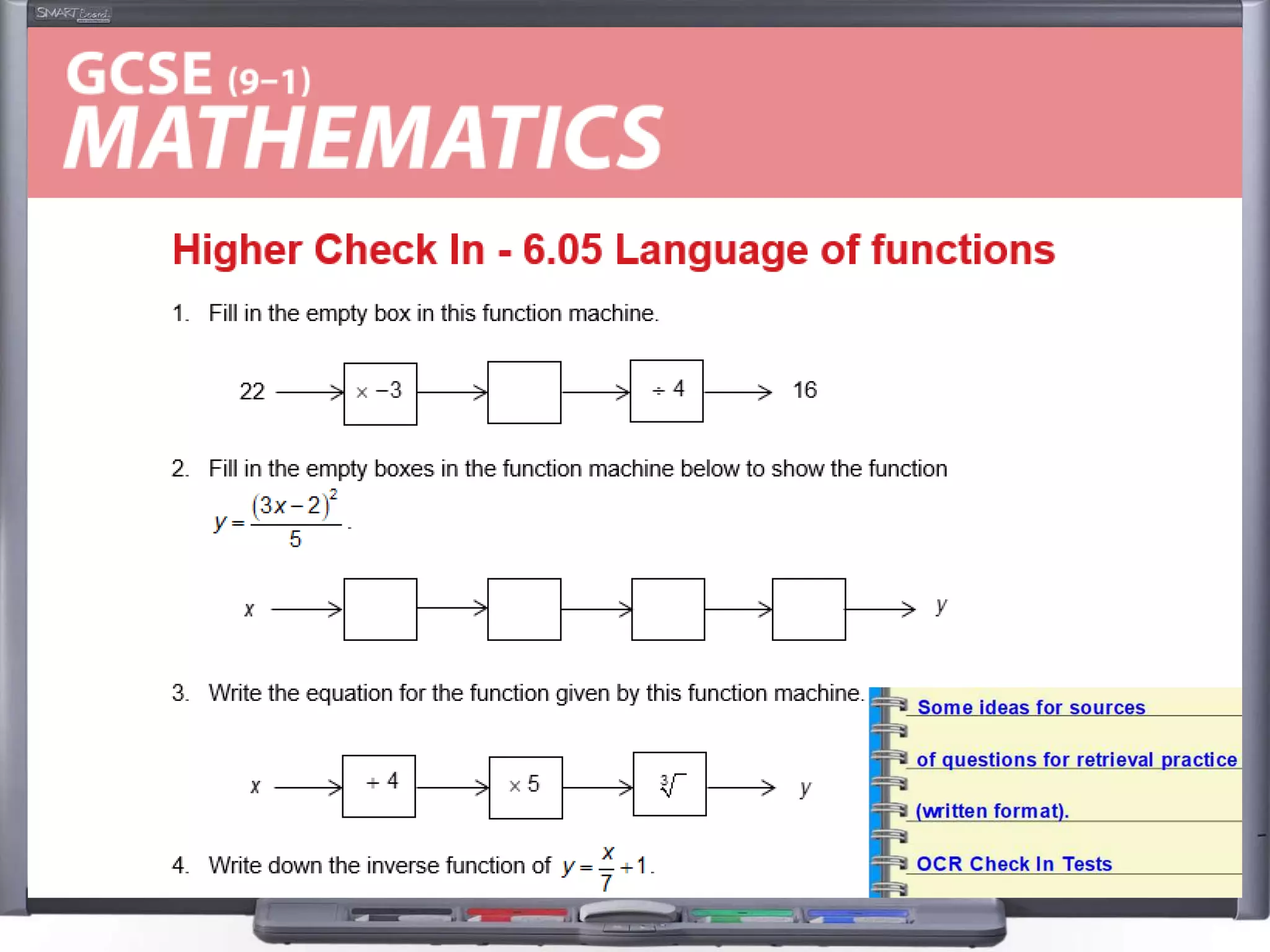
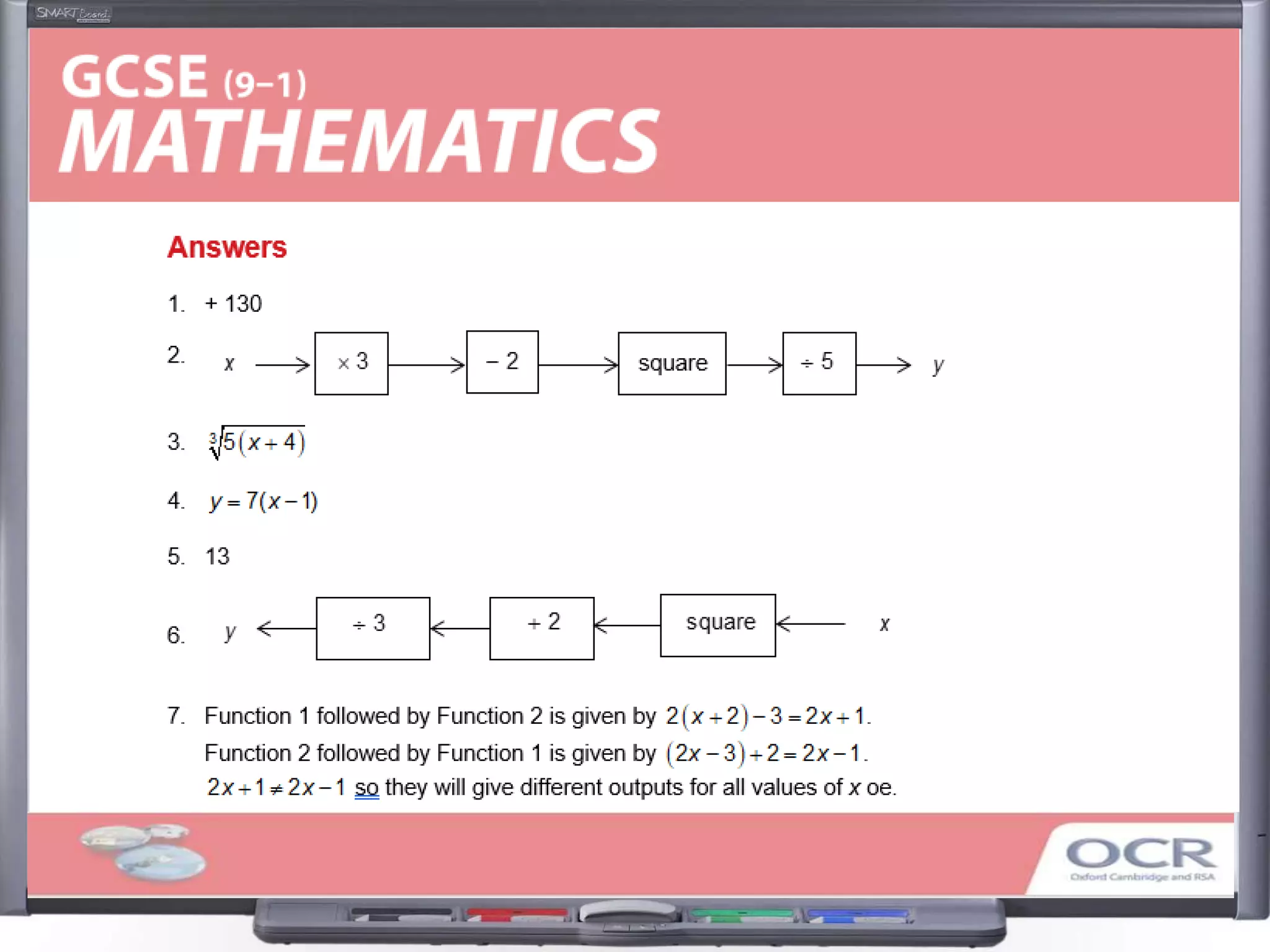
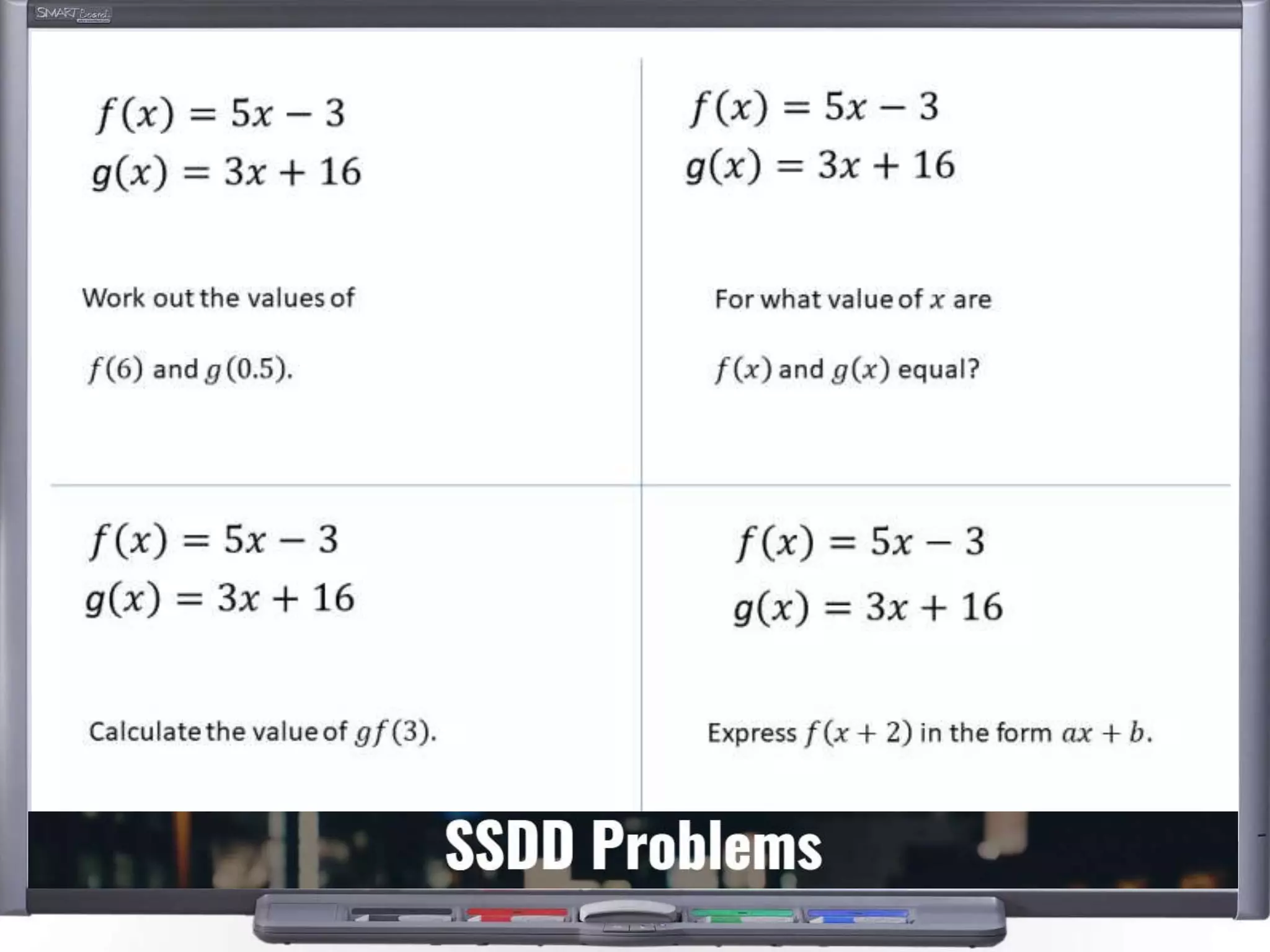
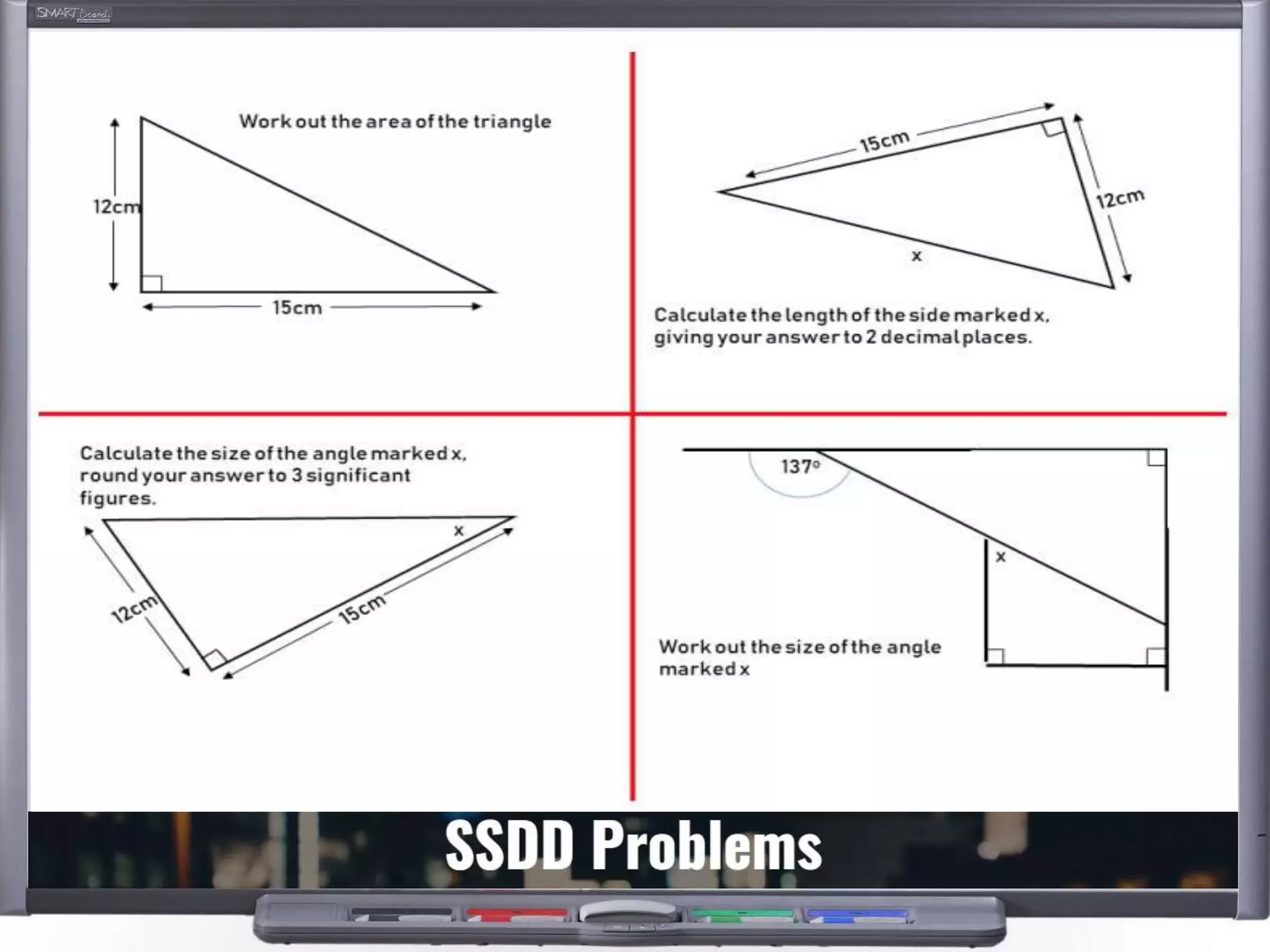
