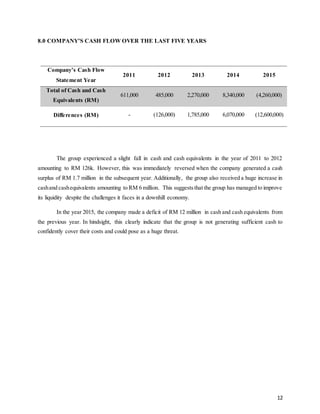
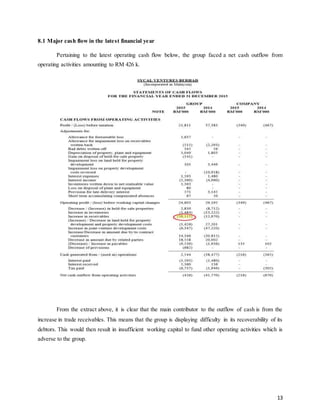
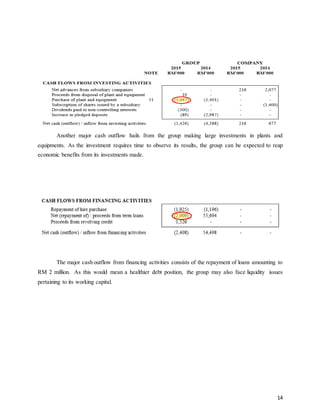
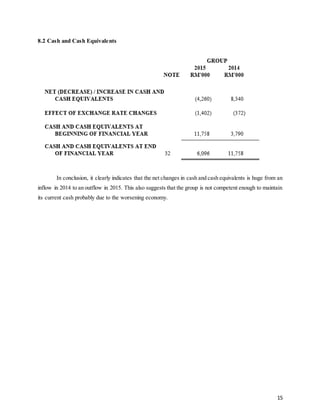
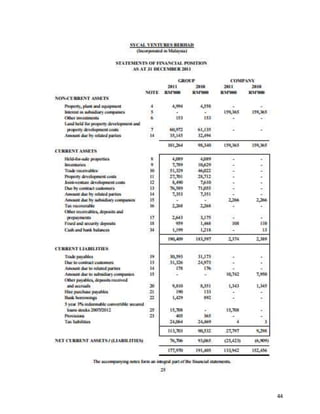
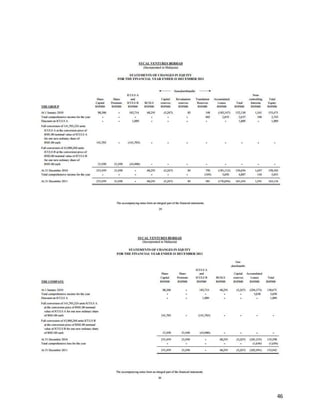
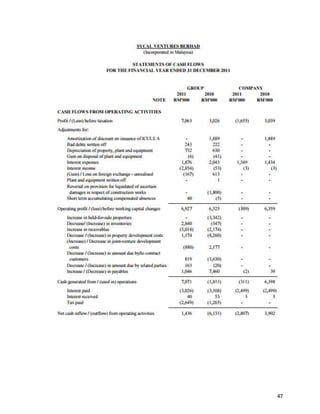
This document provides background information on Sycal Ventures Berhad, a public construction company listed on Bursa Malaysia. It discusses the company's establishment in 1980, core businesses in construction, property development, and hotels/resorts. It also lists the company's major shareholders and key management personnel.




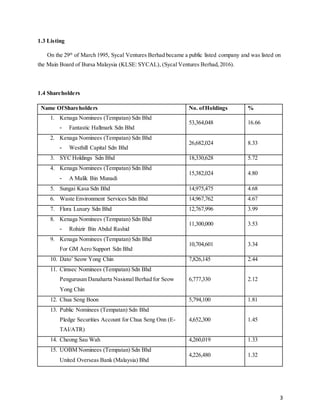
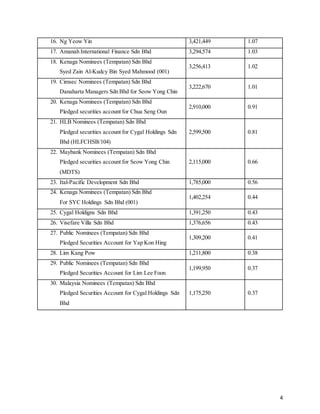

![7
[Grab your
reader’s
attention
witha great
quote from
the
documentor
use this
space to
emphasize a
keypoint.To
place this
textbox
anywhere on
the page,
justdrag it.]
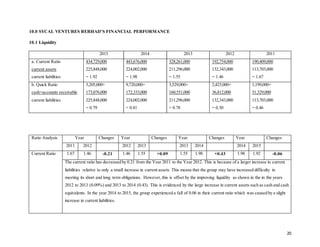
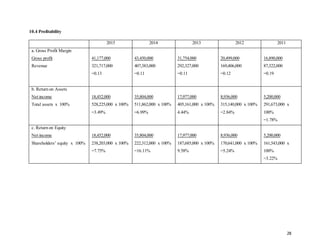
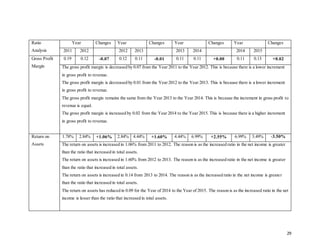
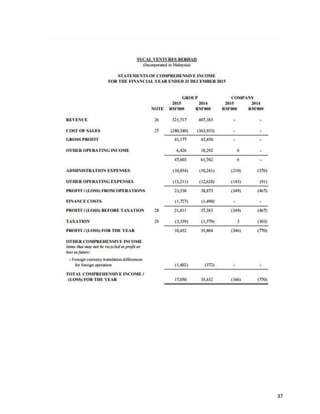
3.0 ANALYSIS OF THE REVENUE CONTRIBUTIONS OF DIFFERENT SEGMENTS
Figure 1.1 showing each segments of revenue of the company in 2014 and 2015.
Table 1.1: Revenue contribution of different segments in 2014 & 2015.
*(Retrieved from Annual Report 2015)
REVENUE
GROUP VARIANCE
2015 2014
RM'000 RM'000 RM'000 %
Revenue comprises:
Contract revenue 248,351 291,859 (43,508) (15%)
Consultation and project management
fee 7,311 1,200 6,111 509%
Property development revenue 1,458 51,715 (50,257) (97%)
Joint venture development revenue 3,182 - 3,182 100%
Sales of goods and services 61,415 62,609 (1,194) (2%)
TOTAL 321,717 407,383 -85,666 (21%)
RM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fm-final-assignment-completed-161205140451/85/Financial-Analysis-Report-for-Sycal-Ventures-Berhad-11-320.jpg)