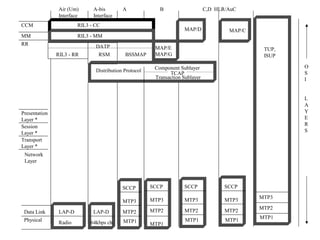
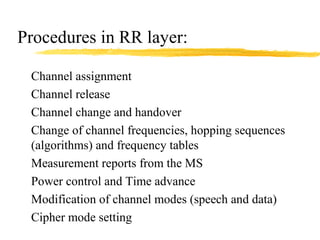
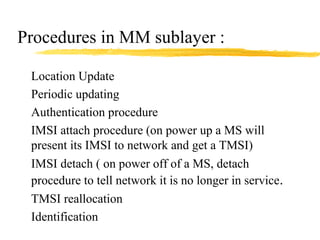
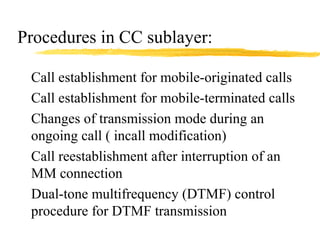
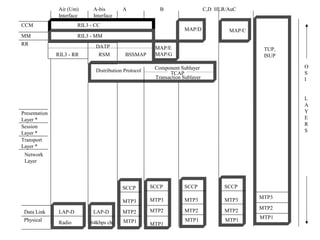
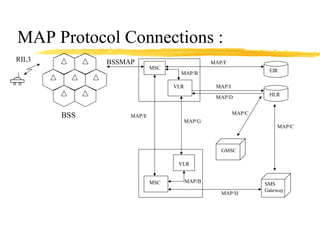
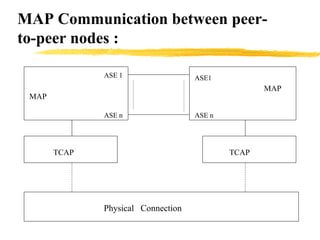
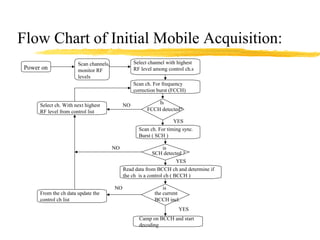
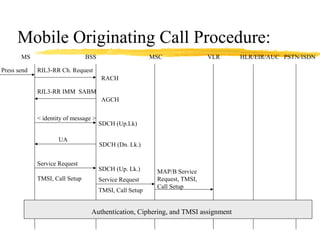
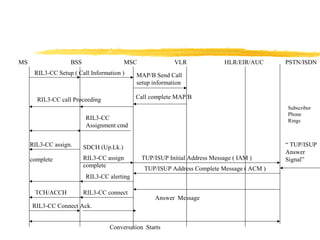
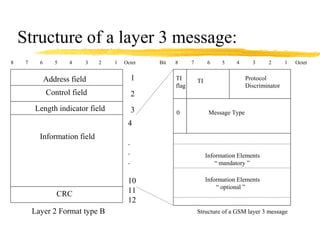
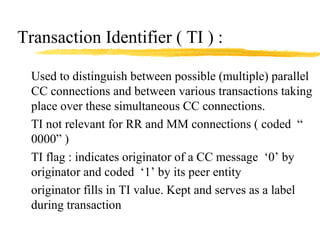
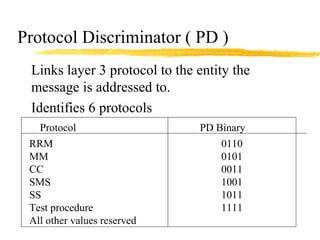
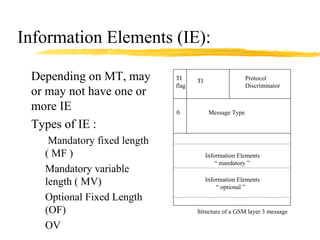
The document discusses the network layer in GSM systems. It describes the main sublayers and protocols in the network layer, including radio resource management (RR), mobility management (MM), and call control (CC). It explains the functions and procedures handled by each sublayer, such as channel assignment and handover (RR), location updating and authentication (MM), and call establishment and clearing (CC). It also outlines some of the key layer 3 protocols used, including RIL3-RR, RIL3-MM, RIL3-CC, and MAP, and provides examples of signaling flows for initial mobile acquisition and a mobile-originating call.