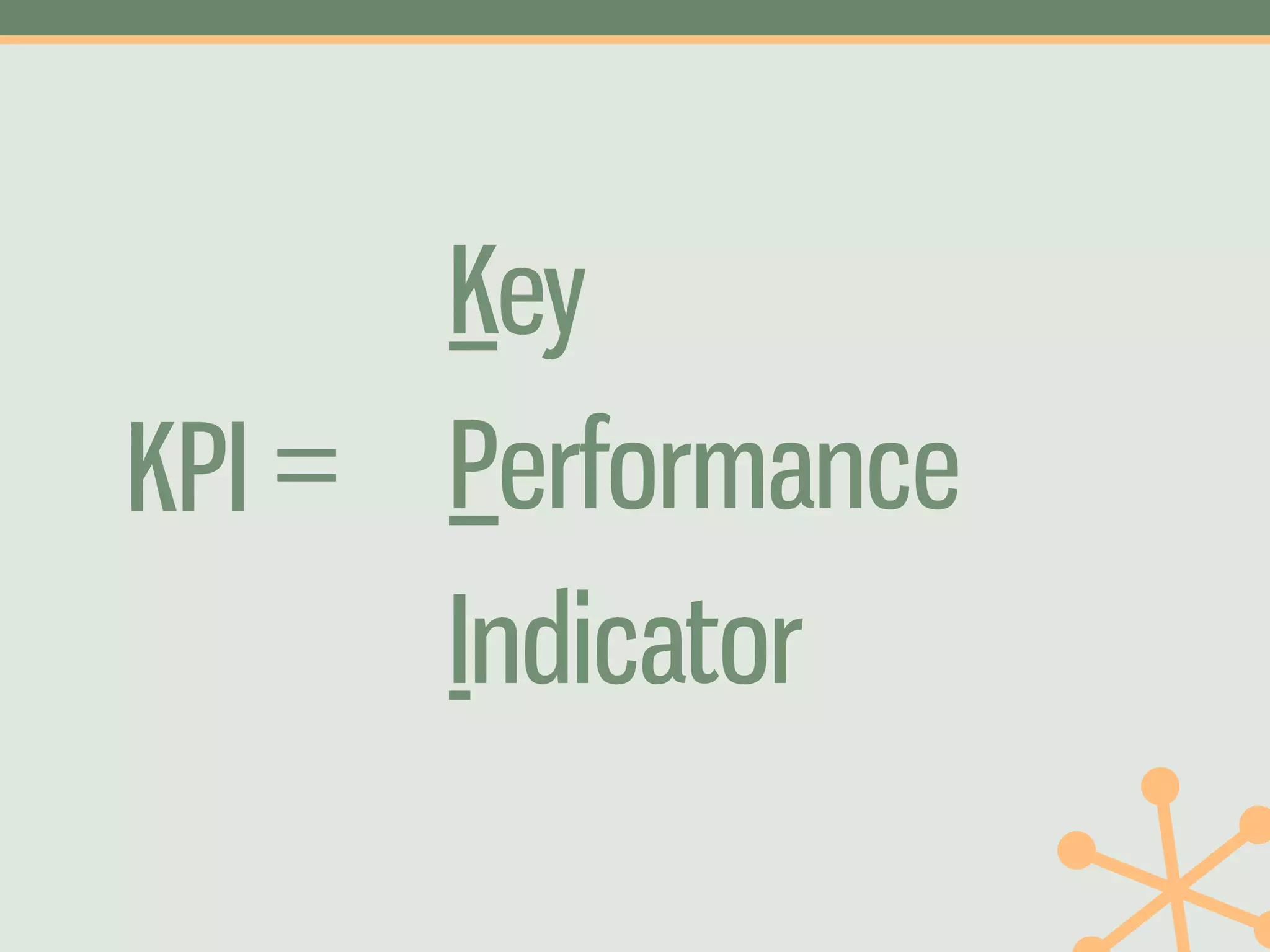
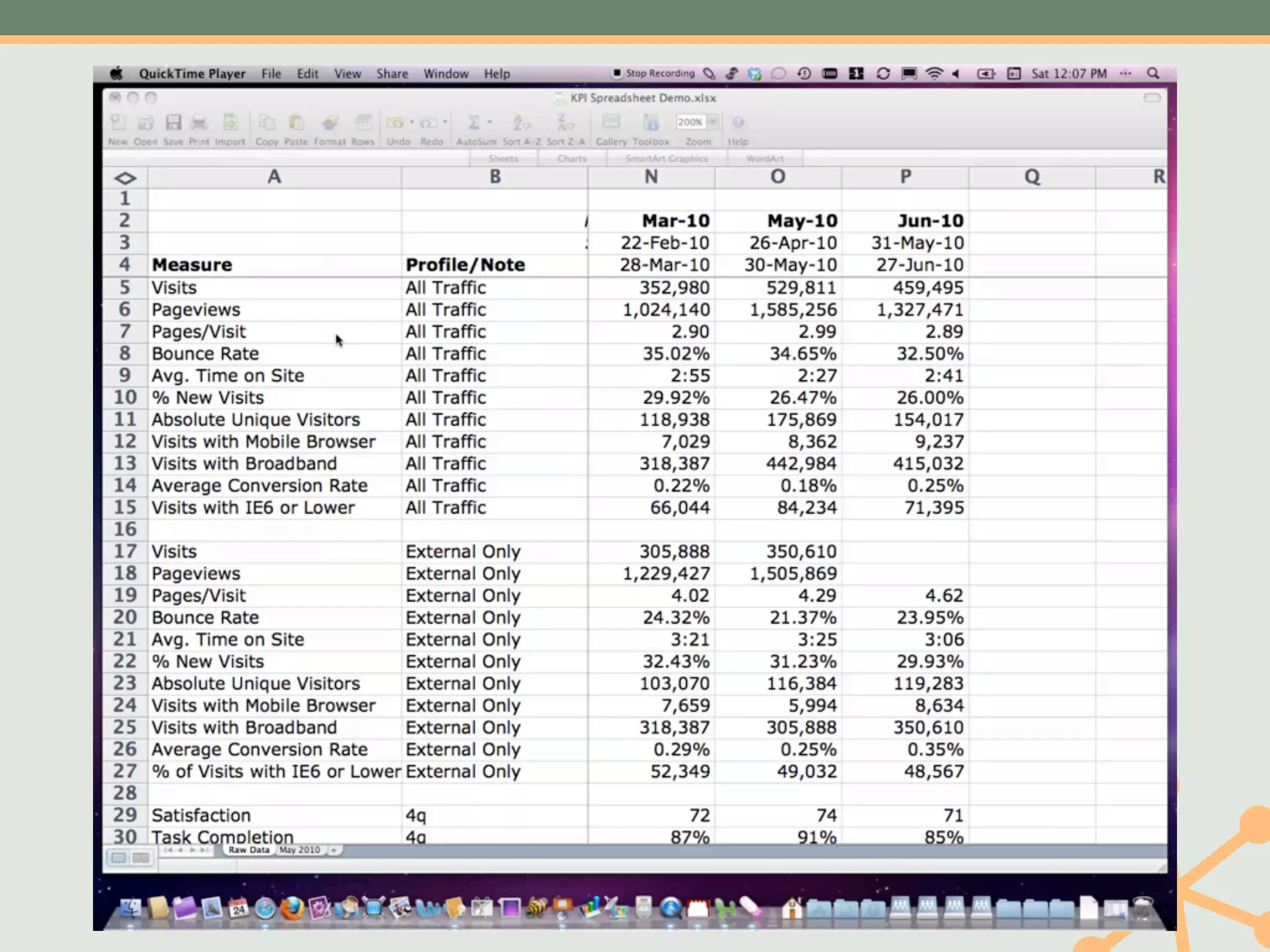
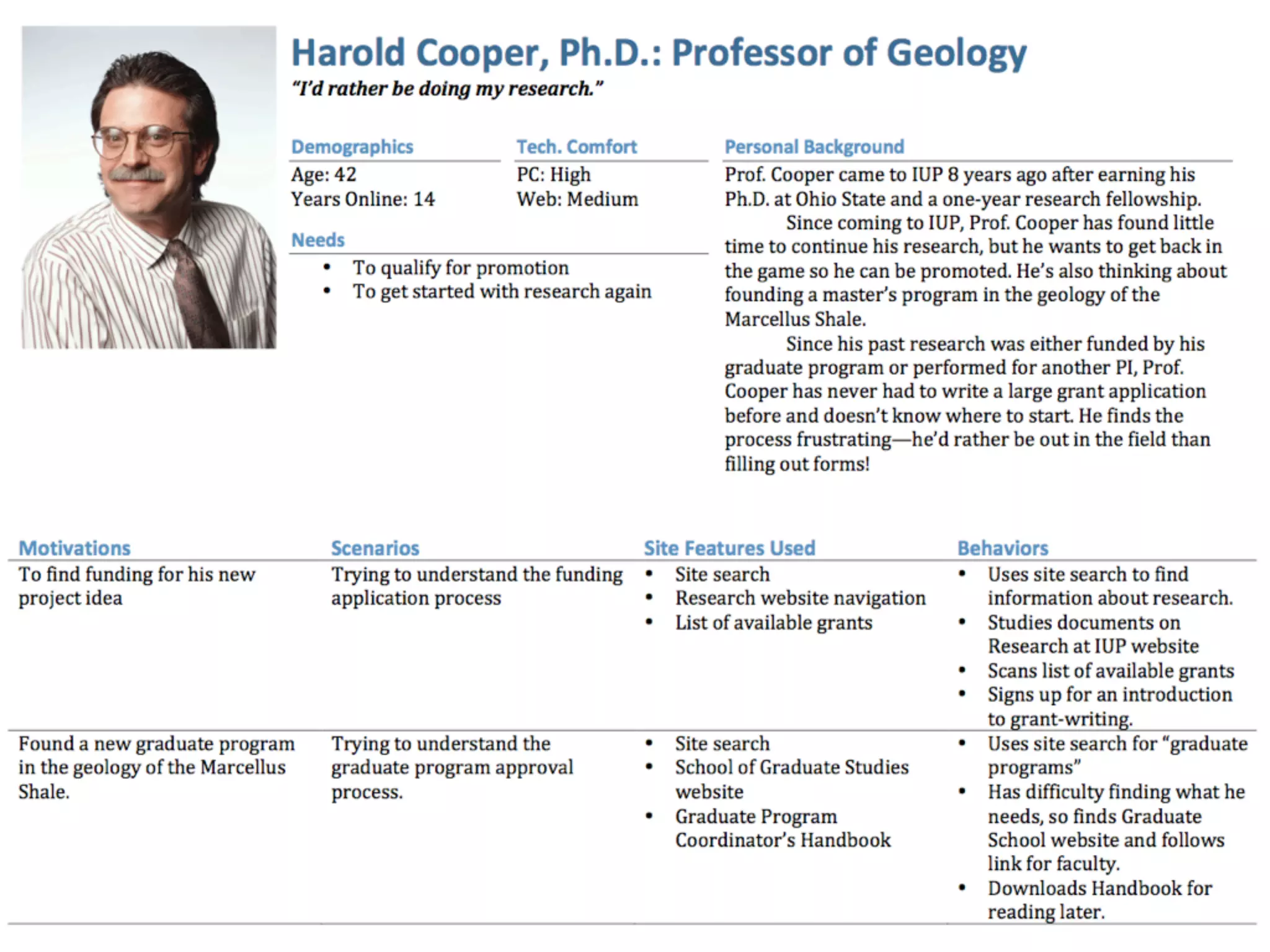
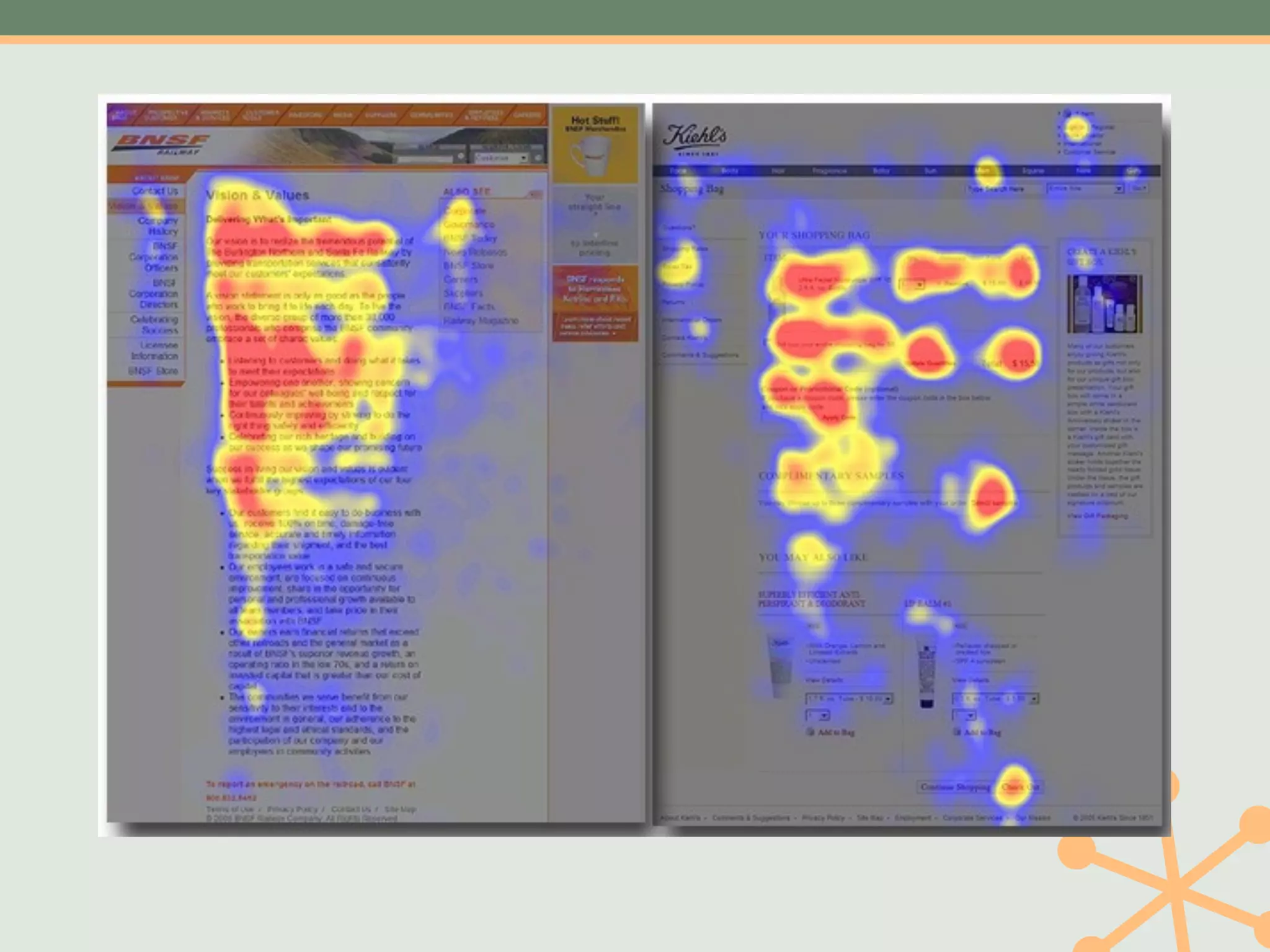
