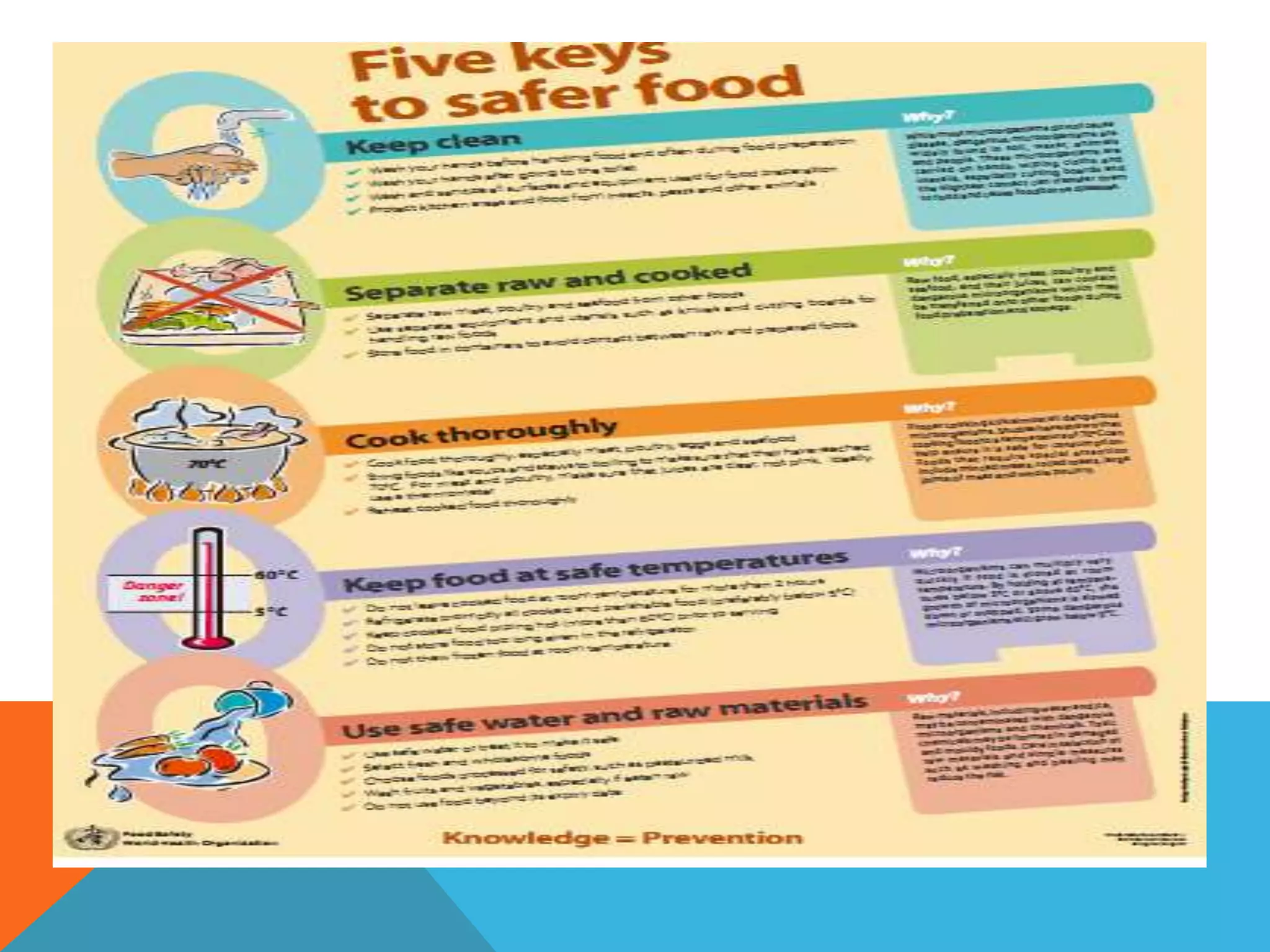
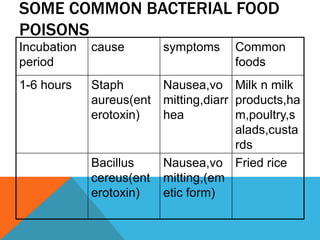
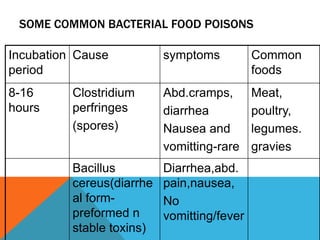
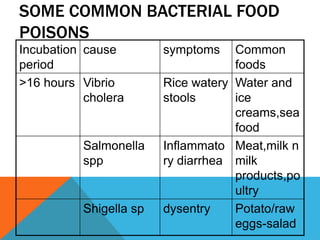
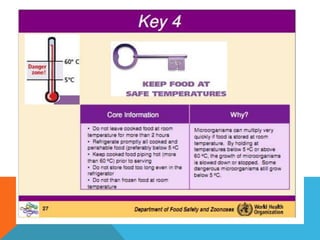
Food borne diseases are illnesses acquired through consumption of contaminated food, causing major global health issues. Common pathogens that cause food borne infections and intoxications include bacteria like Salmonella, E. coli and viruses like norovirus. Food poisoning occurs when toxins or pathogens in contaminated food invade the intestines. Proper cooking and food handling can prevent many food borne illnesses. Timely diagnosis and investigations tracing contaminated foods and transmission routes are important for control.