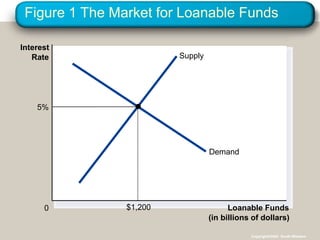
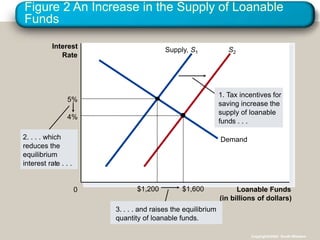
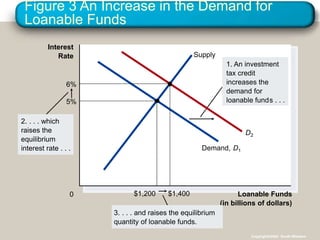
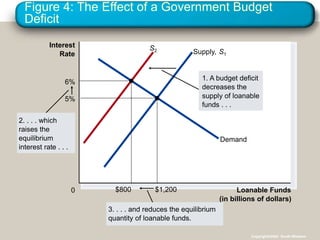
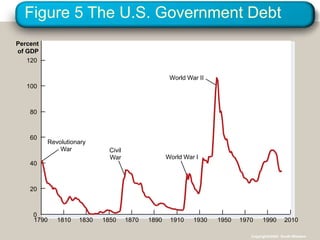
This document discusses financial institutions and markets that coordinate saving and investment. It describes how savers provide funds to borrowers through both direct financial markets like the stock and bond markets, as well as indirect financial intermediaries like banks and mutual funds. The financial system matches savings with investments and determines interest rates through the market for loanable funds, where the supply of saved funds meets demand from borrowers. Government policies around taxes, spending, and deficits can impact incentives for saving and investment and shift supply and demand in this market.