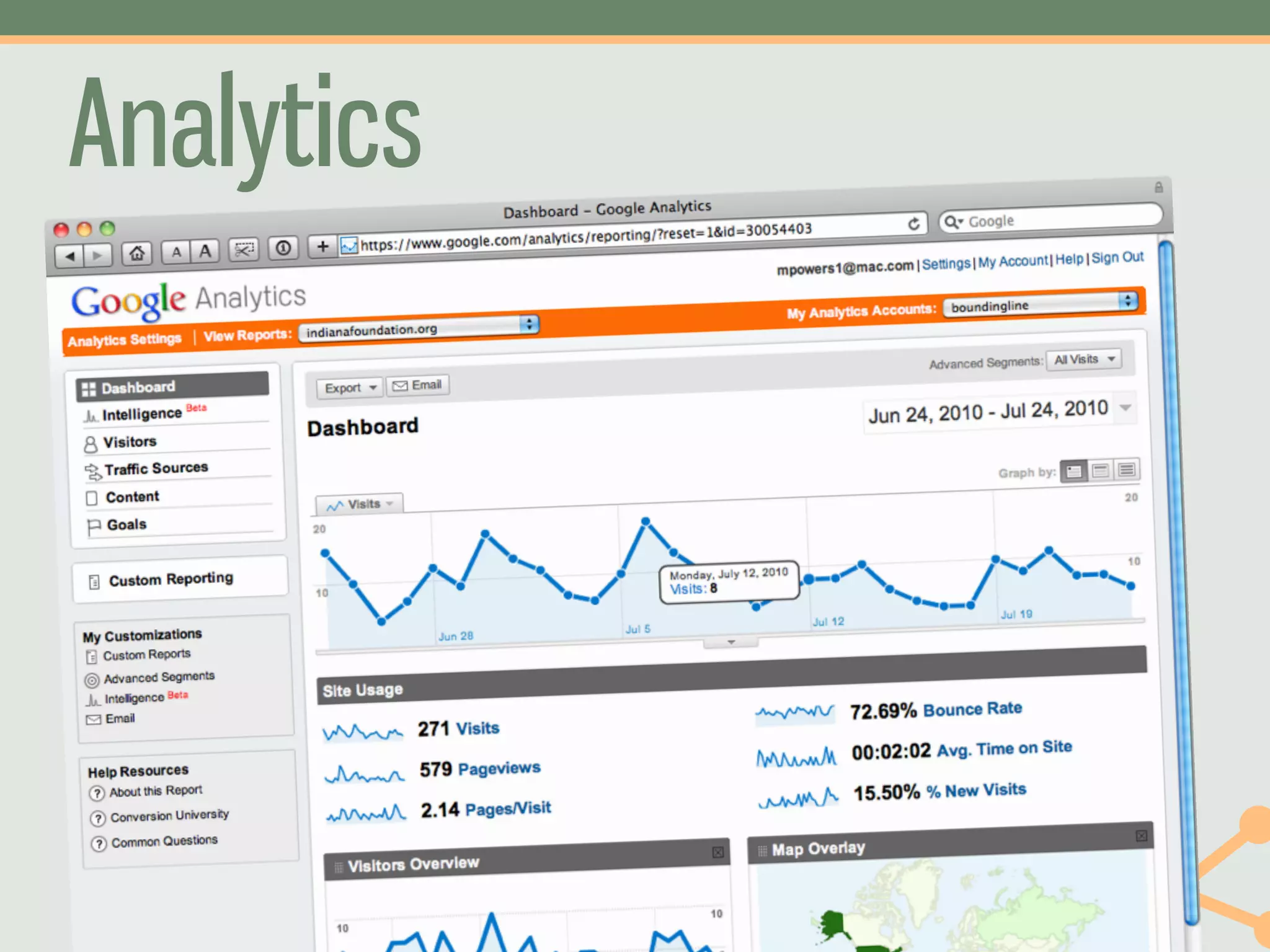
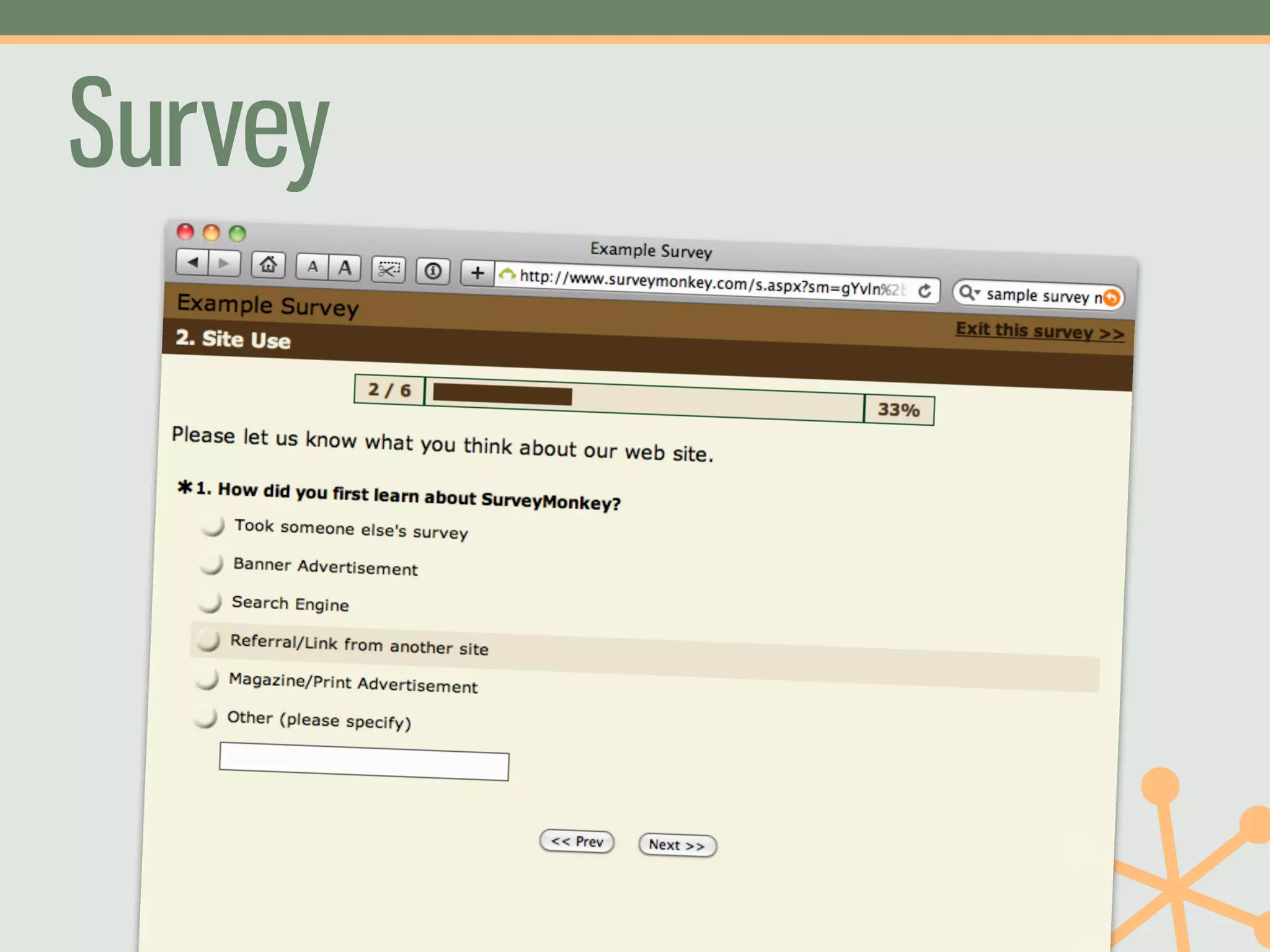
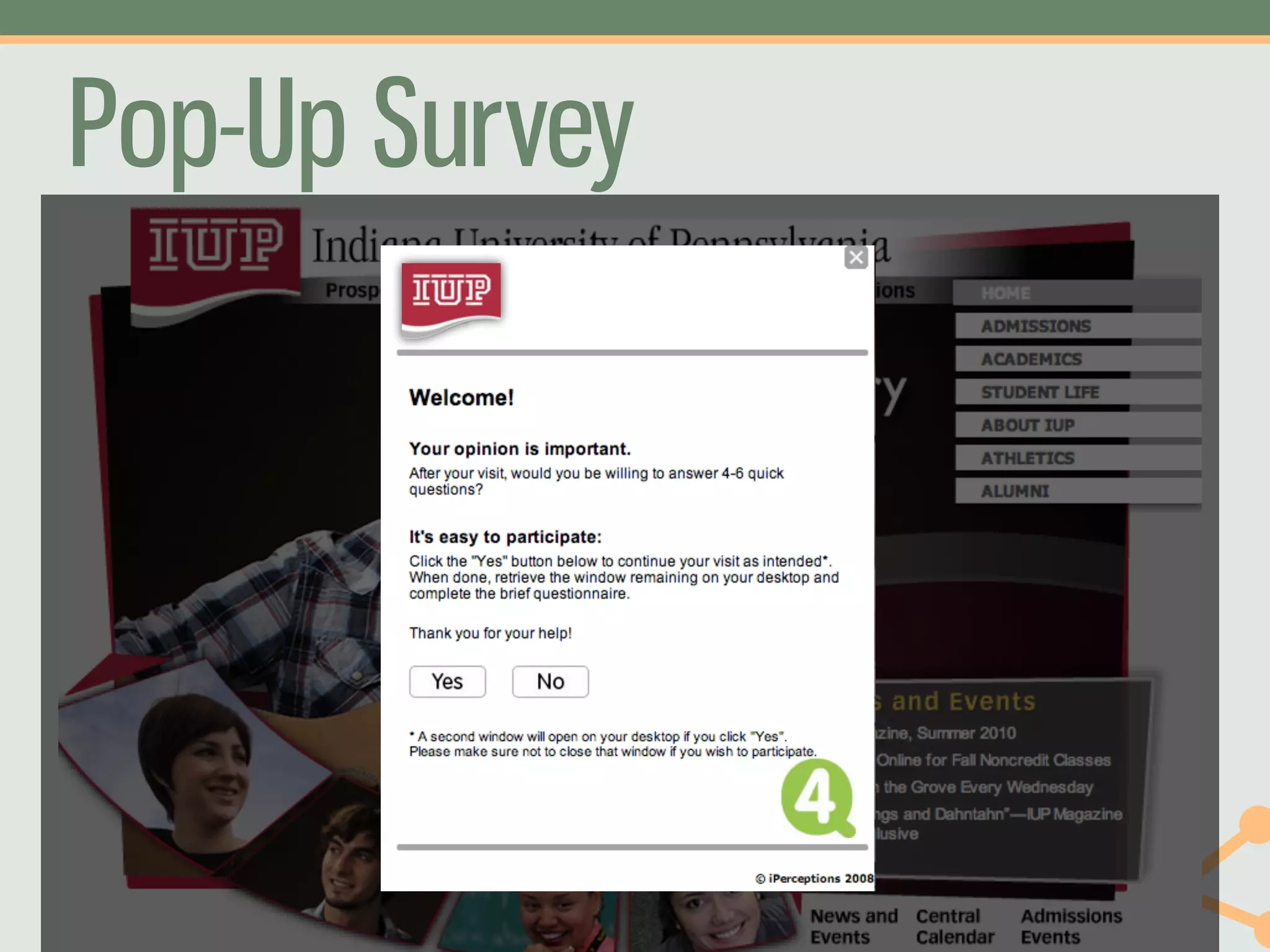
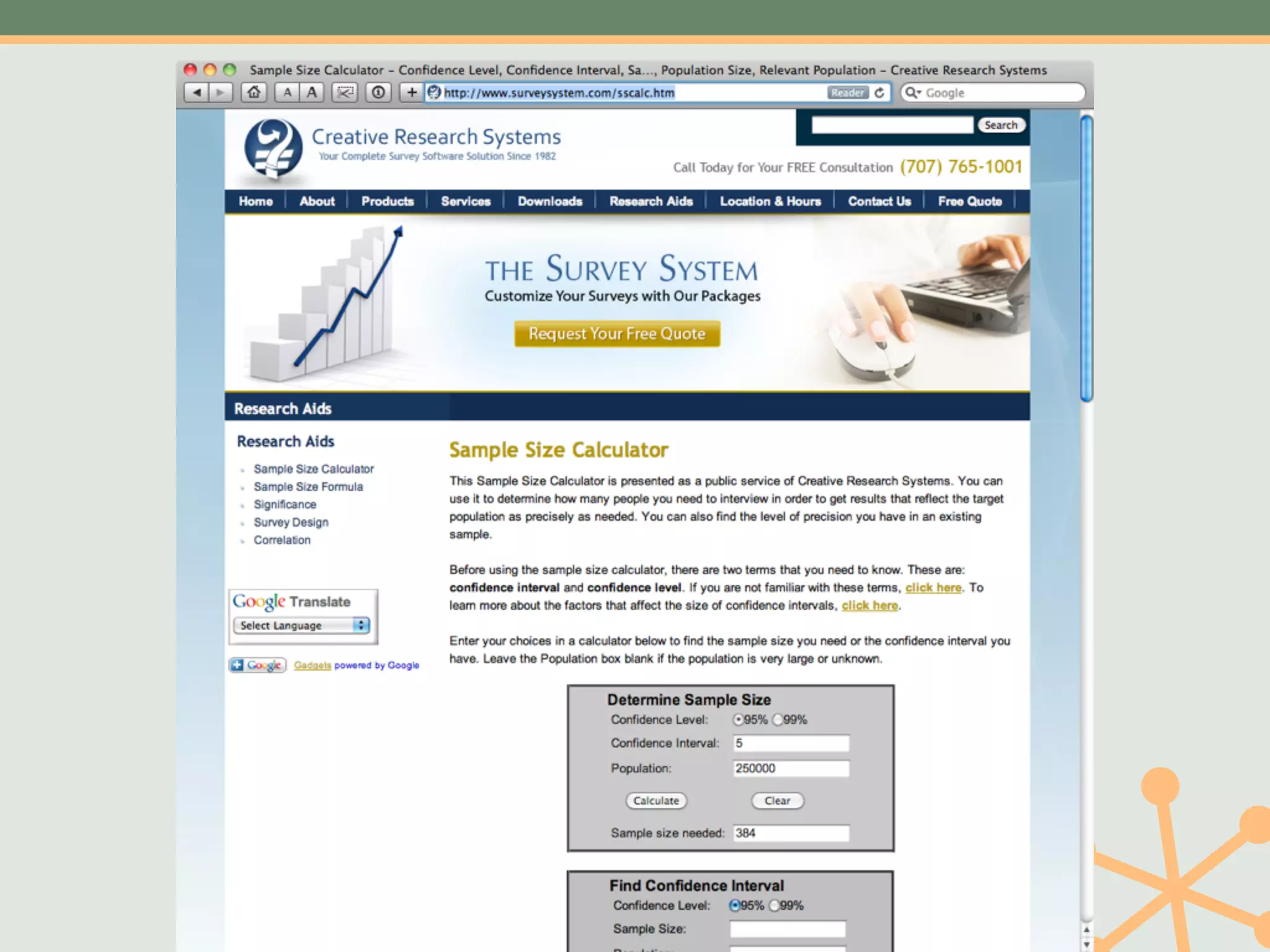
