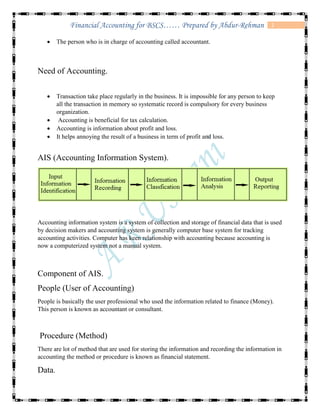
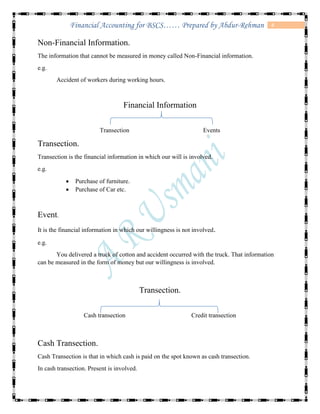
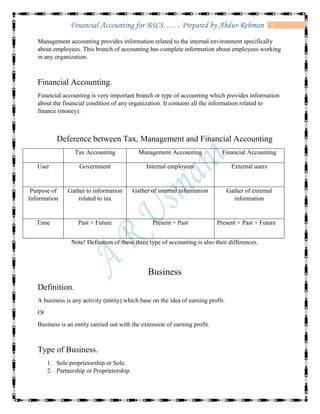
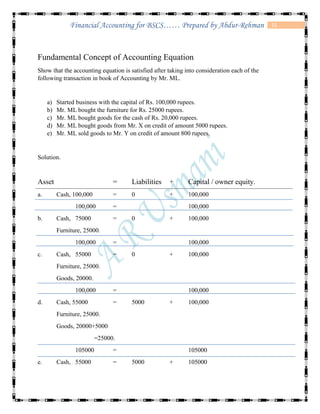
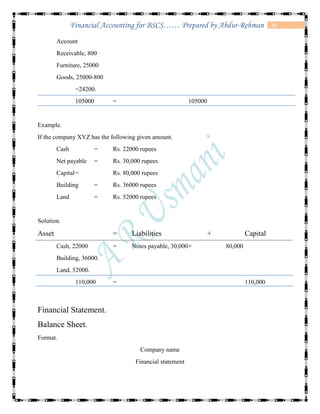
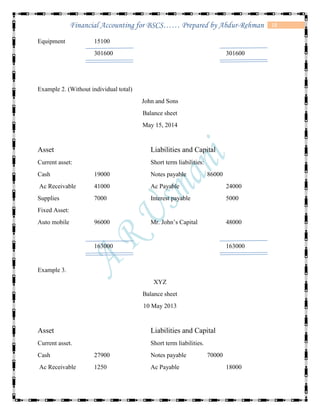
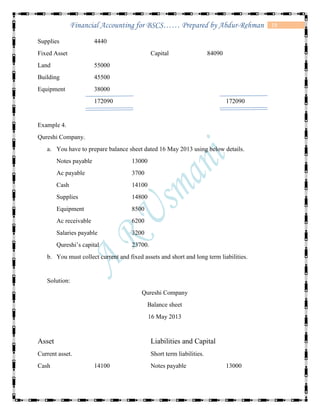
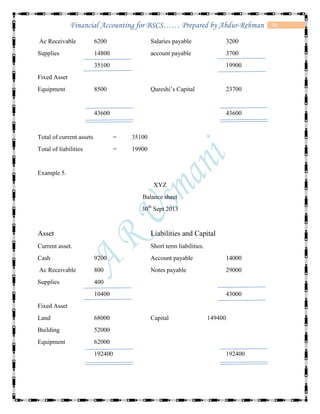
The document defines accounting and discusses its key concepts and principles. It then discusses the components and types of accounting information systems. Finally, it explains the accounting cycle and key financial statements like the balance sheet through examples. The document provides a comprehensive overview of introductory financial accounting concepts.