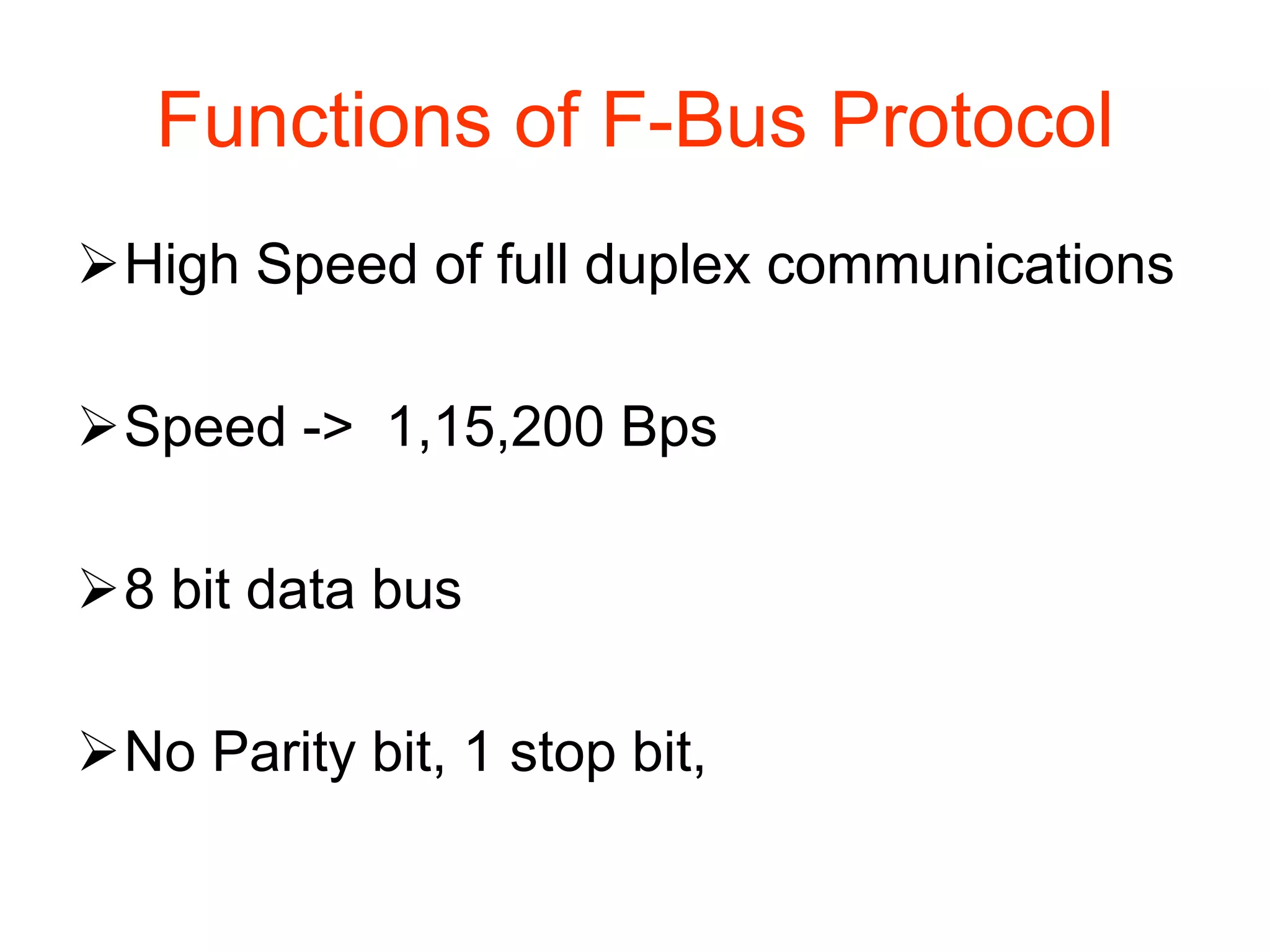
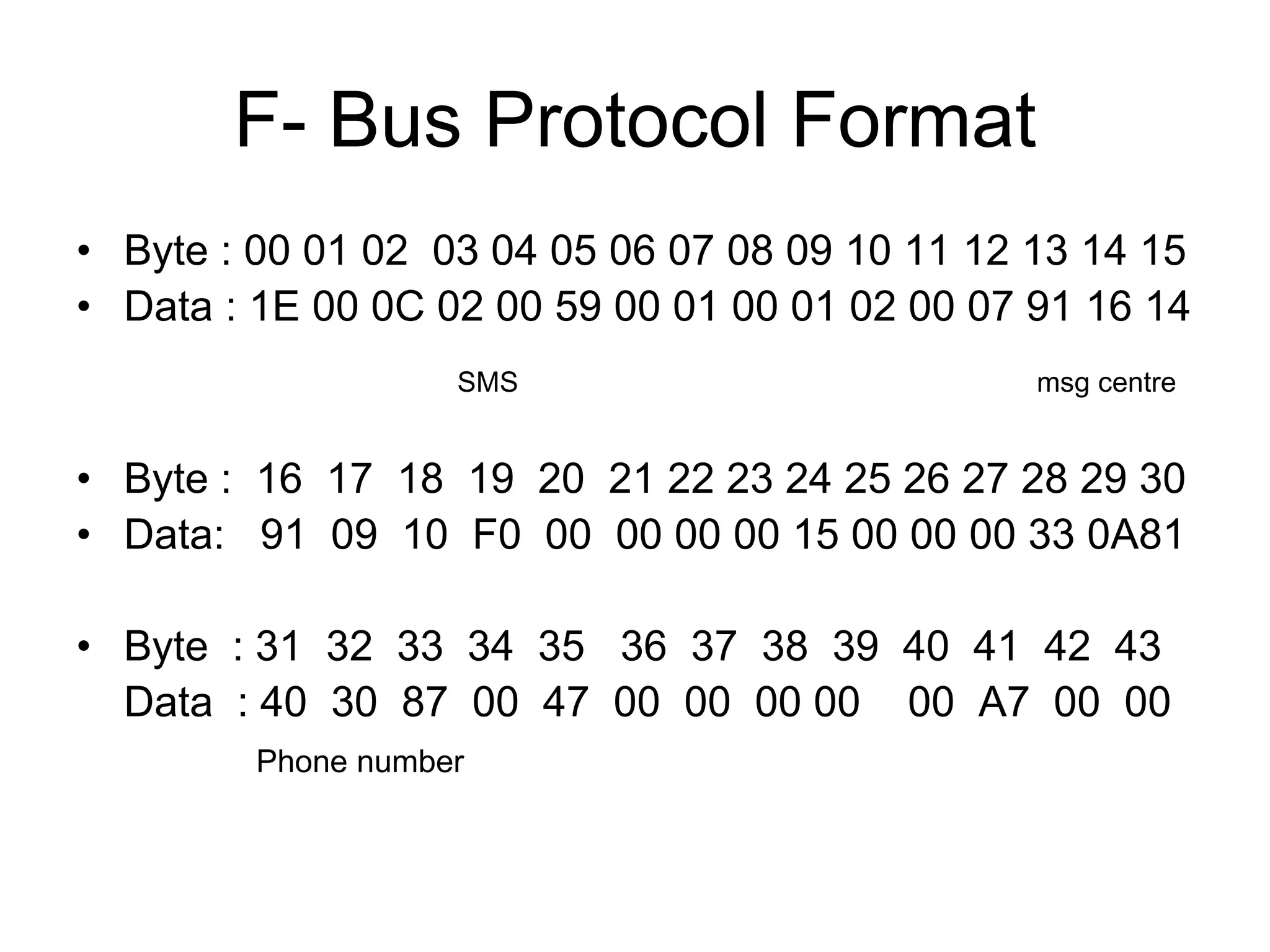
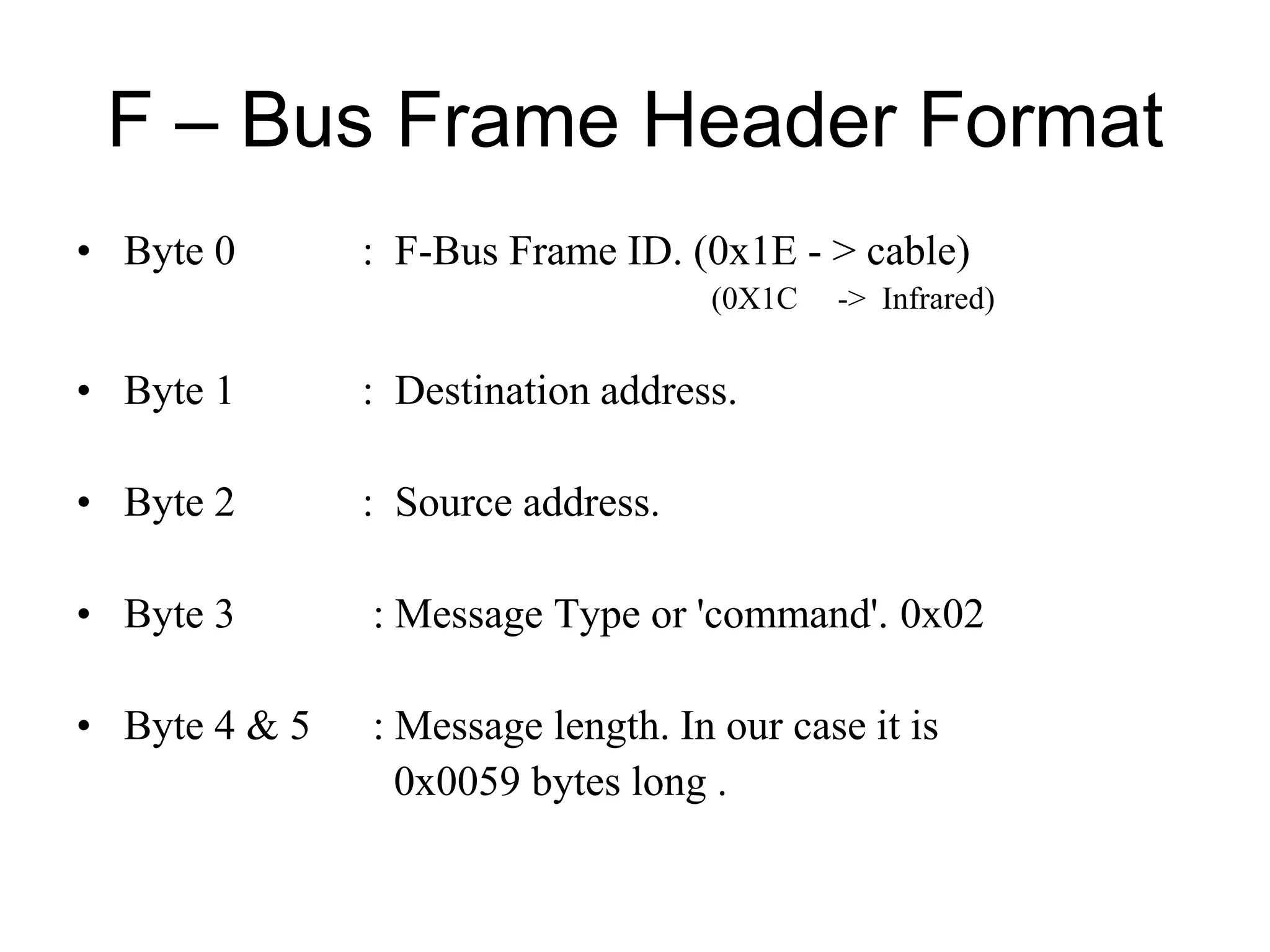
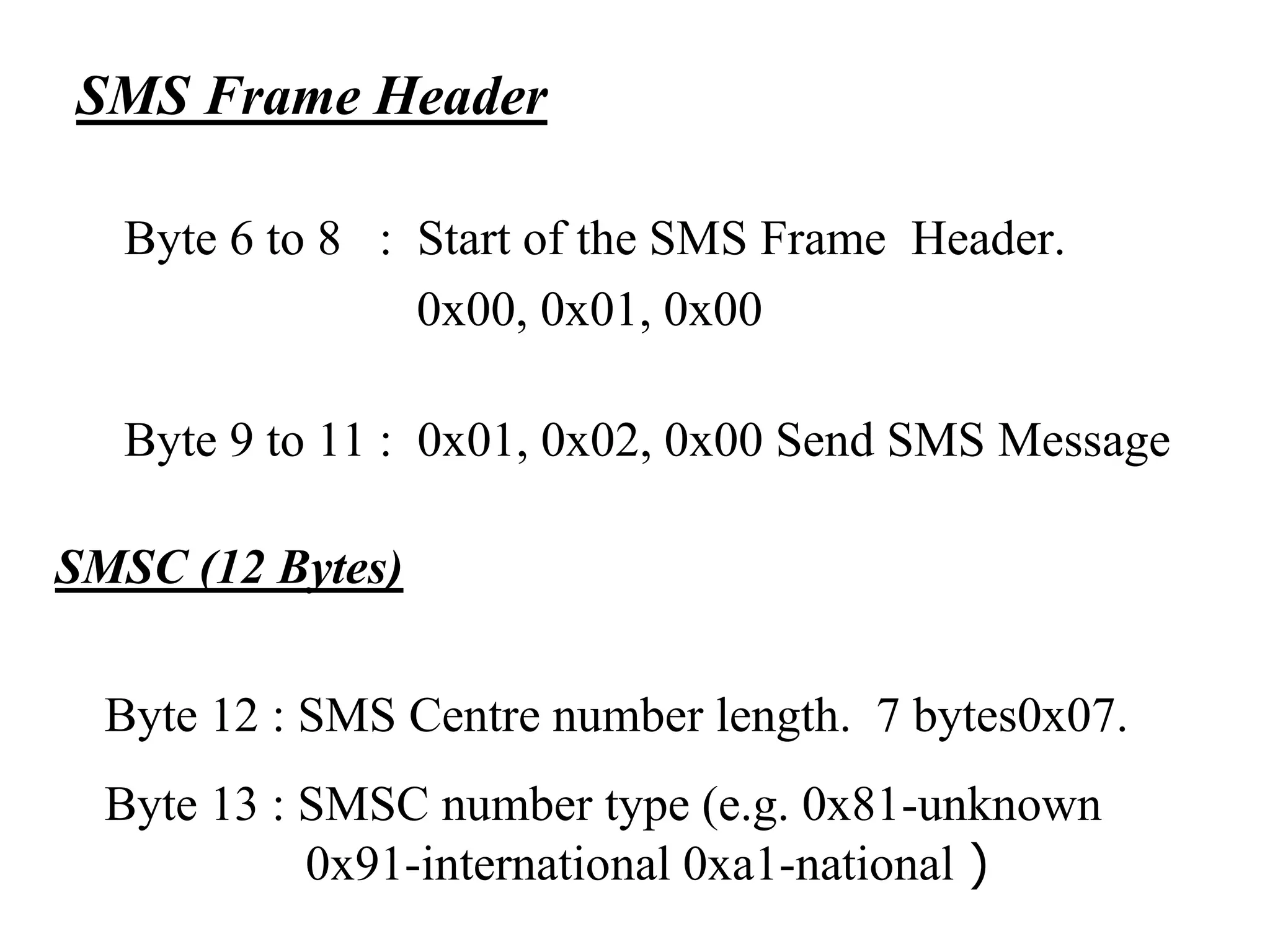
