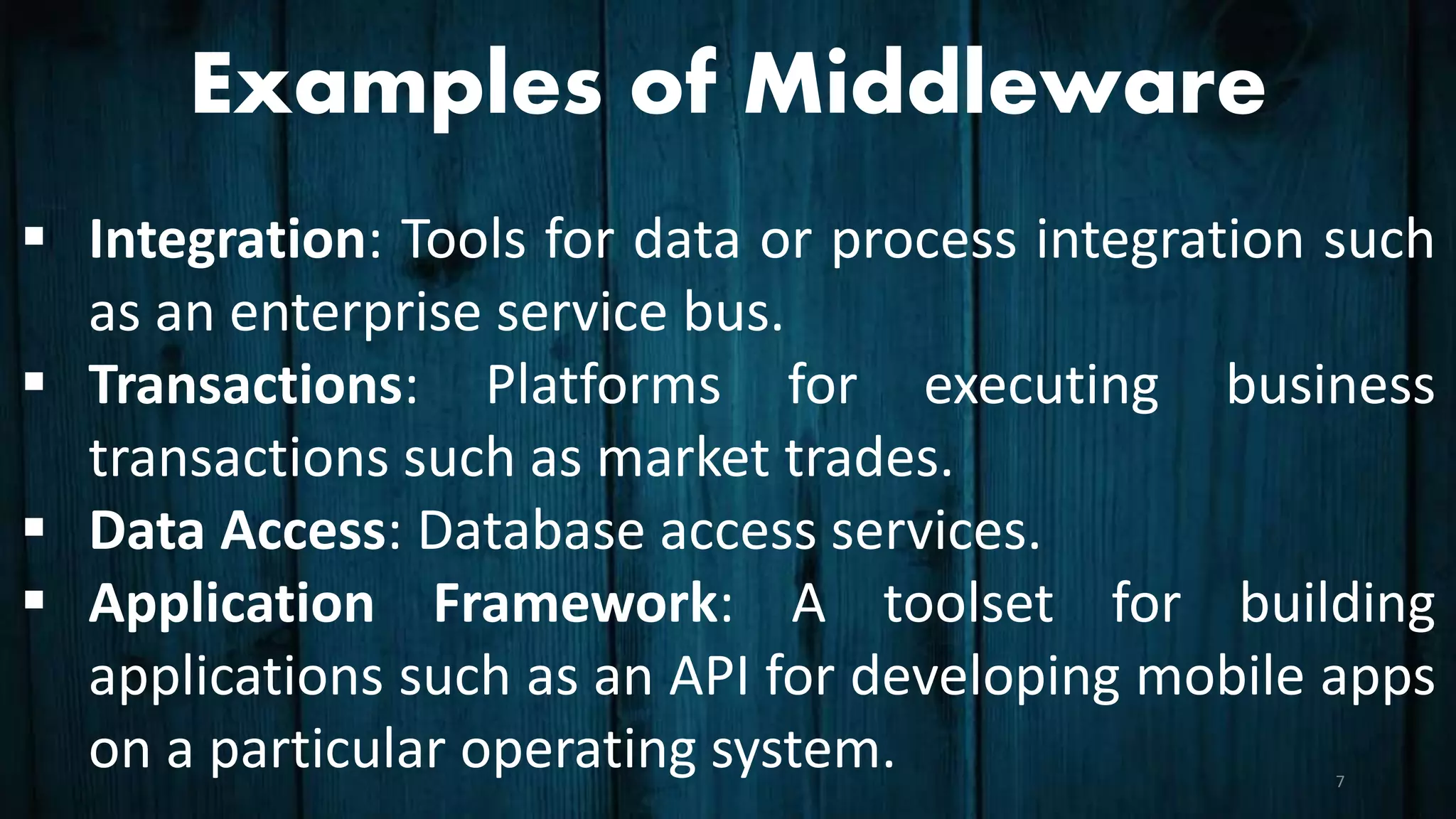
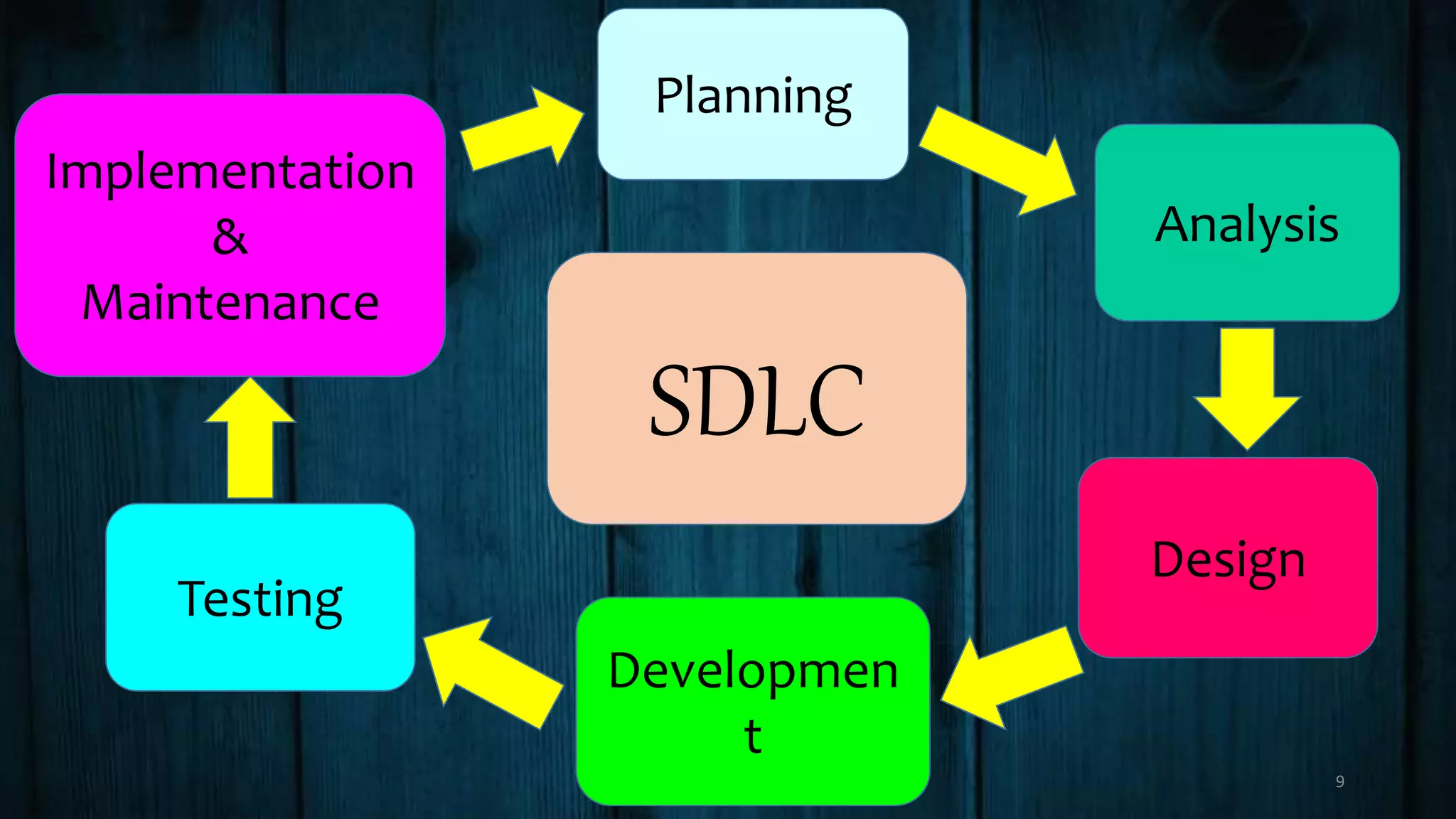
The document explains firmware as a semi-permanent software on hardware devices that facilitates communication, while middleware serves as a 'software glue' offering services to software applications beyond those provided by operating systems. Examples of each include embedded systems and game engines respectively. Additionally, it outlines the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) phases, including planning, analysis, design, development, testing, and maintenance.