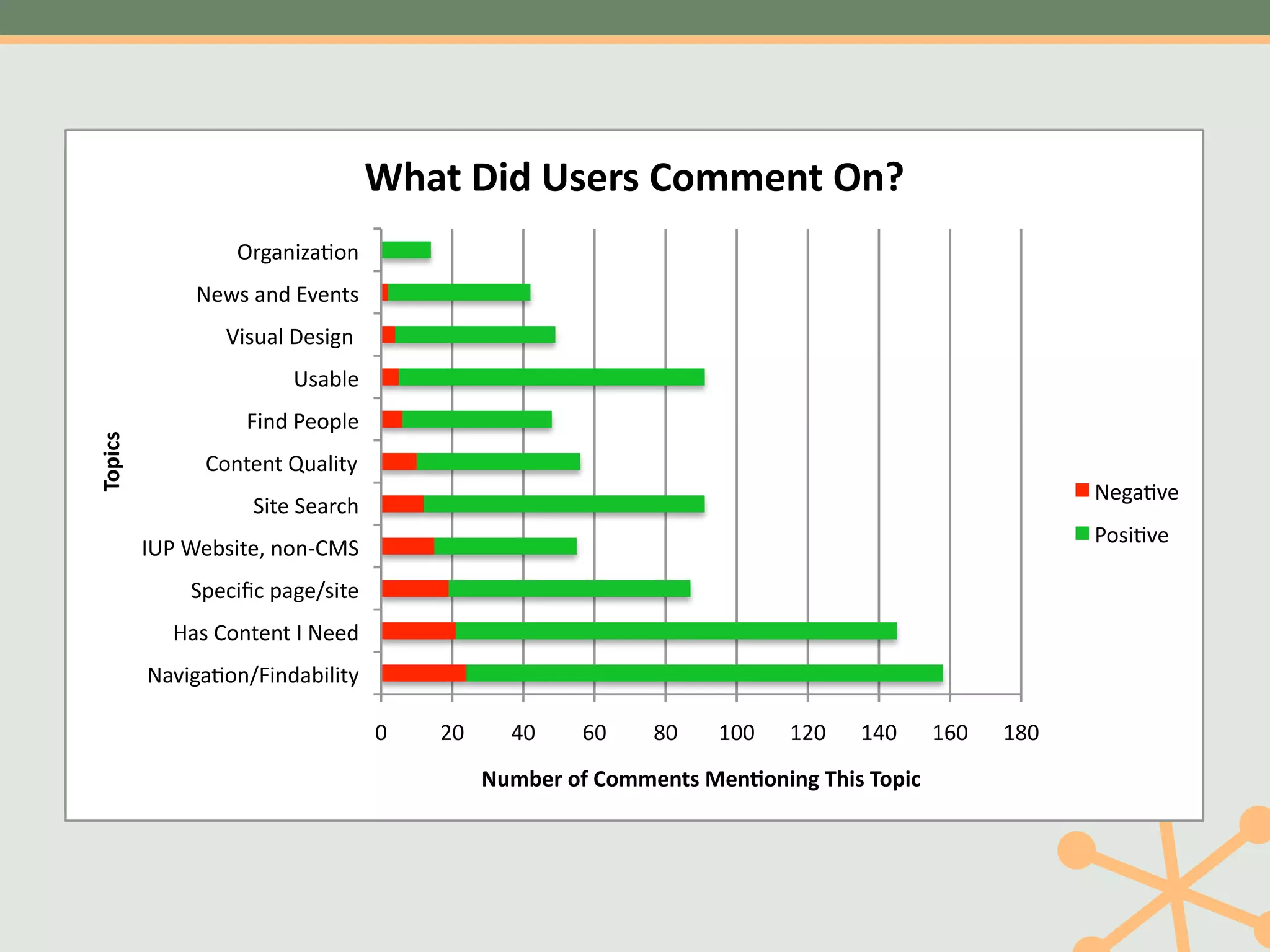
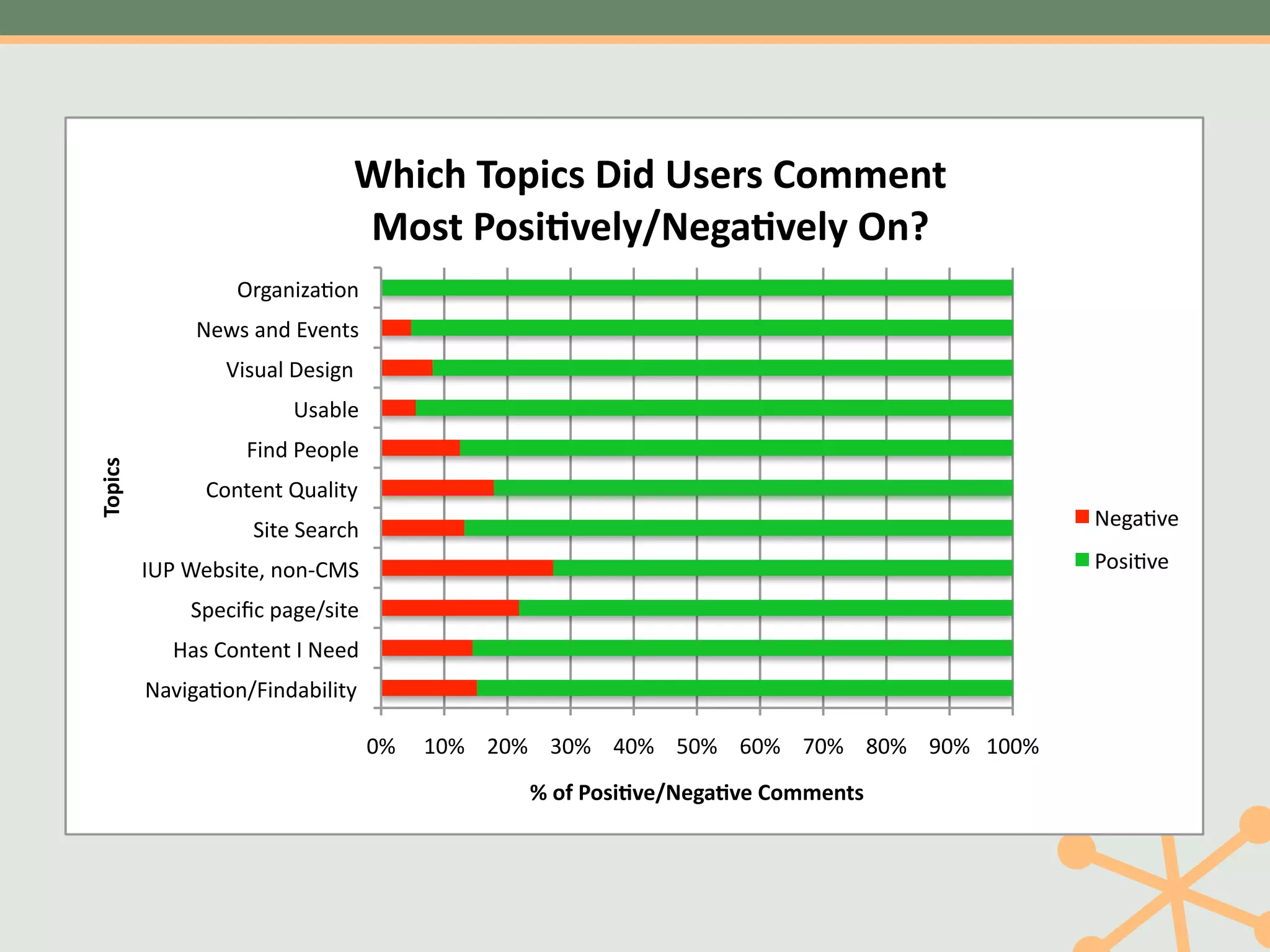
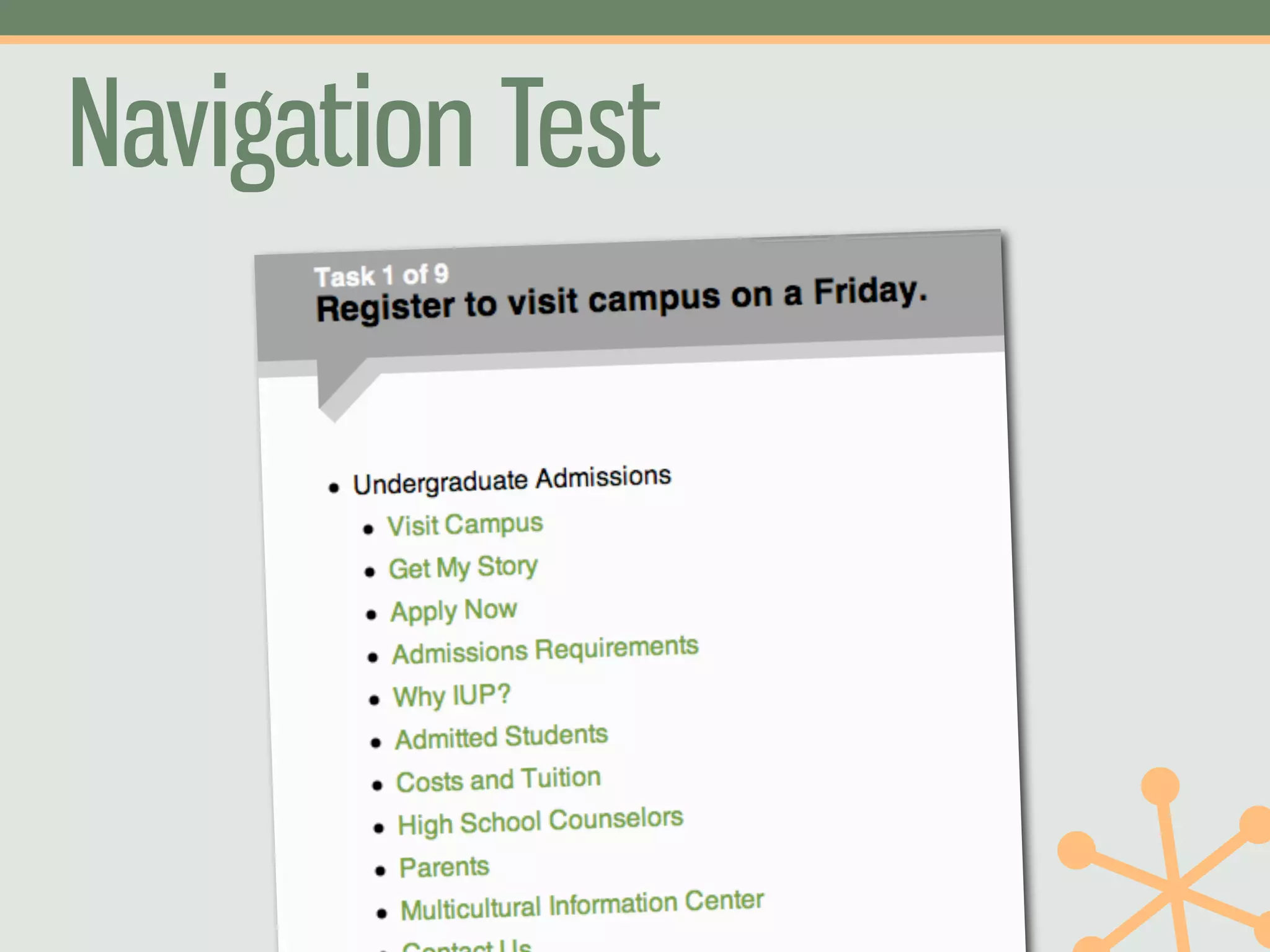
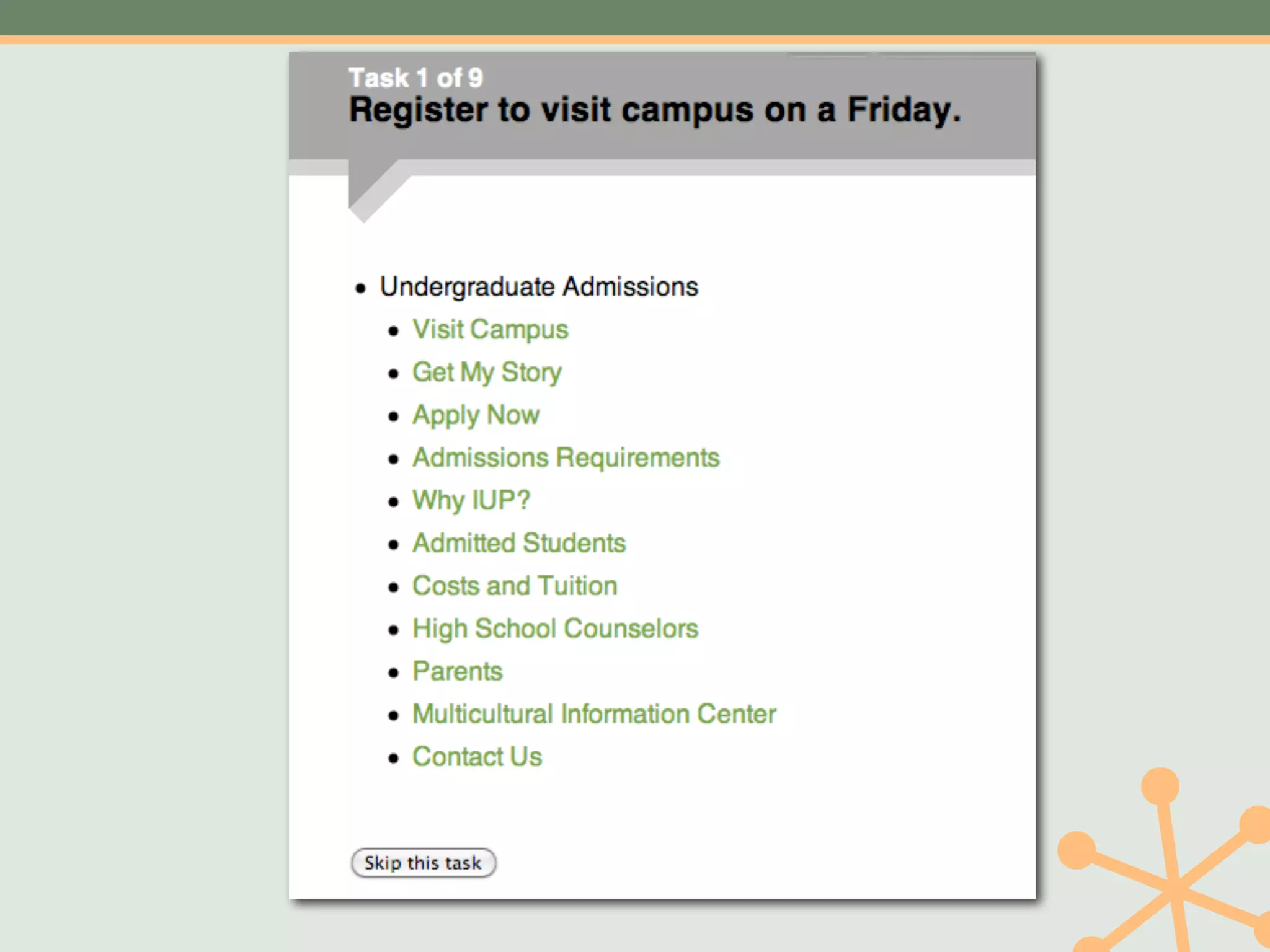