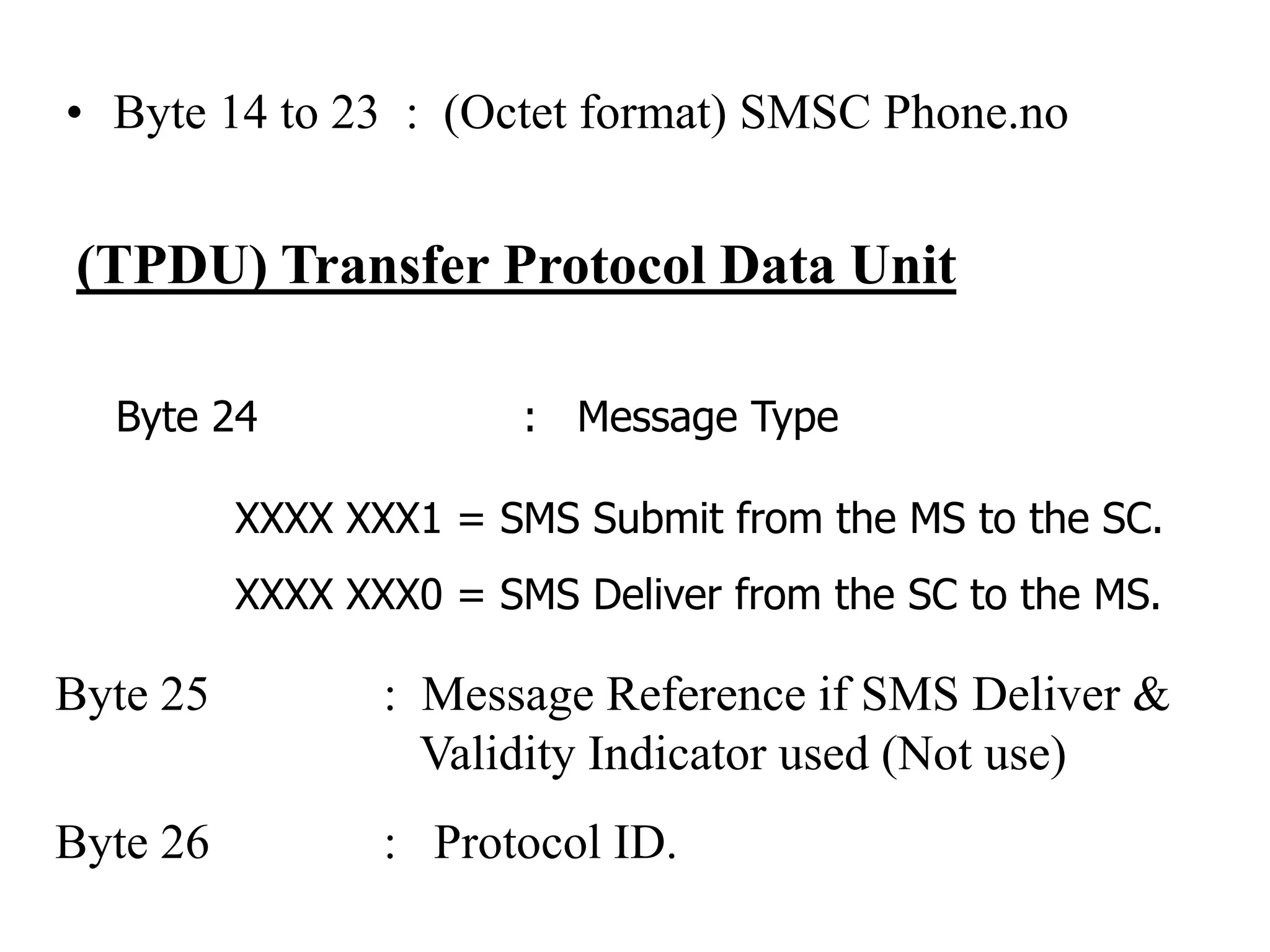
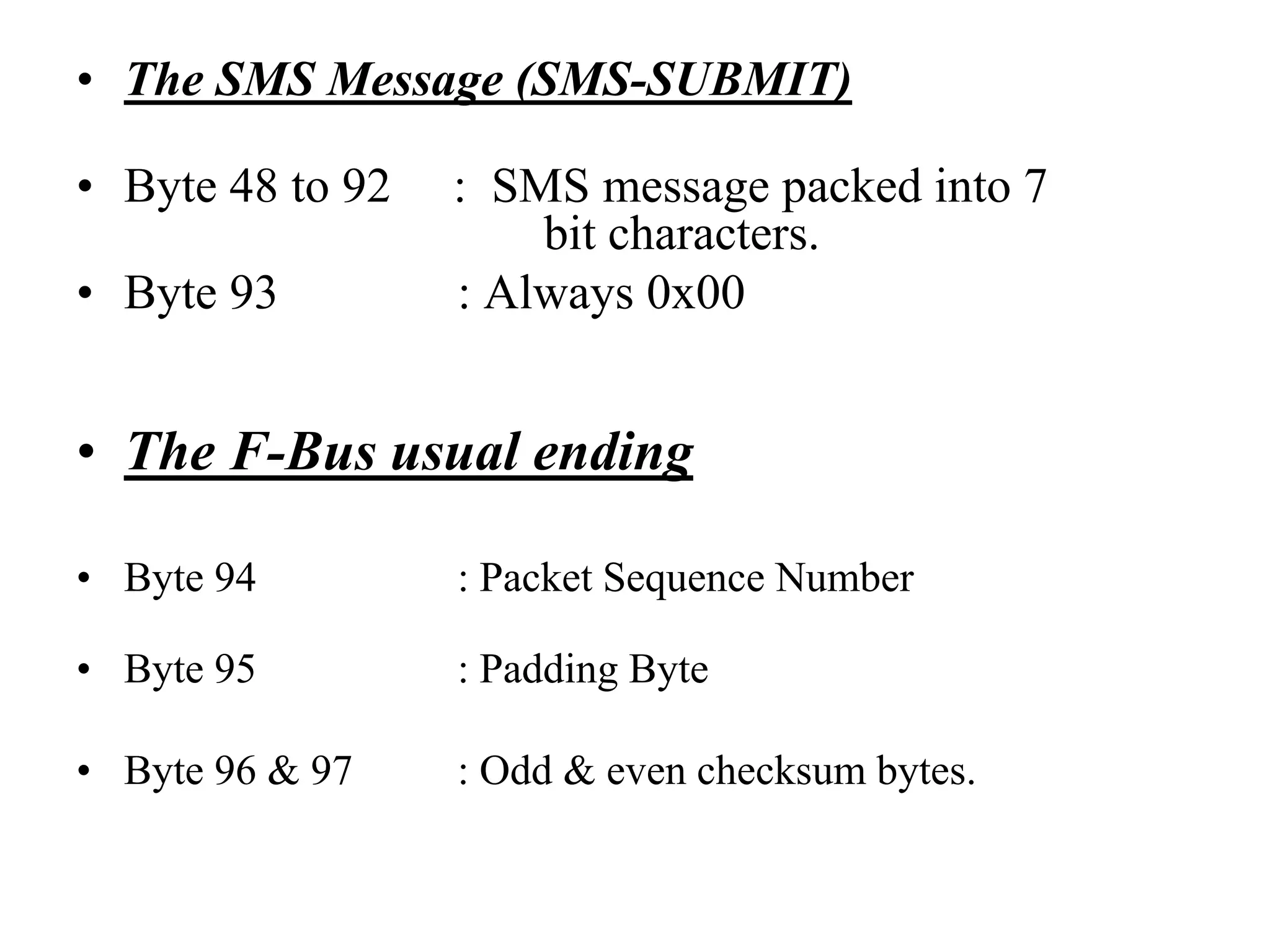
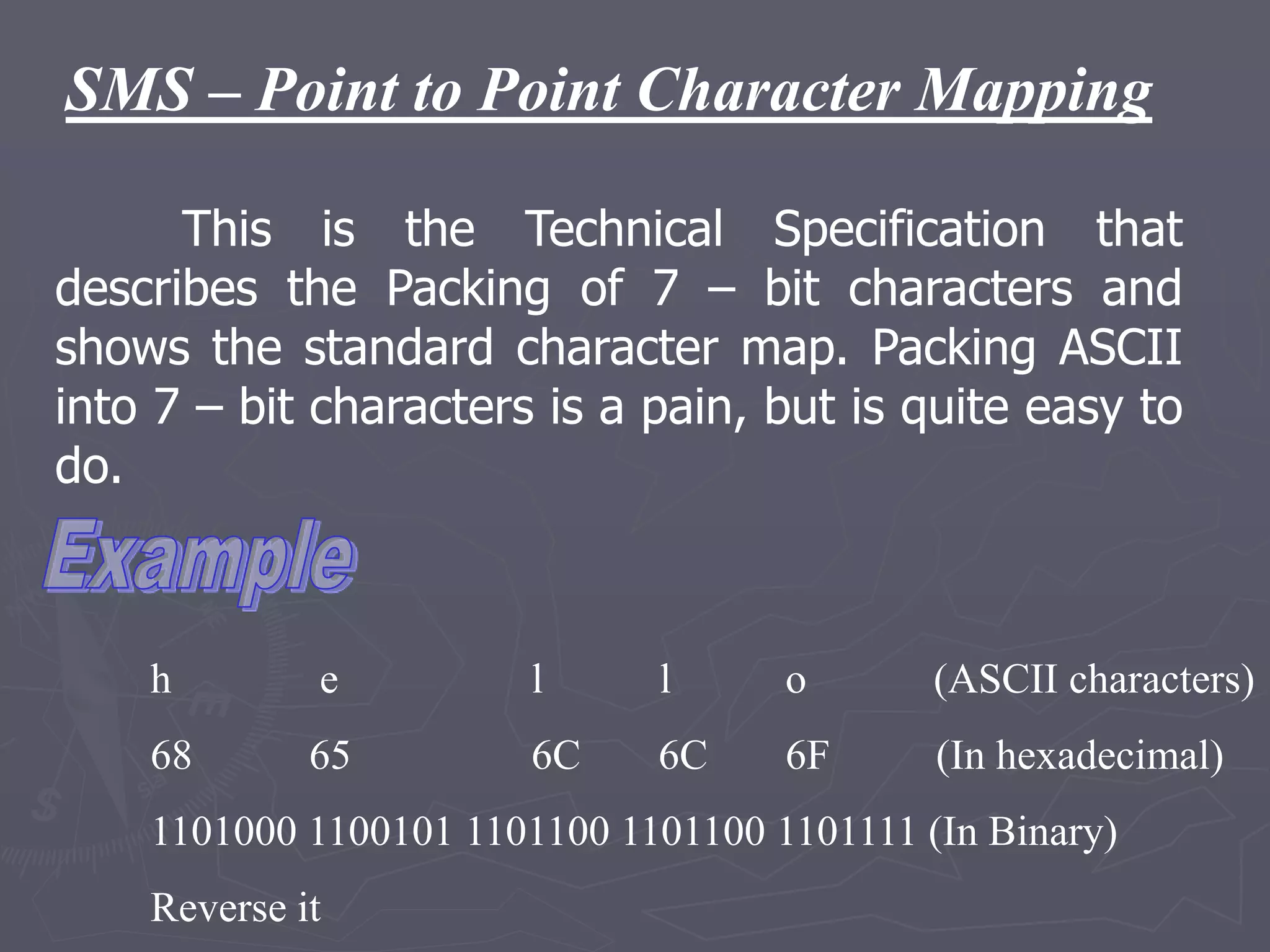
