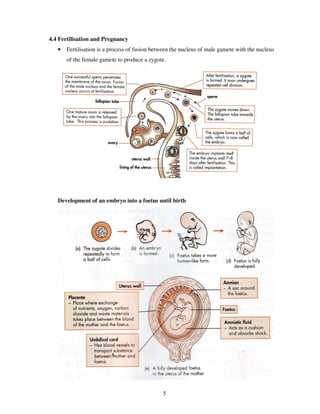
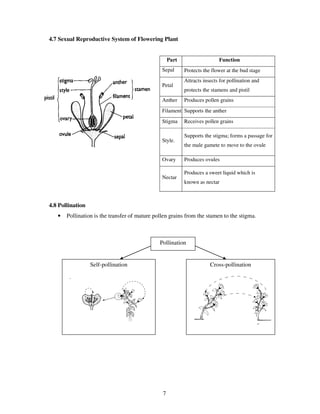
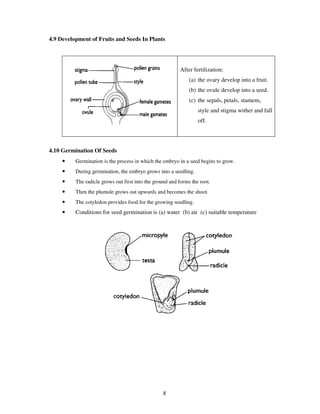
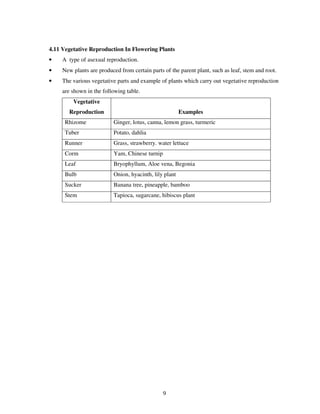
The document discusses various topics related to reproduction including:
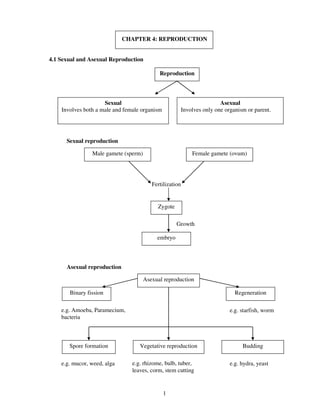
1. Sexual reproduction involves both male and female organisms while asexual reproduction involves only one organism.
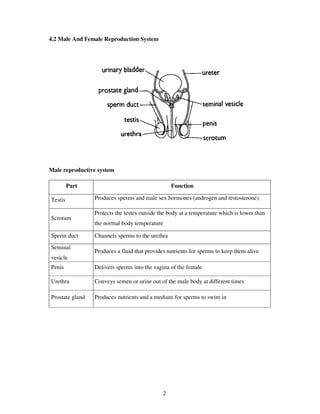
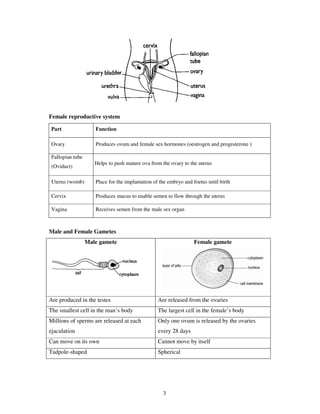
2. It describes the male and female reproductive systems and their key parts.
3. Changes that occur in males and females during puberty including physical and emotional changes.
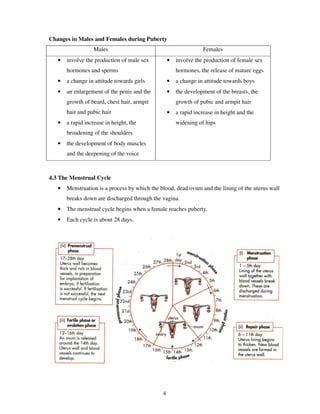
4. The menstrual cycle and process of fertilization and pregnancy are explained.