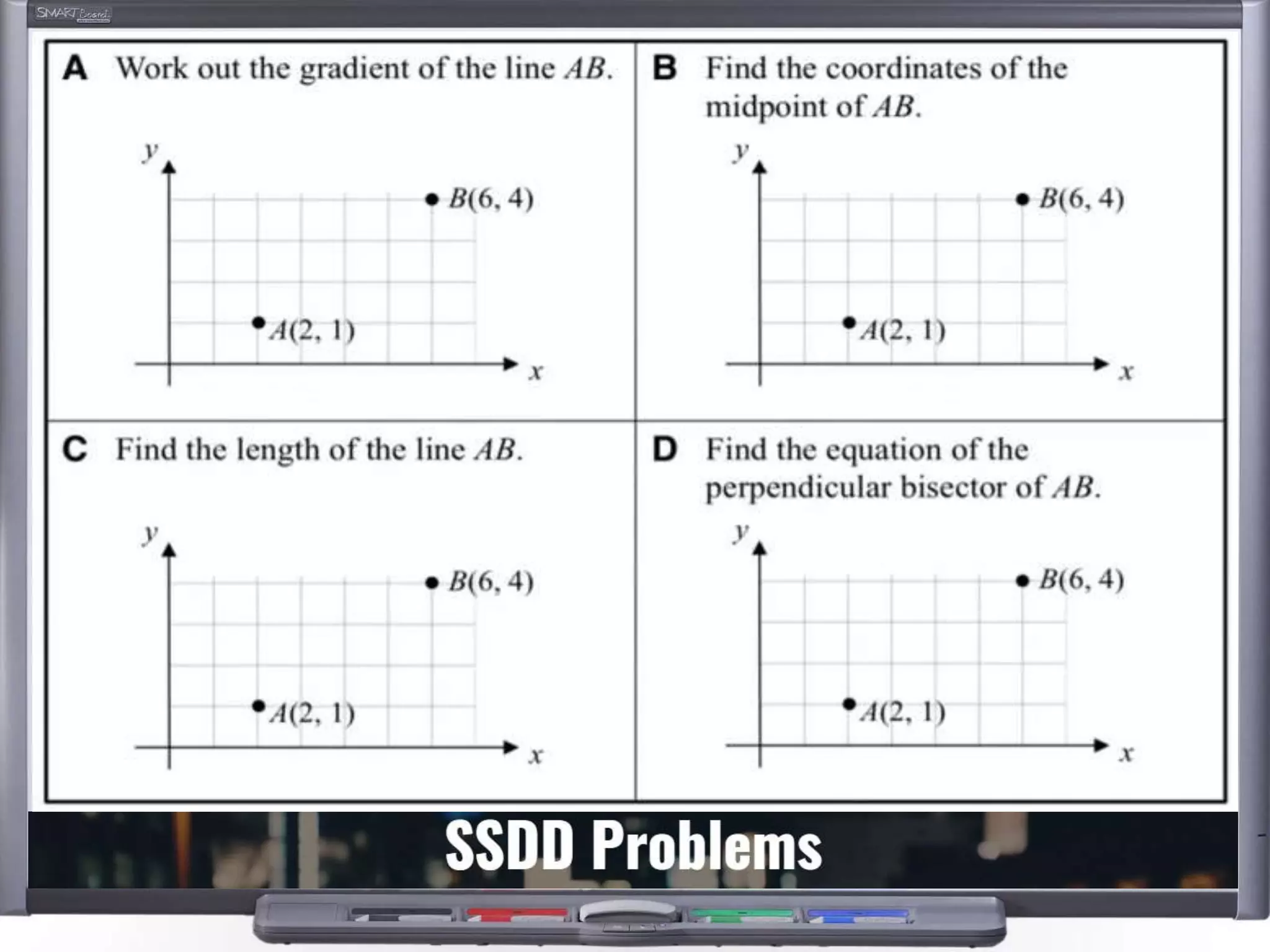
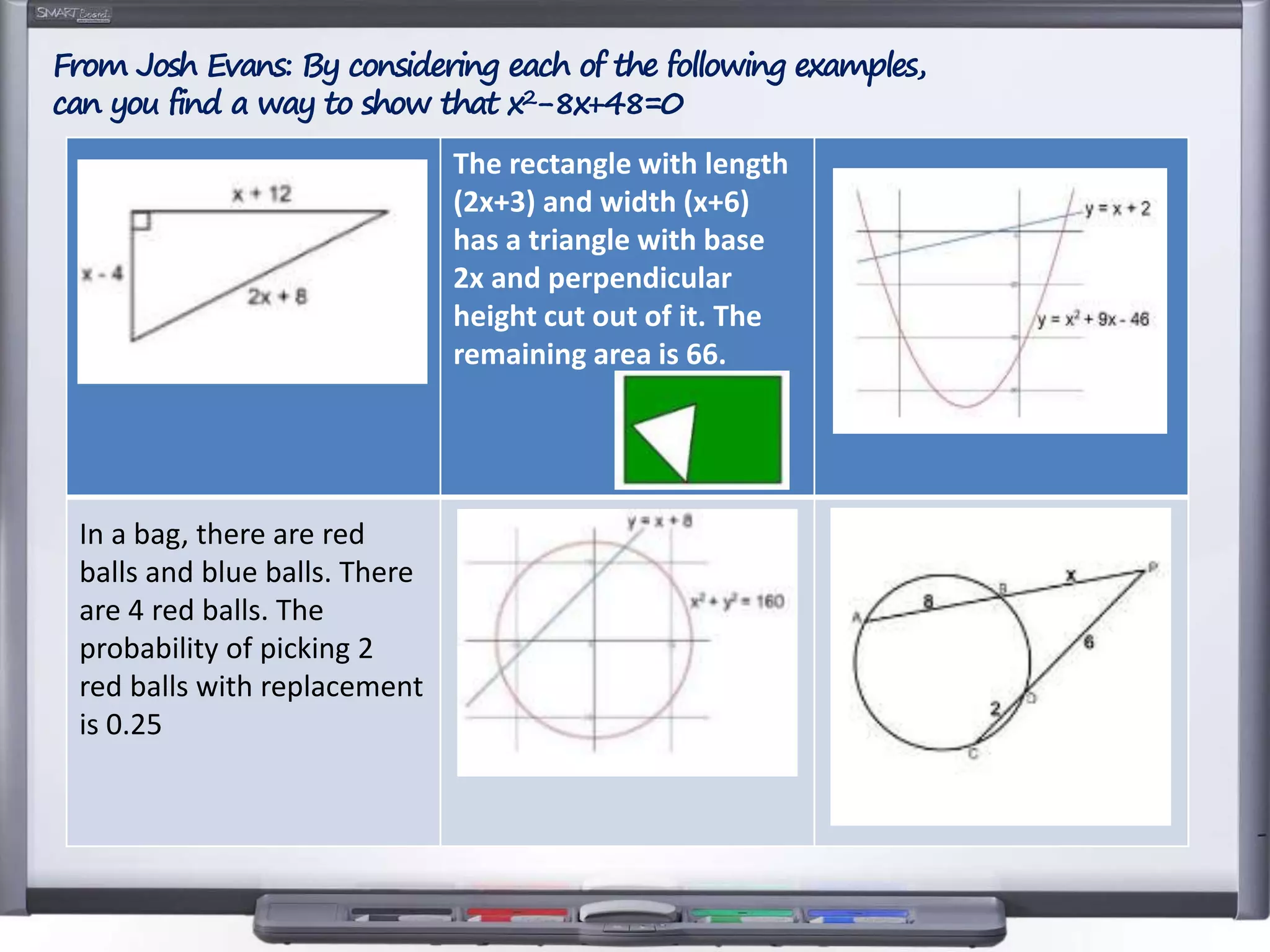
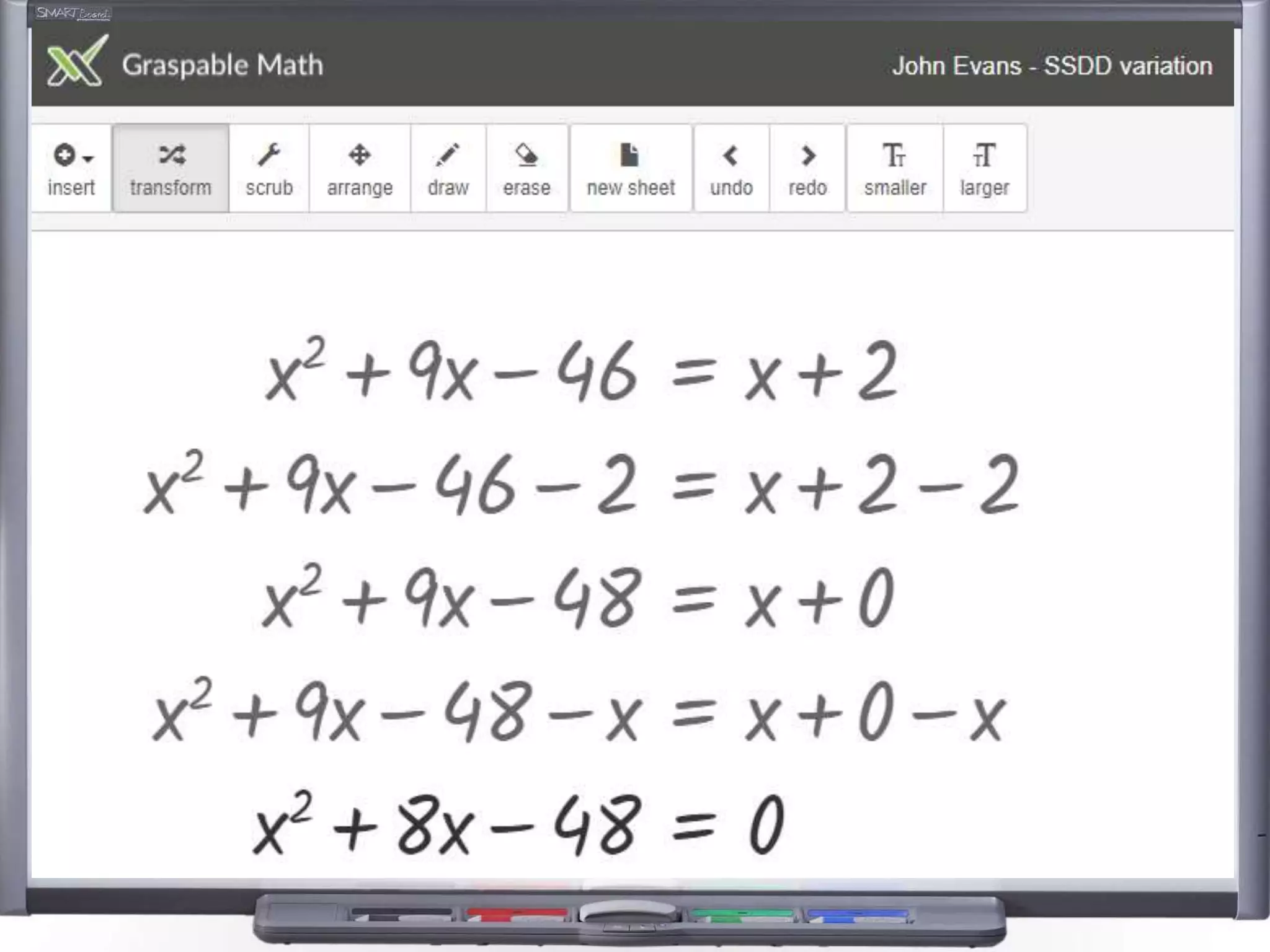
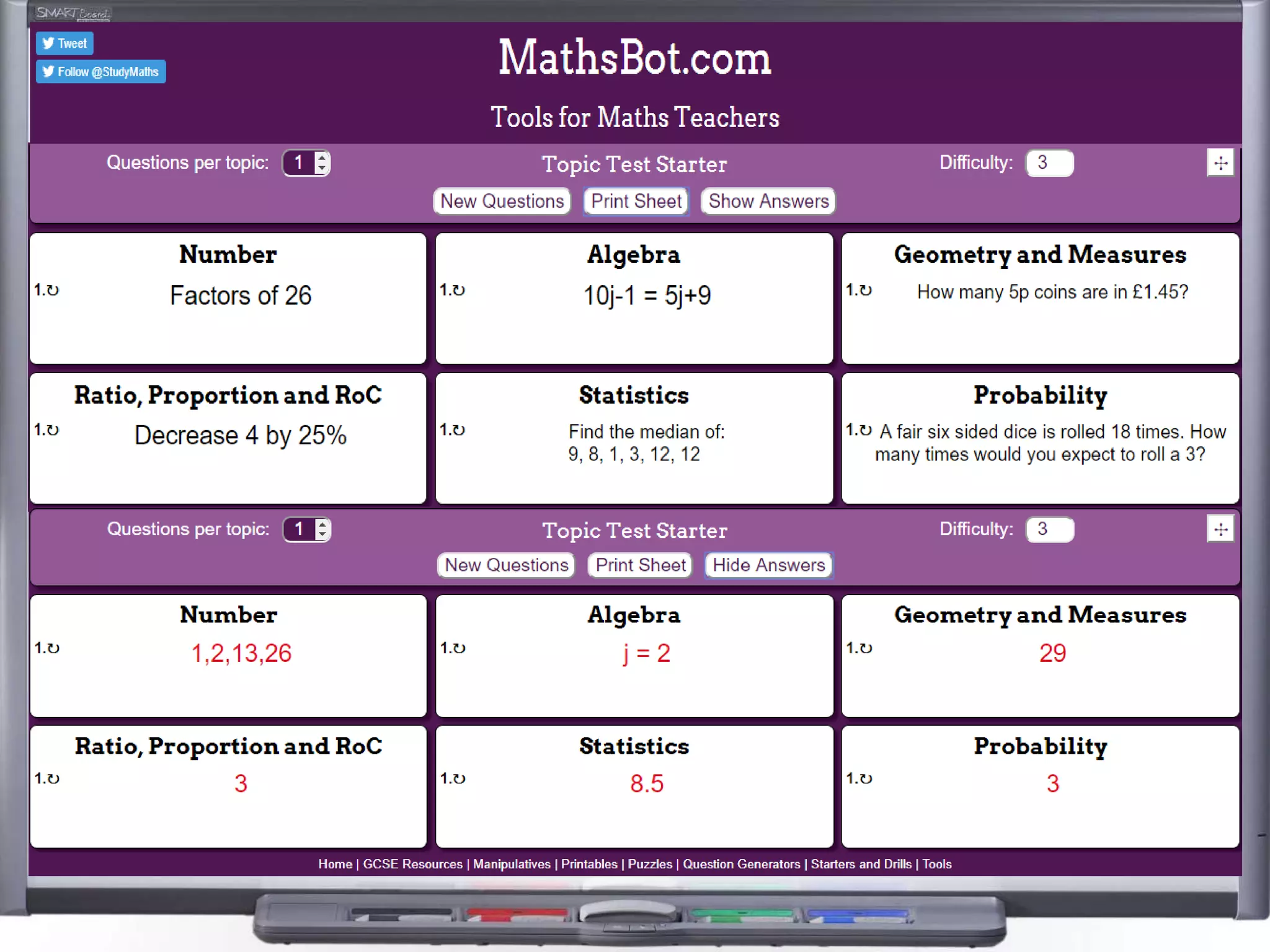
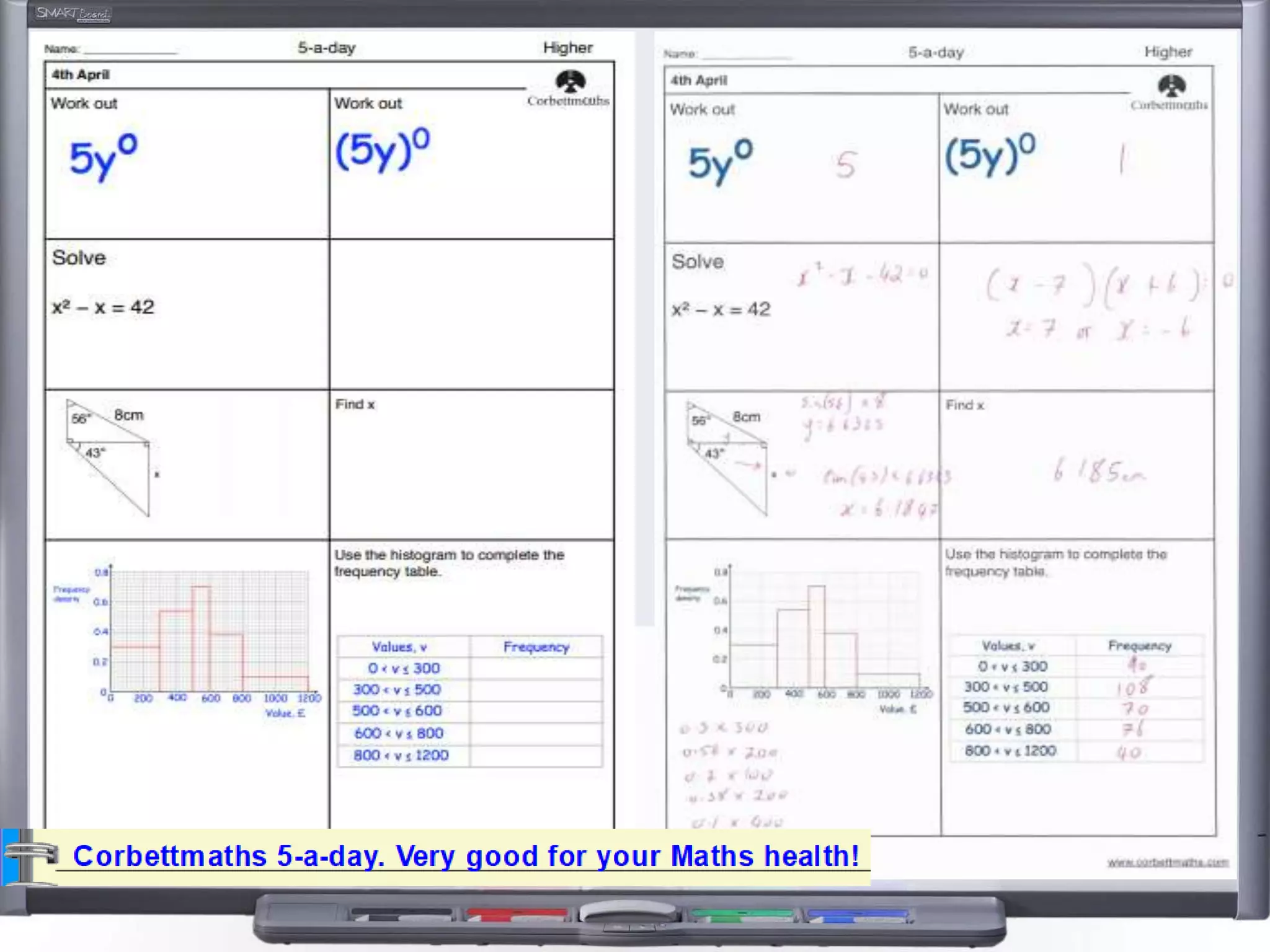