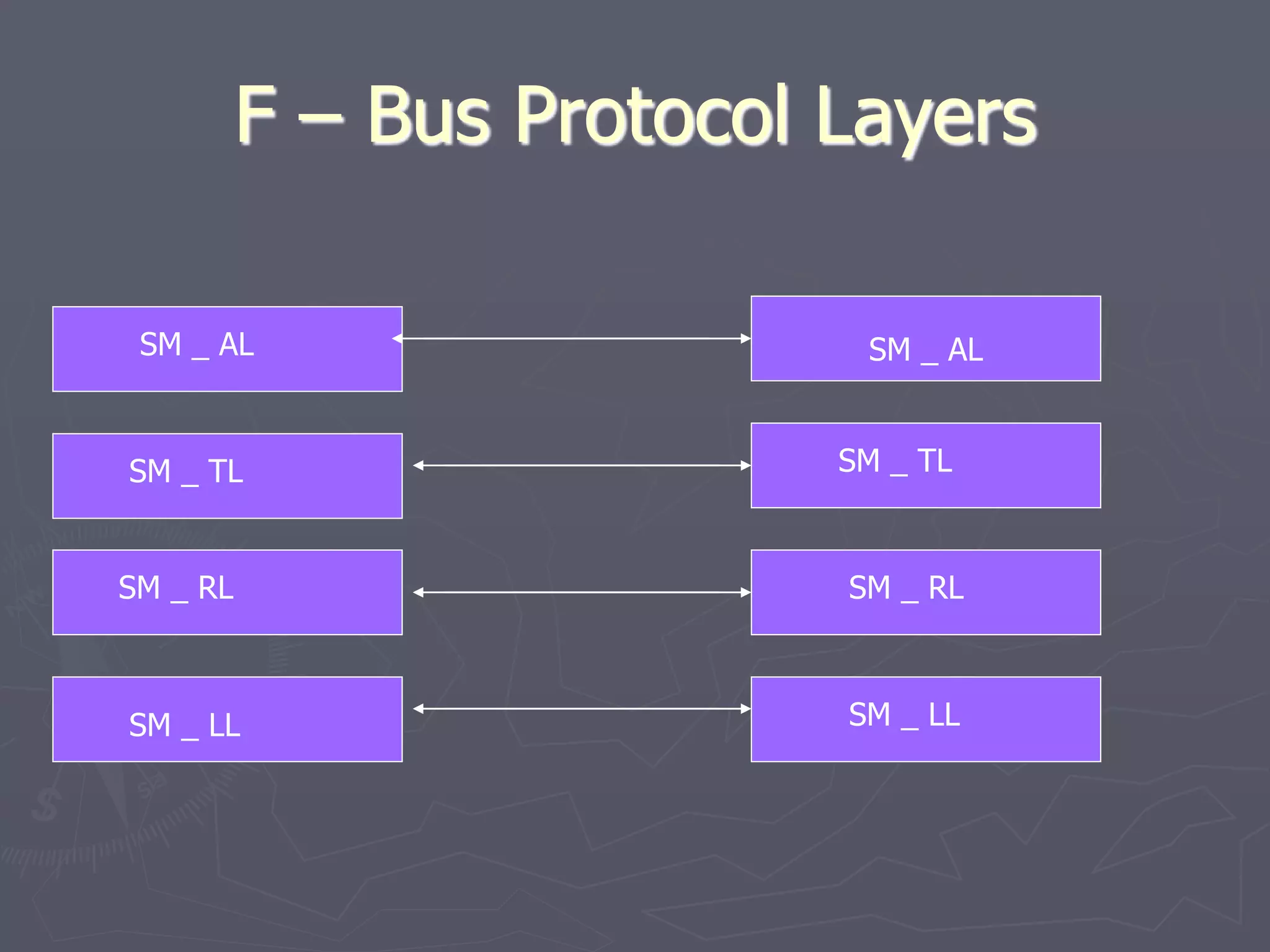
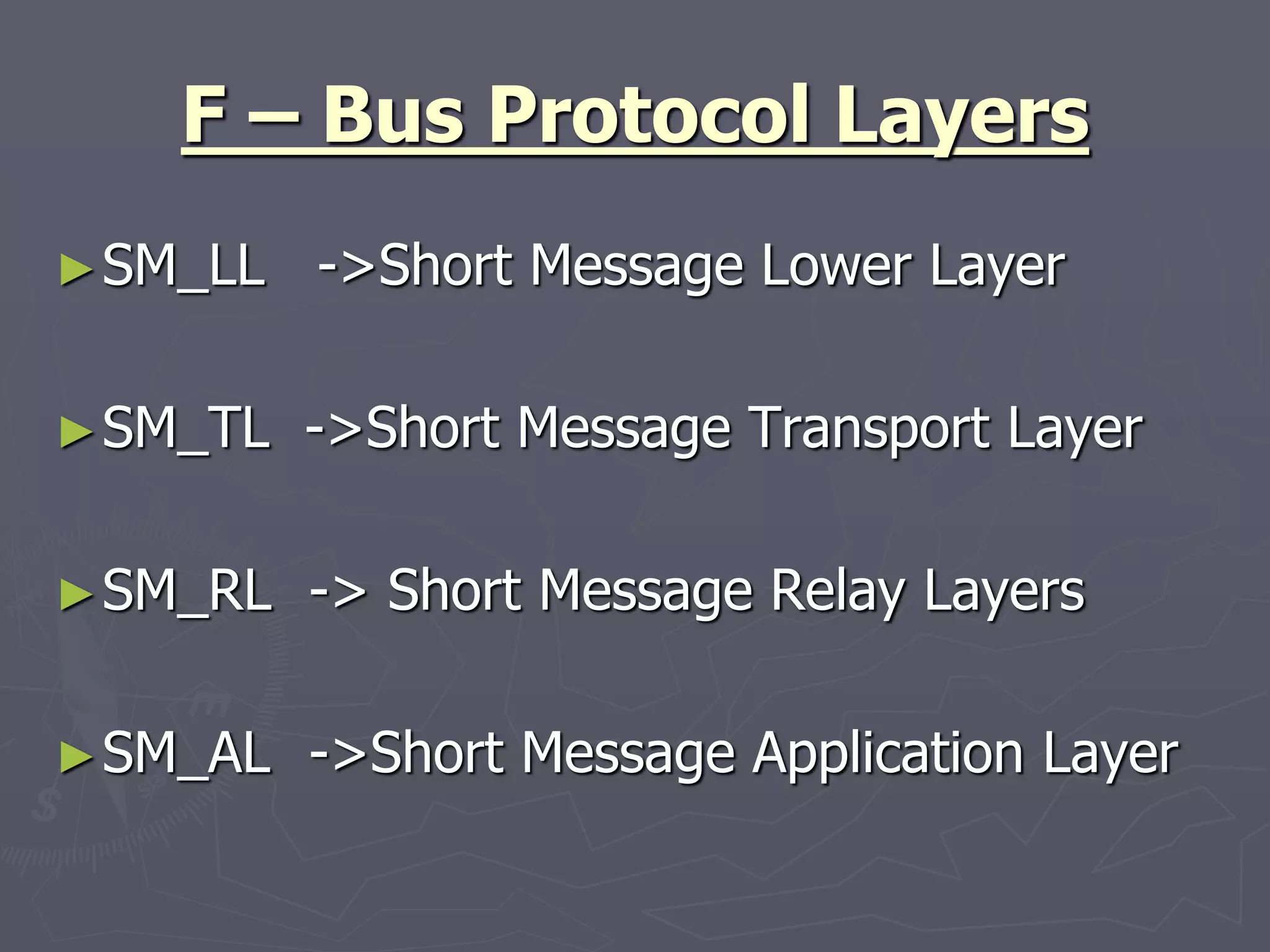
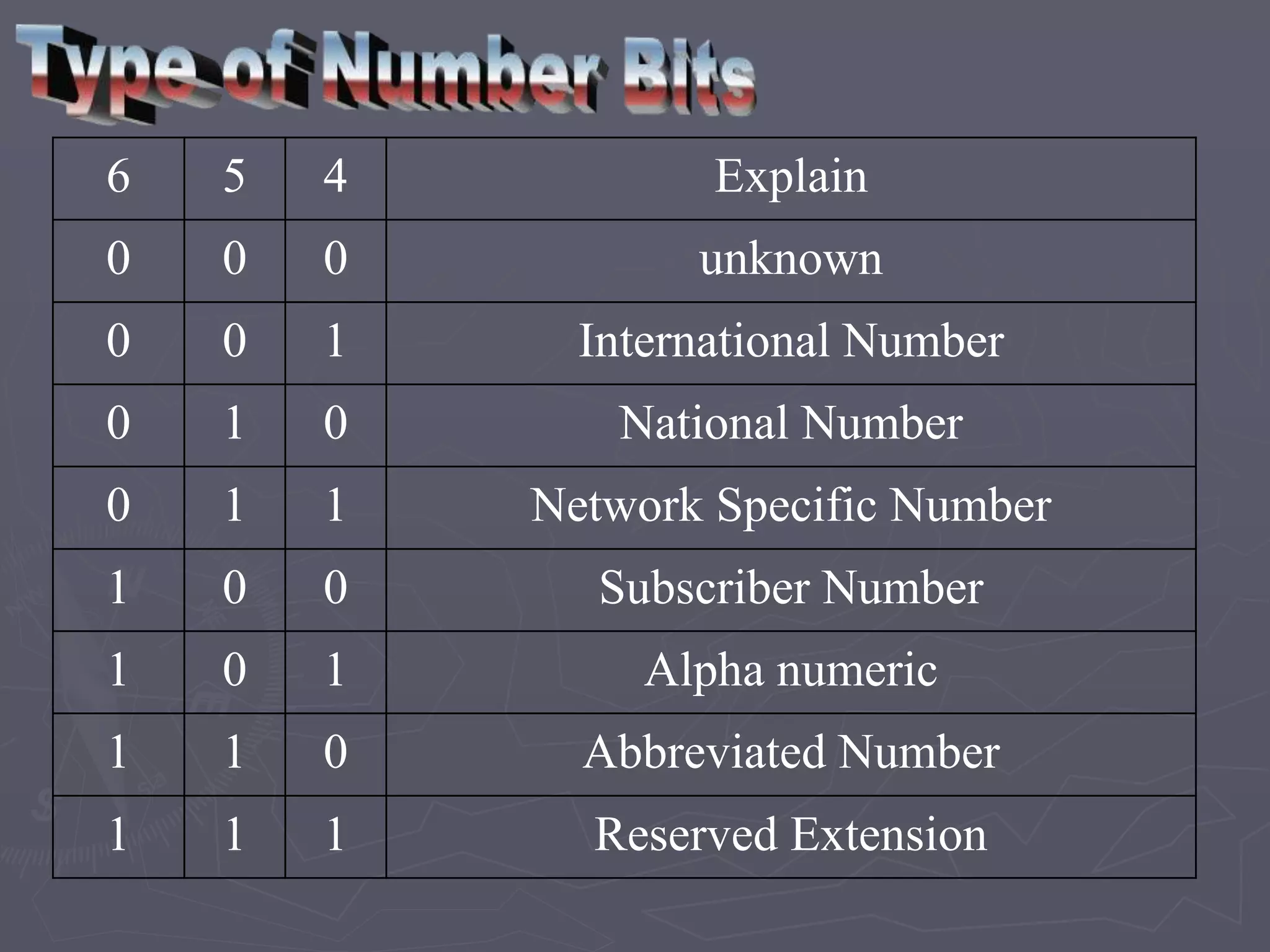
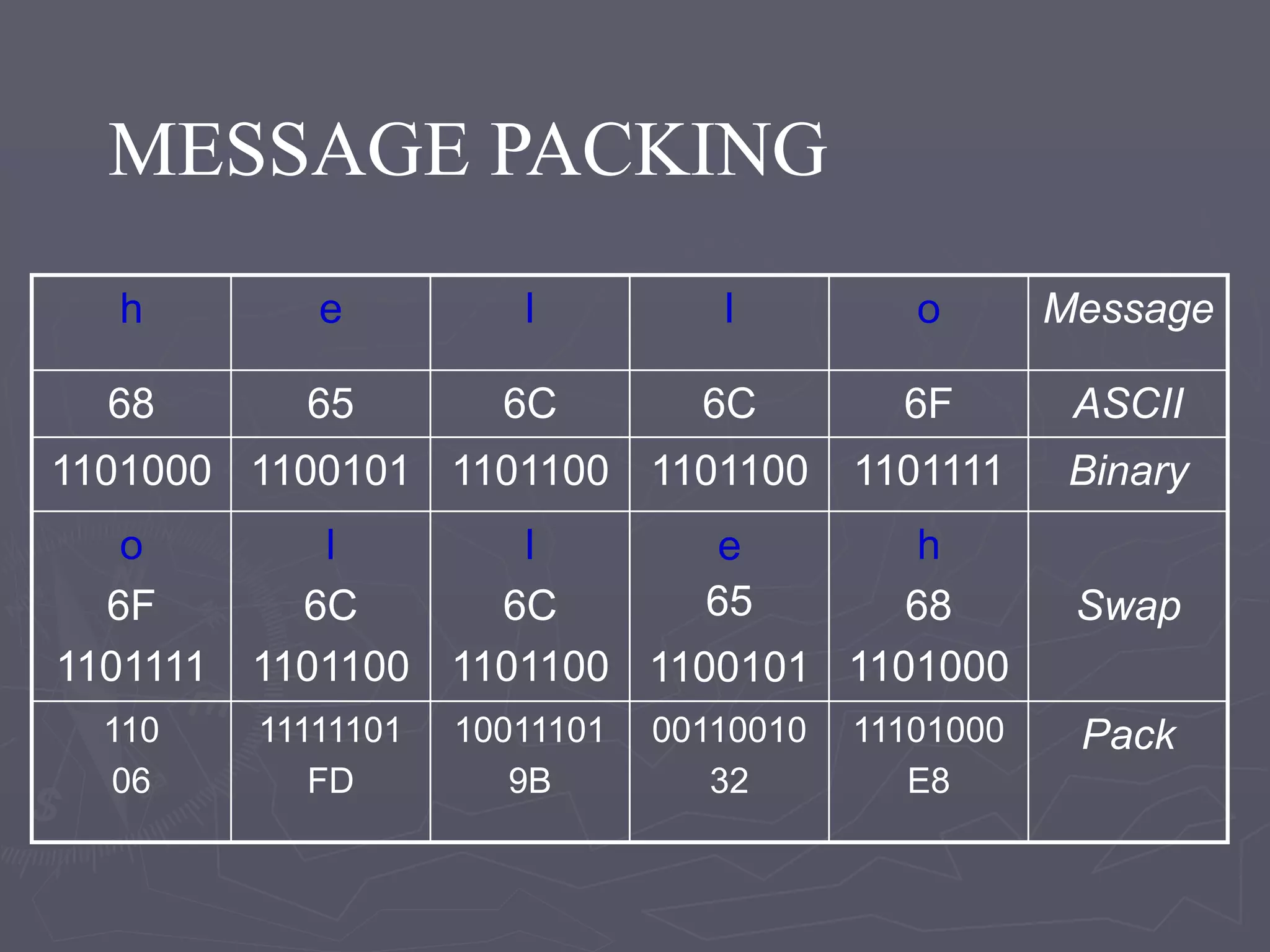
