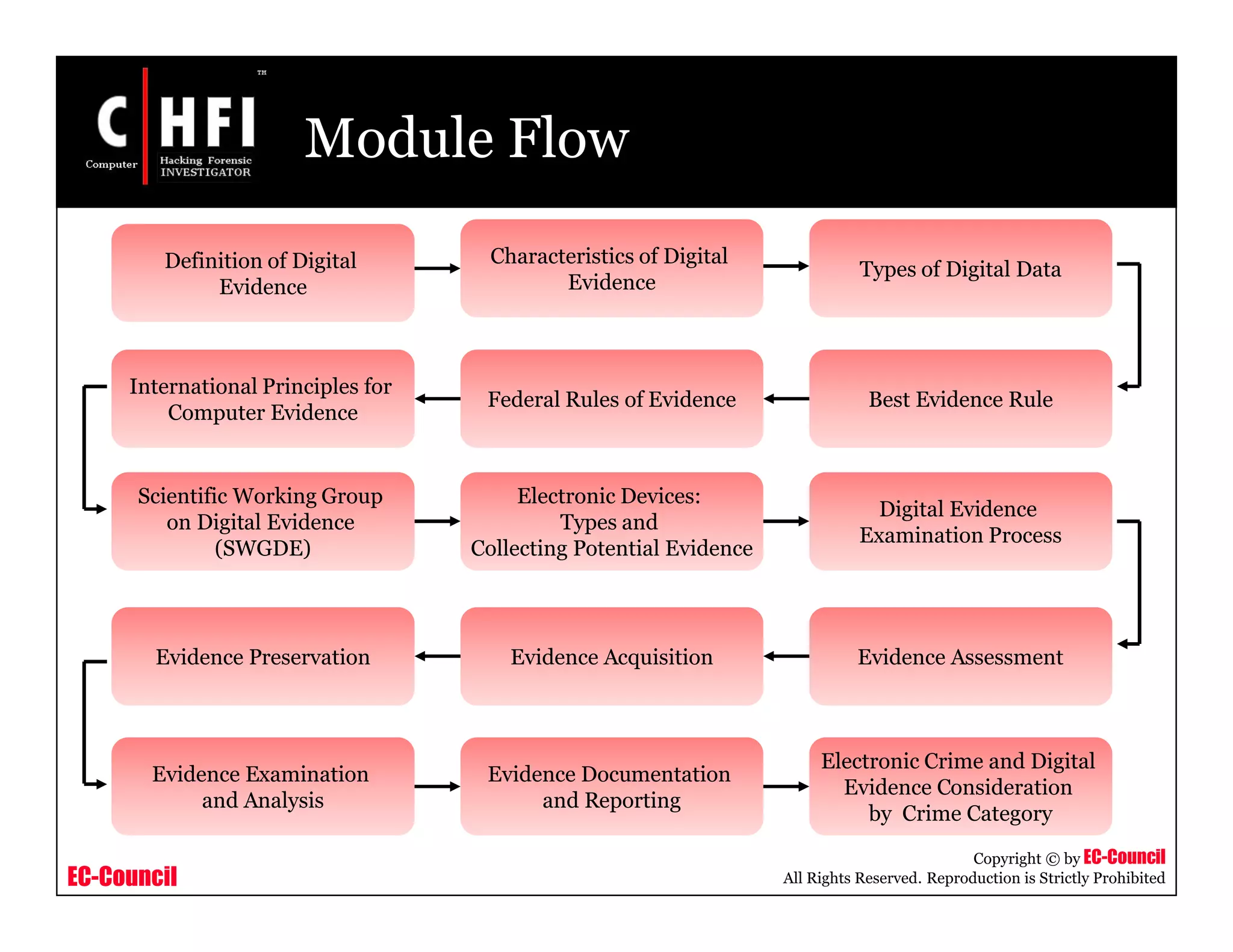
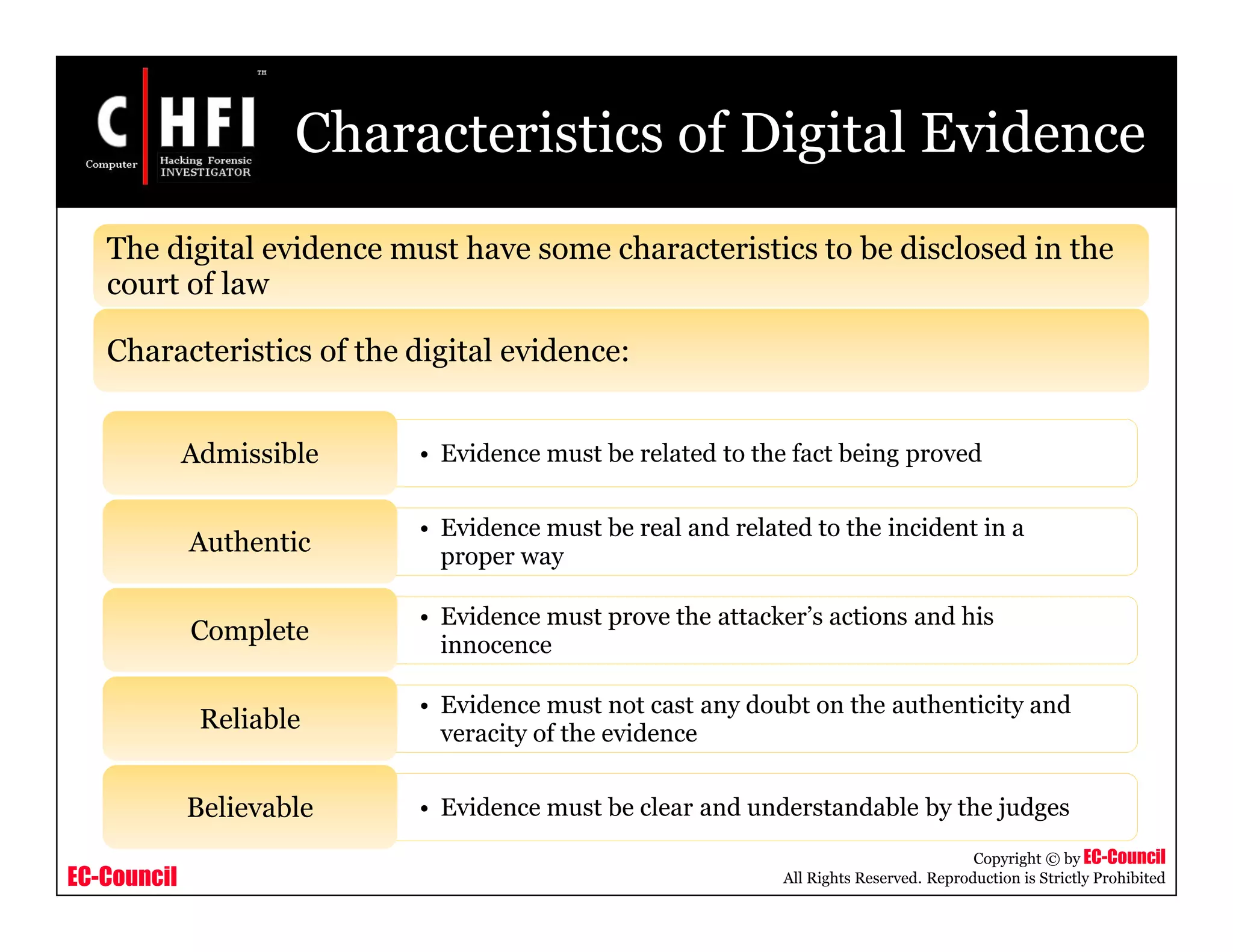
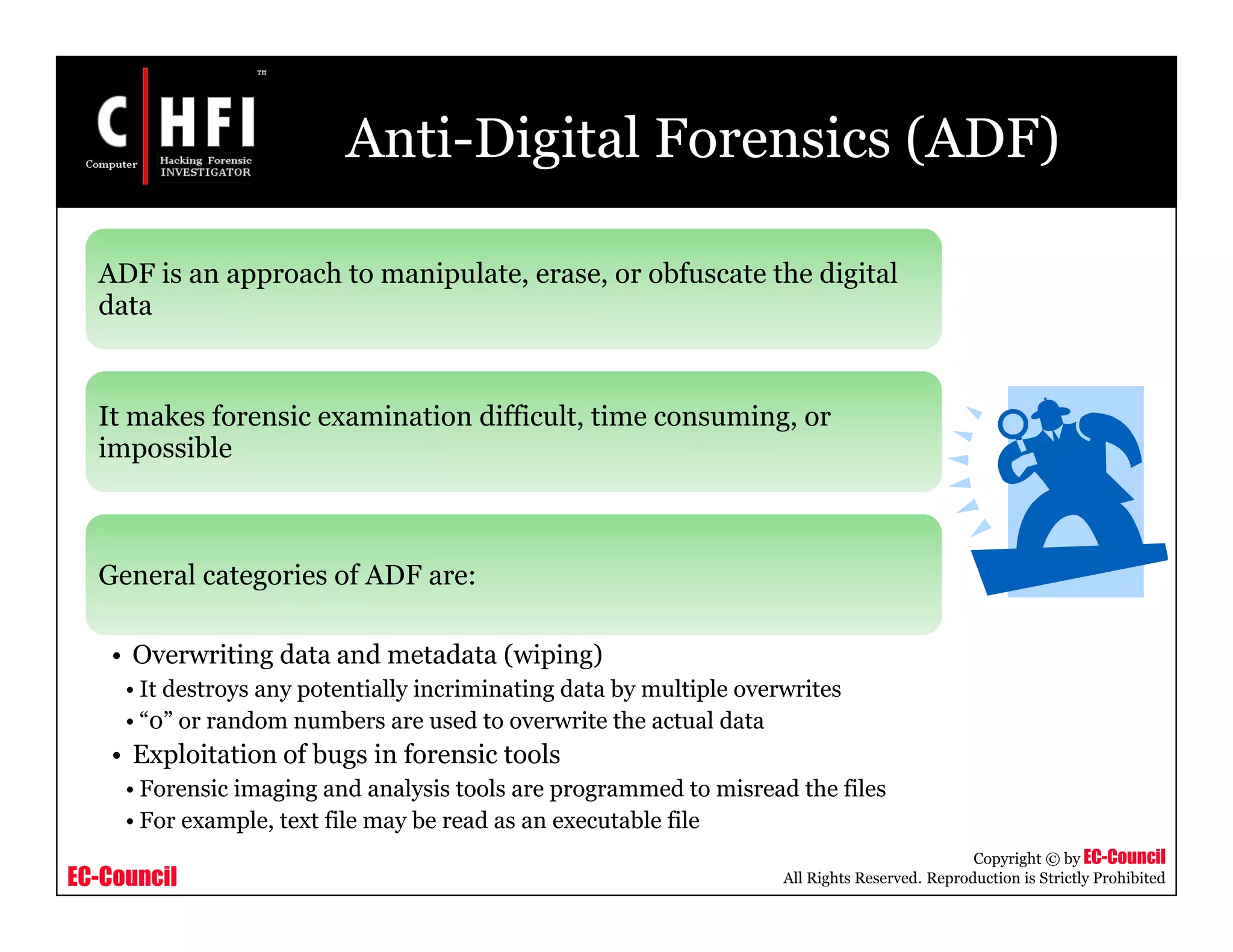
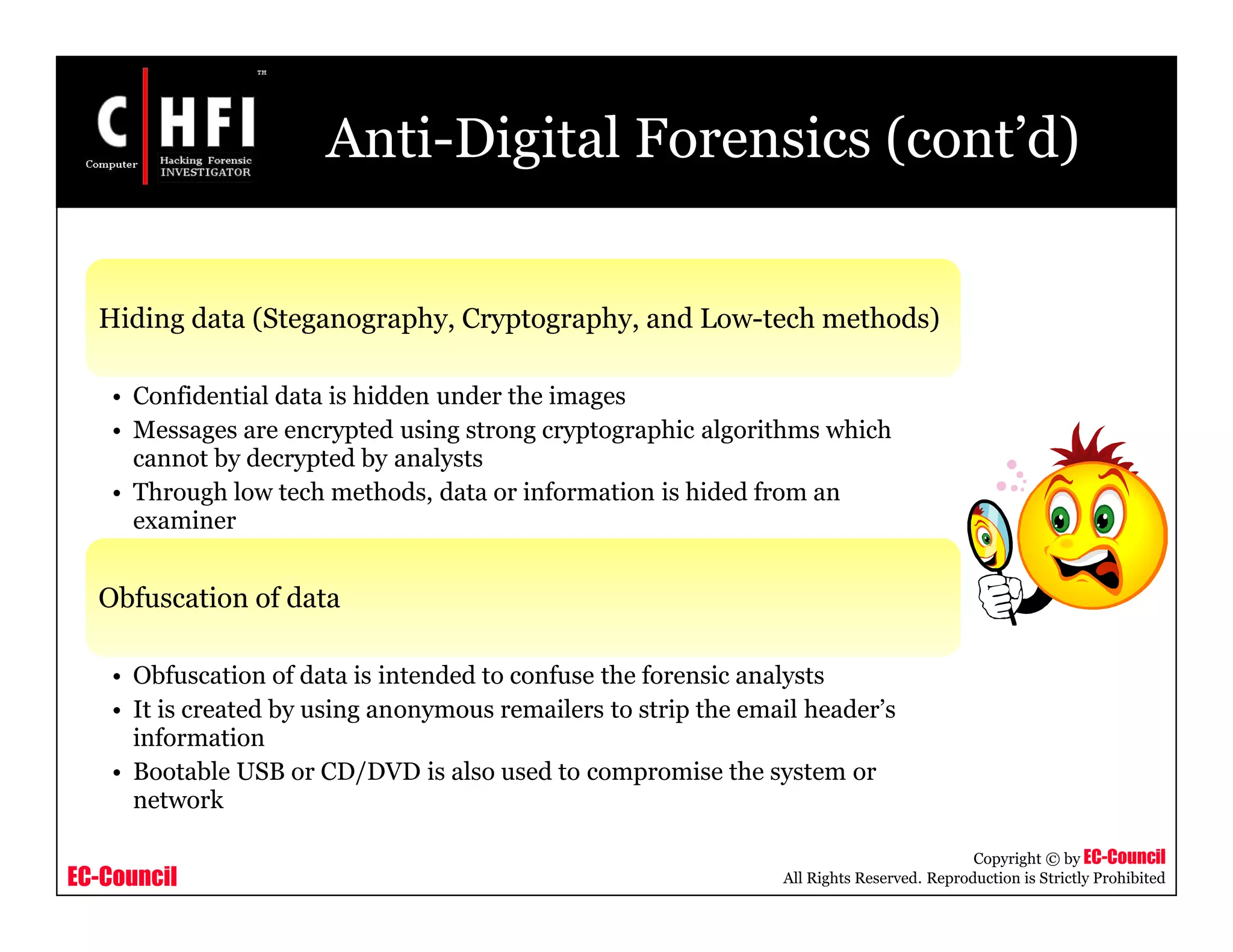
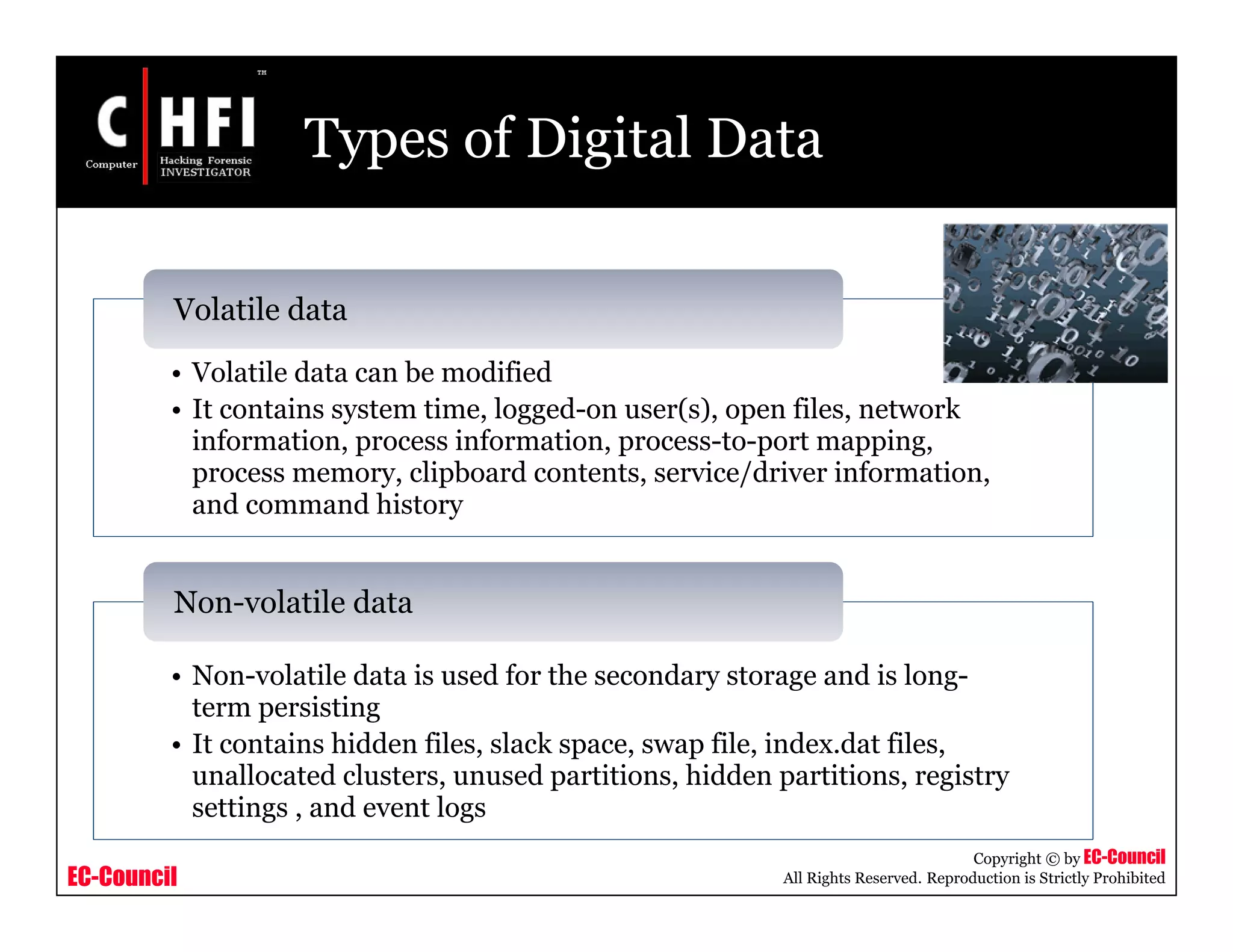