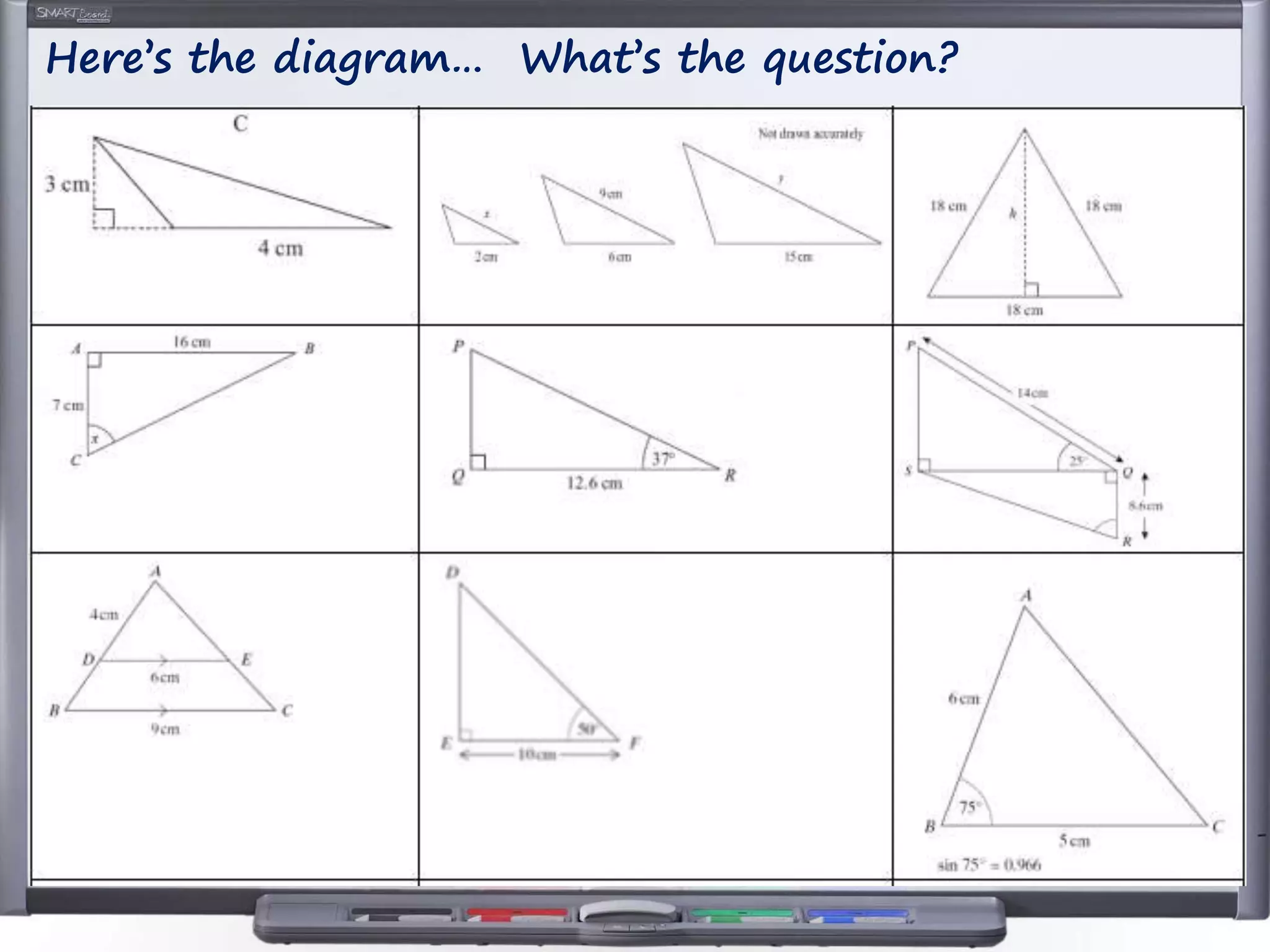
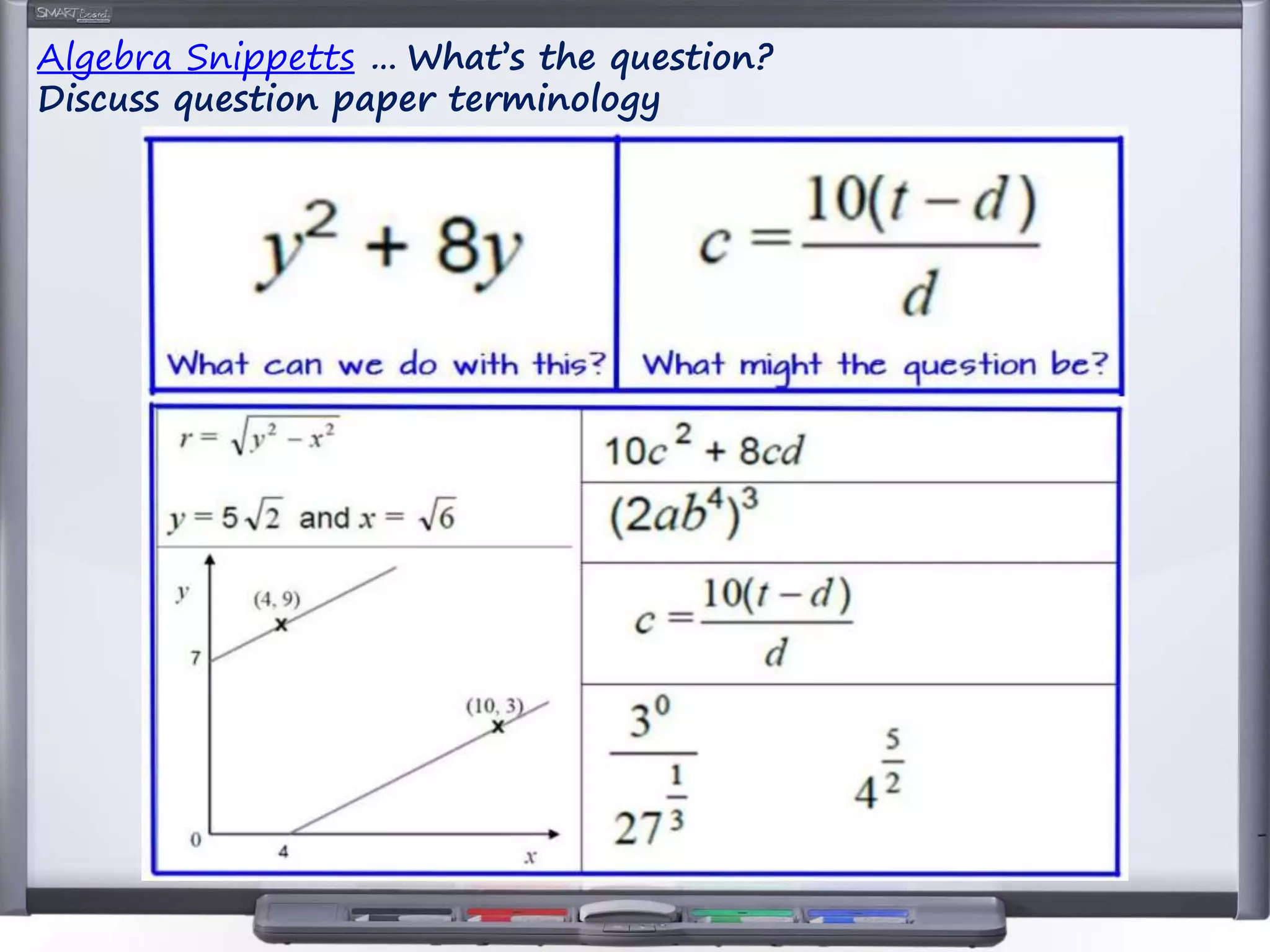
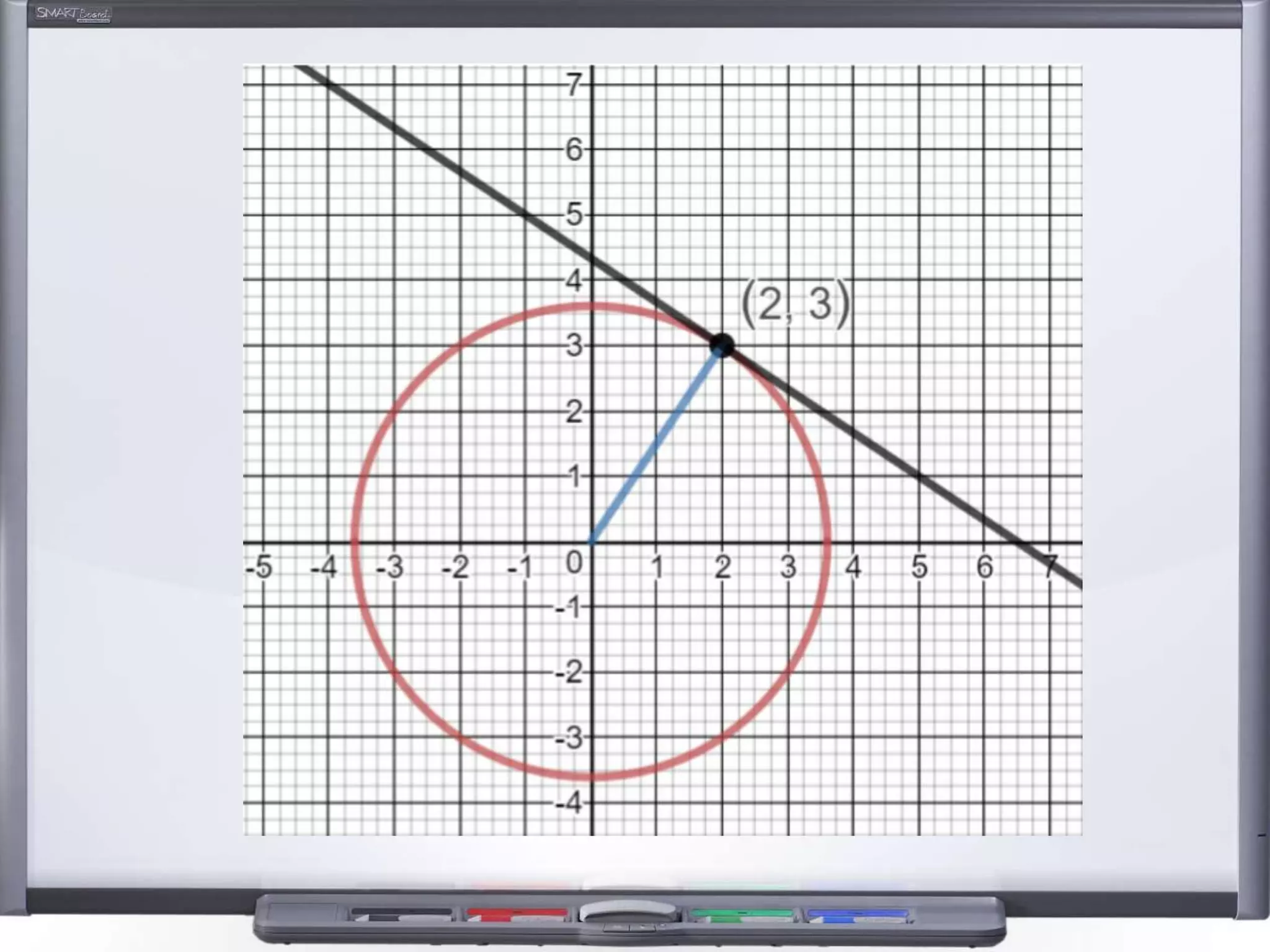
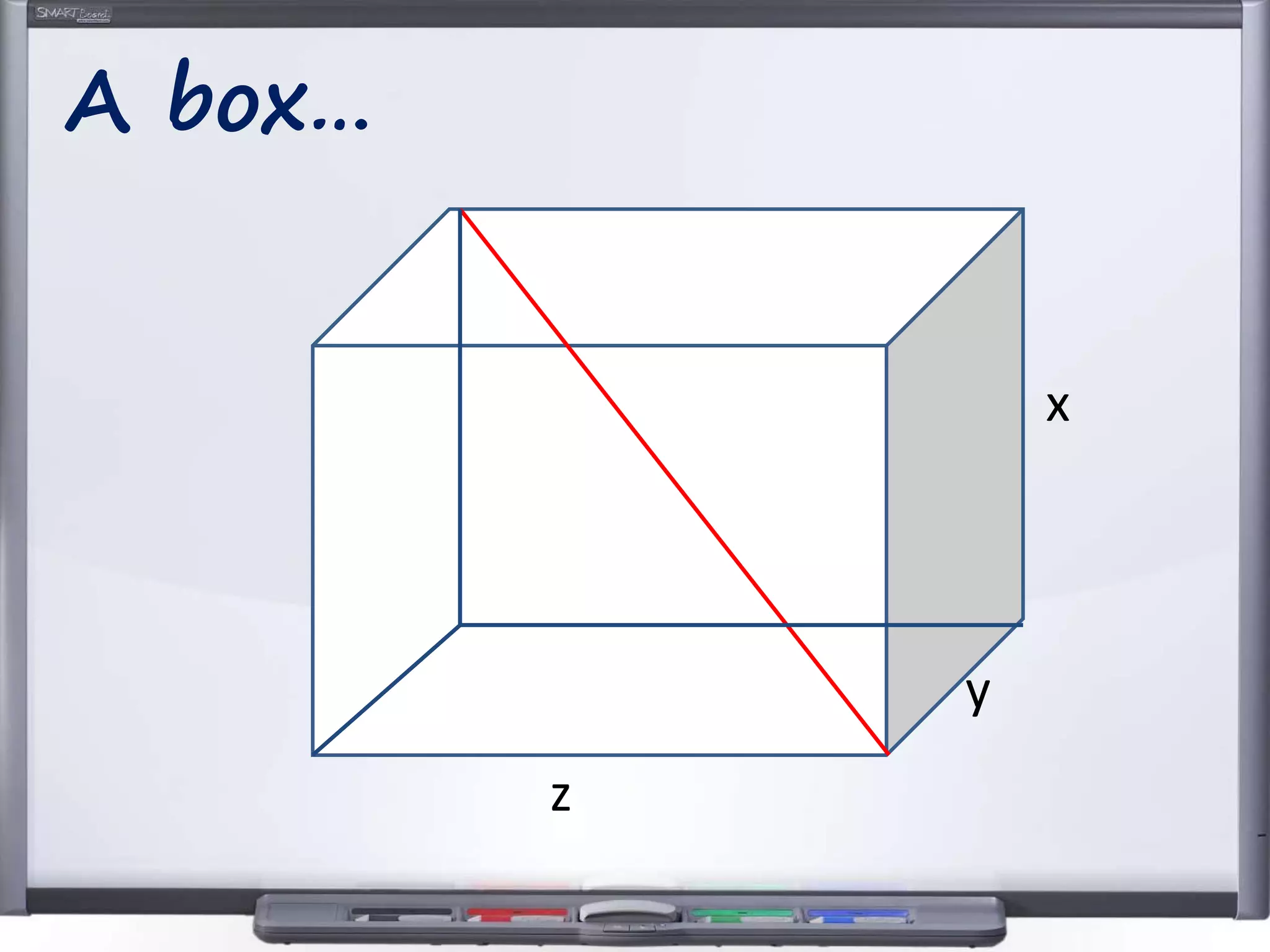