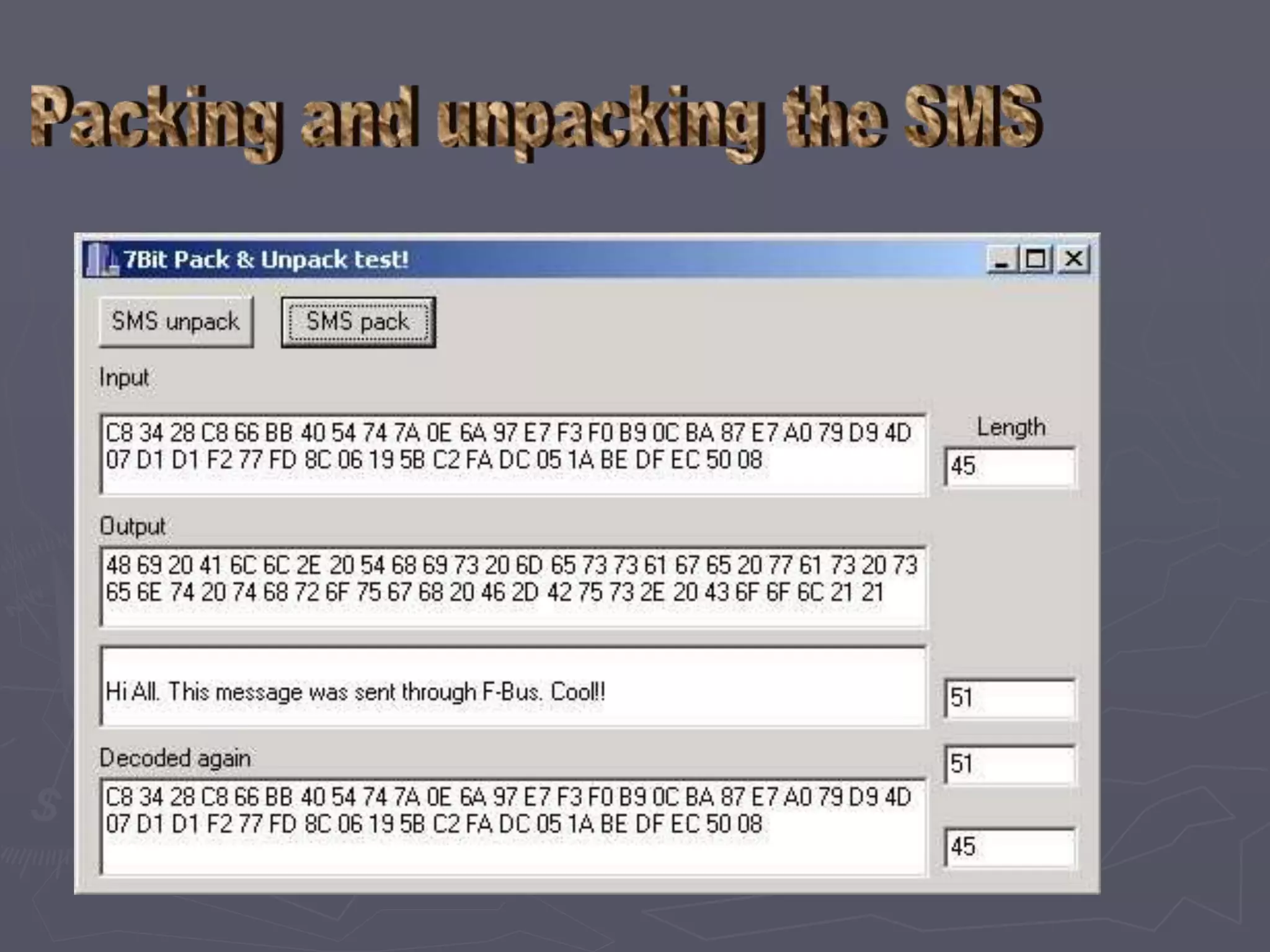
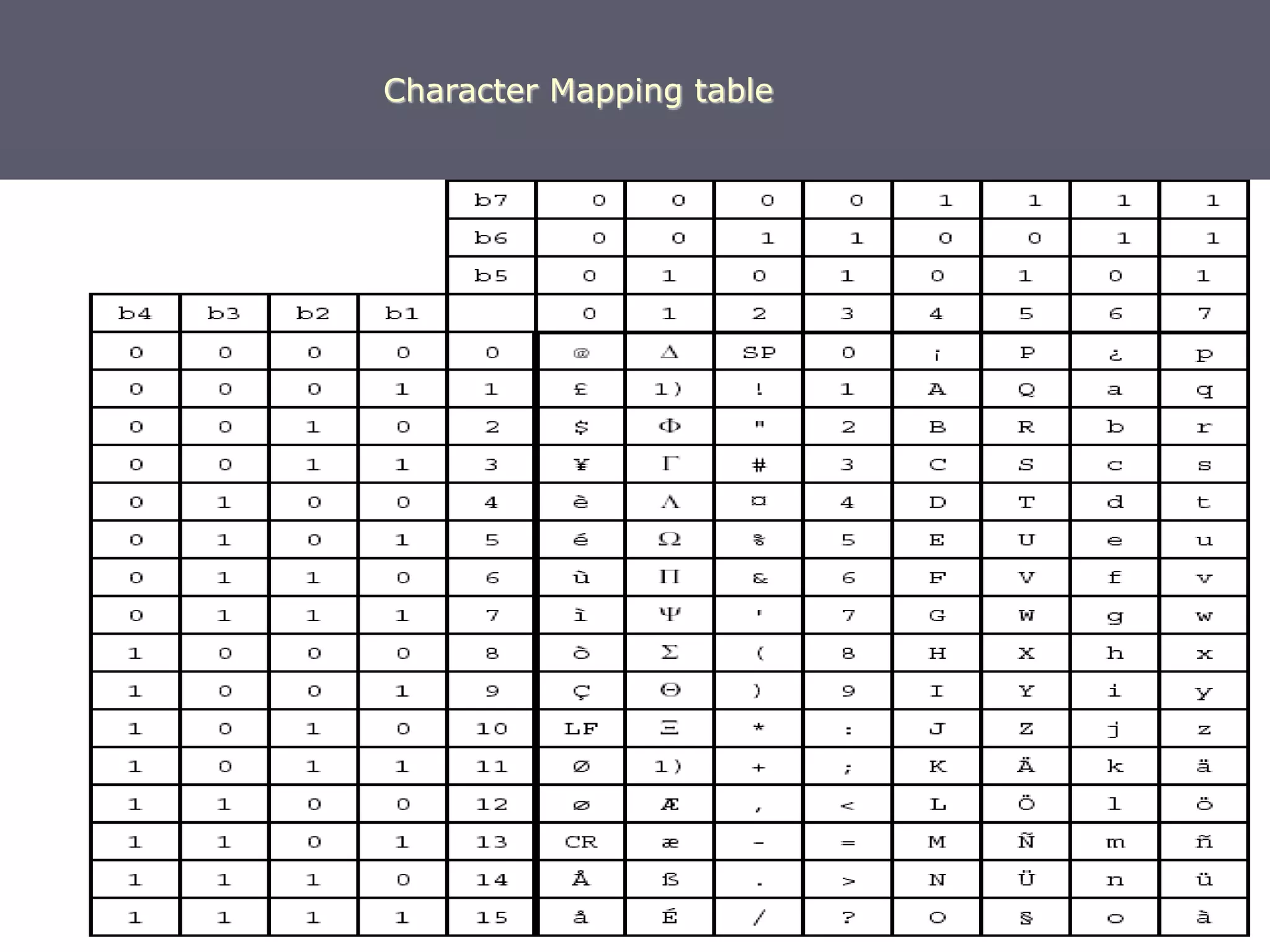
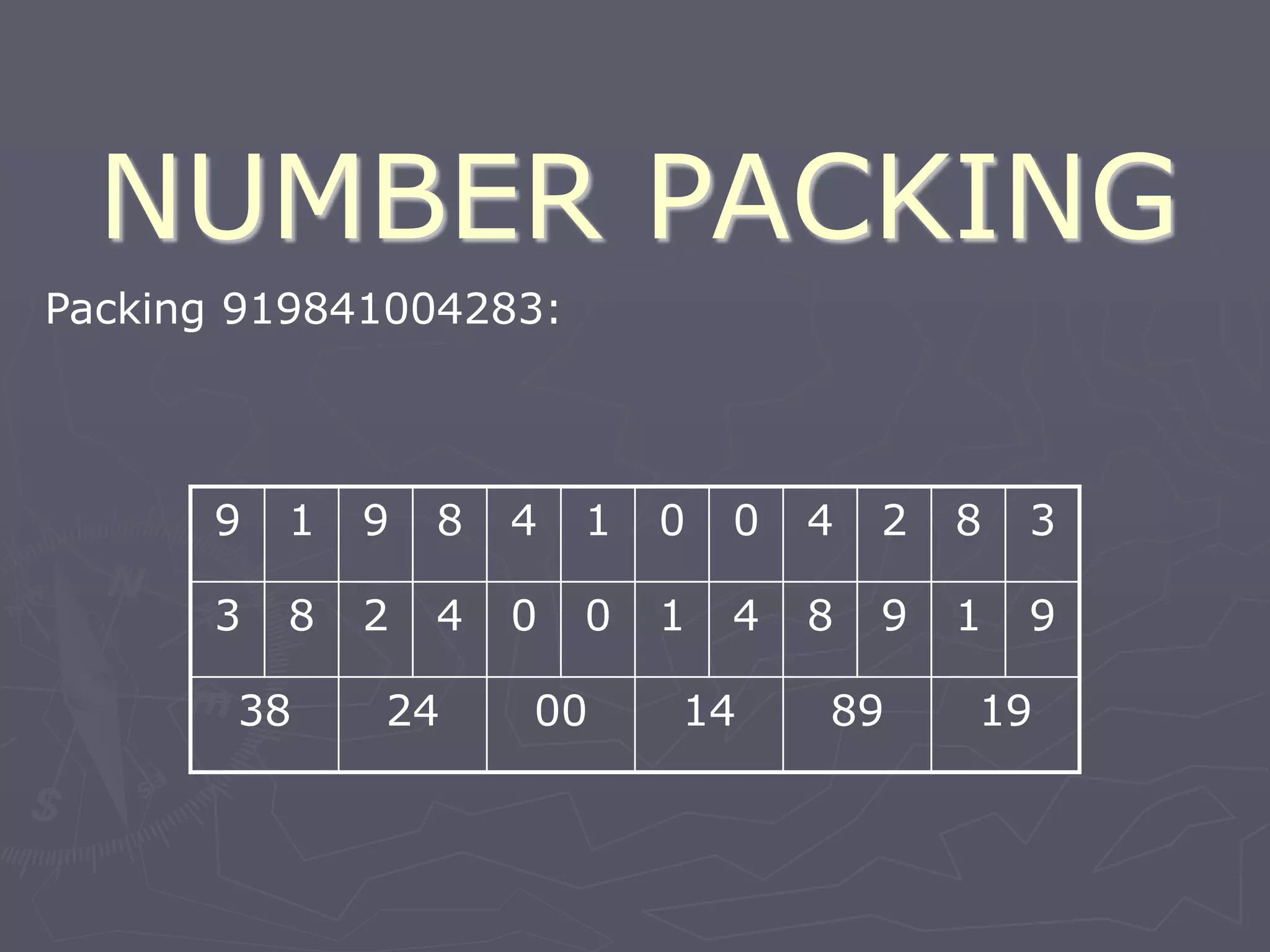
