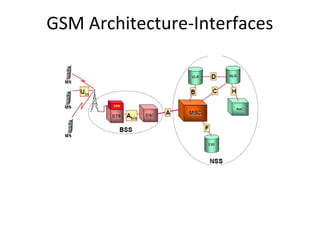
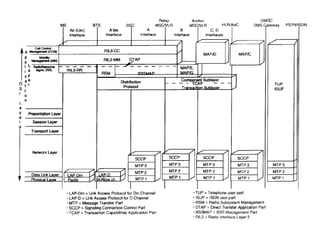
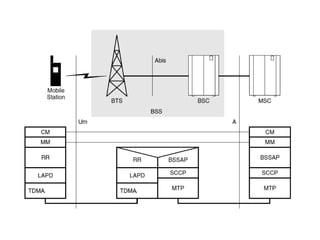
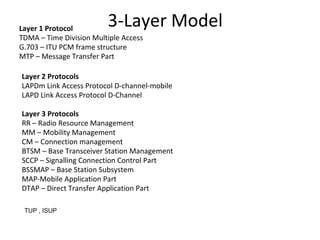
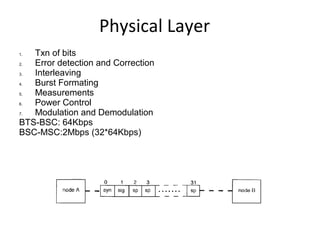
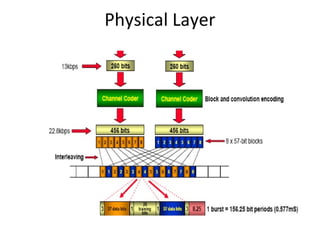
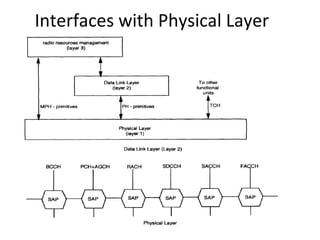
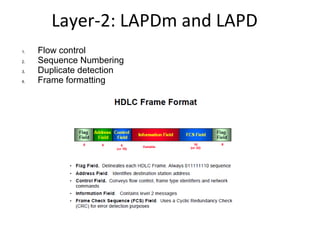
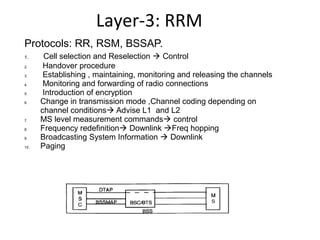
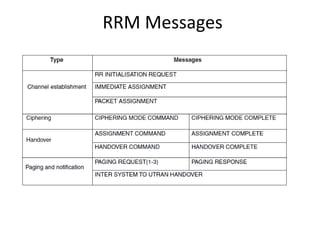
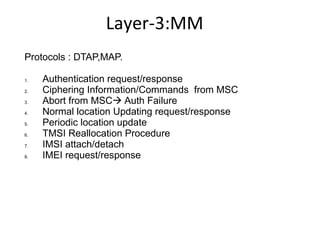
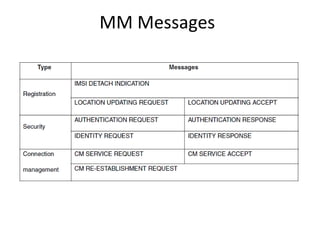
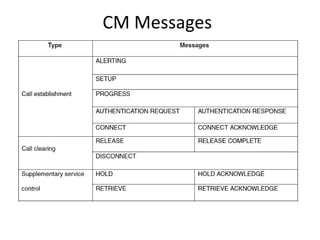
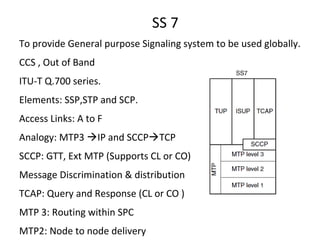
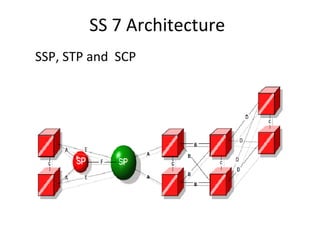
