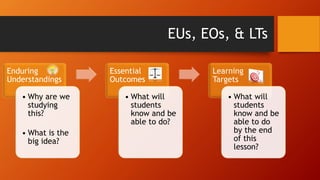
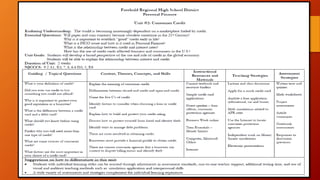
This document discusses enduring understandings (EUs), essential outcomes (EOs), and learning targets (LTs). It defines each term and provides examples. EUs are full sentence generalizations that capture big ideas. EOs include the building blocks, knowledge, and skills needed to achieve the EU. LTs specify what students will know and be able to do by the end of a lesson. The document provides guidance on creating EUs, EOs, and formatting them in a learning management system. Strong and poor examples of each are presented to illustrate the concepts.