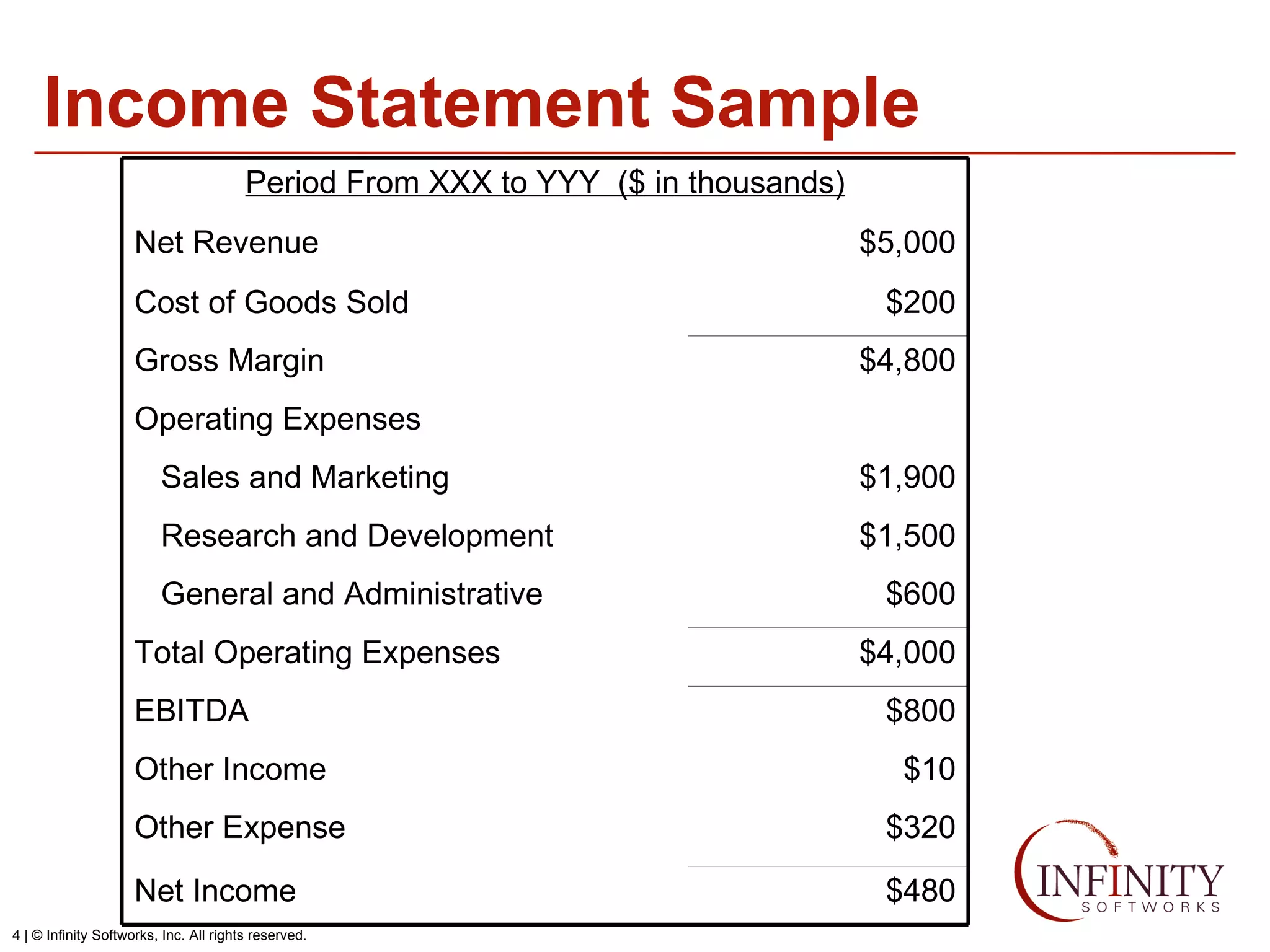
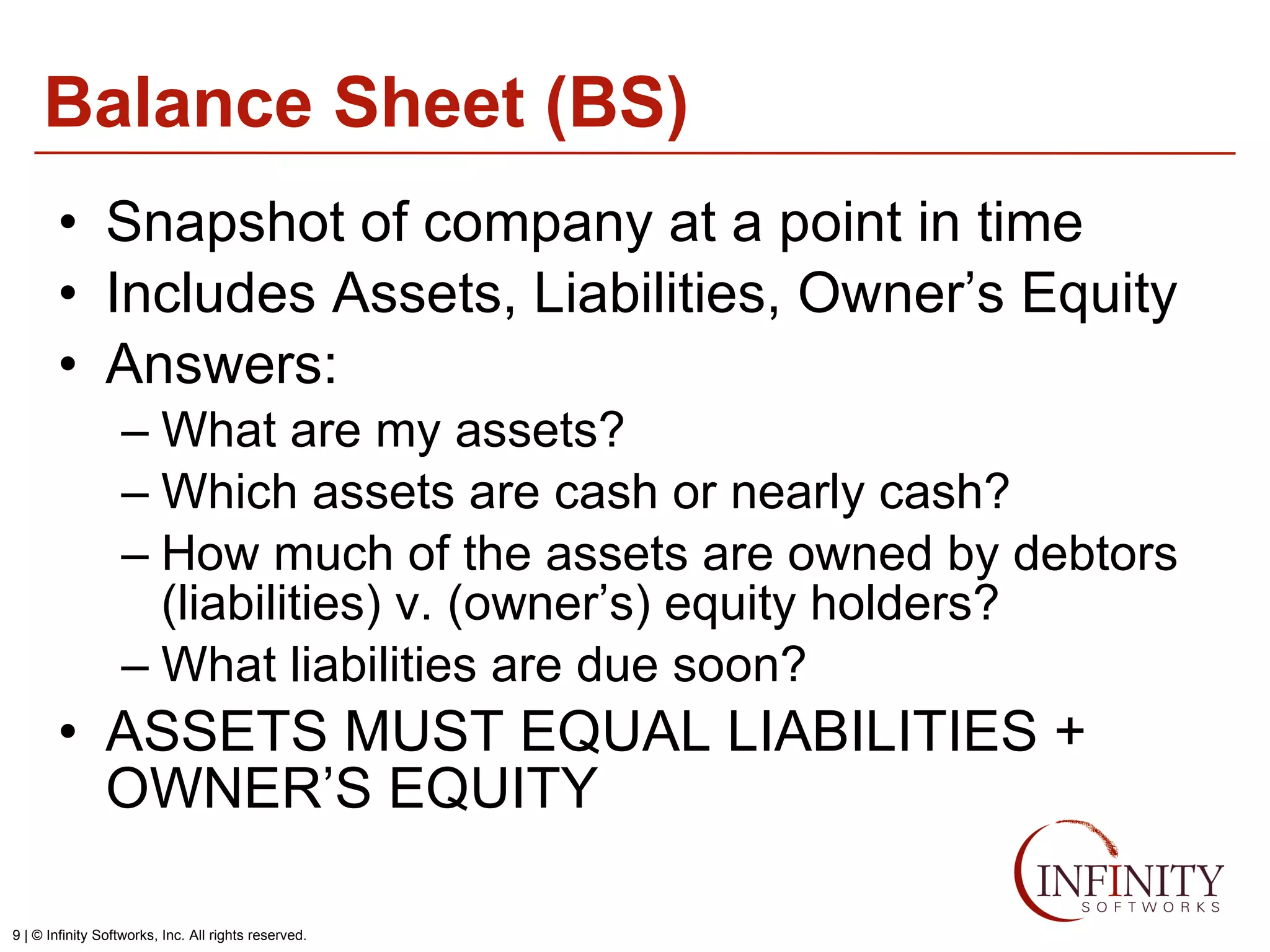
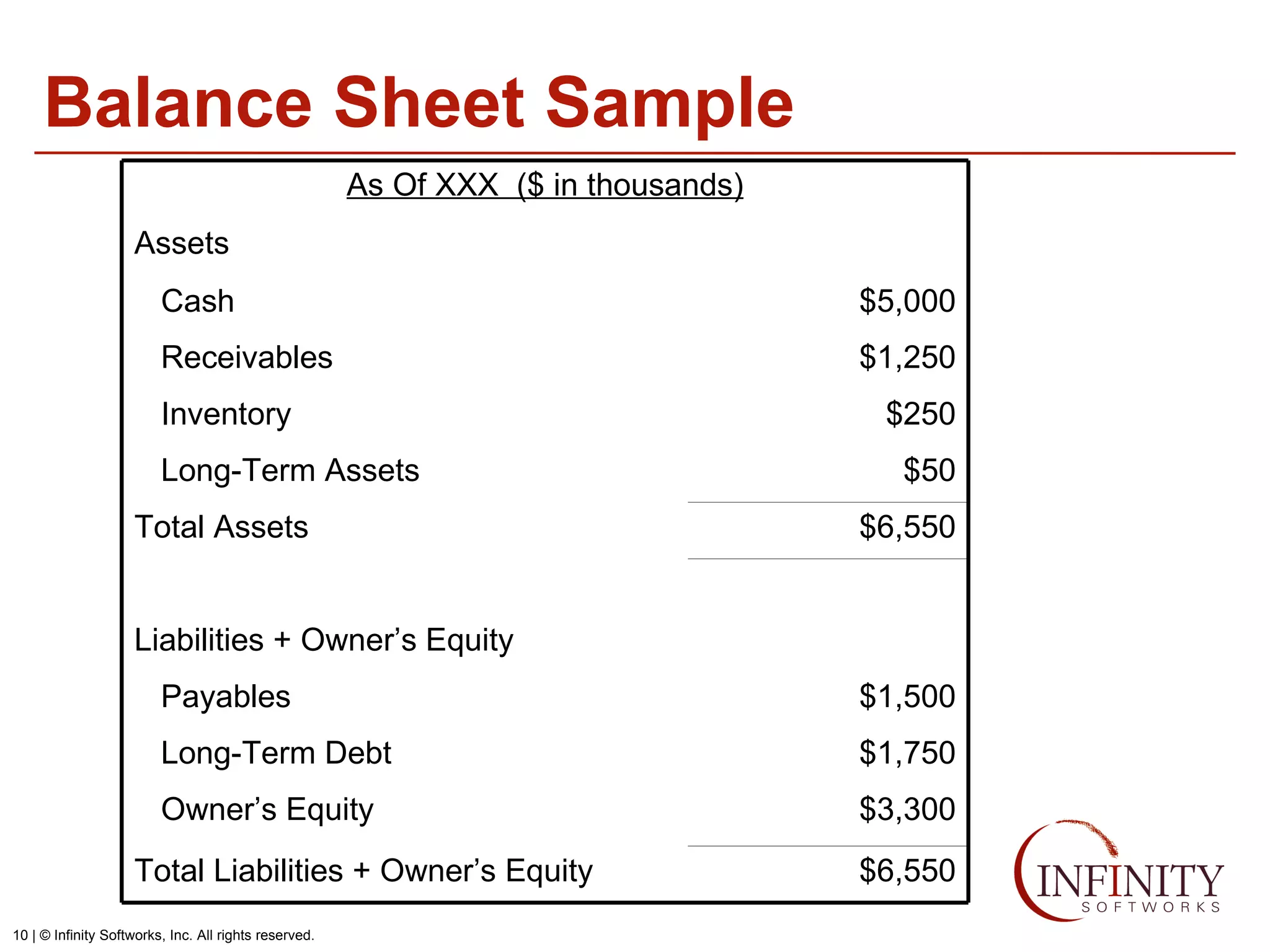
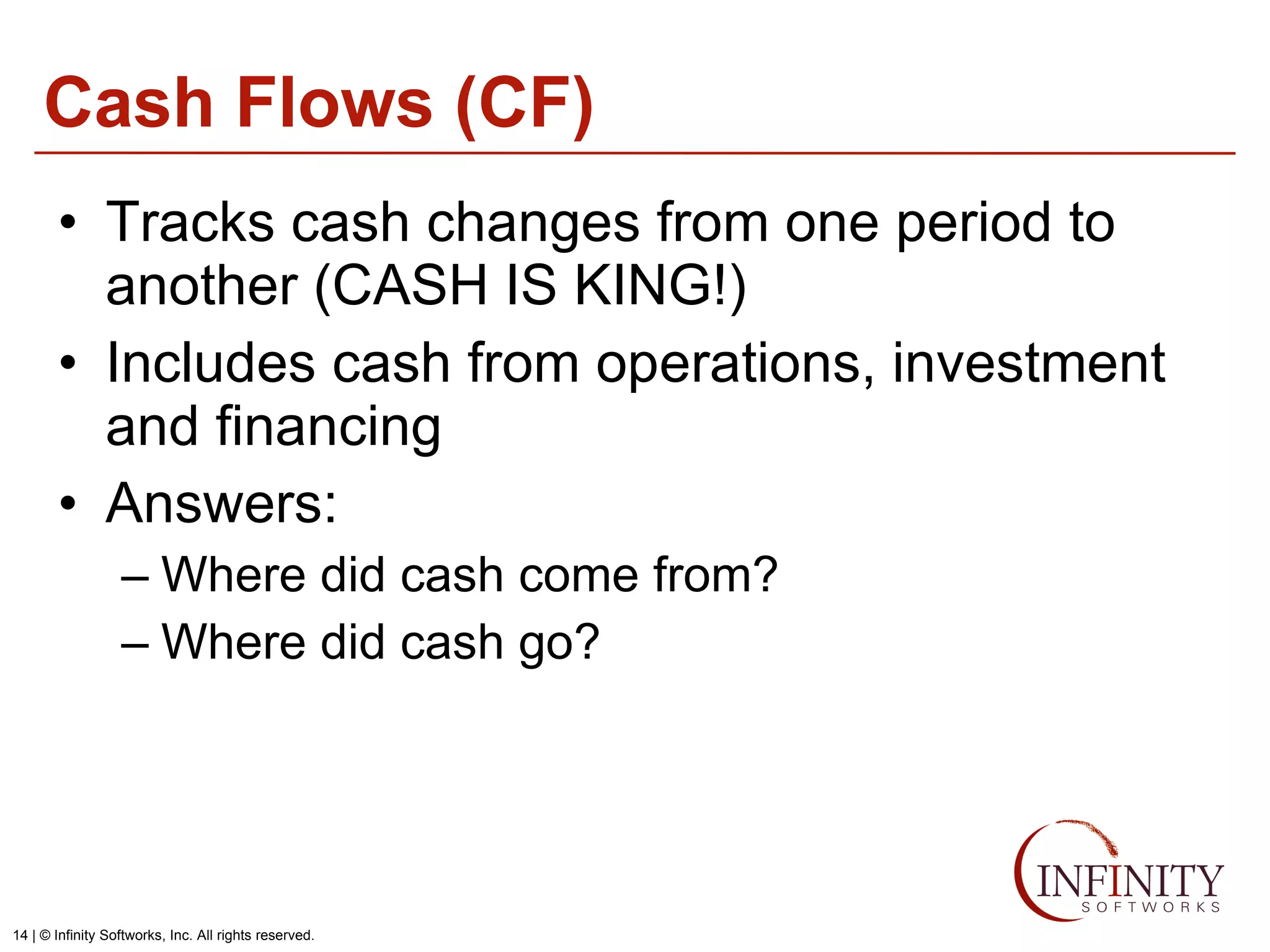