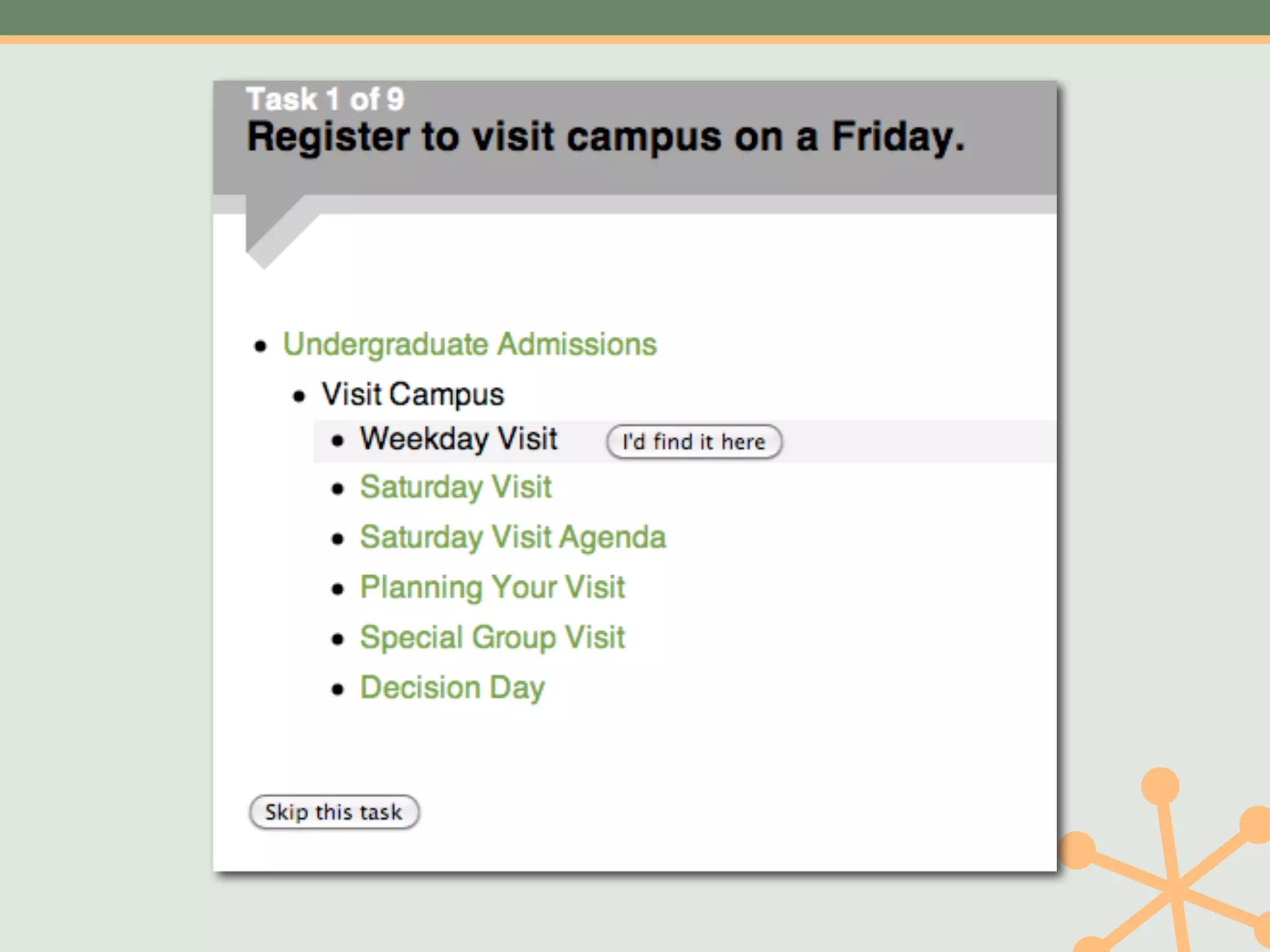
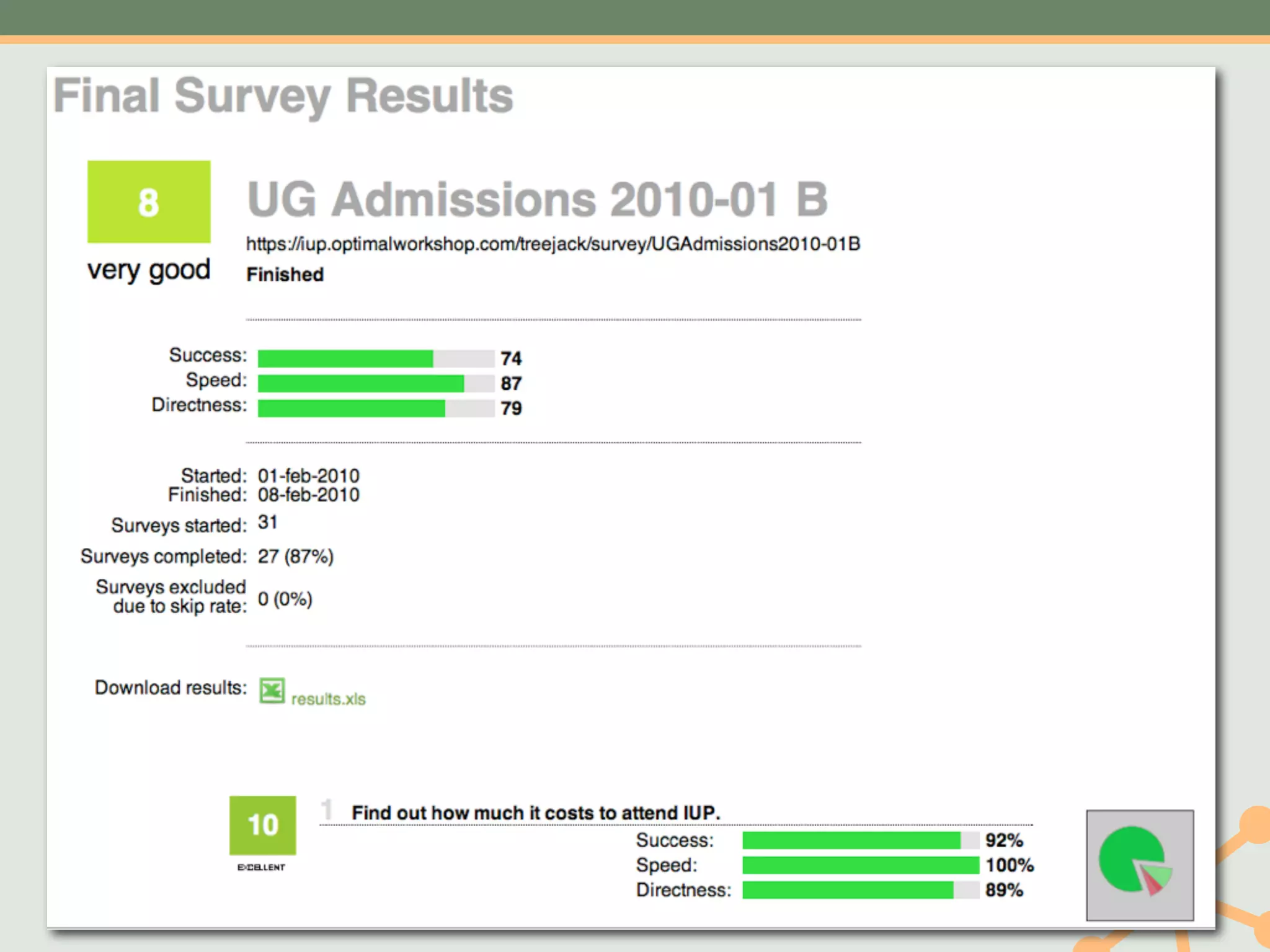
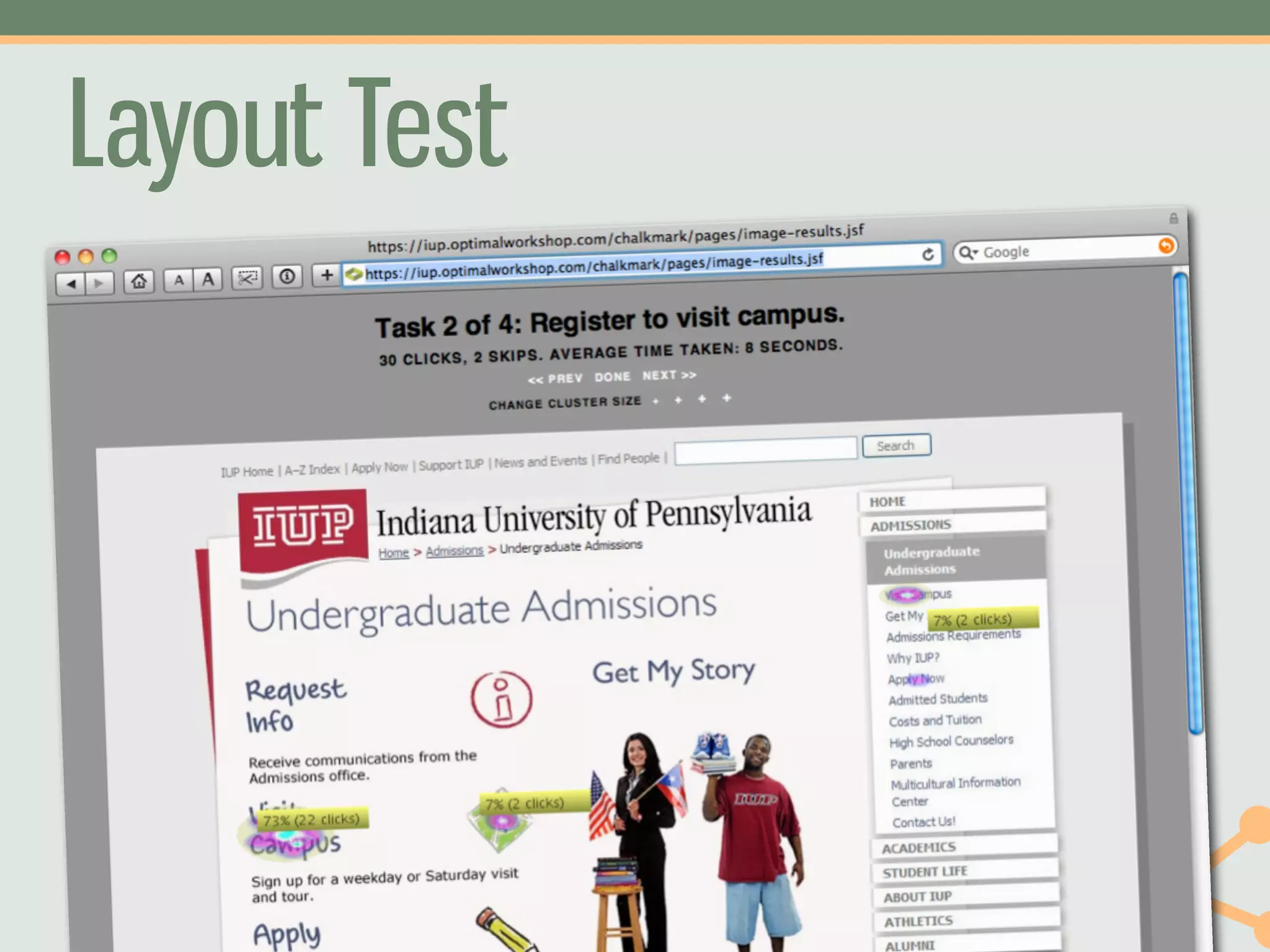
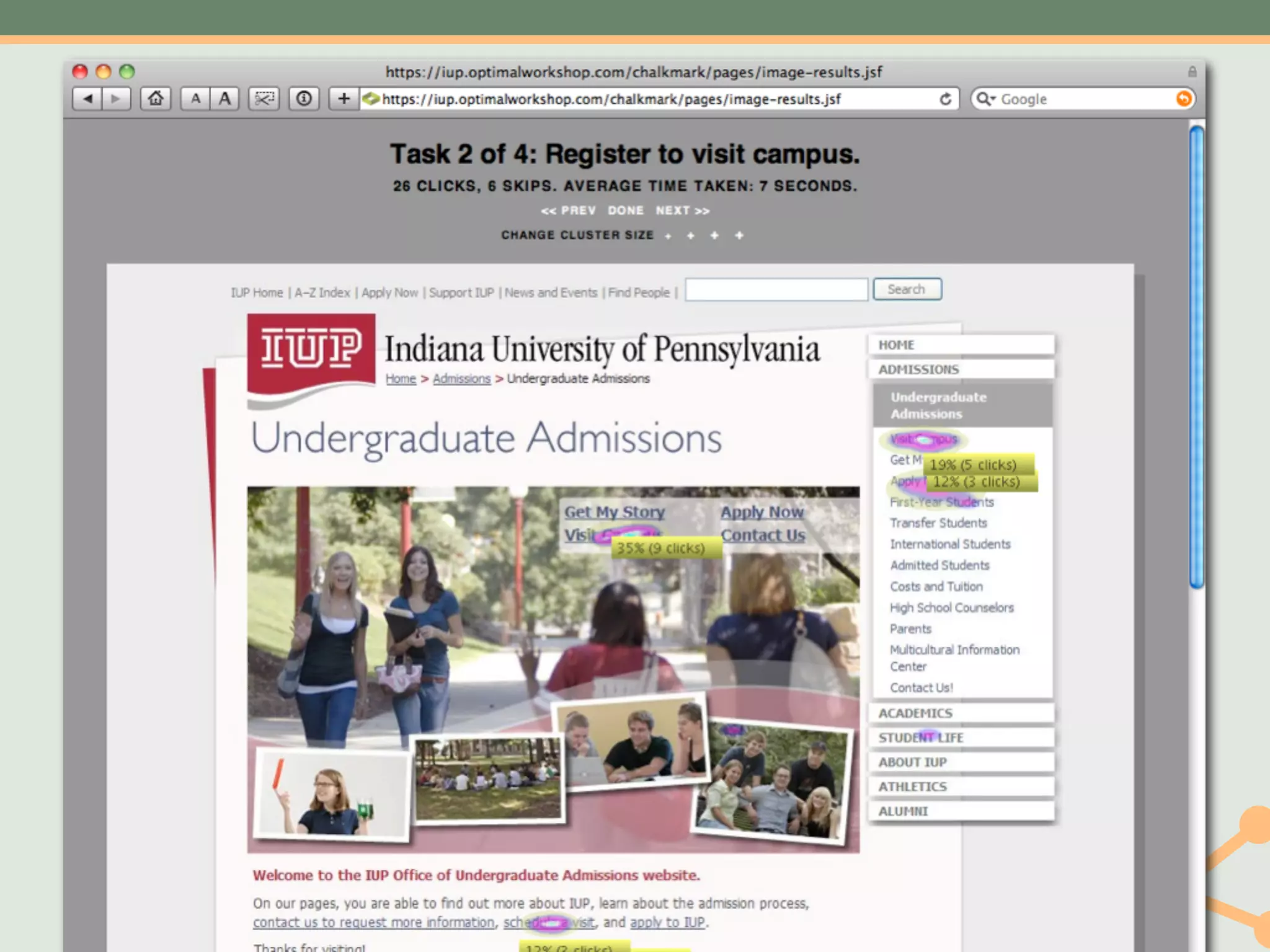
