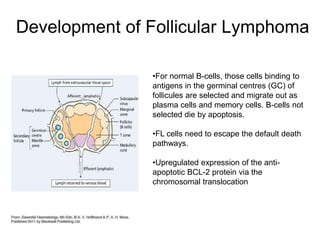
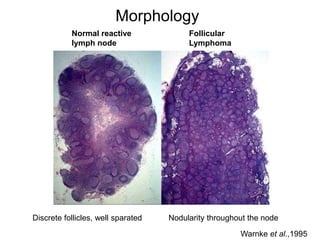
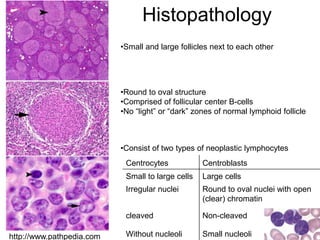
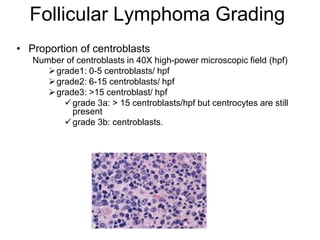
Follicular lymphoma is the second most common non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. It is a neoplasm of follicle center B cells that shows a follicular growth pattern due to a chromosomal translocation resulting in overexpression of the bcl-2 gene. This translocation allows the lymphoma cells to evade apoptosis. Follicular lymphoma usually presents as painless lymphadenopathy and involves lymph nodes as well as extranodal sites. Diagnosis involves lymph node biopsy and immunostaining to detect bcl-2 expression. Treatment options include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and monoclonal antibody therapy.