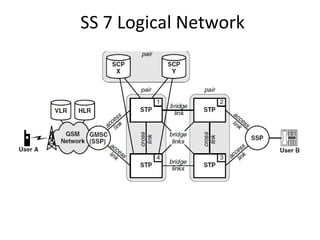
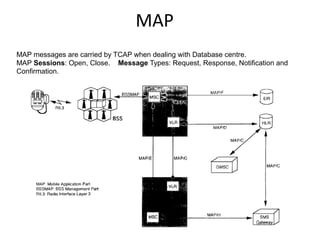
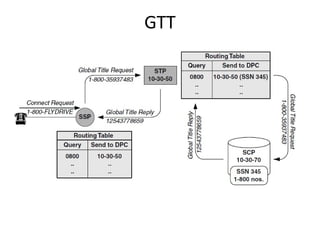
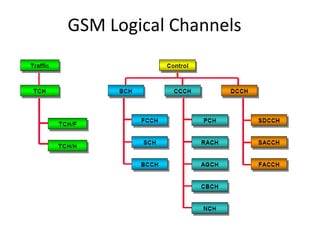
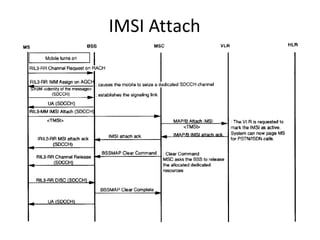
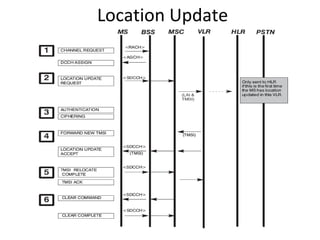
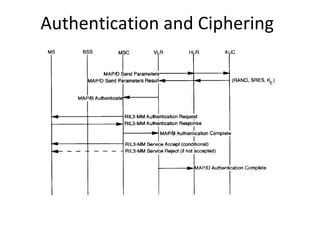
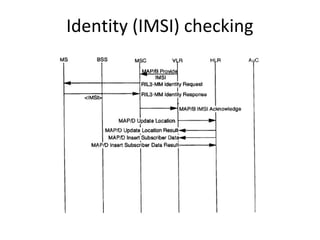
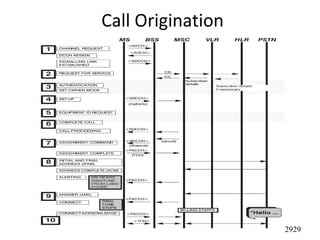
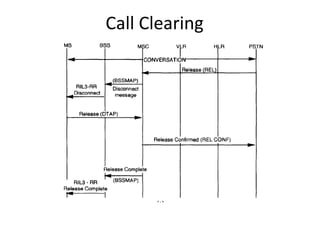
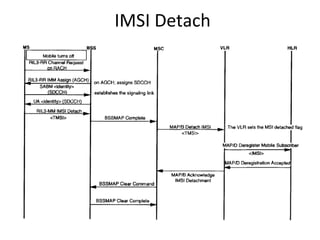
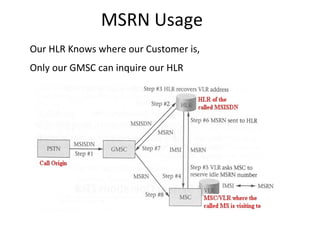
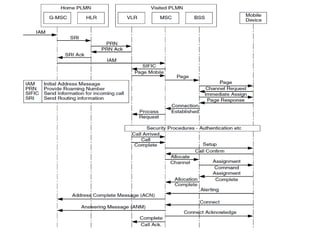
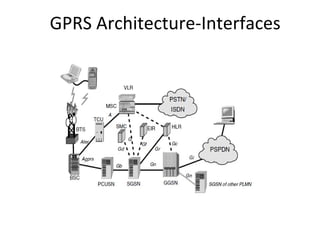
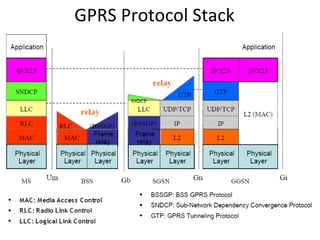
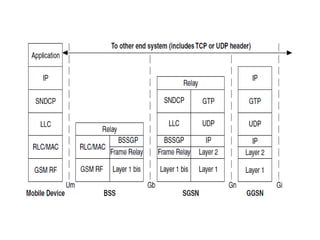
