The document provides information on various financing options for businesses, including:
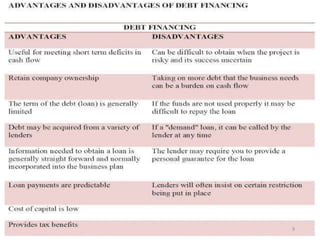
- Debt financing sources like bank loans, overdrafts, and asset-based finance. Common types of debt financing include bank term loans, receivables finance, and invoice discounting.
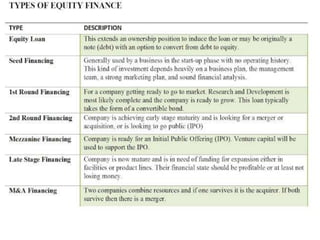
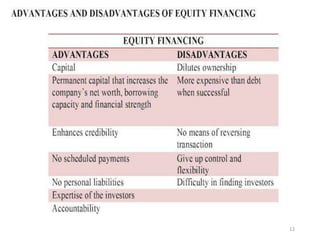
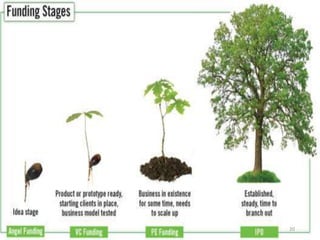
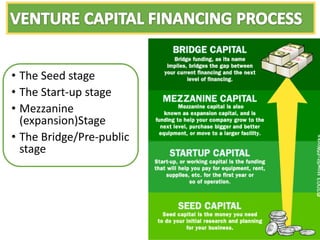
- Equity financing sources like funds from friends and family, angel investors, venture capitalists, and strategic investors. The document discusses the different stages of financing for startups.
- Other long term financing options like internal accruals, preference capital, debentures, and term loans. International sources of financing mentioned include foreign direct investment, American depository receipts, global depository receipts, and foreign institutional investors.