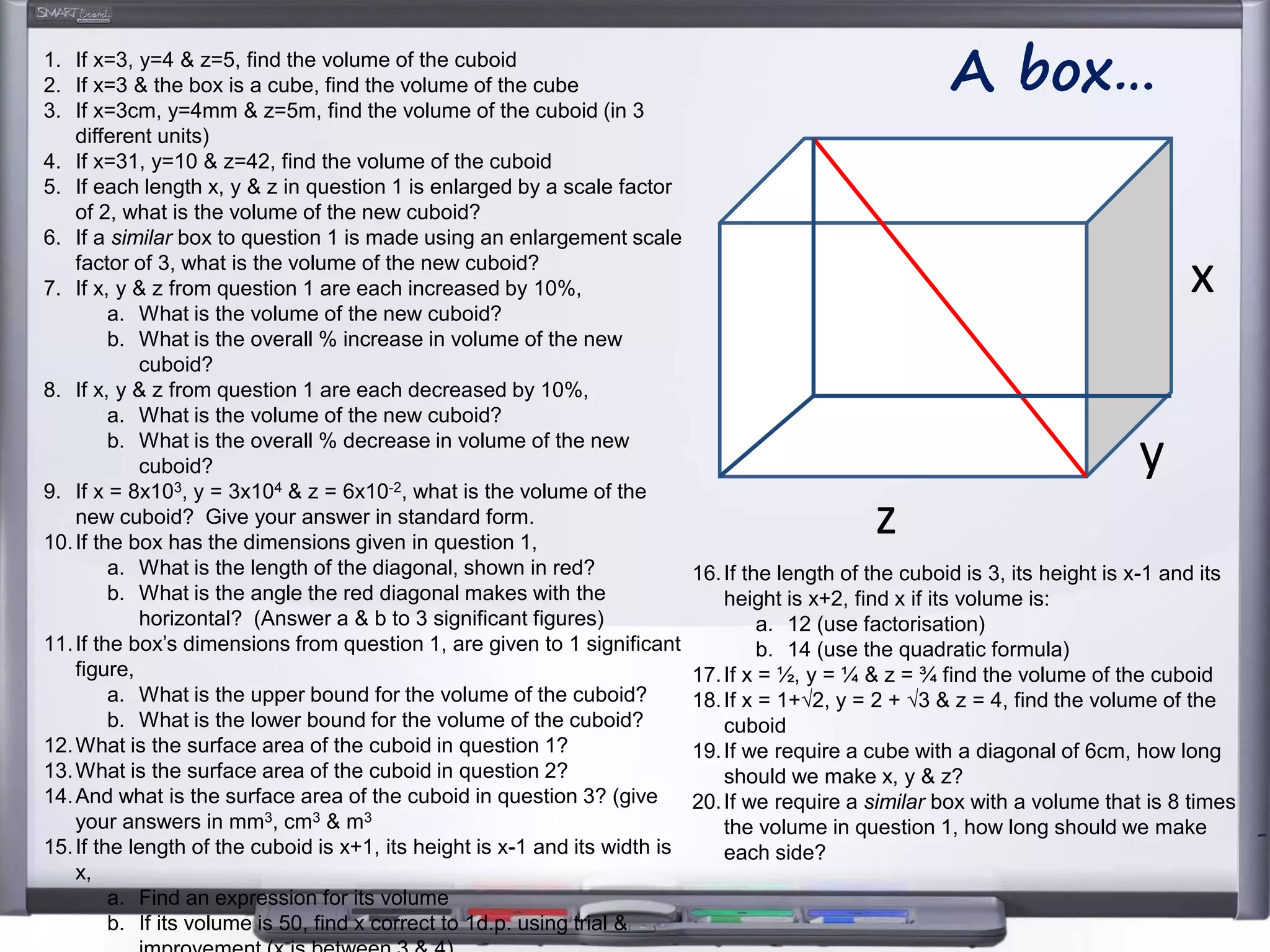
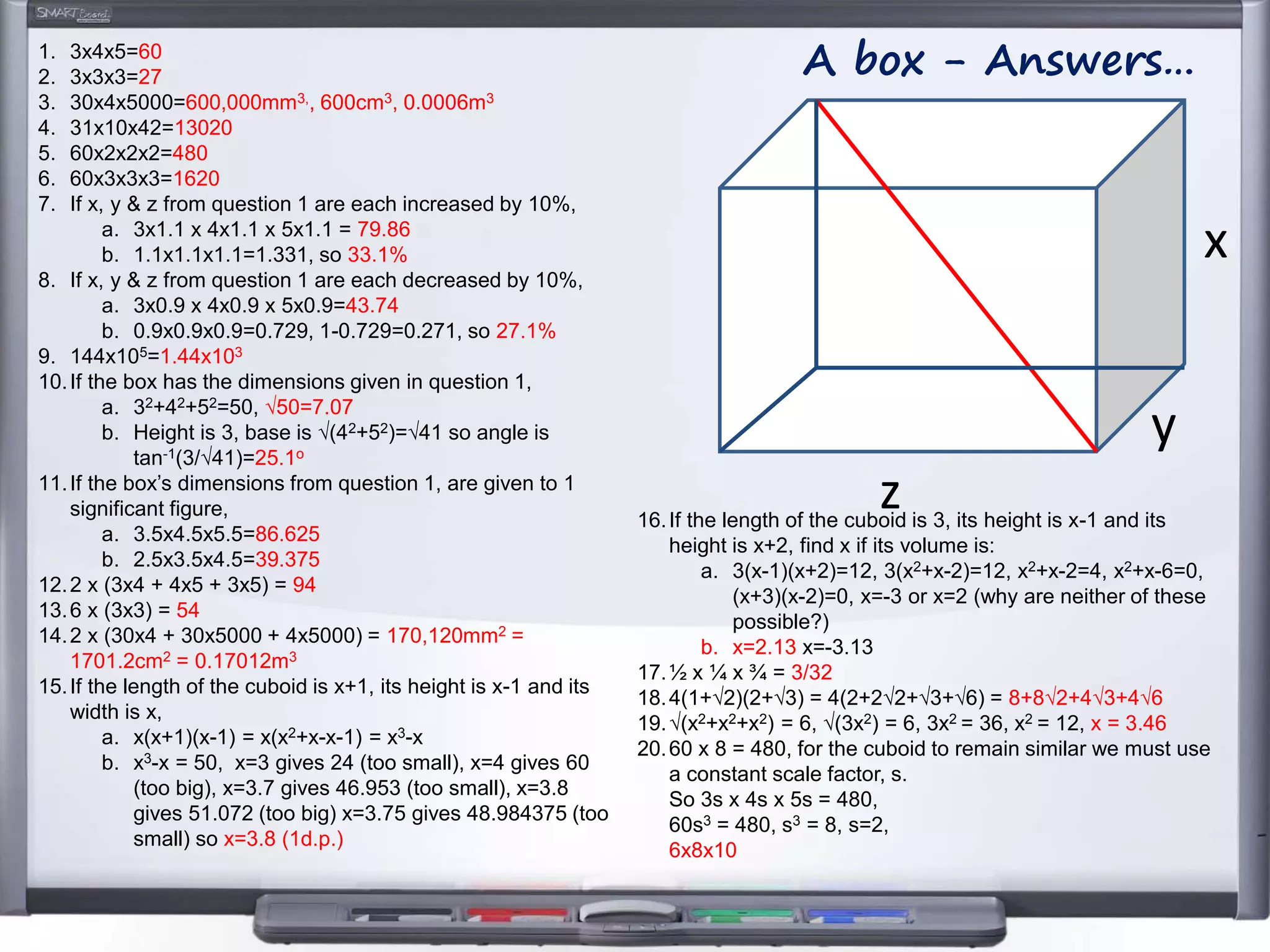
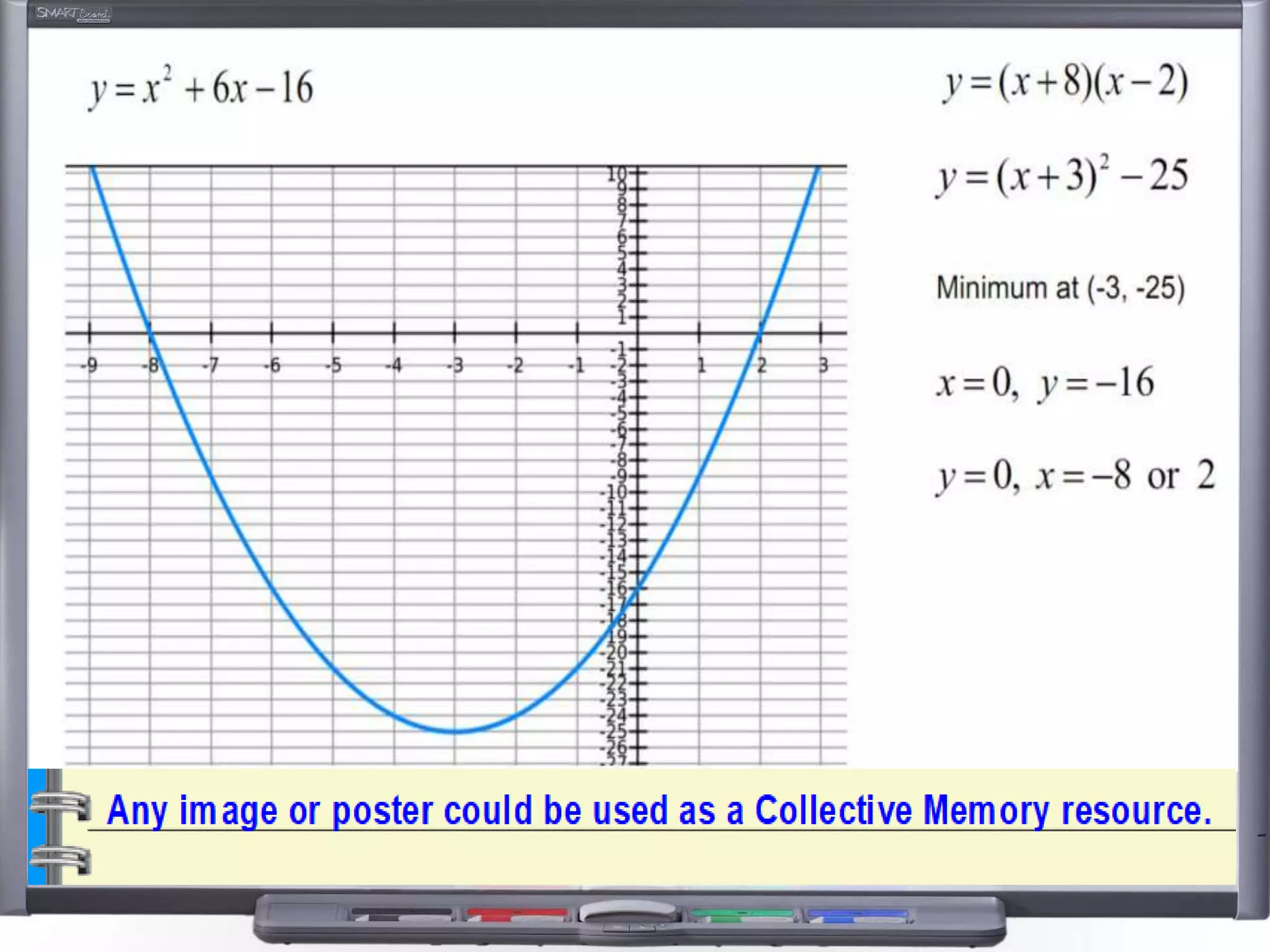
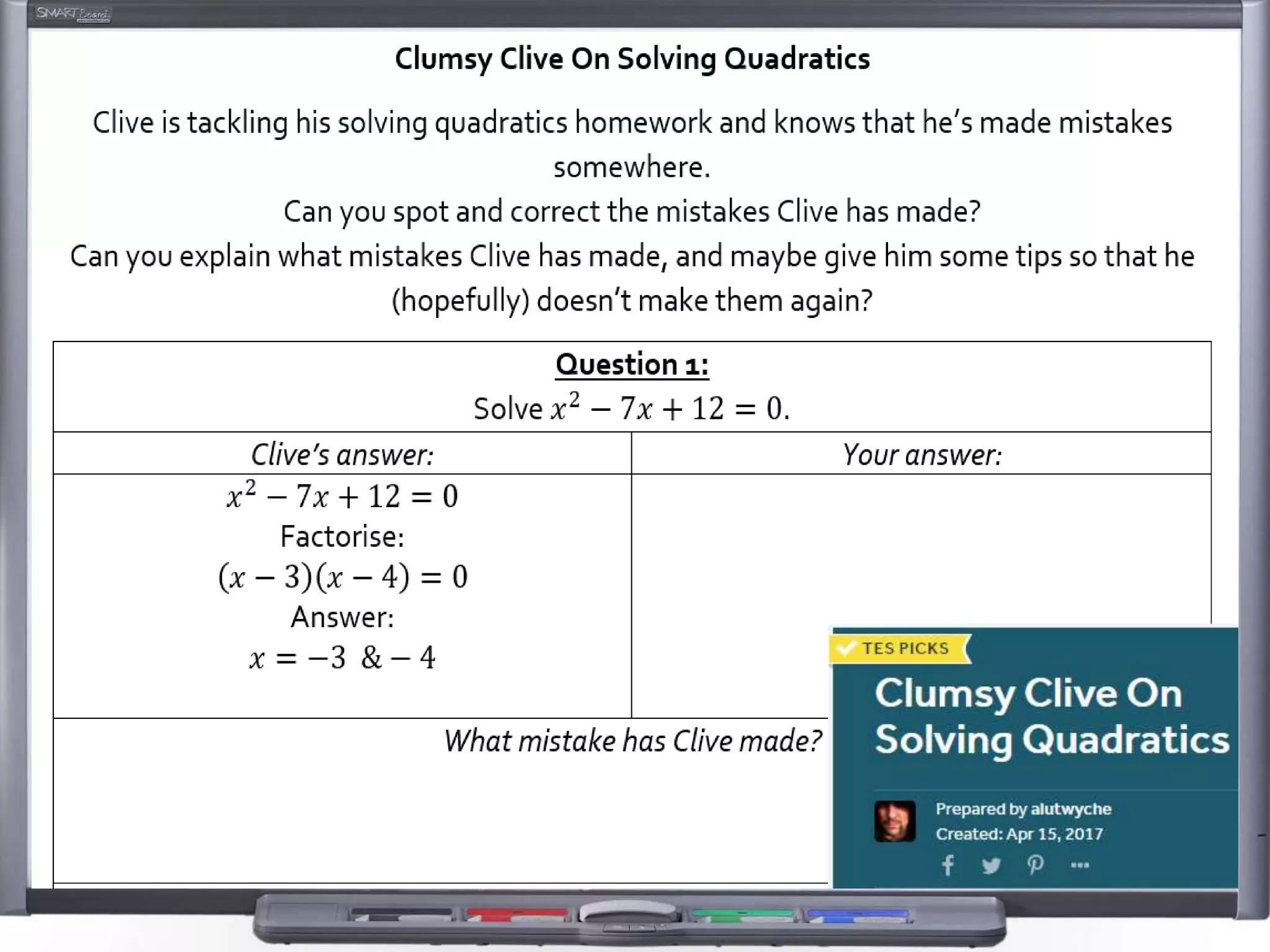
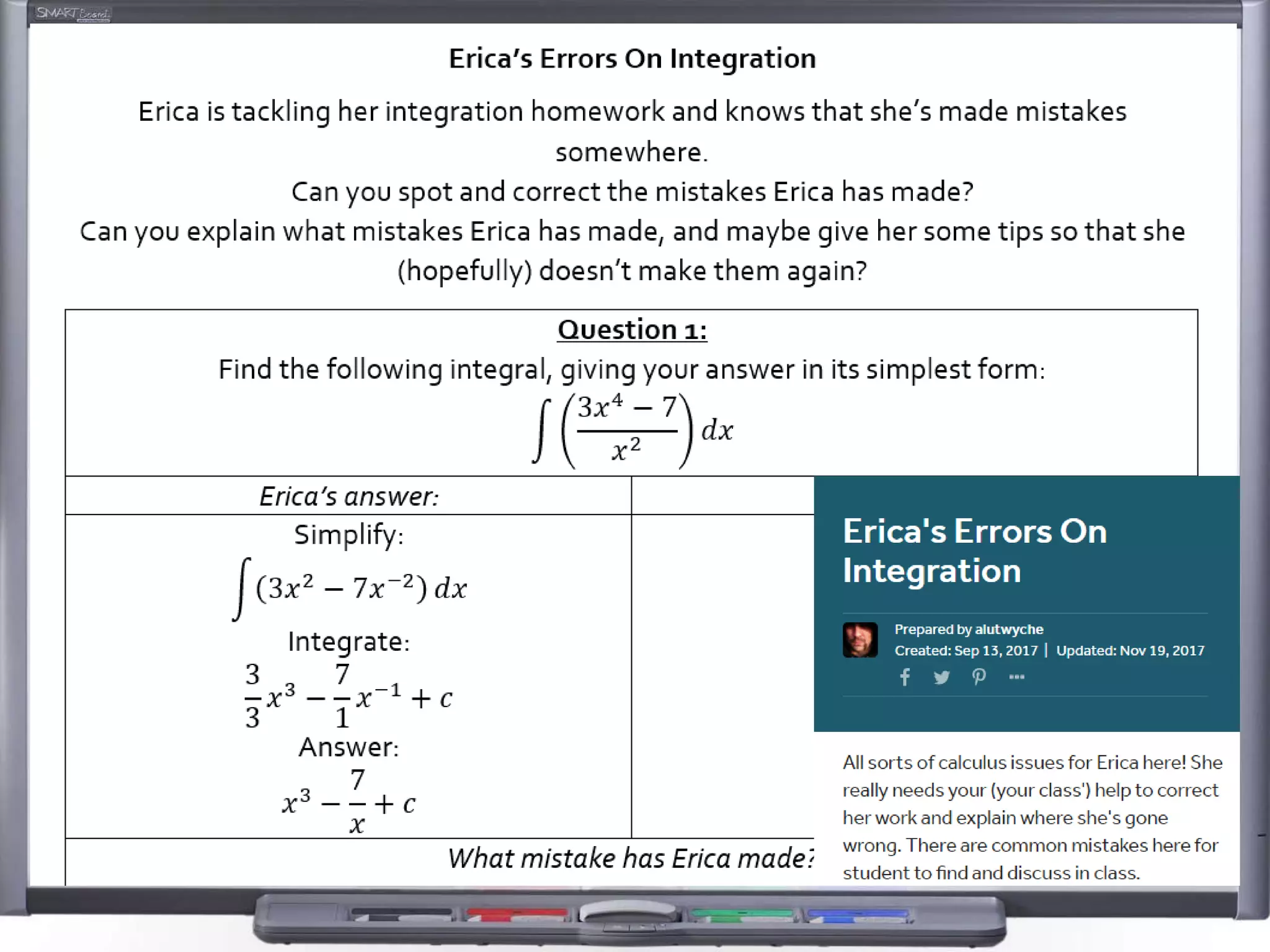
