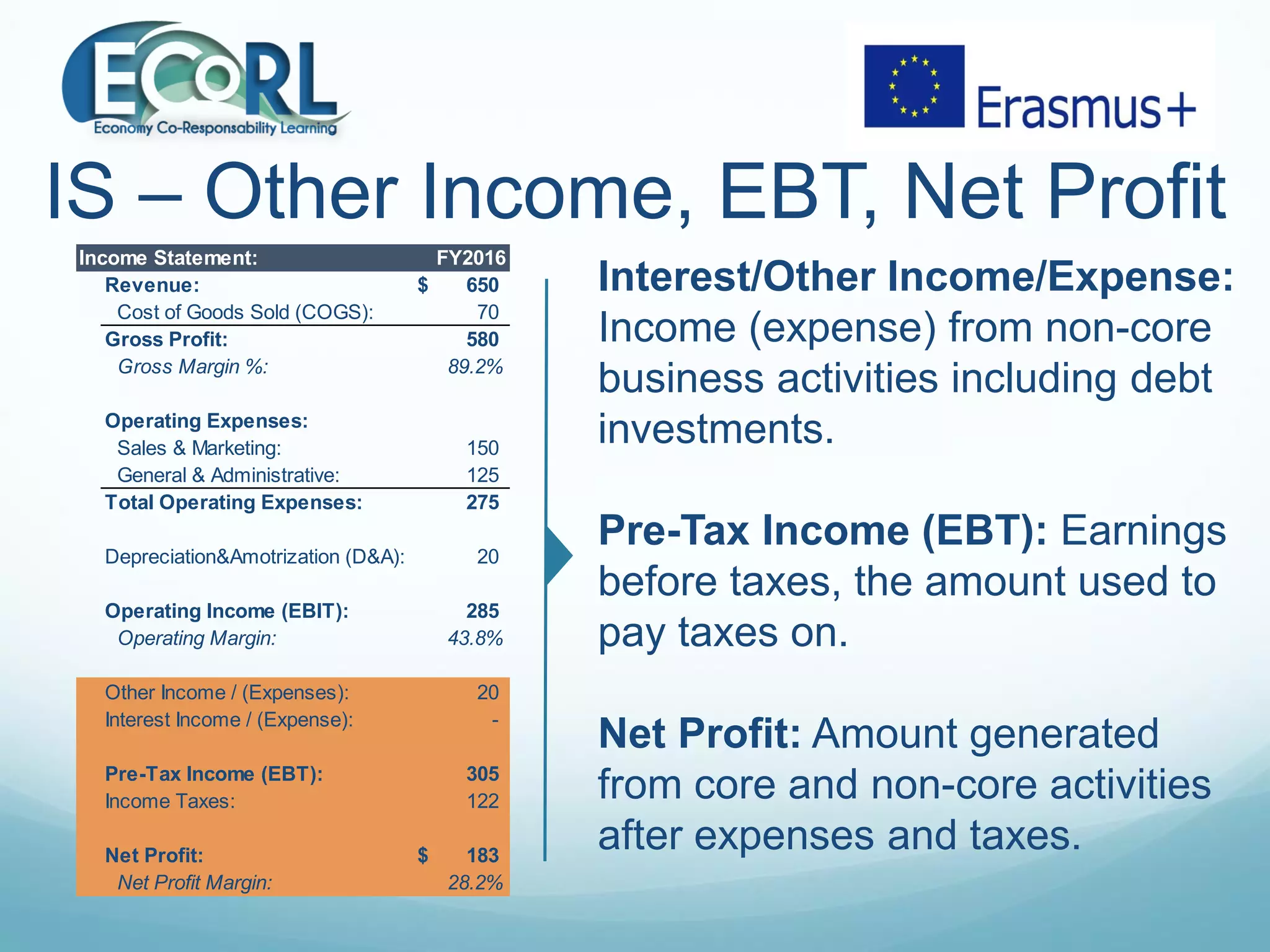
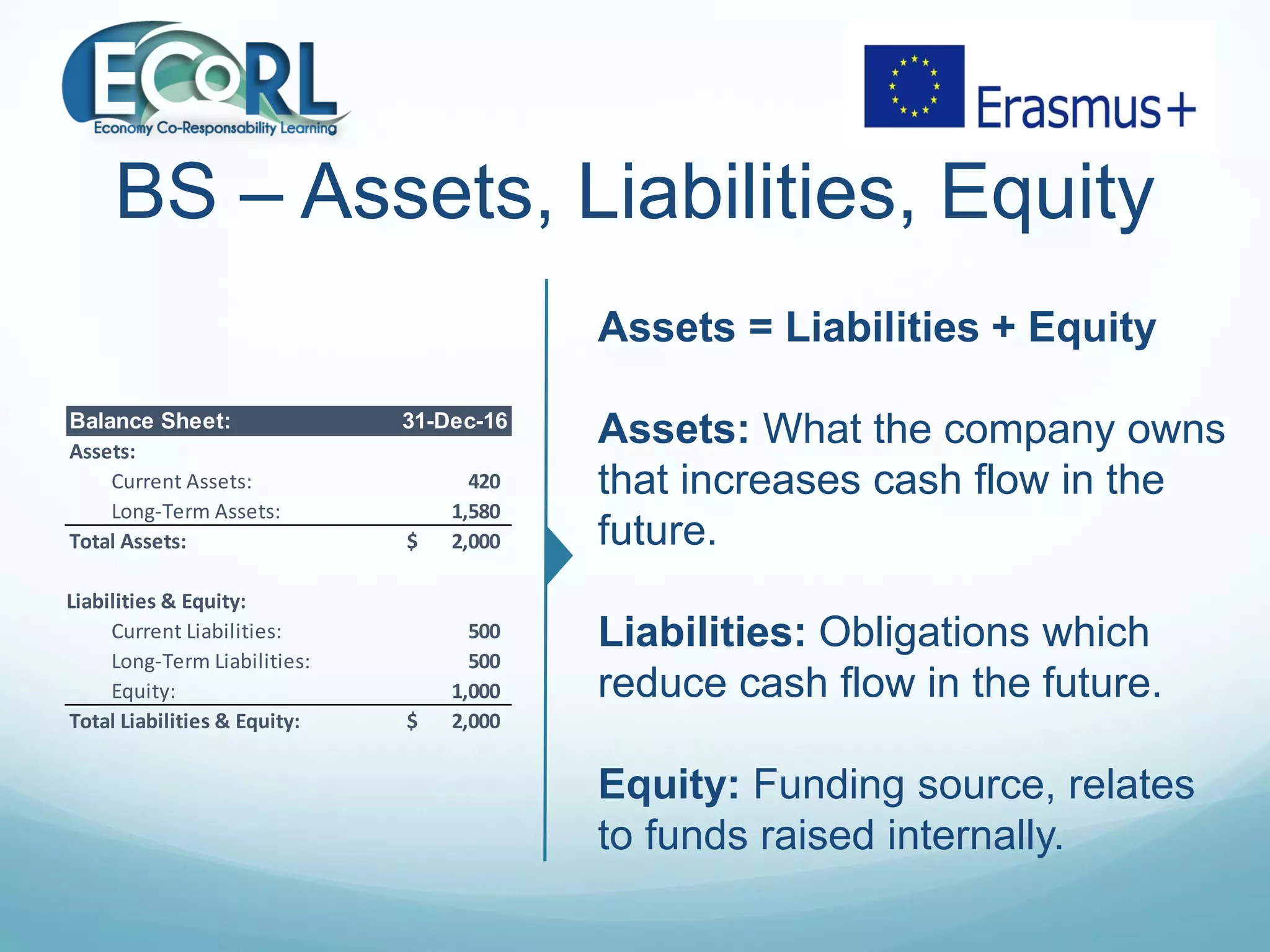
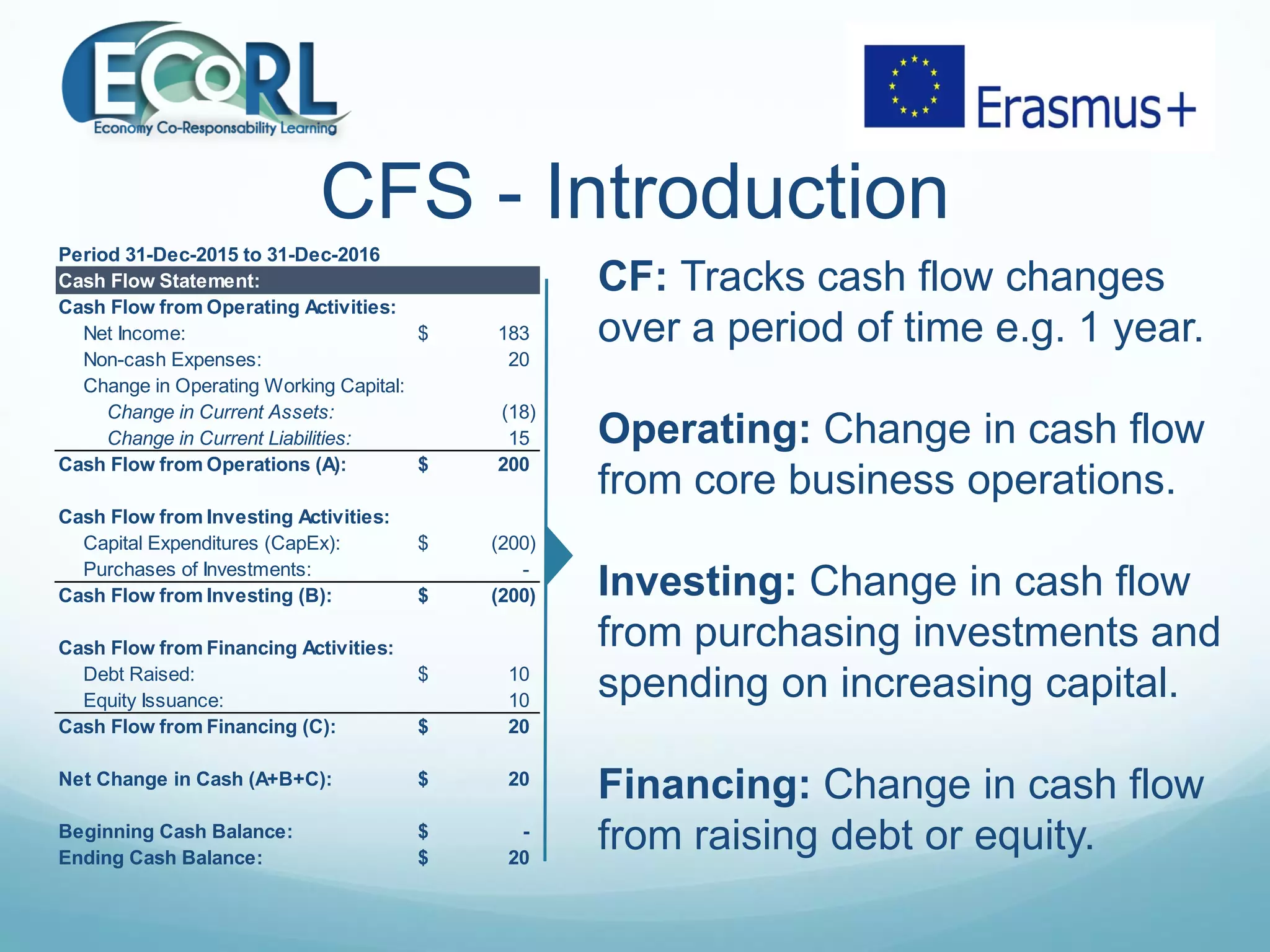
The document provides information on three key financial statements: the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. The income statement shows revenue, expenses, and profits over a period of time. The balance sheet outlines a company's assets, liabilities, and equity at a point in time. The cash flow statement tracks changes in a company's cash balance over a period from operating, investing, and financing activities.