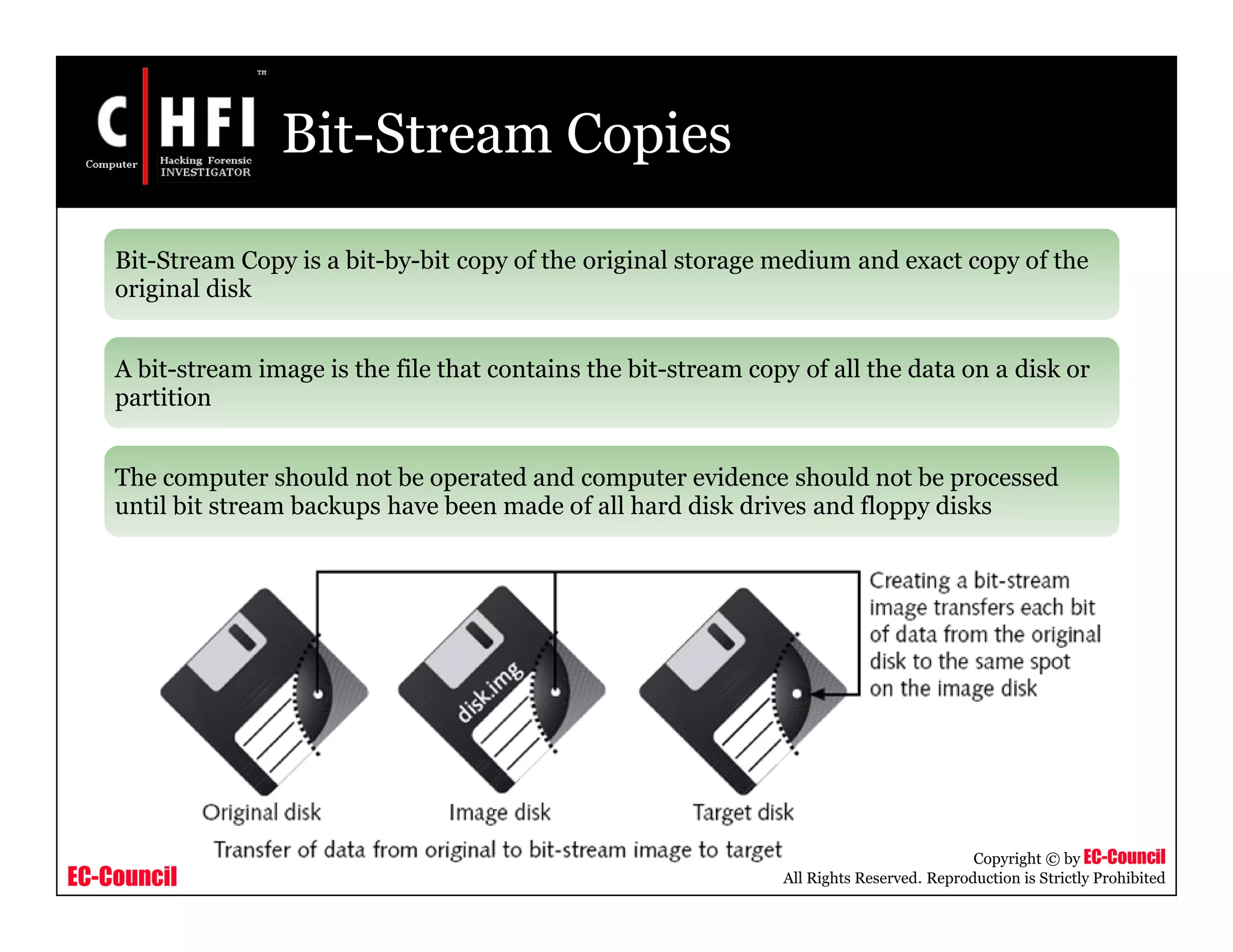
This document provides an overview of Module IV - Digital Evidence from an EC-Council course. It defines digital evidence and discusses the characteristics, types, and fragility of digital evidence. It also covers topics like anti-digital forensics, rules of evidence such as the Best Evidence Rule and Federal Rules of Evidence, and the examination process for digital evidence including acquisition, preservation, analysis, and documentation. The module aims to familiarize students with these important concepts regarding digital evidence.










































