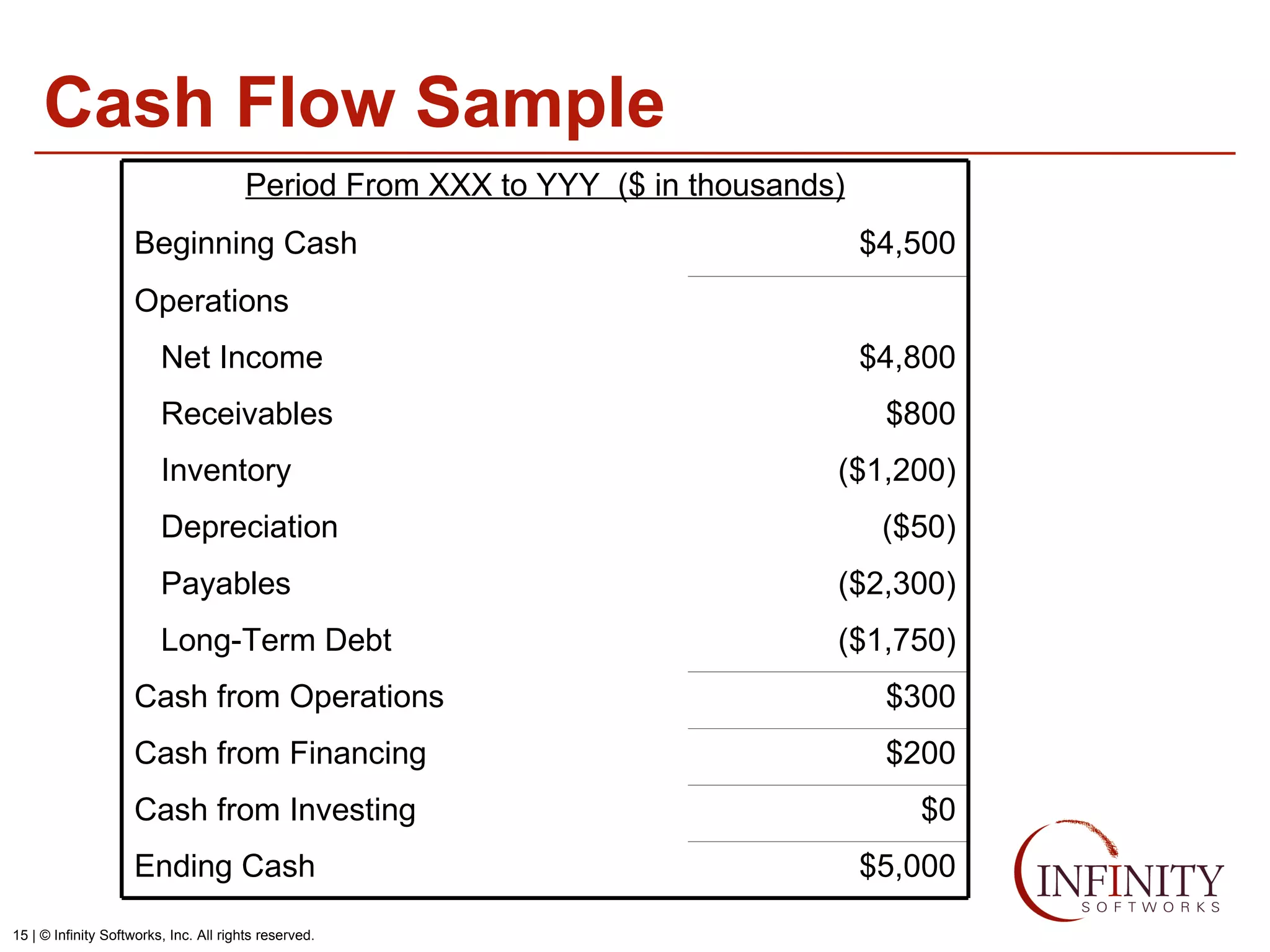
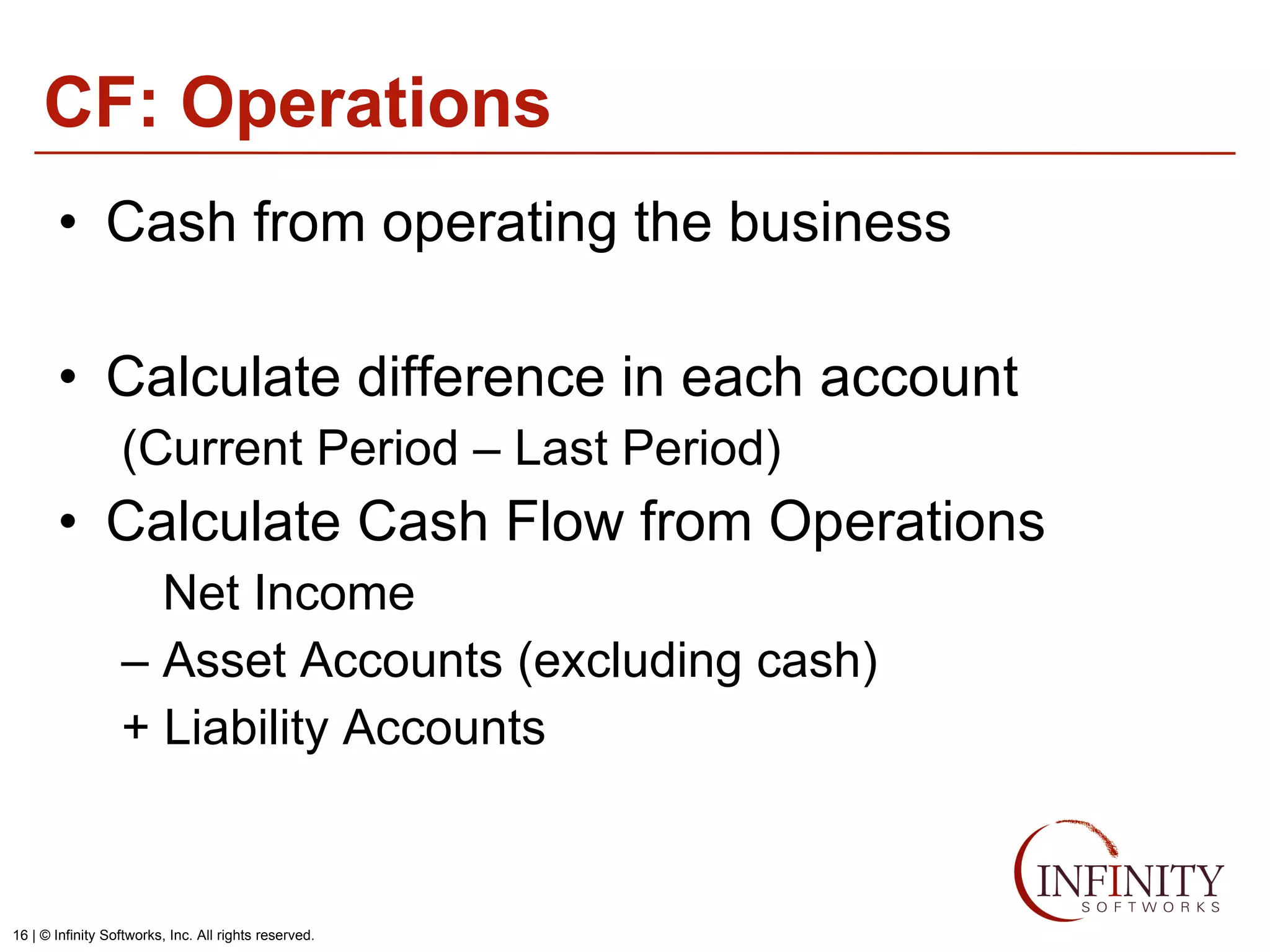
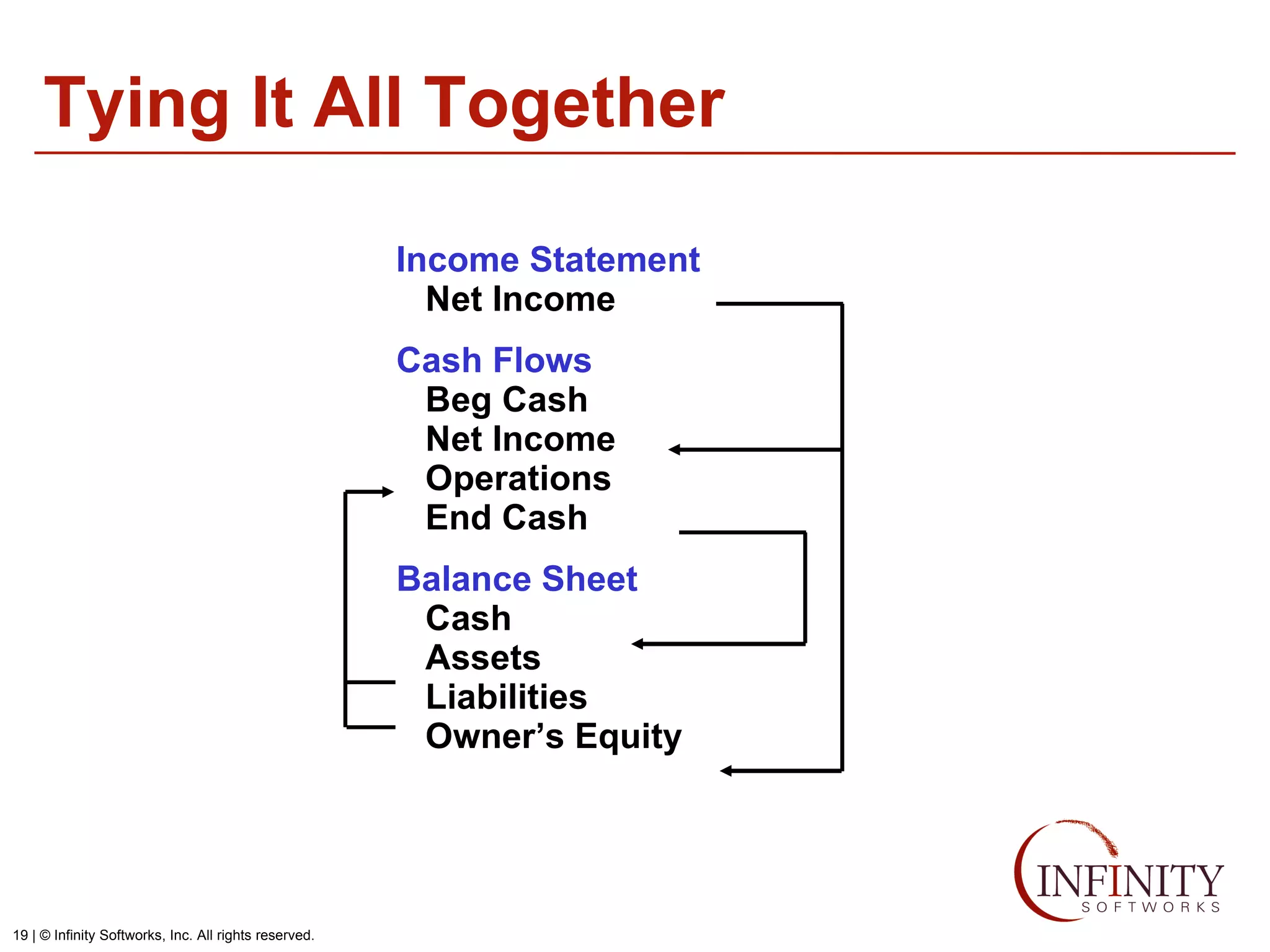