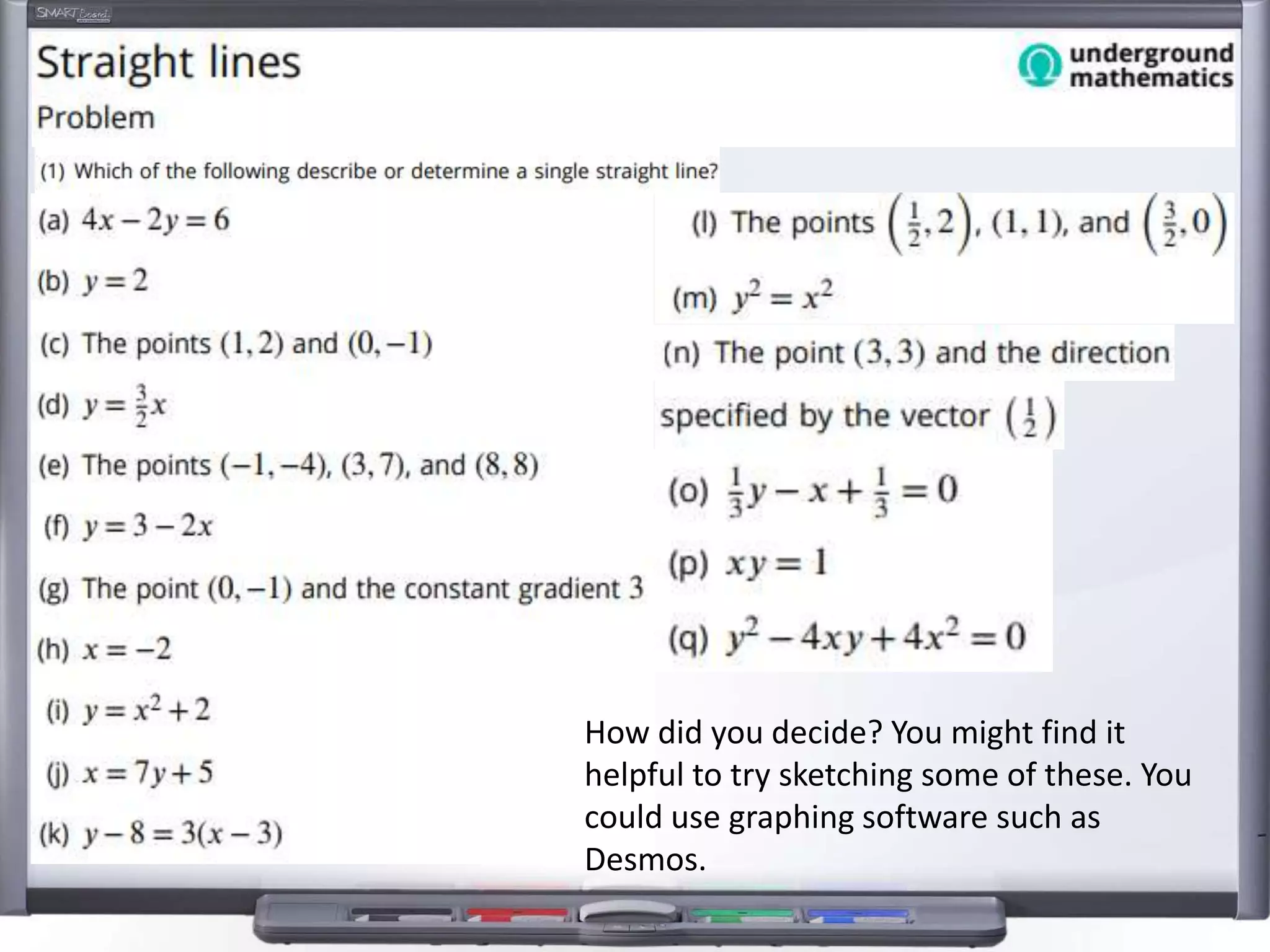
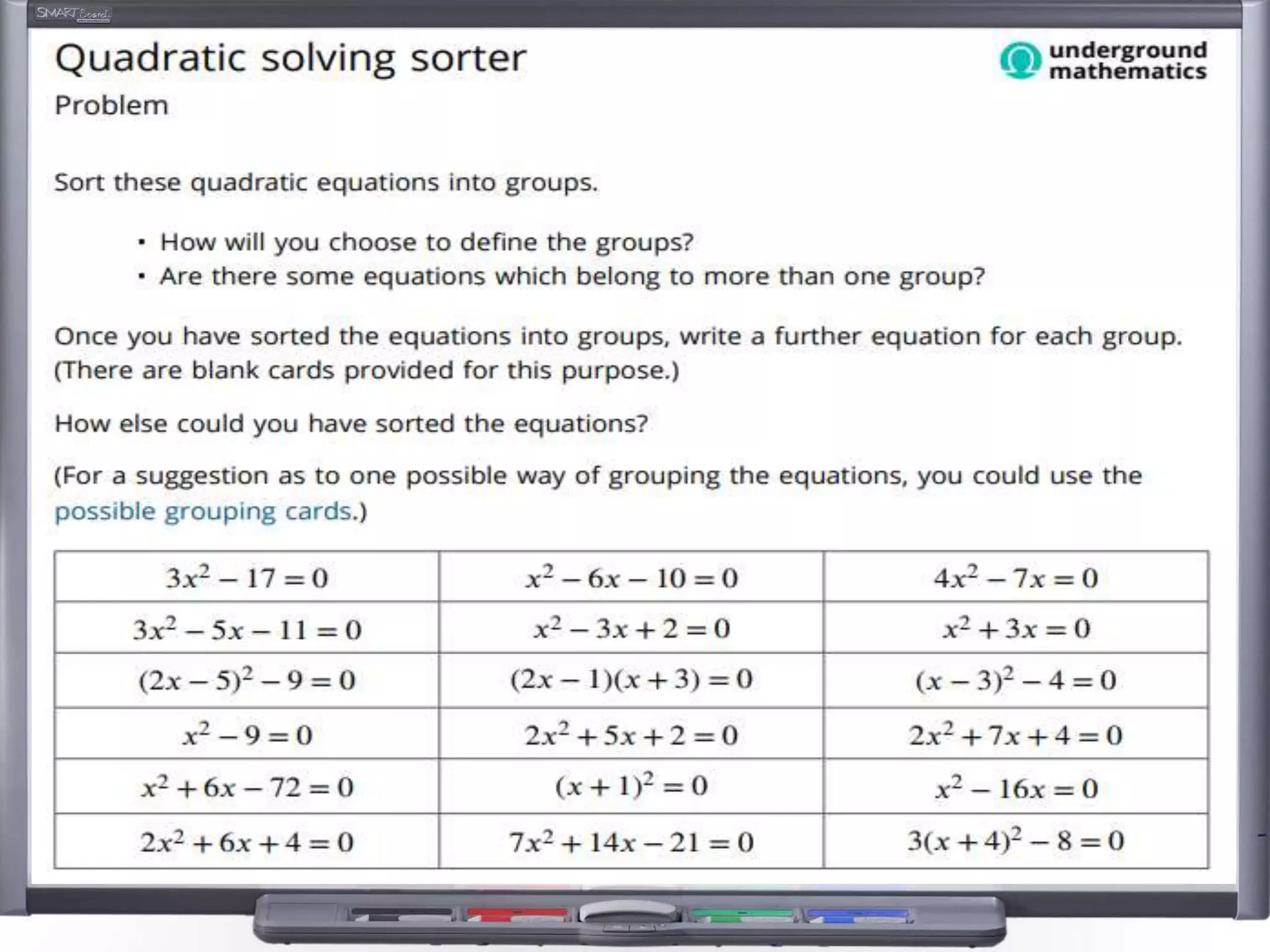
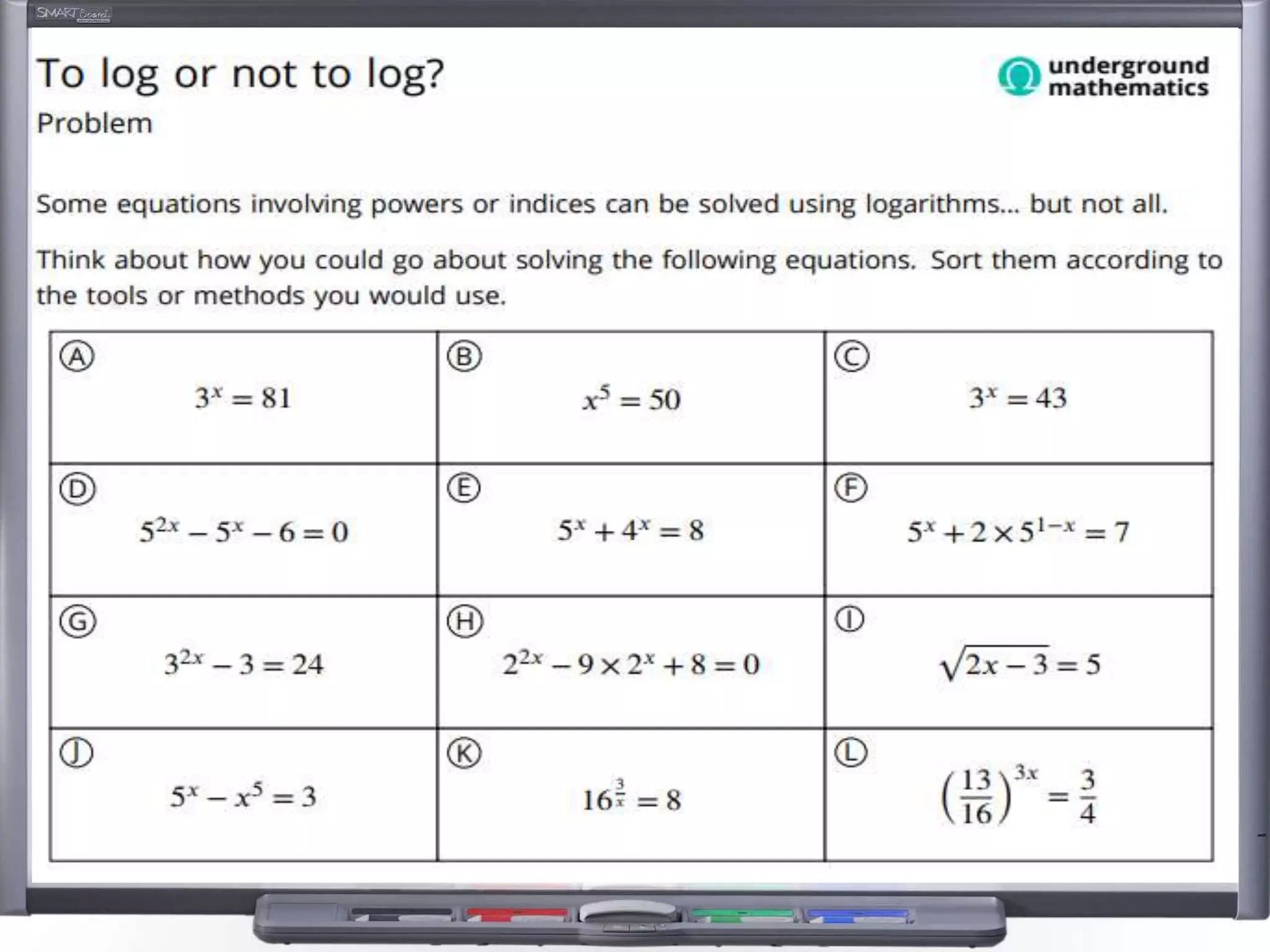
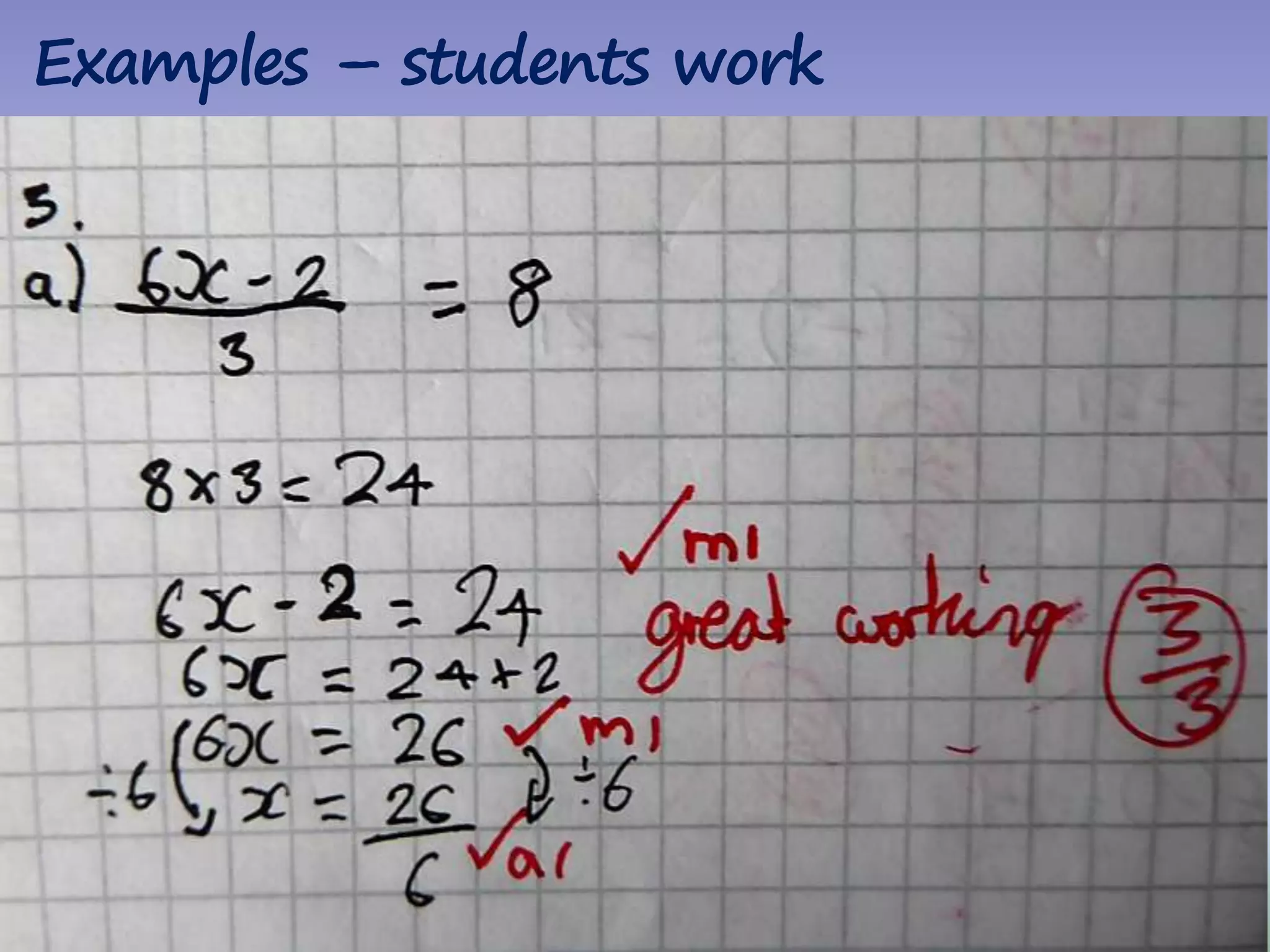
