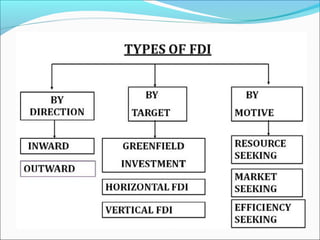
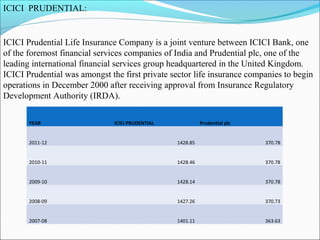
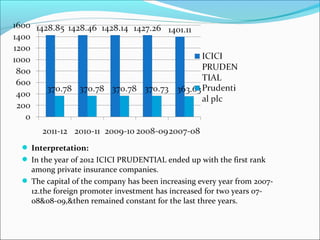
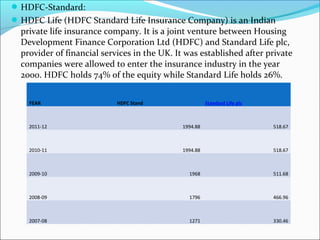
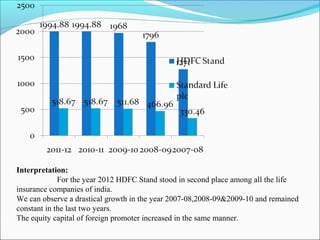
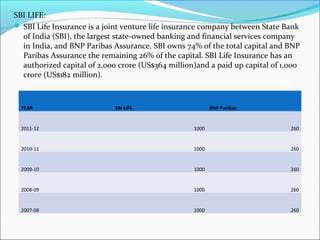
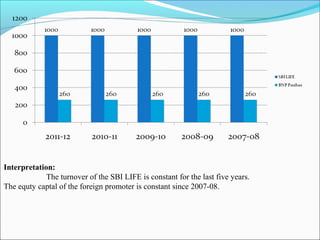
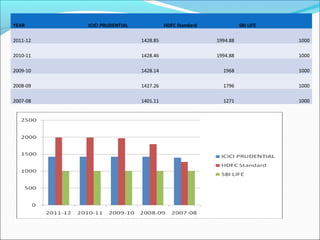
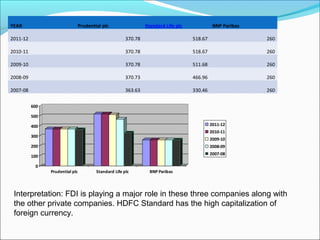
The document discusses foreign direct investment (FDI) in the Indian insurance sector. It provides background on the liberalization of the insurance industry in India and the growth of private insurance companies. The summary analyzes data on three major life insurance companies (ICICI Prudential, HDFC Standard Life, and SBI Life) that have benefited from FDI. It shows increasing capitalization from foreign partners Prudential, Standard Life, and BNP Paribas over several years. FDI is playing a key role in the development and increased capacity of the private insurance industry in India.