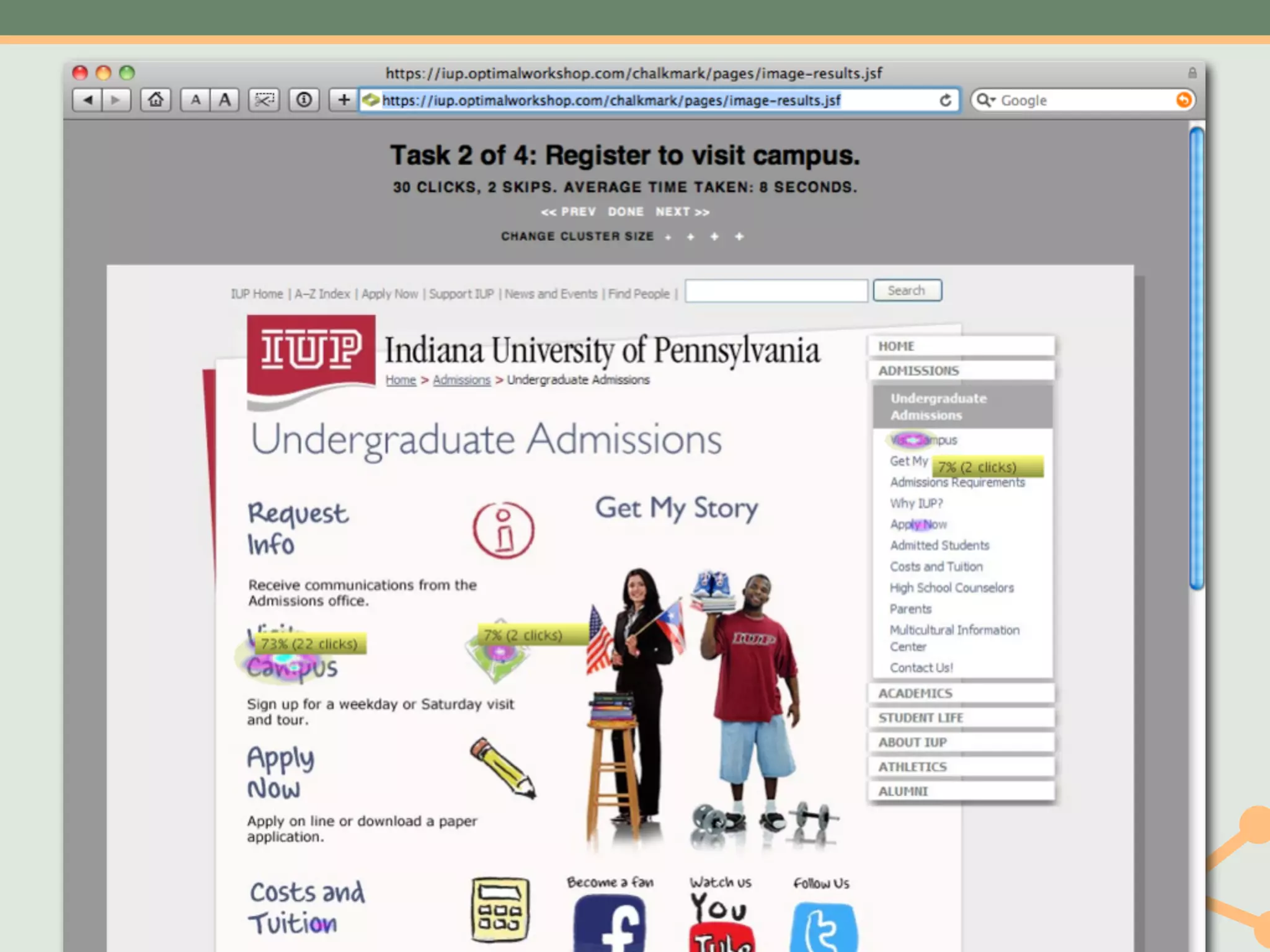
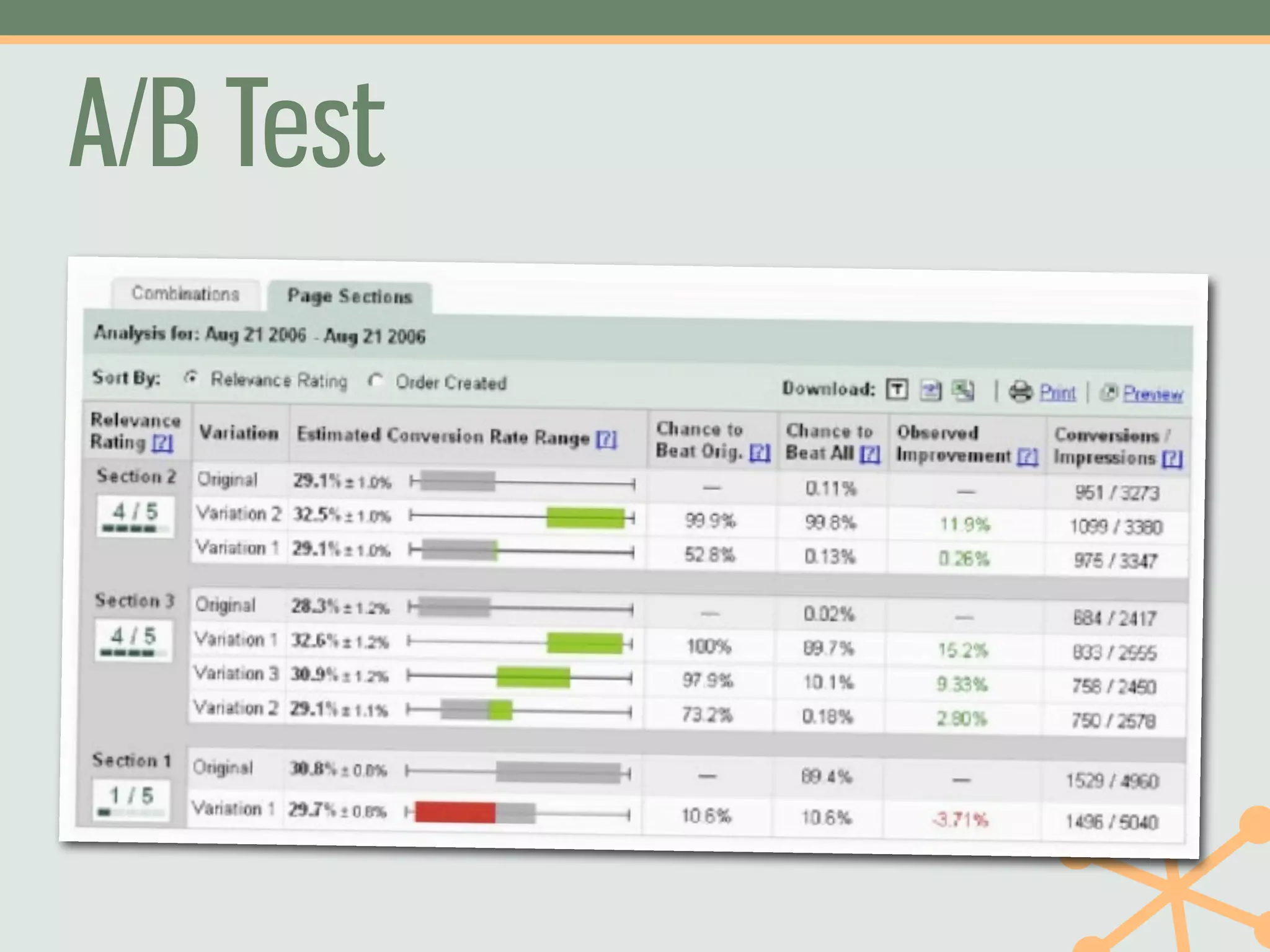
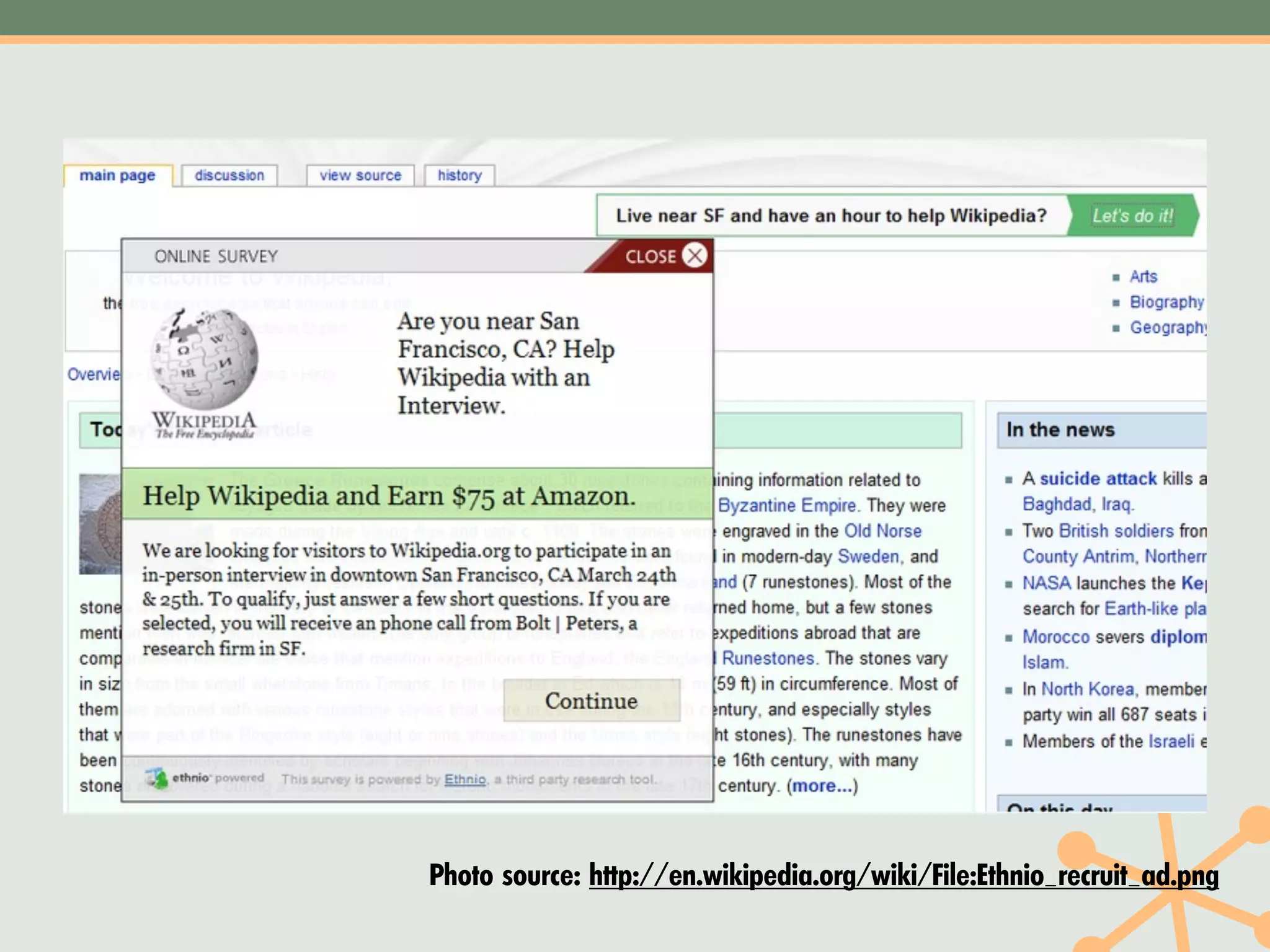
The document outlines a fast and affordable approach to creating a user research program, emphasizing actionable insights for improving websites. It details a structured user research process, including framing questions, selecting study types, and engaging participants, while also providing tools and metrics like Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and user personas. The goal is to integrate user research into regular operations to enhance user experience and achieve organizational objectives.