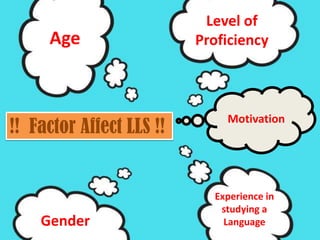
The document discusses five main factors that can affect language learning strategies: gender, age, level of proficiency, motivation, and experience studying a language. Regarding gender, several studies found that female students tend to use compensation and affective strategies more than males. Younger learners rely more on cognitive and social strategies, while older adults use metacognitive self-management strategies more. Beginner language learners employ fewer strategies than intermediate learners. Motivation is a primary driver of language learning, influencing how long and hard students pursue the language. Experience studying abroad positively impacts thinking and language learning abilities.