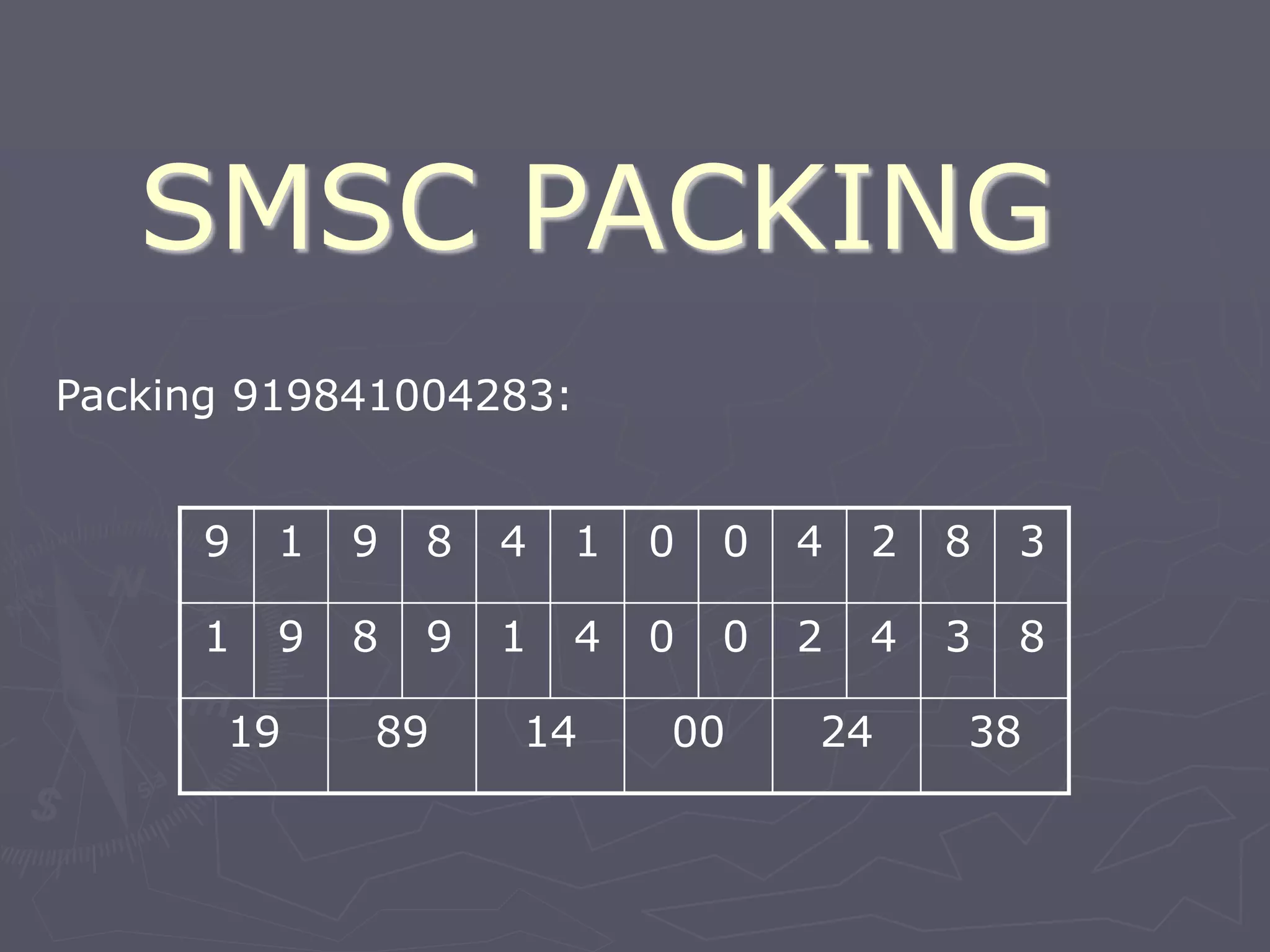
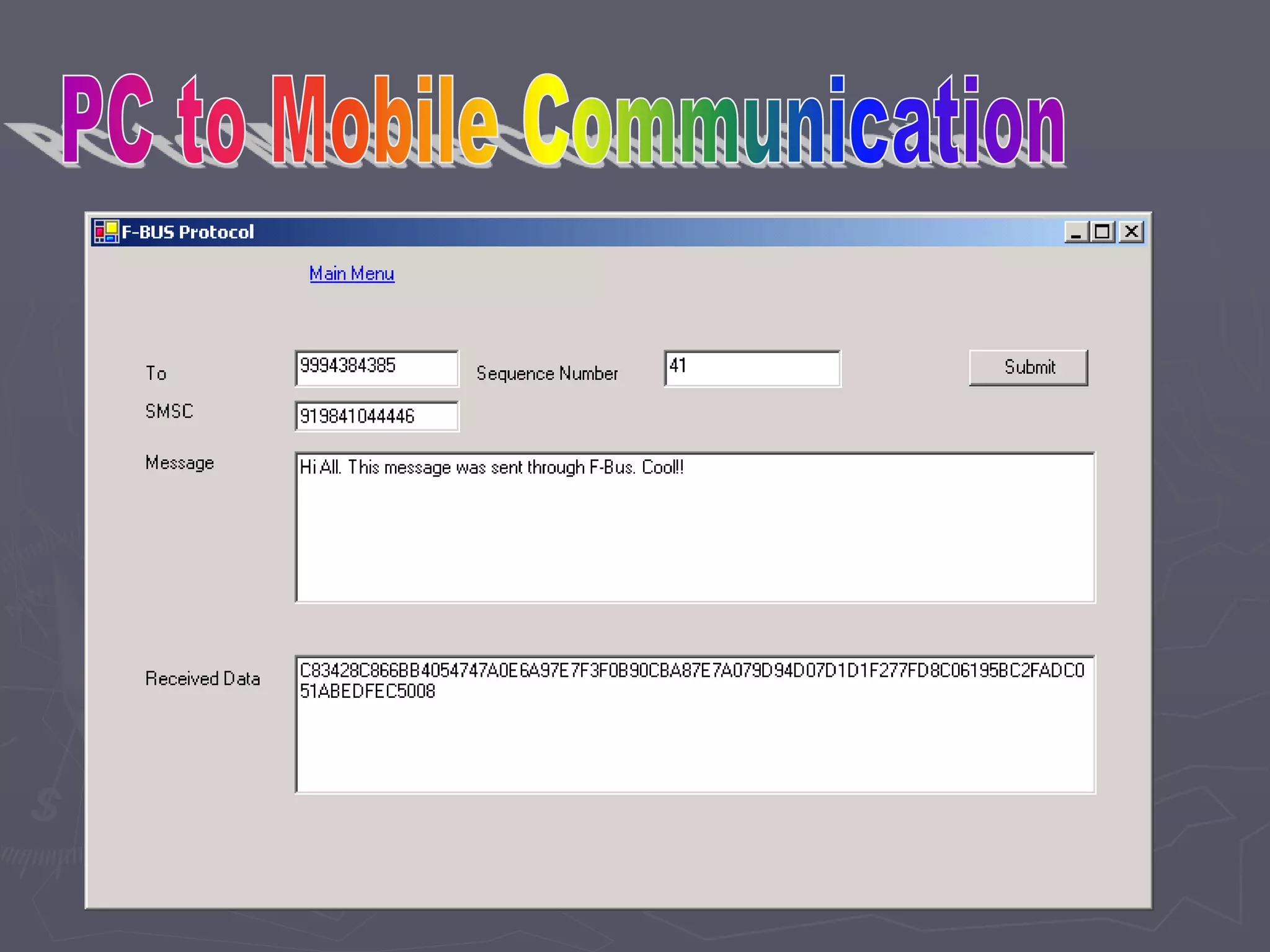
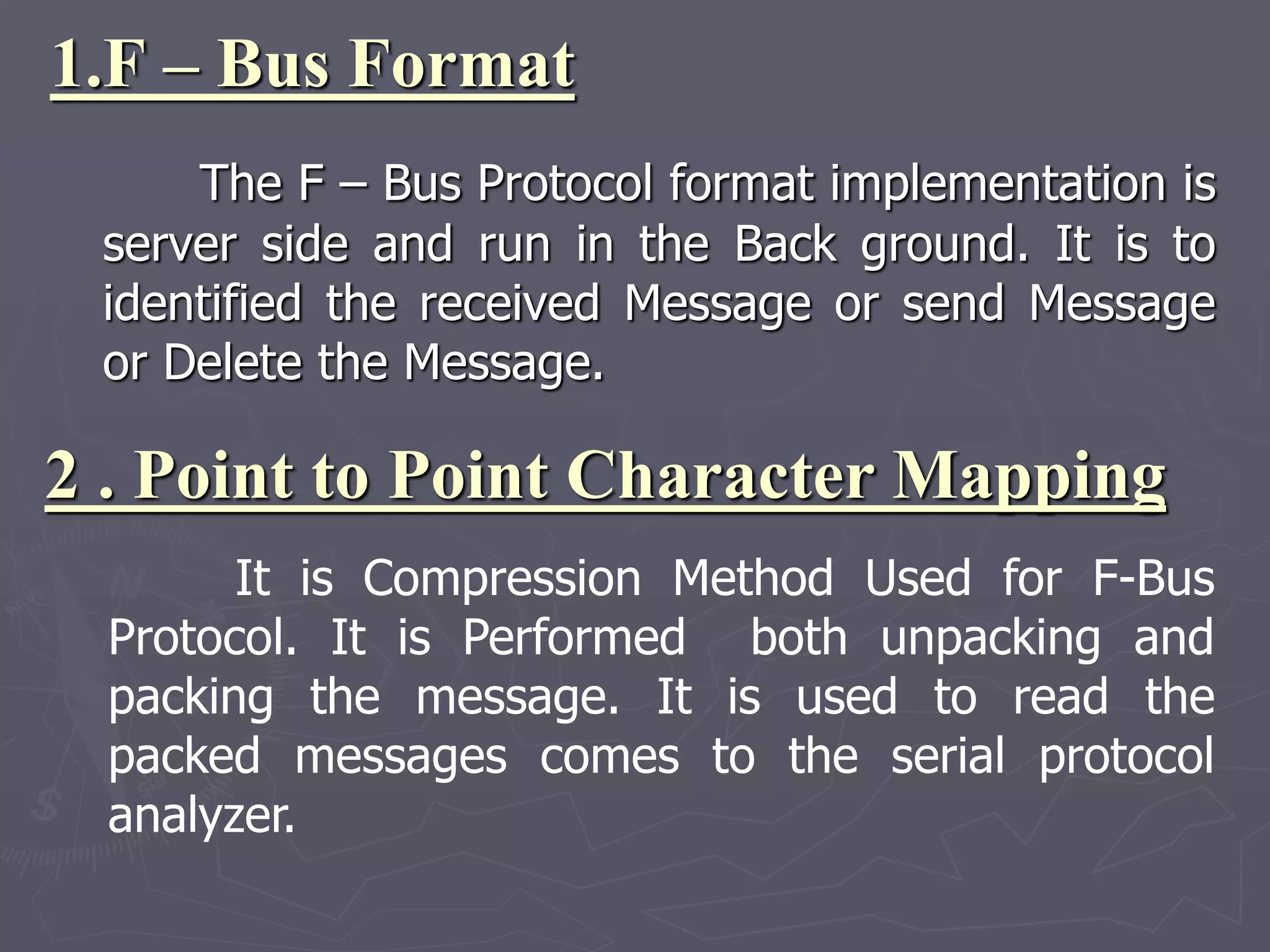
F-Bus protocol allows communication between mobile devices and embedded systems using a data cable. It operates at a high speed of 115.2 kbps using an 8-bit data bus. The document describes how to connect a mobile phone to a PC using F-Bus and extract SMS messages and send commands to delete messages. It also explains the various layers and formats used in F-Bus including the point-to-point character mapping for packing 7-bit characters in SMS transmission.