![EC-Council
Copyright © by EC-Council
All Rights Reserved. Reproduction is Strictly Prohibited
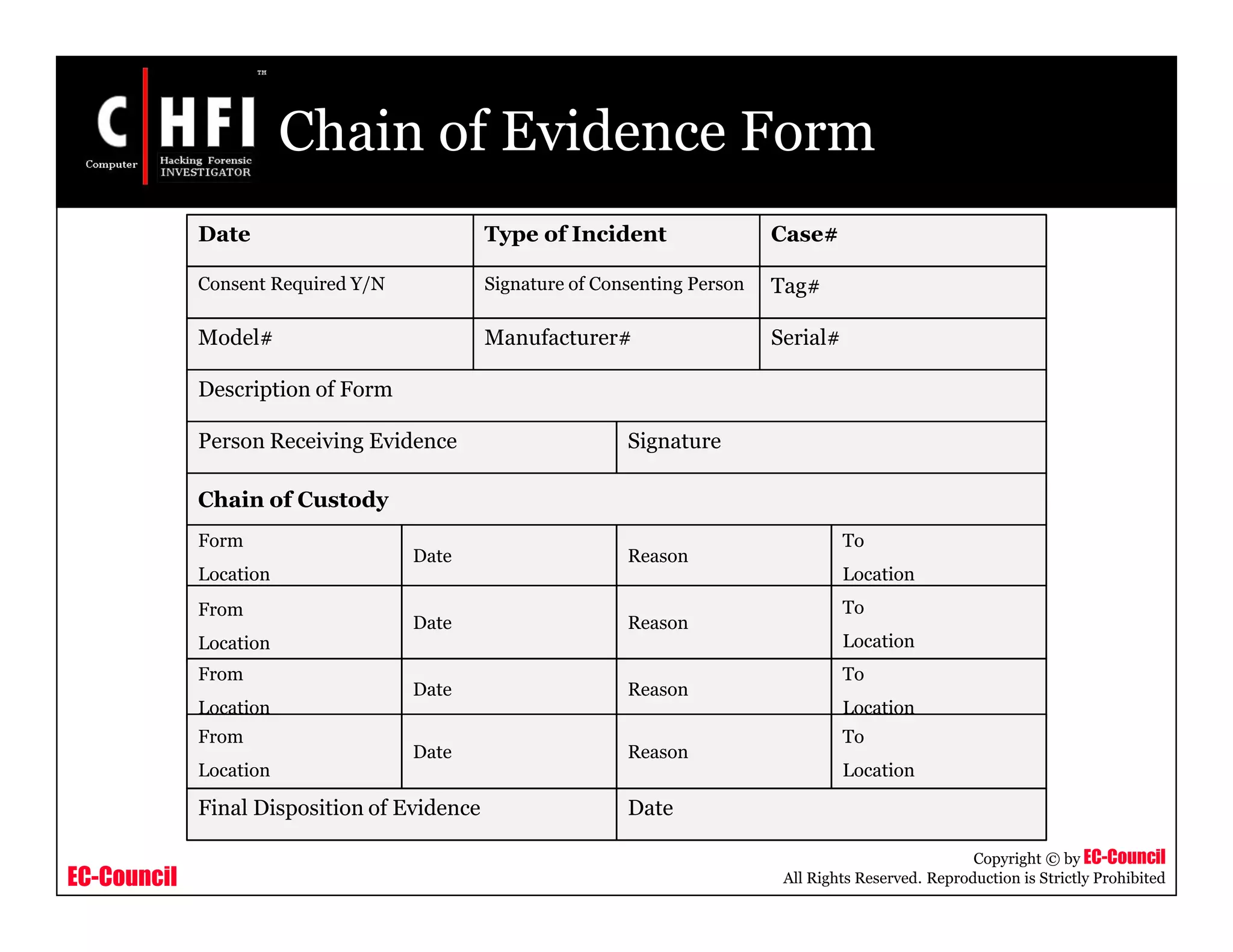
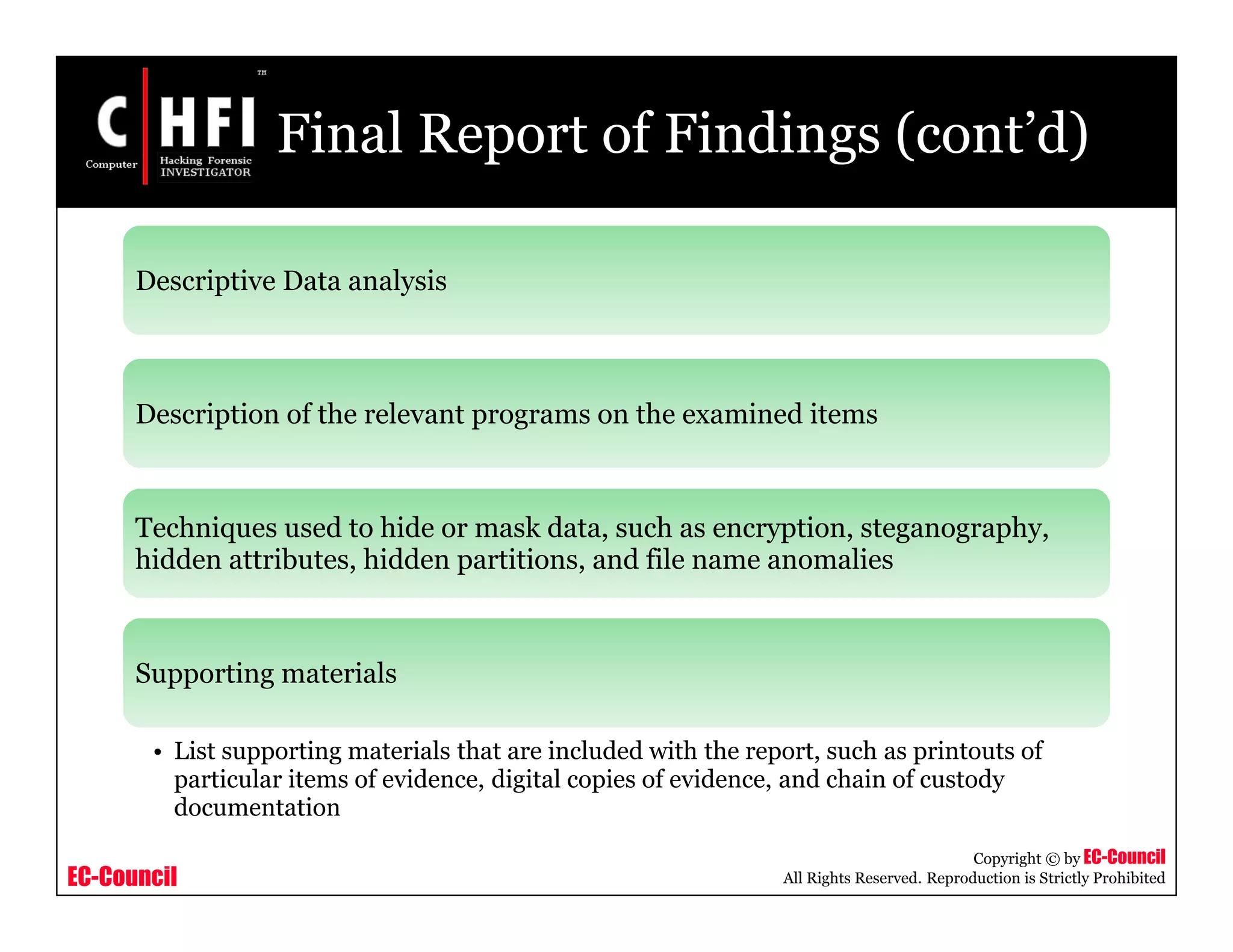
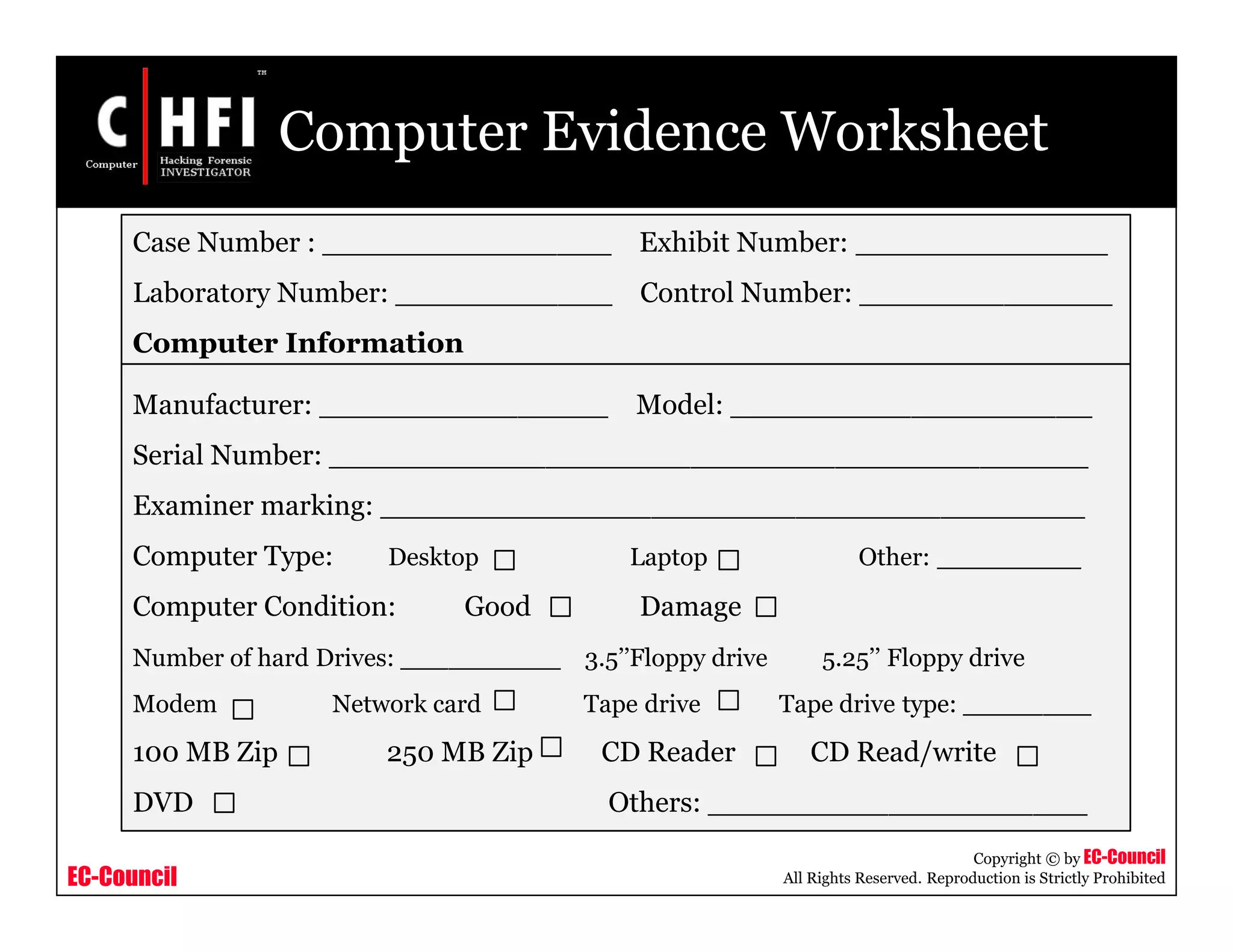
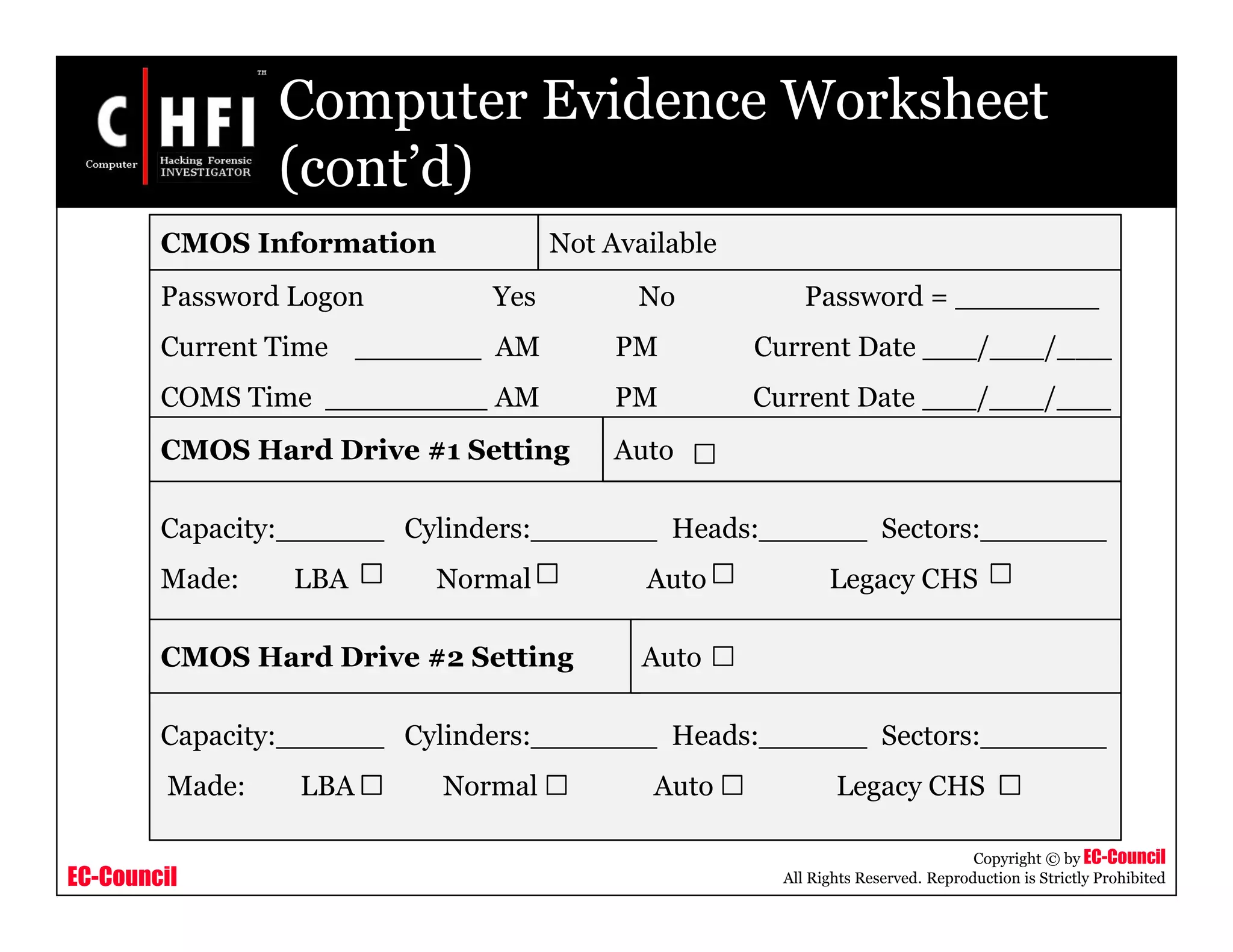
Hard Drive Evidence Worksheet
Case Number : ________________ Exhibit Number: ______________
Laboratory Number: ____________ Control Number: ______________
