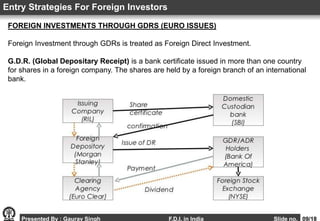
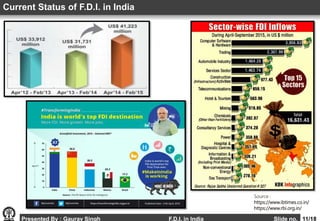
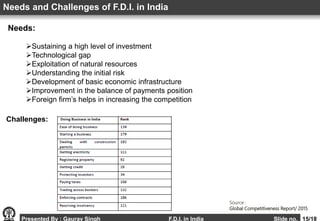
This document provides an overview of foreign direct investment (FDI) in India. It discusses the definition of FDI, why countries pursue it, the sectors it is allowed in and restricted from in India. The major routes for FDI approval in India are outlined, along with the current status of FDI inflows in recent years. Factors affecting FDI in India are examined, along with the needs it fulfills and challenges it faces. The advantages and disadvantages of FDI for India are summarized, and recommendations are provided for how to further promote FDI.