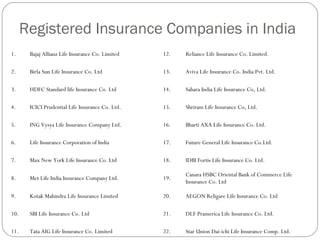
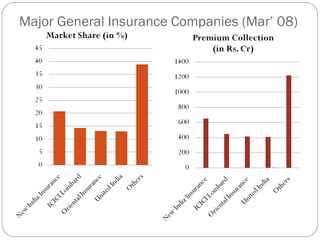
This document provides an overview of the insurance sector in India, including its history, current state, and prospects. It discusses key milestones in the development of life and general insurance in India. It outlines the current regulatory framework and major players. It also places the Indian insurance sector in a global context, noting opportunities for growth. While penetration and density are still low compared to other countries, factors like deregulation, technology, and a large population provide potential for expansion. Issues around product diversification and quality of agents need addressing. The sector is poised for continued growth if it offers innovative products tailored to customer needs.