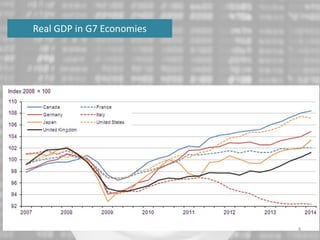
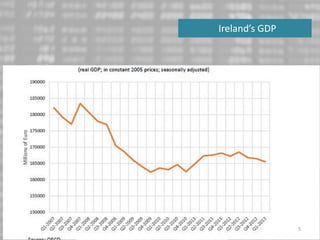
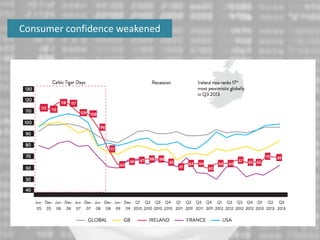
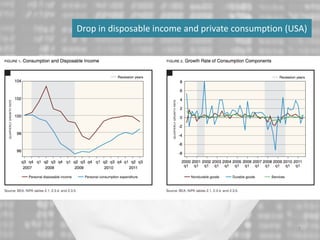
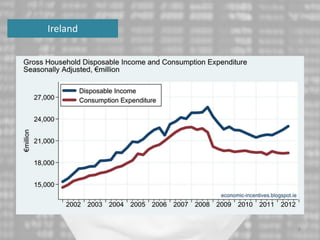
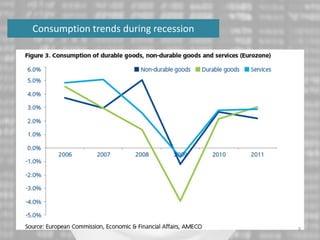
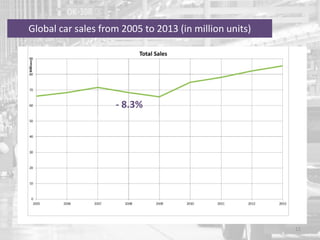
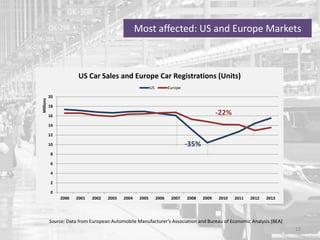
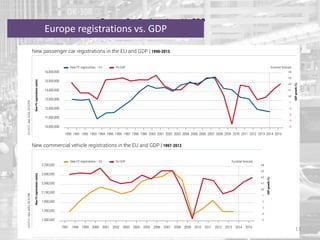
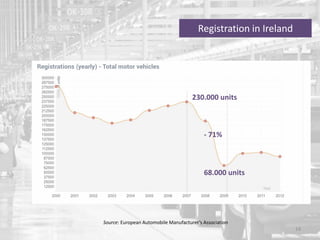
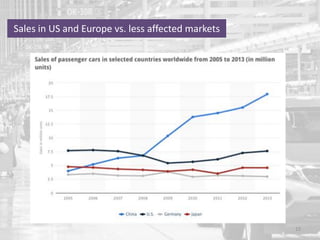
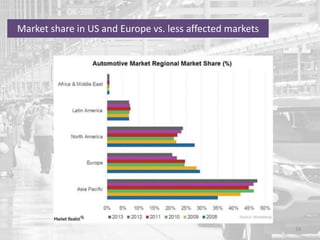
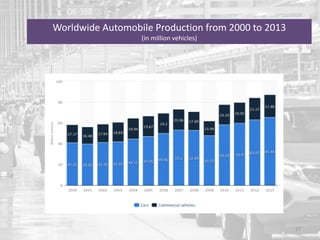
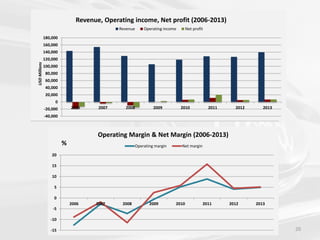
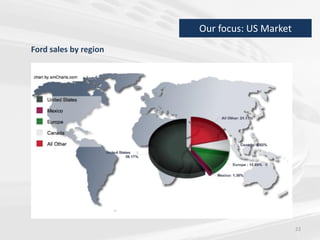
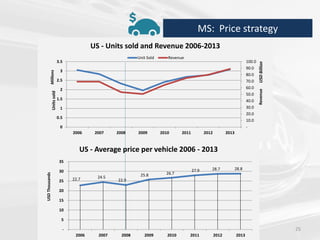
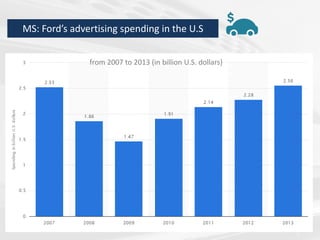
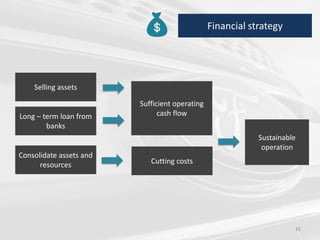
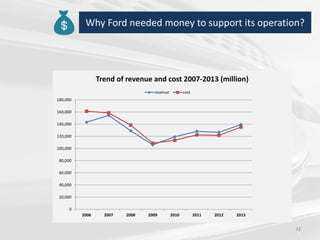
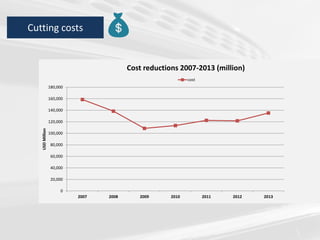
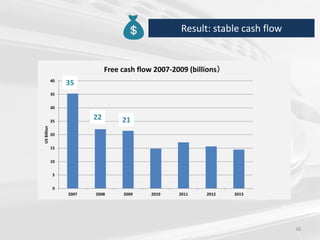
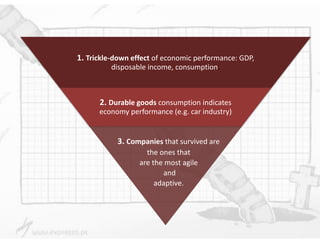
The document discusses the impact of the global recession from 2007-2010 on the automotive industry. It analyzes declines in global car sales, particularly in the US and European markets. Ford is presented as a case study of how a major automaker survived the recession through leadership changes, marketing strategies like the Ford Fiesta campaign, financial moves like loans and asset sales, and cost cutting. The conclusions drawn are that economic downturns negatively impact durable goods industries and that companies must be agile and adaptive to withstand recessions.