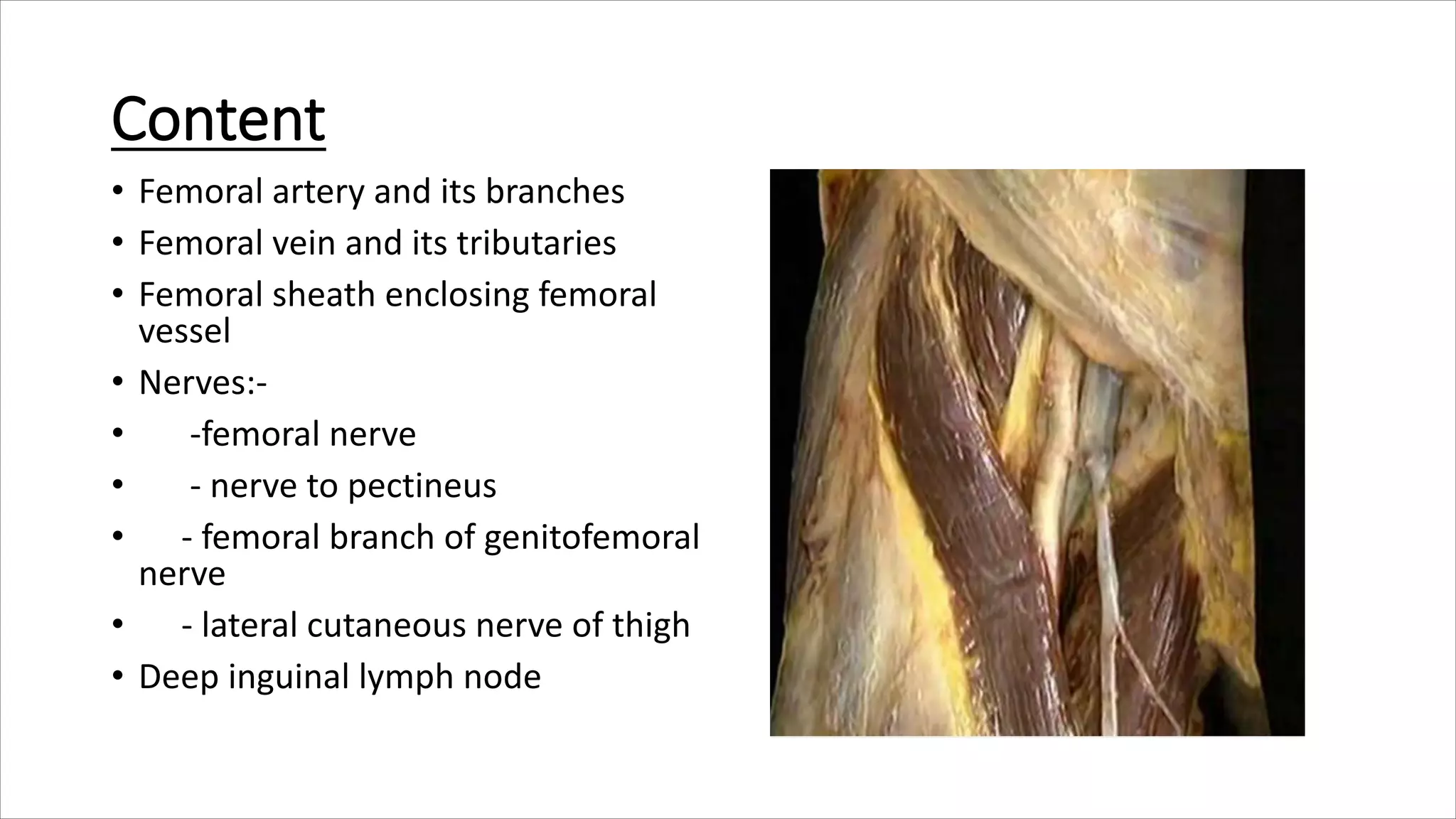
The femoral triangle is a triangular depression in the upper thigh bounded laterally by the sartorius muscle, medially by the adductor longus muscle, and at its base by the inguinal ligament. It contains the femoral artery and vein as well as the femoral nerve. The femoral sheath encloses the femoral vessels in three compartments - lateral arterial, intermediate venous, and medial lymphatic/femoral canal compartments. The femoral canal is a conical passage located medially that contains lymph nodes and drains the genitals. The femoral triangle and its structures are clinically important as sites for hernias, nerve injuries, and arterial access.