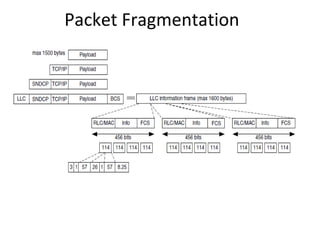
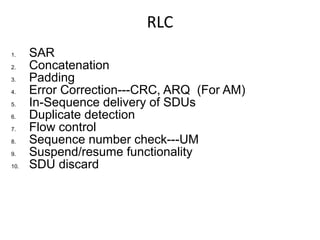
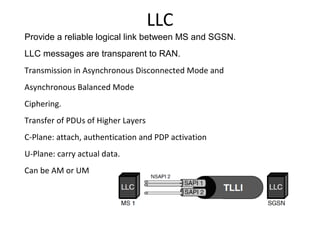
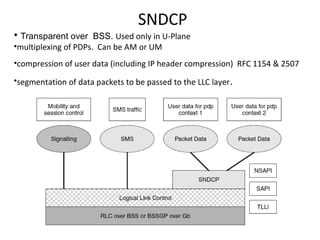
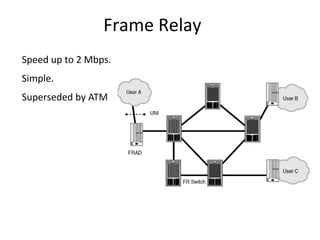
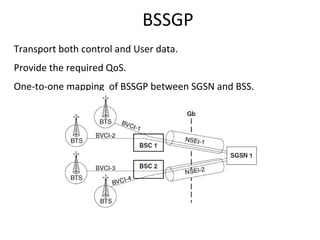
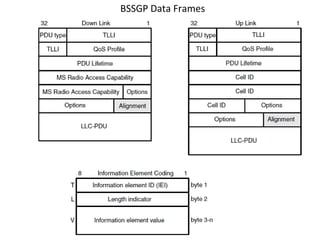
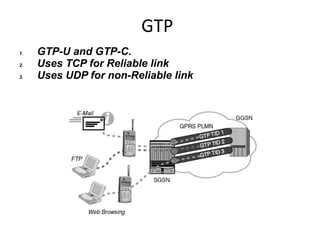
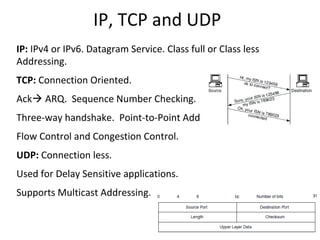
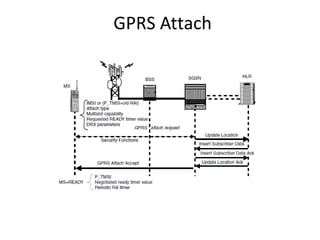
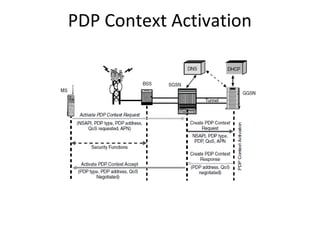
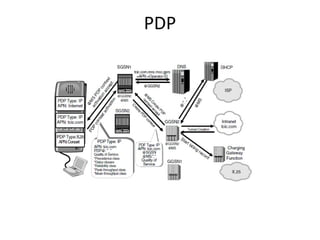
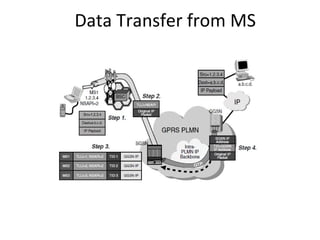
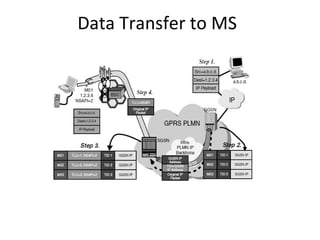
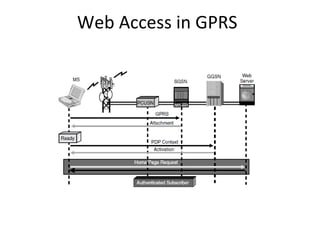
