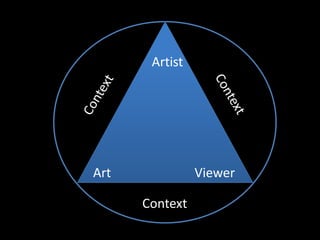
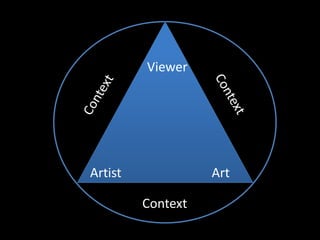
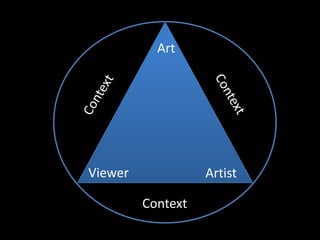
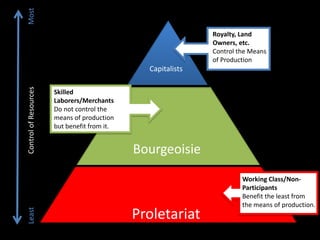
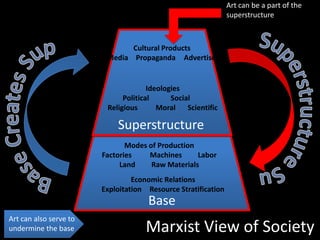
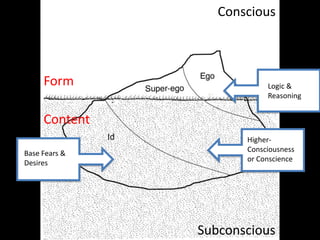
Form refers to the physical and visual aspects of a work of art. Content refers to the meaning of a work of art, including the subject matter, artist's intent, and viewer's interpretation. There are several major theories for analyzing and interpreting artworks based on their form and content, including formalist theories that focus on form, expressionist theories that view art as a means of expression, contextual theories that examine art within its social and historical context, Marxist theories that analyze art's relationship to economic systems and class struggle, psychoanalytic theories that view art as revealing the unconscious, and postcolonial theories that examine issues of colonialism, identity, and cultural difference.