Hard Drive #1 Label Information [Not Available ] Hard Drive #2 Label Information [Not Available ]
Manufacturer: ________________
Model: _____________________
Serial Number: _______________
Capacity:_______ Cylinders:_________
Heads:_________ Sectors:__________
Controller Rev.____________________
IDE 50 Pin SCSI
68 Pin SCSI 80 Pin SCSI Other
Jumper: Master Slave
Cable Select Undetermined
Manufacturer: ________________
Model: _____________________
Serial Number: _______________
Capacity:_______ Cylinders:_________
Heads:_________ Sectors:__________
Controller Rev.____________________
IDE 50 Pin SCSI
68 Pin SCSI 80 Pin SCSI Other
Jumper: Master Slave
Cable Select Undetermined](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/file000117-140617045153-phpapp02/75/File000117-111-2048.jpg)
![EC-Council
Copyright © by EC-Council
All Rights Reserved. Reproduction is Strictly Prohibited
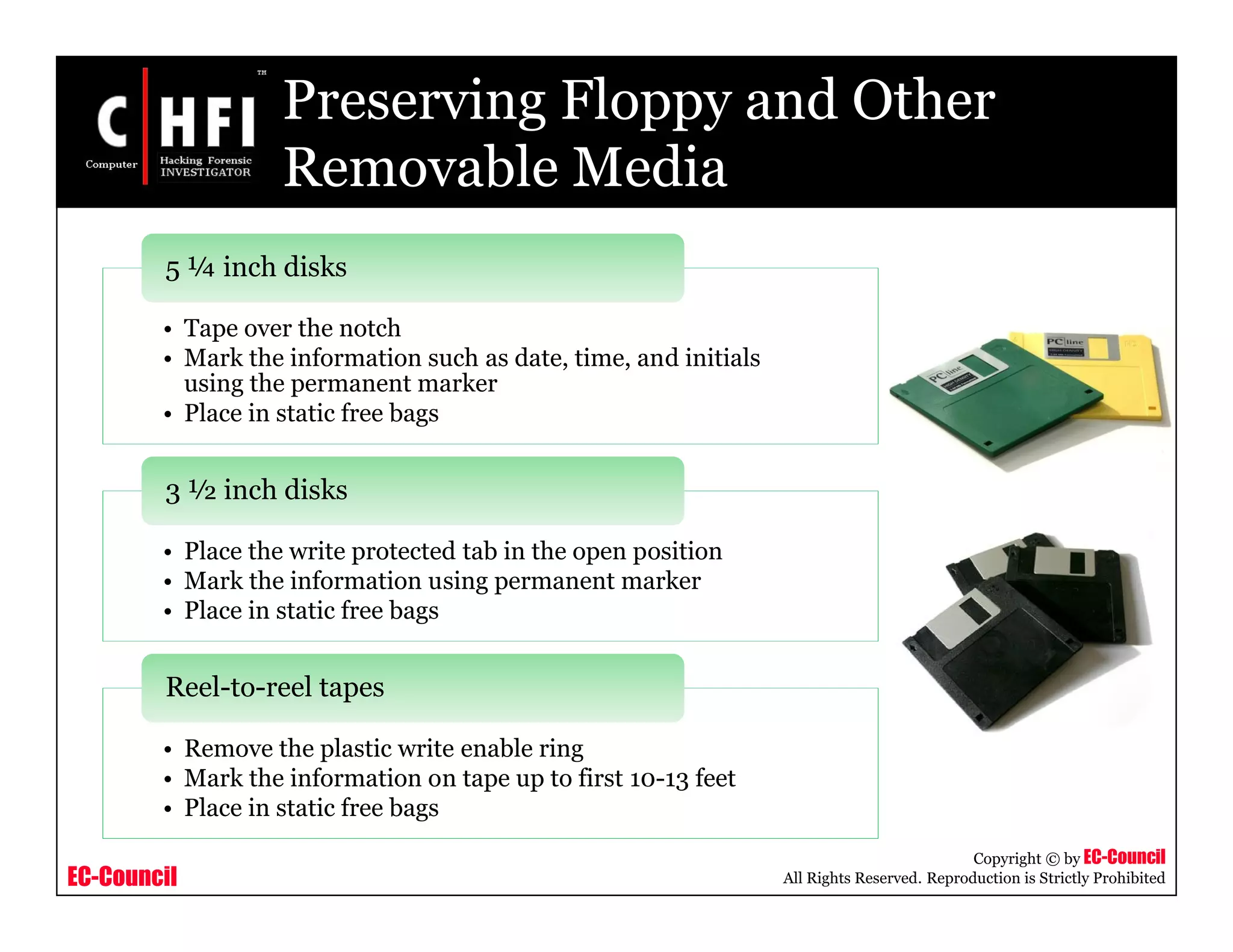
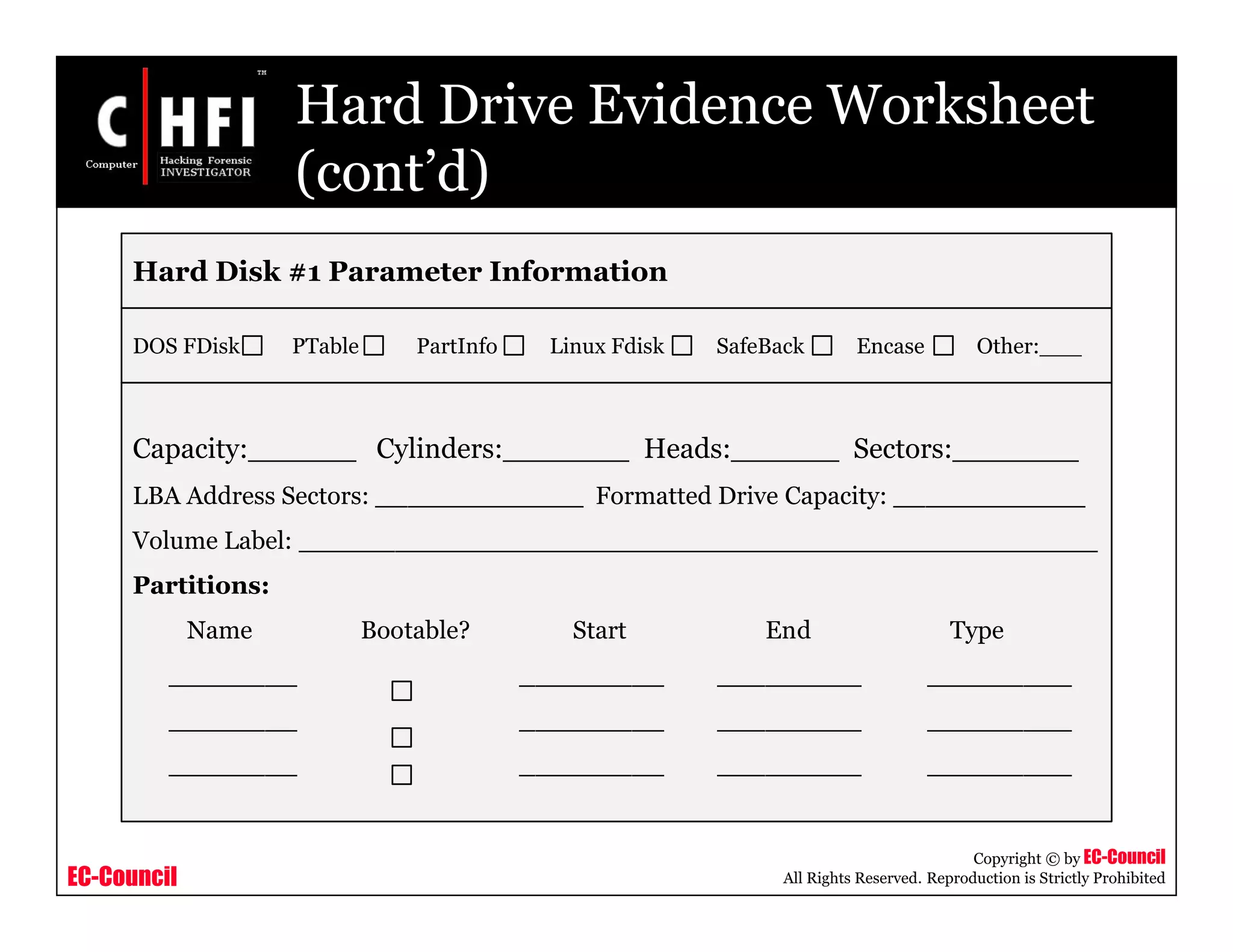
Removable Media Worksheet
Case Number : ________________ Exhibit Number: ___________
Laboratory Number: ____________ Control Number: ___________
Media Type / Quality
Diskette [ ] LS 120 [ ] 100 MB Zip [ ] 250 MB Zip [ ]
1 GB Jaz [ ] 2 GB Jaz [ ] Magneto-optical [ ] Tape [ ]
CD [ ] DVD [ ] Other [ ]
Examination
Exhibit #
Sub-Exhibit #
Triage Duplicated Browse Unerase
Keyword
Search](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/file000117-140617045153-phpapp02/75/File000117-113-2048.jpg)