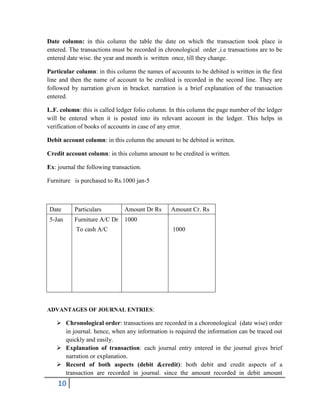
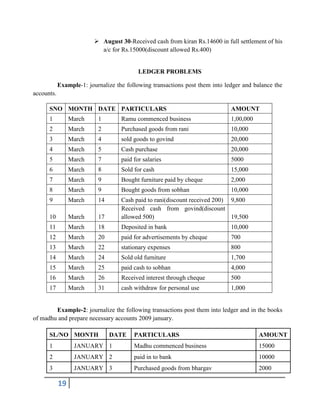
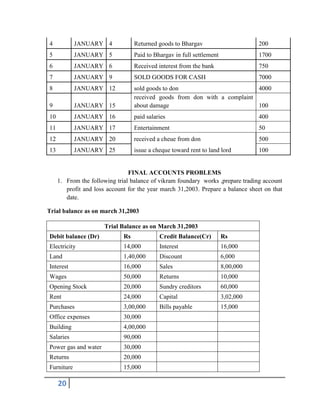
The document provides an overview of financial accounting, emphasizing the importance of maintaining accurate records to determine profits, monitor business activities, and fulfill legal obligations. It covers various accounting concepts, principles, and the functions of accounting, as well as the significance of financial statements for different stakeholders like owners, creditors, and employees. Additionally, it distinguishes between single and double entry bookkeeping systems, detailing their advantages and the process of preparing financial statements such as the trial balance and final accounts.