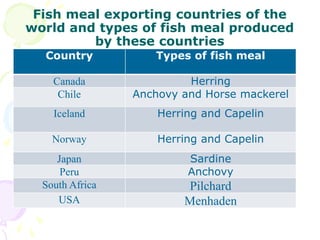
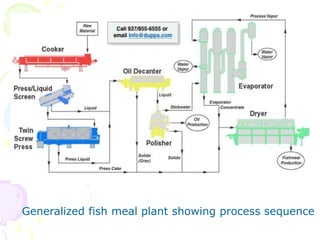
Approximately one-third of global fish catch is used for by-products rather than direct consumption, with applications ranging from animal feed to industrial uses. Fish meal, a significant by-product, is produced from various fish species and is a nutrient-rich supplement primarily for animal diets. The document discusses the nutritional benefits, production methods, and key species used in the manufacture of fish meal.