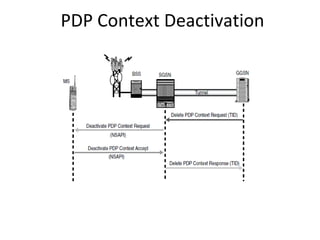
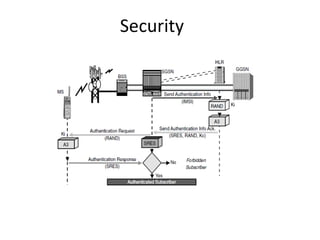
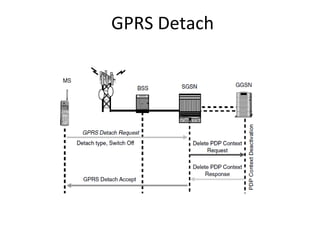
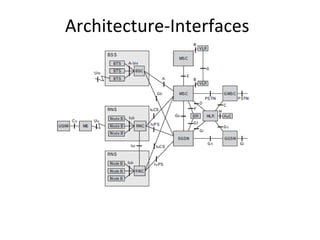
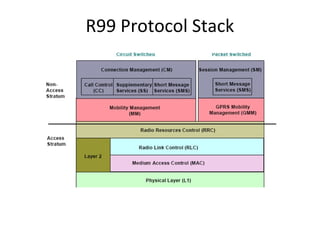
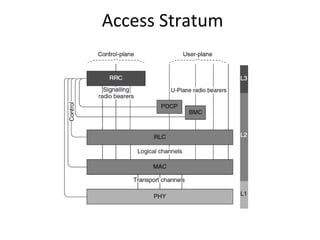
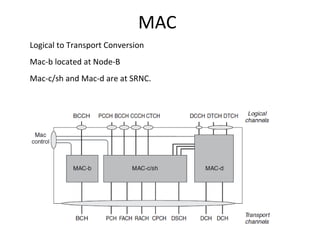
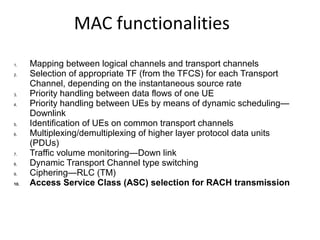
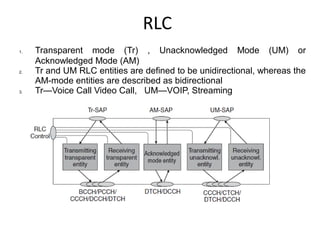
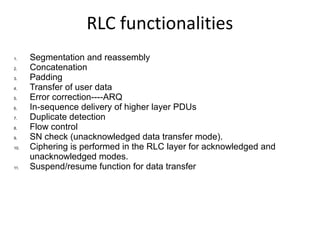
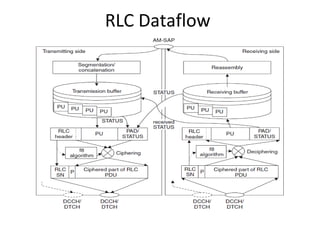
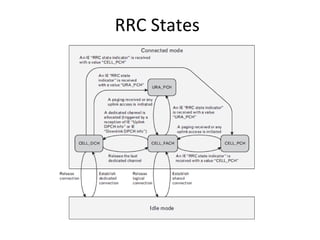
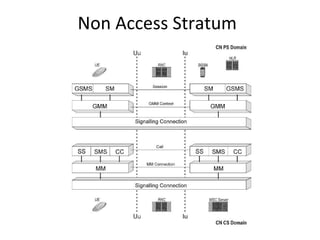
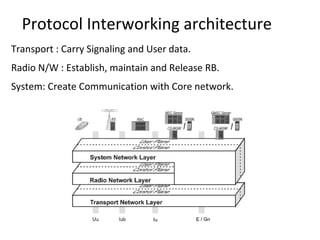
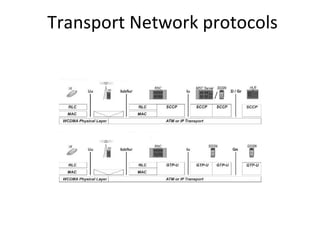
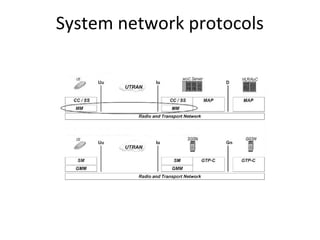
