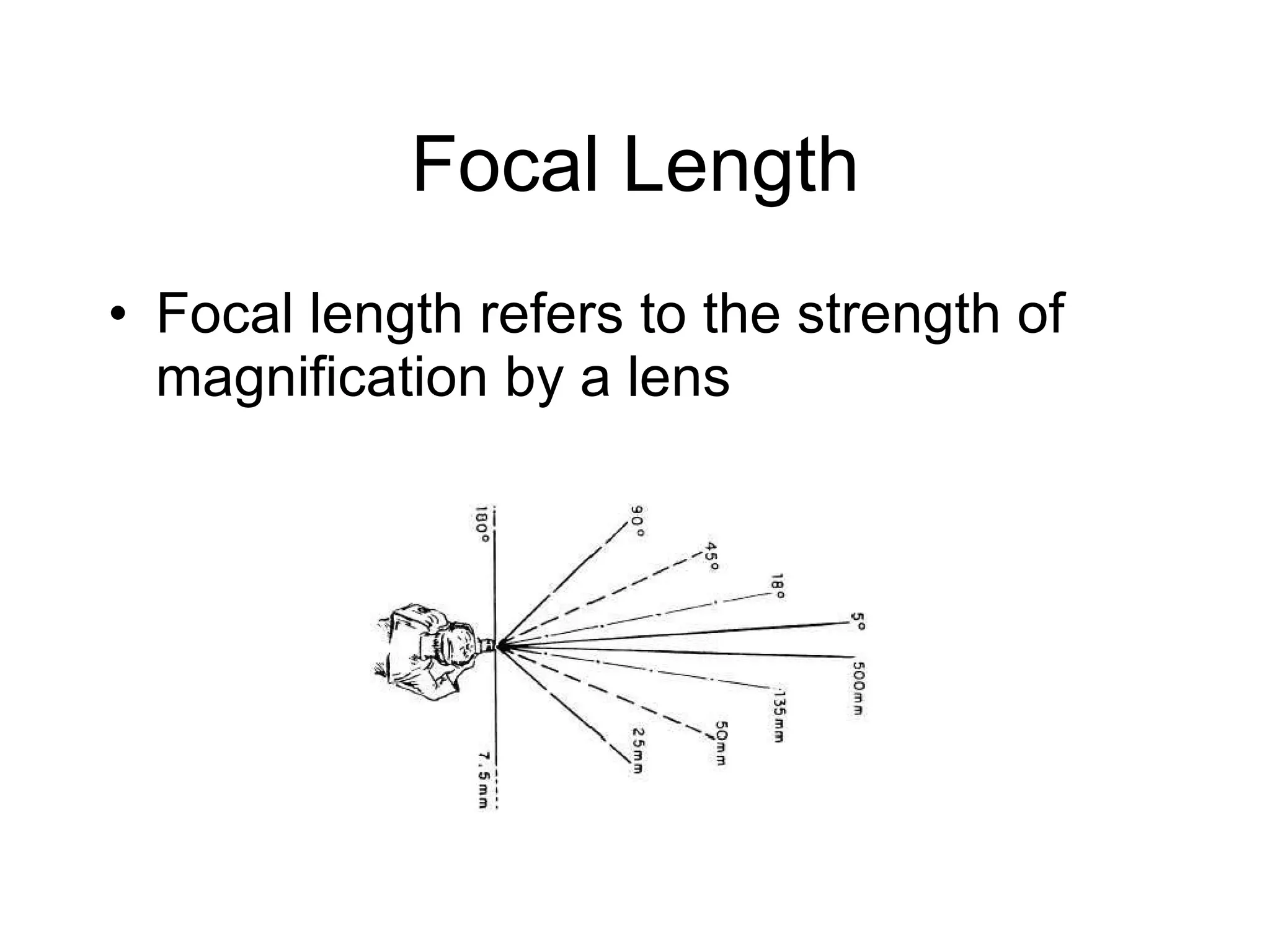
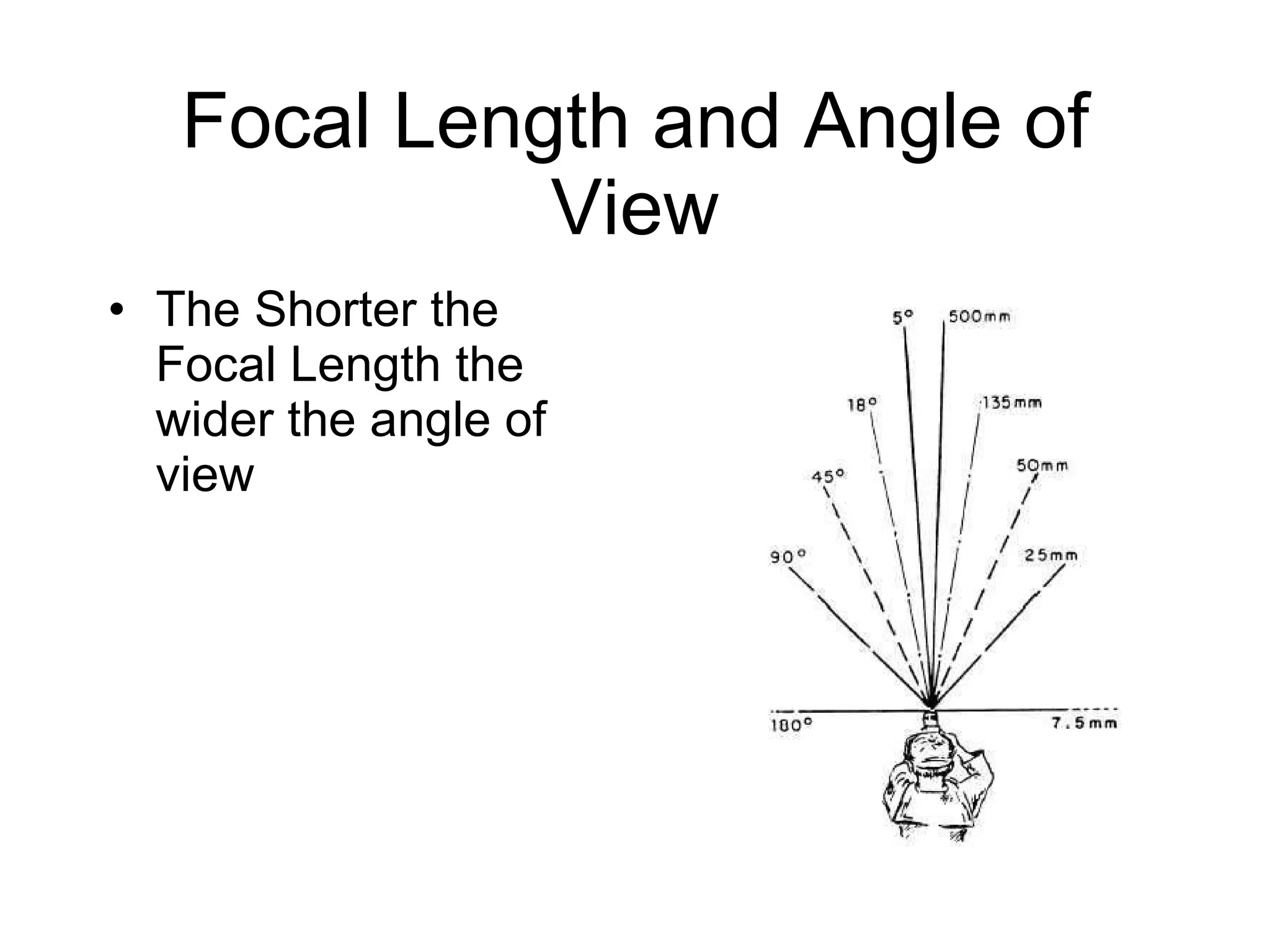
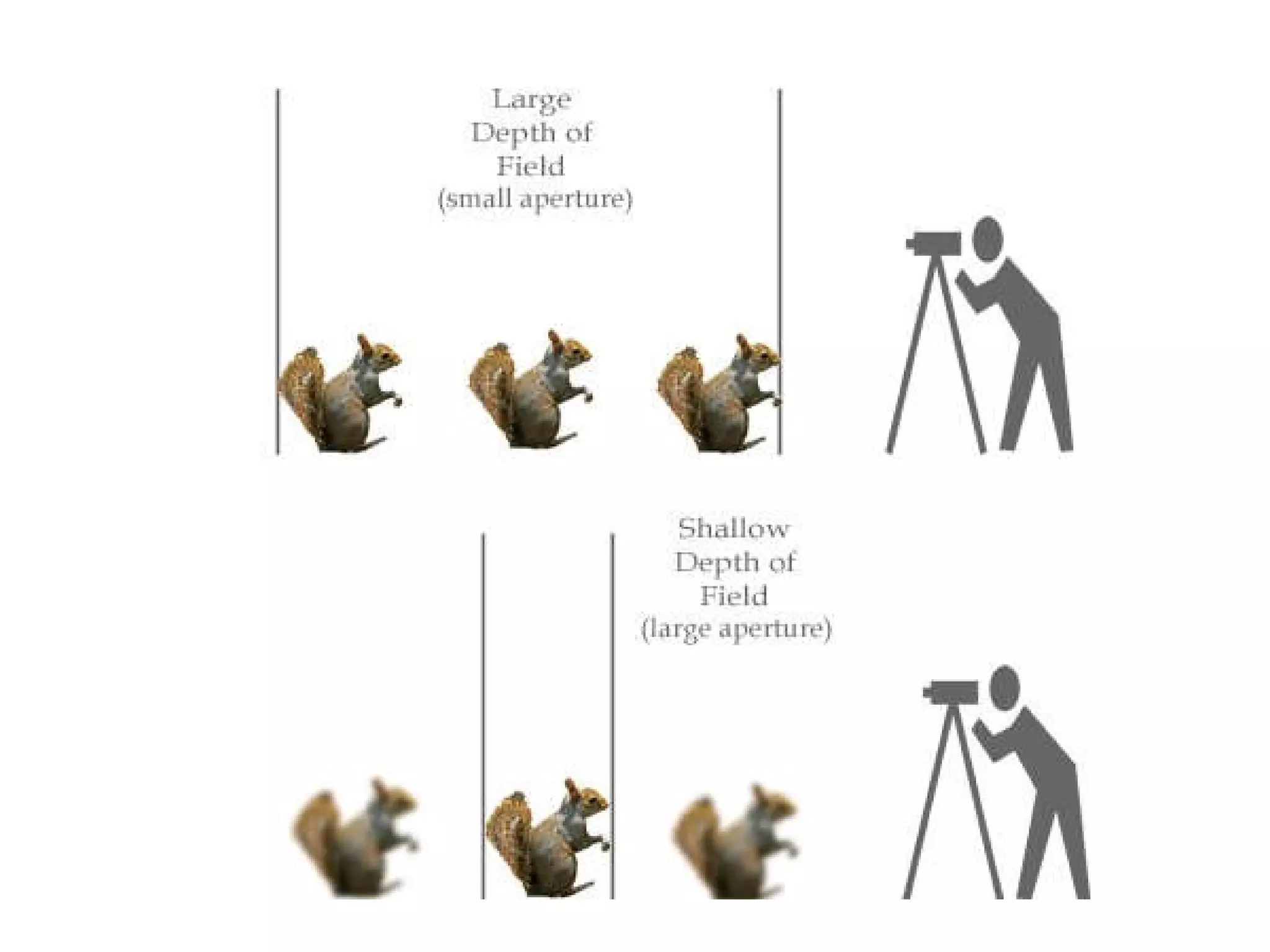