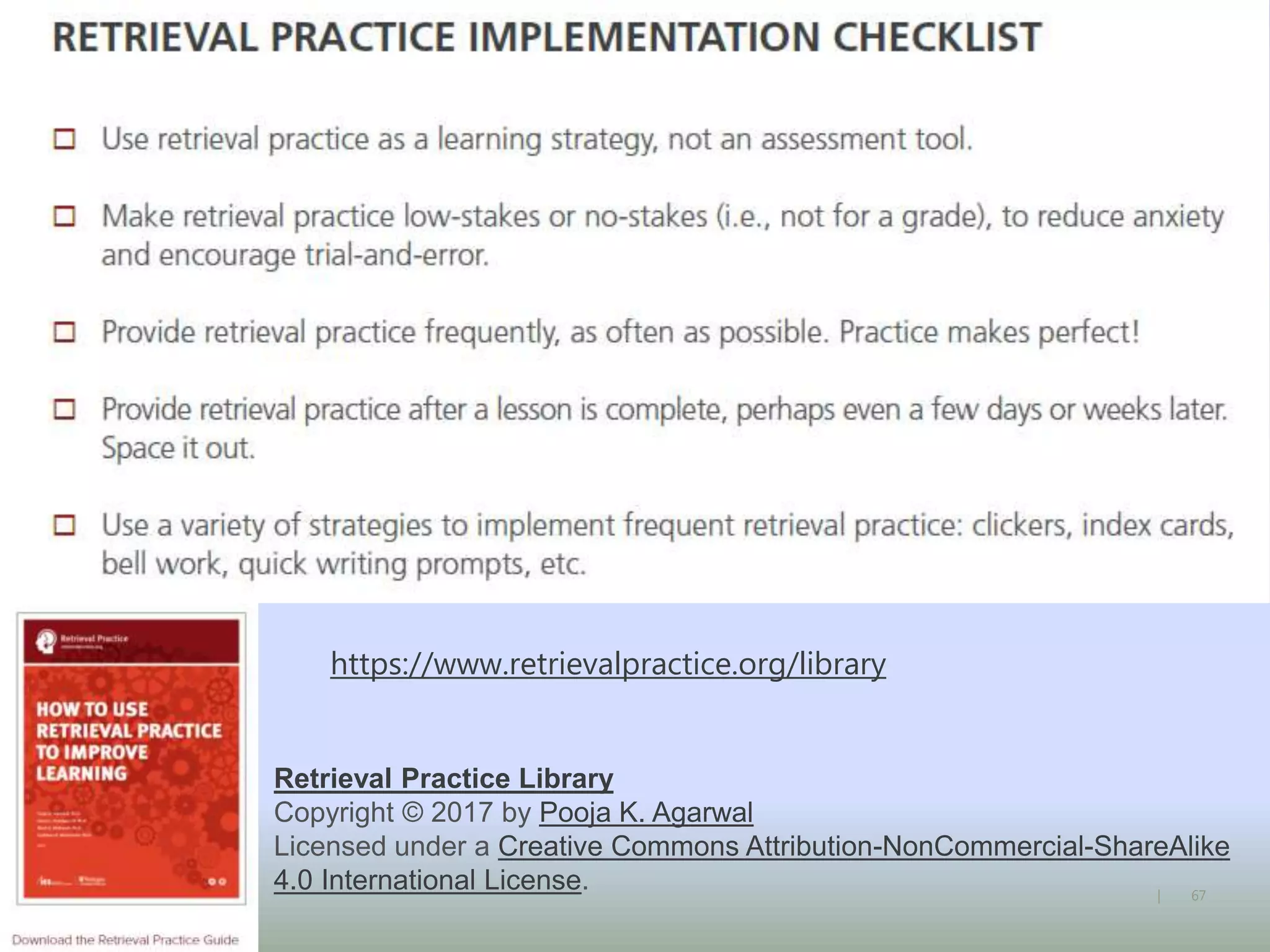
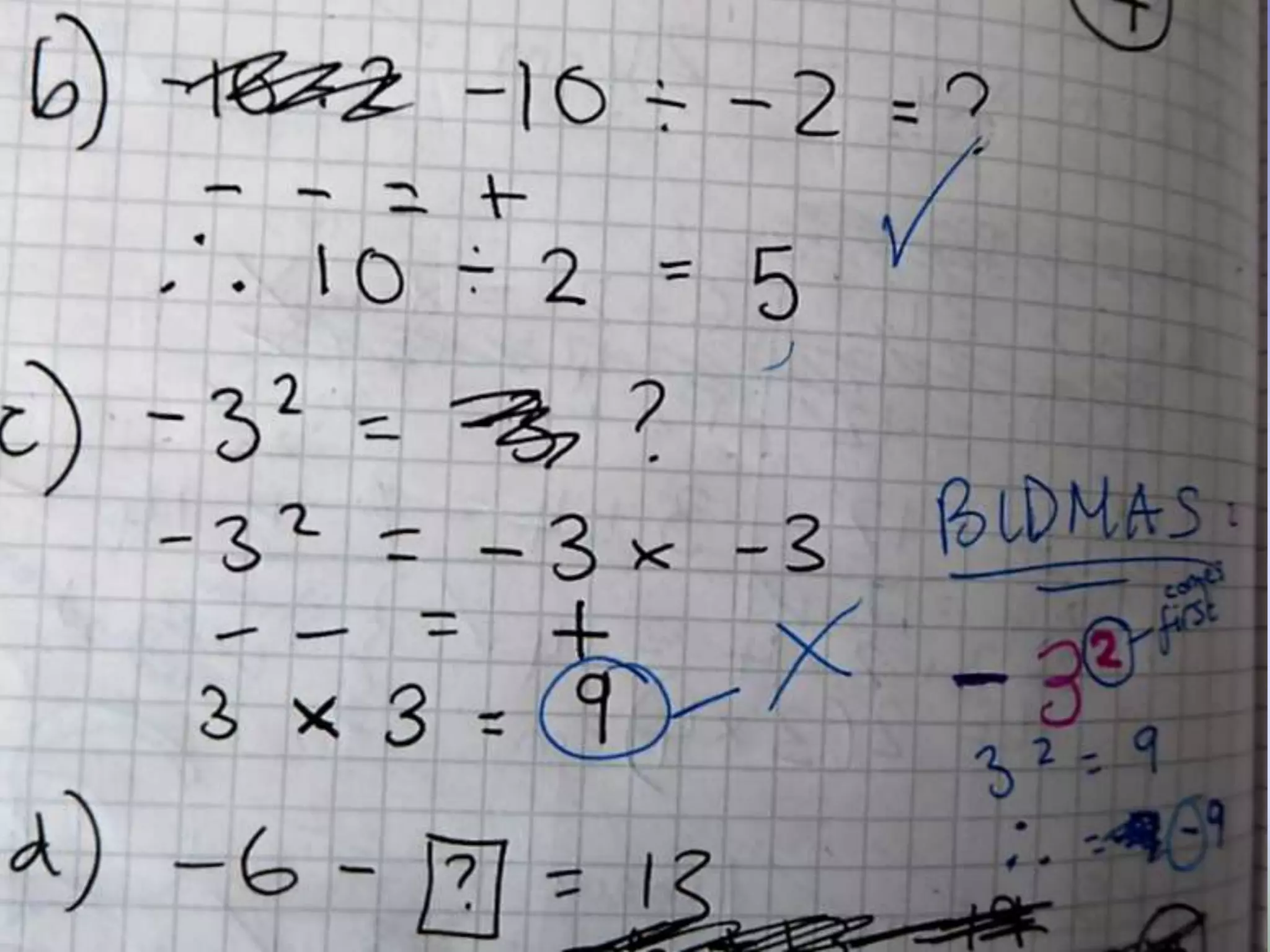The document discusses strategies for using retrieval practice, or testing, to help students learn in the classroom. It provides examples of how teachers can incorporate retrieval practice into their lessons in short bursts through activities like asking students questions and having them write down answers without resources, then checking their responses. Retrieval practice is presented as an effective way to help students recall and retain information.