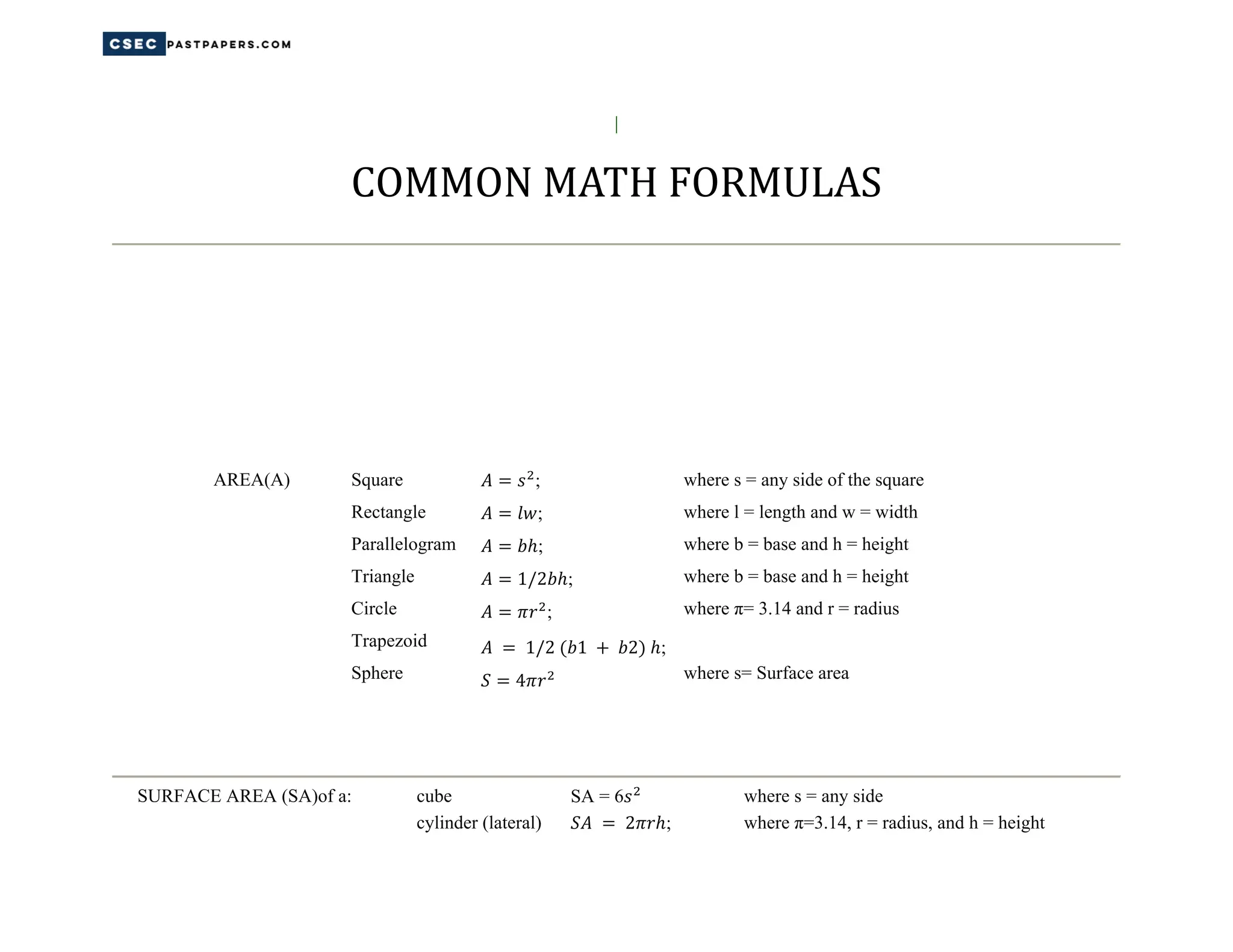
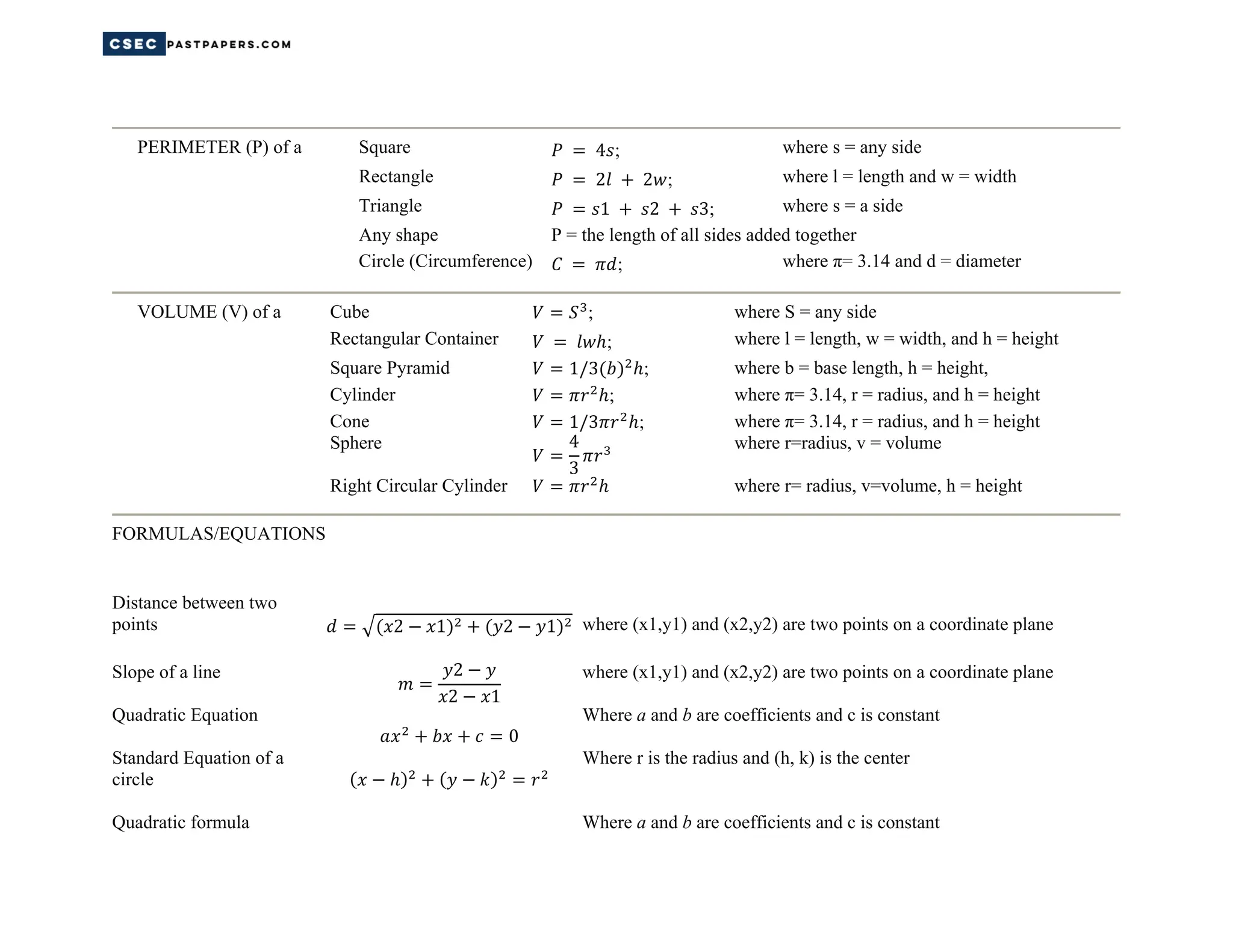
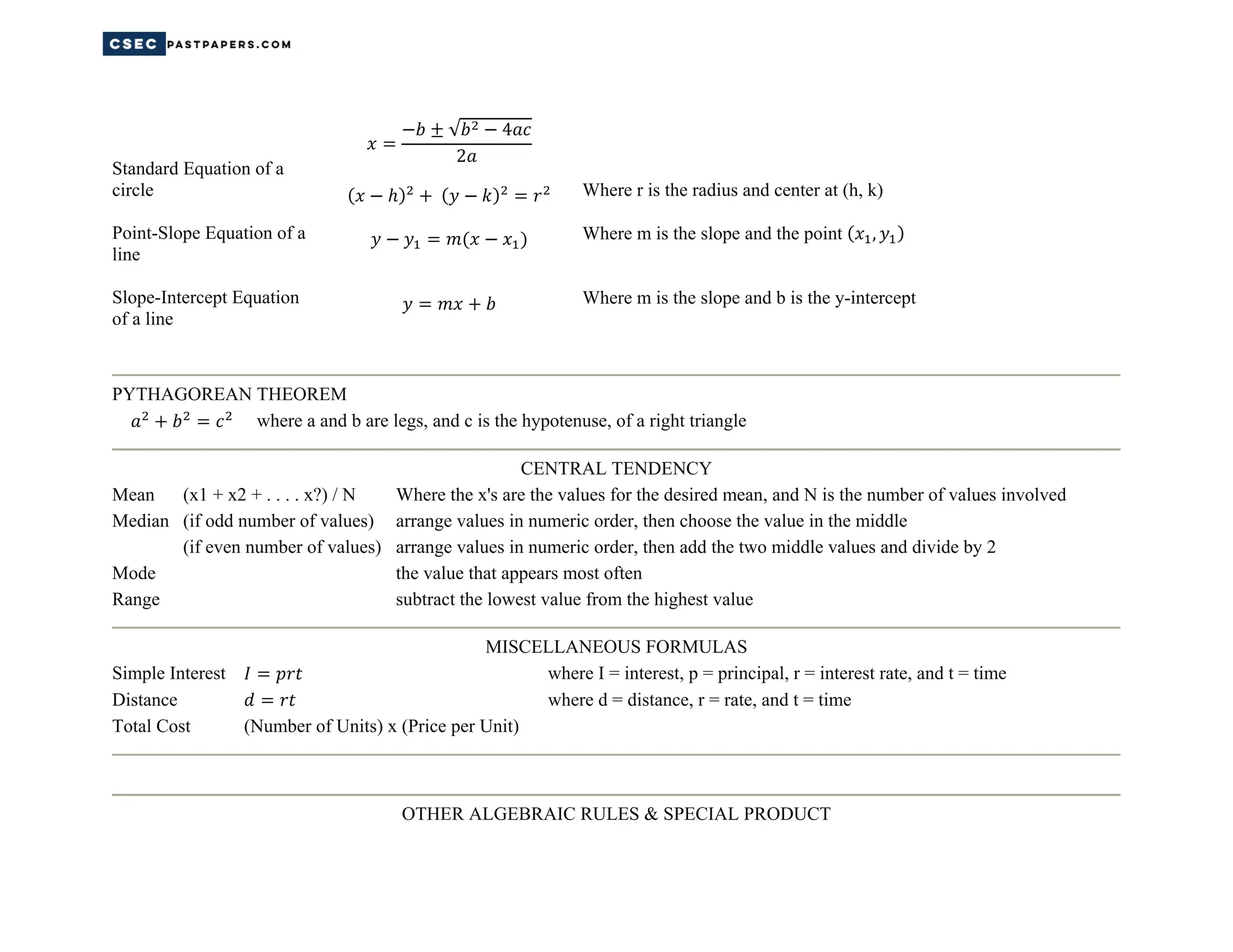
This document contains summaries of common math formulas for calculating area, surface area, perimeter, volume, distance, slope, rates of change, means, medians, modes, and other statistical measures. It also includes the Pythagorean theorem, algebraic rules like the product, power, and quotient rules, and formulas for simple interest, distance, and total cost.