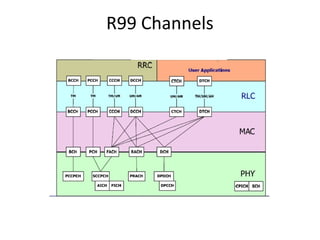
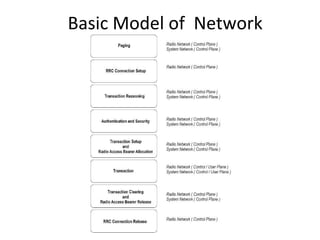
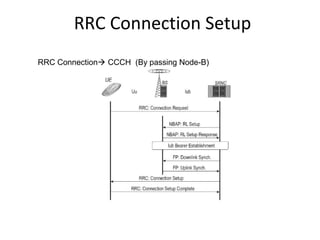
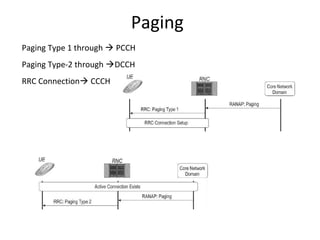
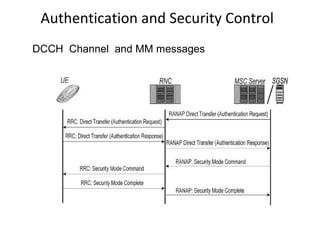
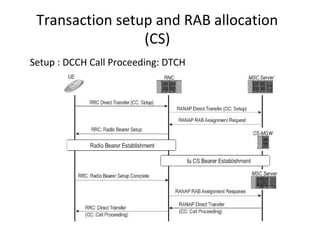
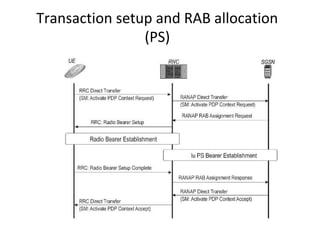
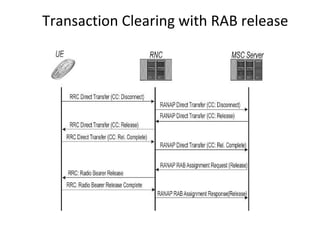
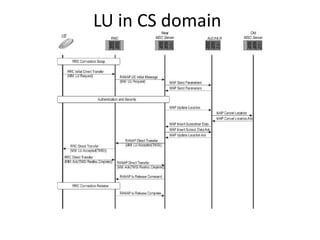
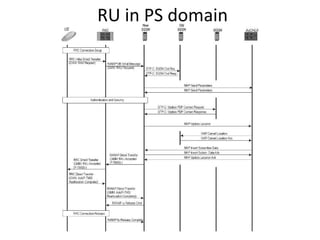
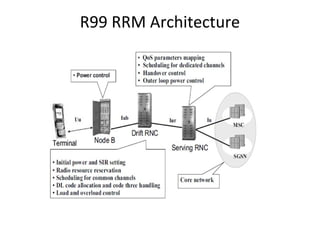
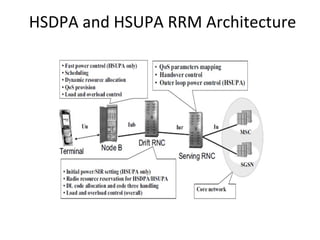
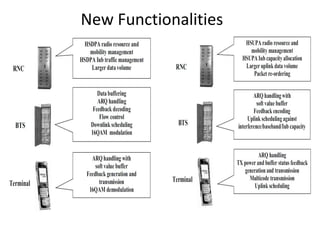
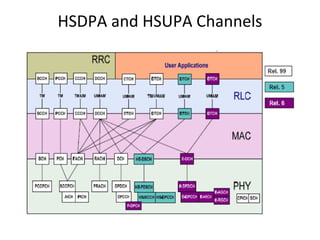
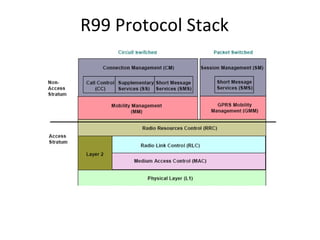
