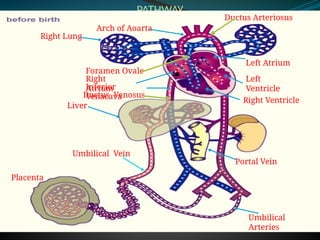
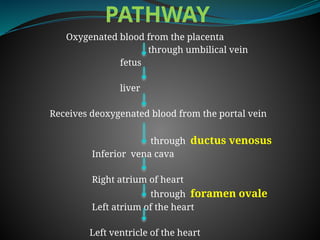
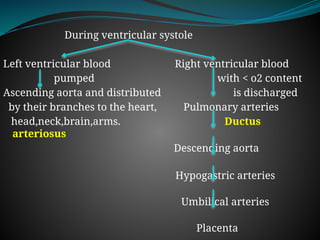
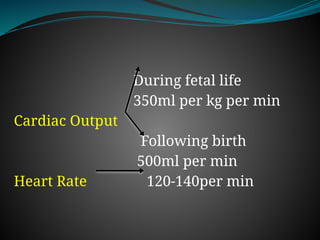
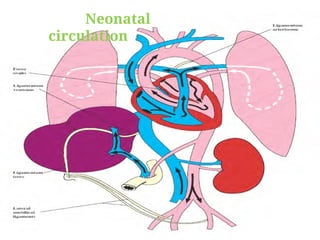
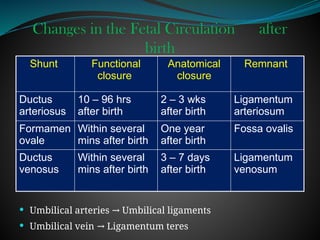
The document discusses fetal circulation, detailing the circulatory system of a human fetus, including the roles of the umbilical cord and placenta. It describes key pathways and structures such as the umbilical veins and arteries, ductus venosus, ductus arteriosus, and foramen ovale, along with the changes that occur in circulation after birth. The transition from a low-pressure to a high-pressure system, as well as the closures of fetal shunts, are also highlighted.