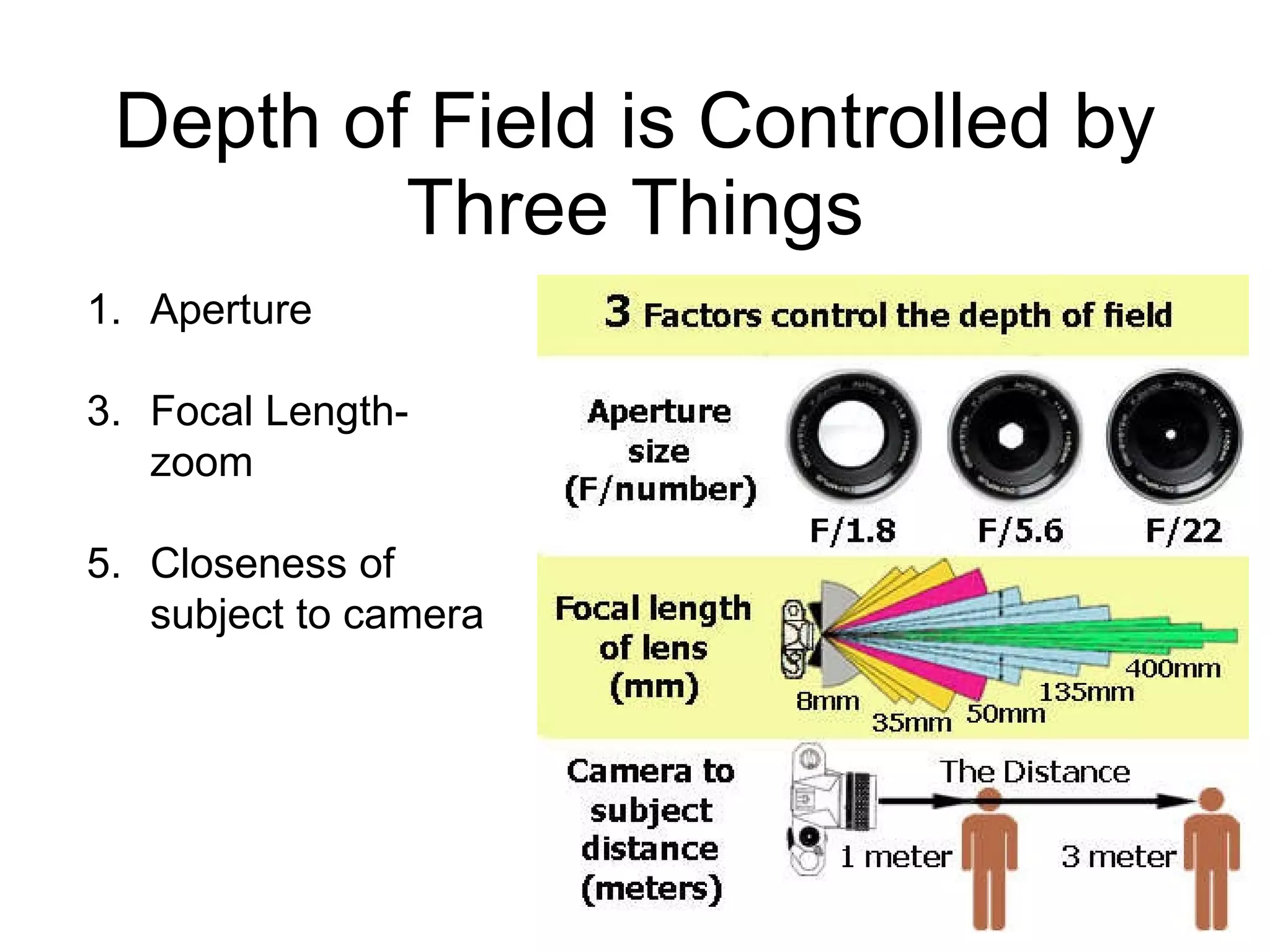
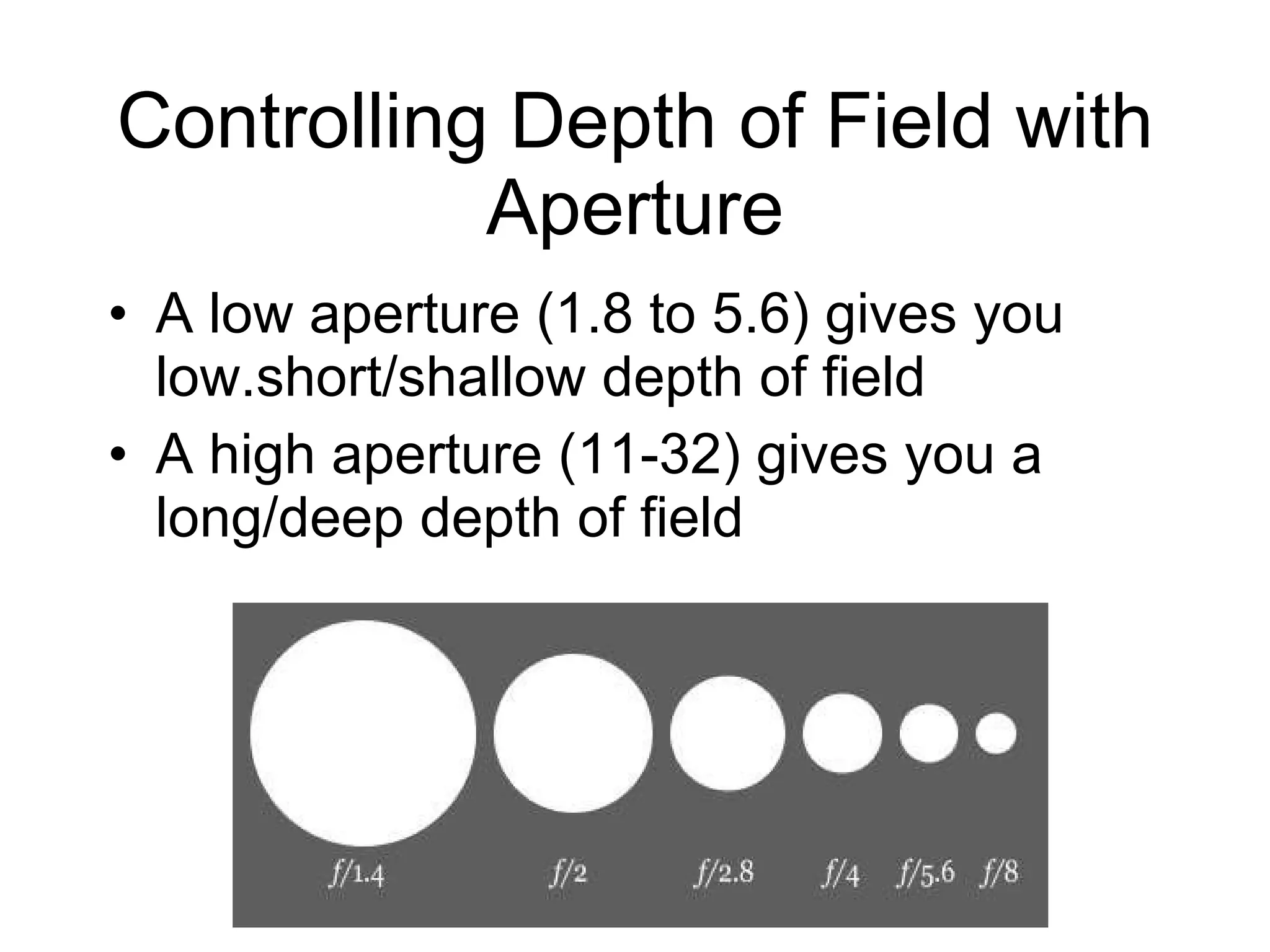
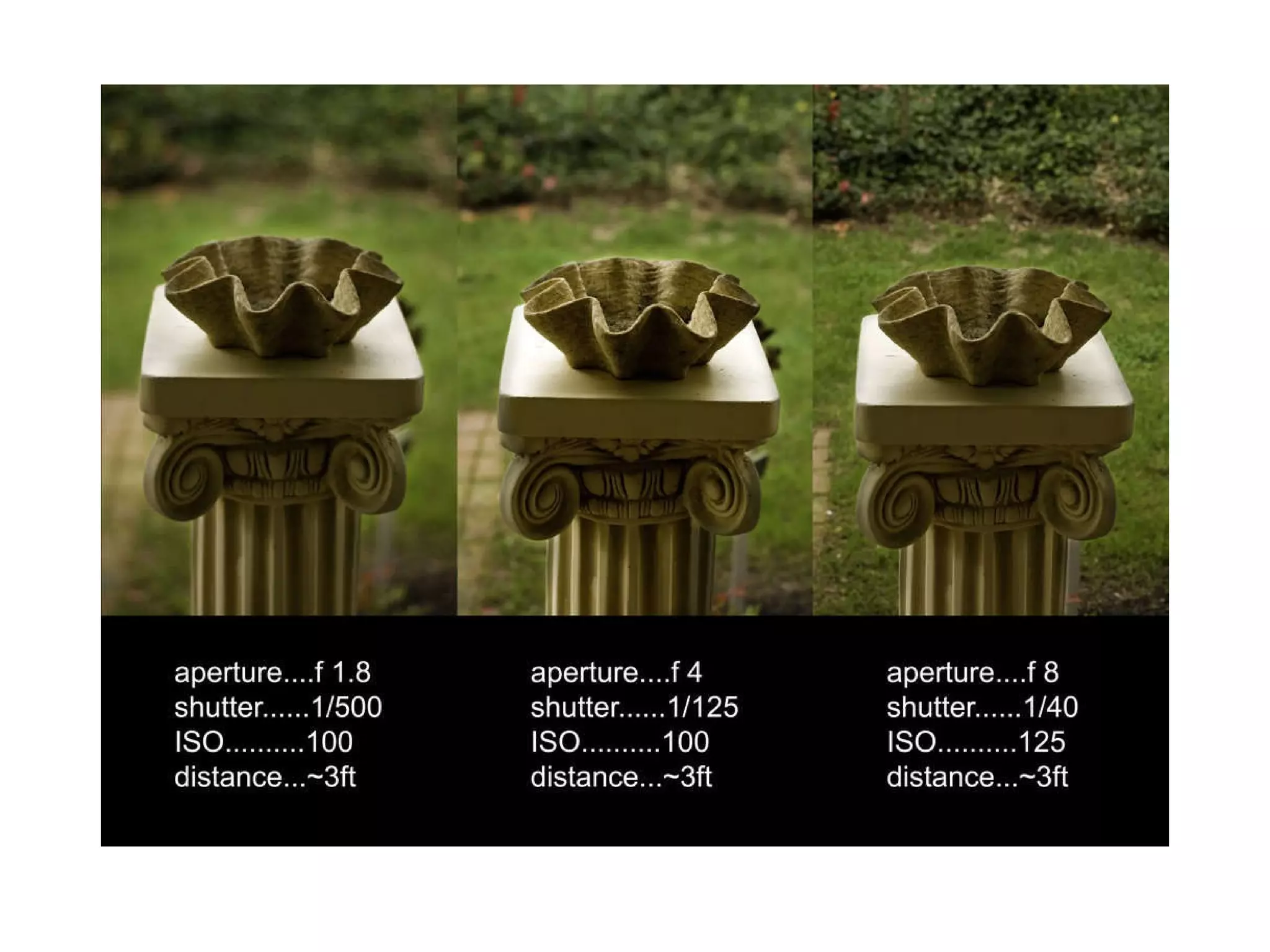
Focal length refers to a lens's magnification strength, with shorter focal lengths providing a wider angle of view. Depth of field is the range of distance in a scene that appears in focus, and it is controlled by aperture size, focal length, and a subject's distance from the camera. A low aperture, long focal length, or closer subject position results in a shallower depth of field and less focus range, while a high aperture, wider lens, or farther subject provides a deeper depth of field and more focus range.