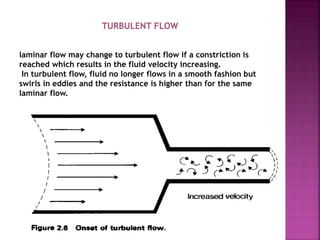
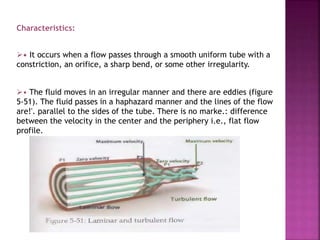
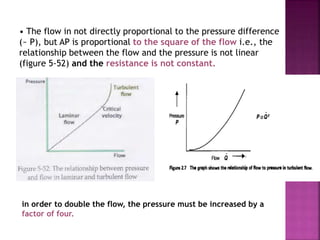
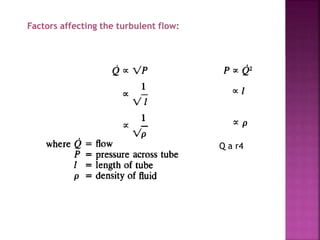
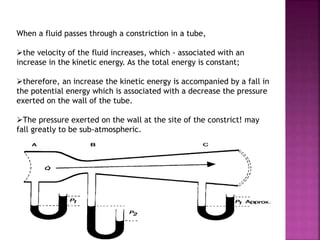
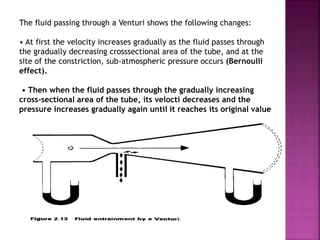
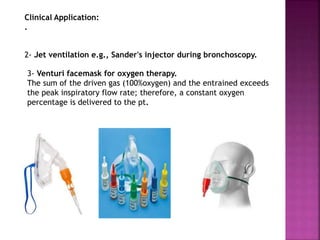
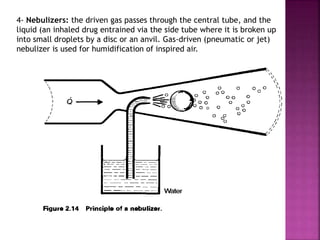
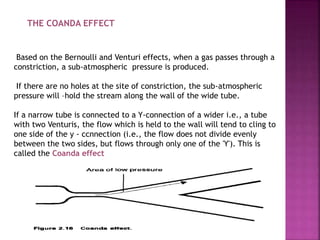
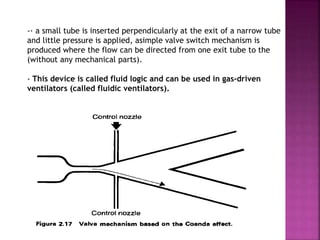
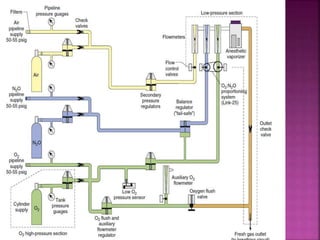
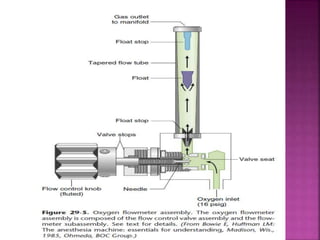
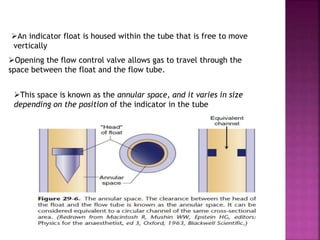
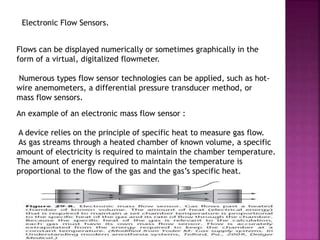
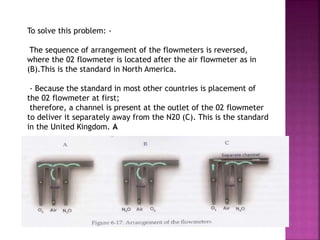
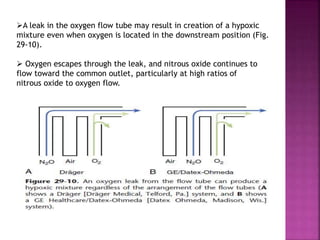
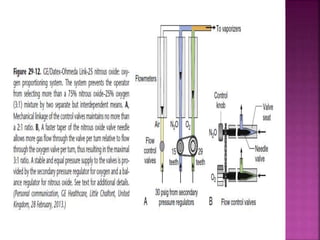
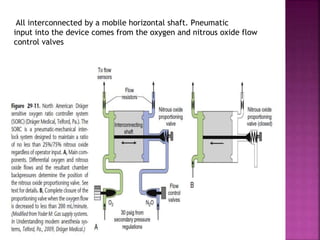
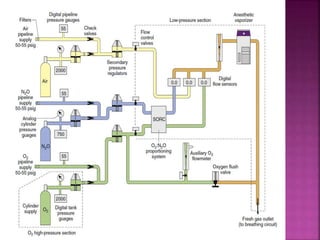
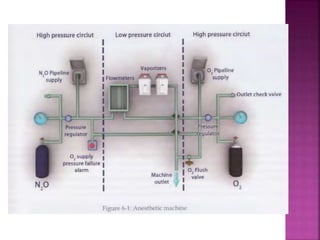
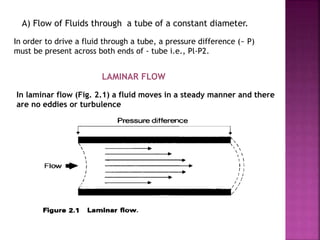
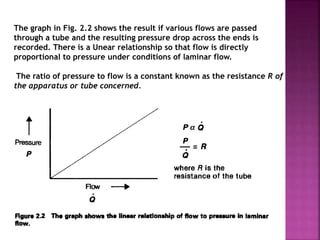
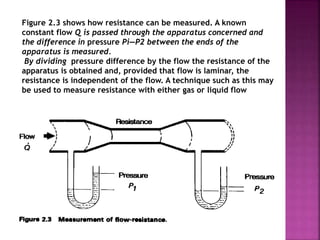
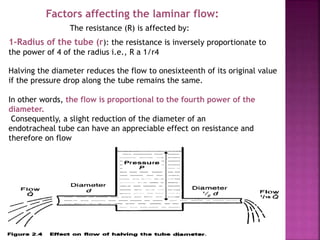
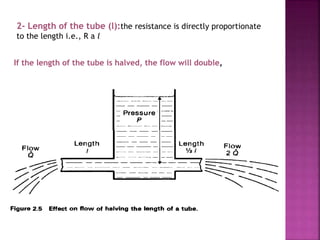
Dr. Mohammad Abdeljawad discusses fluid flow through tubes. He defines flow as the quantity of fluid passing a point over time. Flow can occur through tubes of constant or variable diameter, or an orifice. In tubes of constant diameter, laminar flow is steady without eddies, while turbulent flow is irregular with eddies above a critical velocity. Factors like radius, length, and viscosity affect laminar flow and resistance according to the Hagen-Poiseuille equation. In tubes of variable diameter, the Bernoulli effect causes pressure and velocity changes. Clinical applications include increasing flow rates and managing asthma and respiratory resistance.





![3-Viscosity of fluid (q): the resistance is directly proportionate to
the viscosity i.e., R a I]
Viscosity is a measure of the frictional forces acting between the
layers of the fluid as it flows along the tube
the viscosity of the fluid affects resistance to laminar flow in such
a way that the higher the viscosity the slower is the flow.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/flowandflowmeter-200718051705/85/Flow-and-Flowmeter-11-320.jpg)