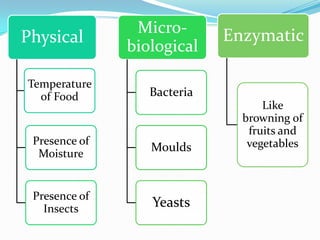
This document discusses food contamination and spoilage. It identifies key stages where contamination can occur, such as during food handling, preparation, and storage. Temperature, moisture levels, insects, and microbes can all lead to contamination if safe practices are not followed. Bacteria growth is favored between 4-60 degrees Celsius and killed at 100 degrees. Contamination can cause foodborne illnesses with symptoms like nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Enzymes from bacteria can also cause food to spoil faster by producing a slimy coating on raw foods. Proper temperature control and hygiene are important to prevent contamination and spoilage at all stages of food production.