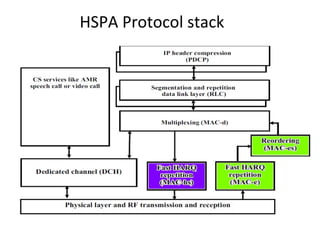
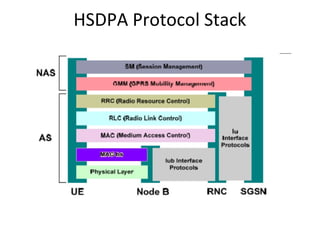
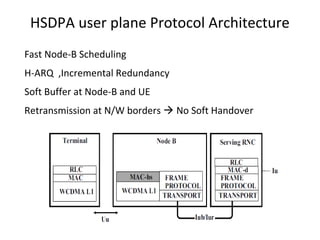
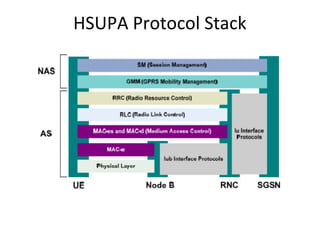
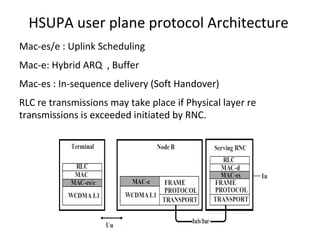
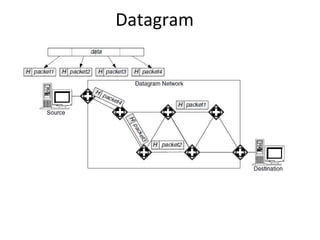
This document provides an overview of GSM, GPRS, UMTS, HSDPA and HSUPA protocols and call flows. It describes the protocol stacks and architectures of these mobile communication standards. Key topics covered include physical layer protocols, MAC, RLC, RRC, SNDCP, GTP, MAP, mobility management, call establishment flows and channel types. The document also lists references for further information.