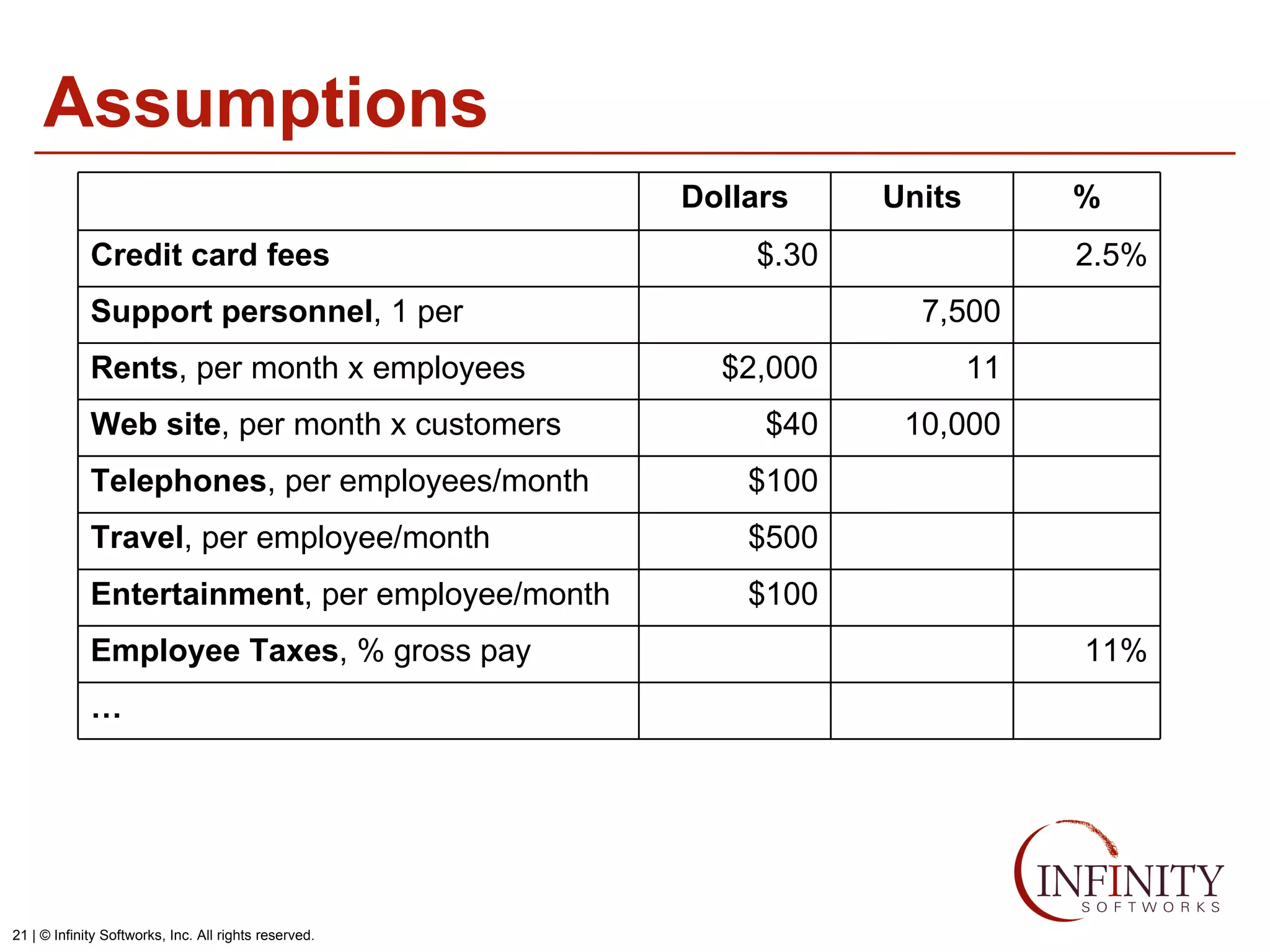
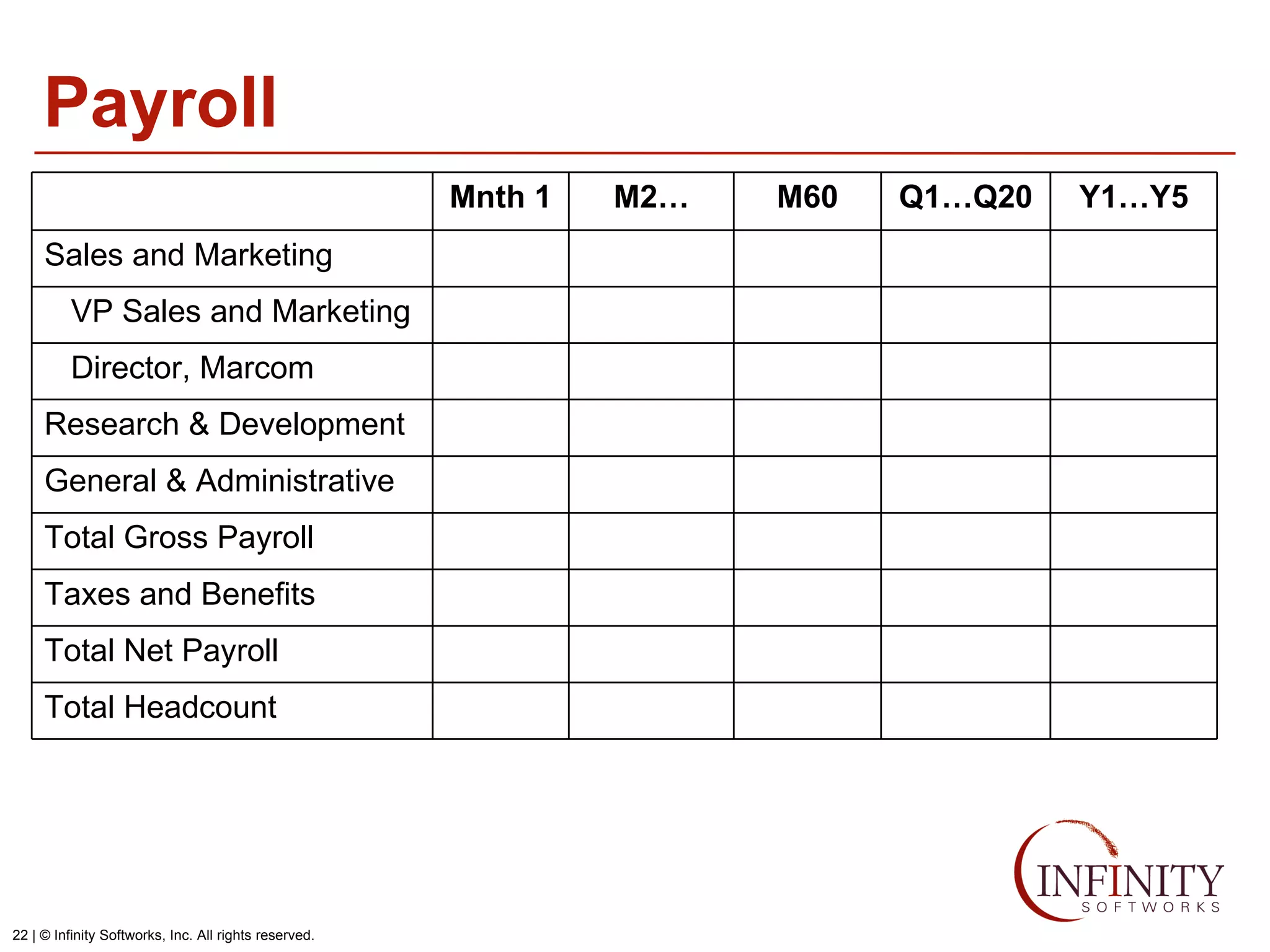
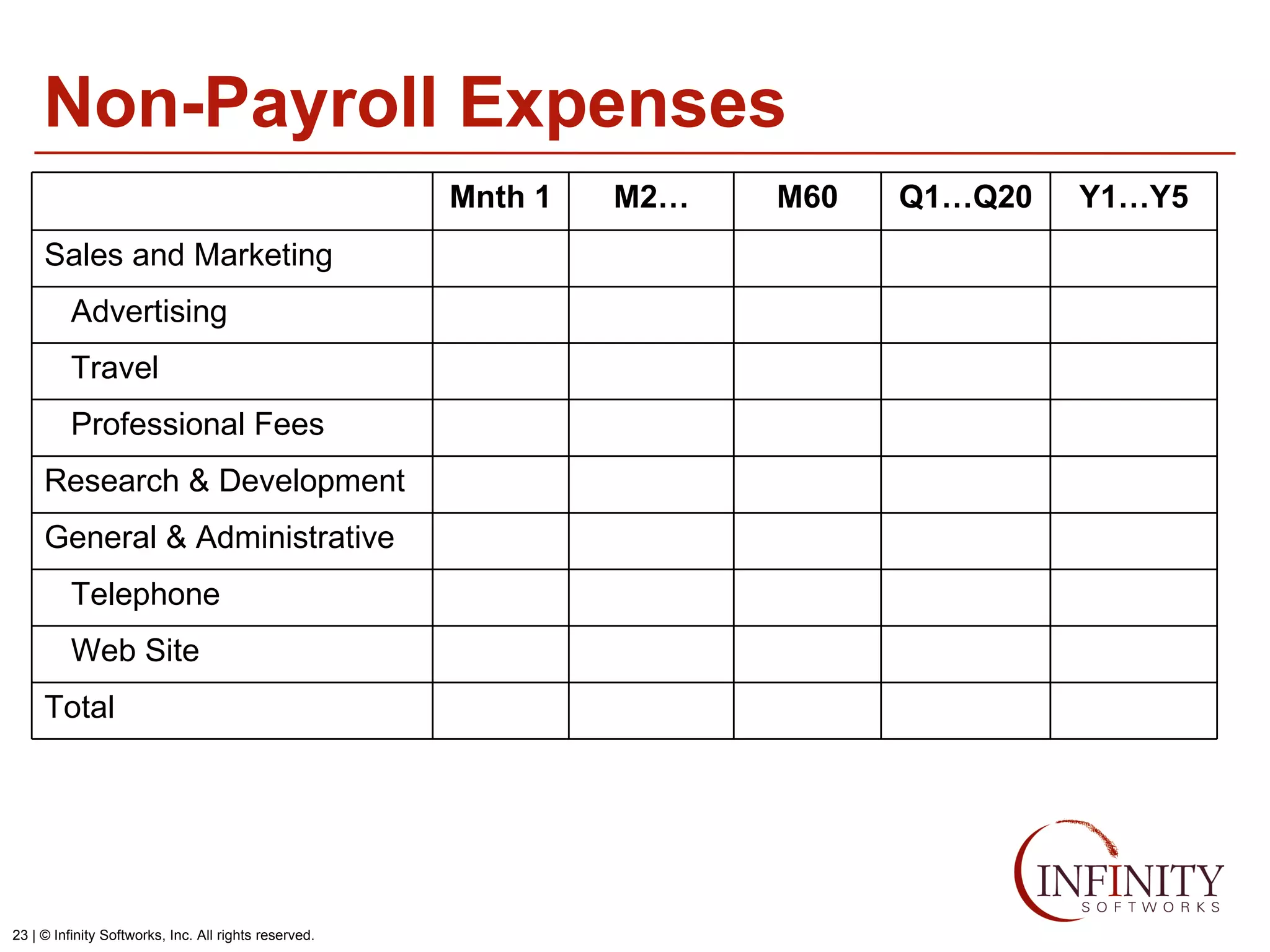
The document discusses the three core financial statements used to understand a company's financial performance and position. The income statement measures profits and losses over a period of time. The balance sheet provides a snapshot of assets, liabilities, and owner's equity at a point in time. The cash flow statement tracks cash changes from one period to the next. Key components of each statement are outlined, including revenue, expenses, assets, liabilities, and cash flows from operations, investing, and financing activities. Building financial projections involves making assumptions for items like headcount, expenses, revenue, and presenting the projections across time periods in an organized format similar to the core financial statements.