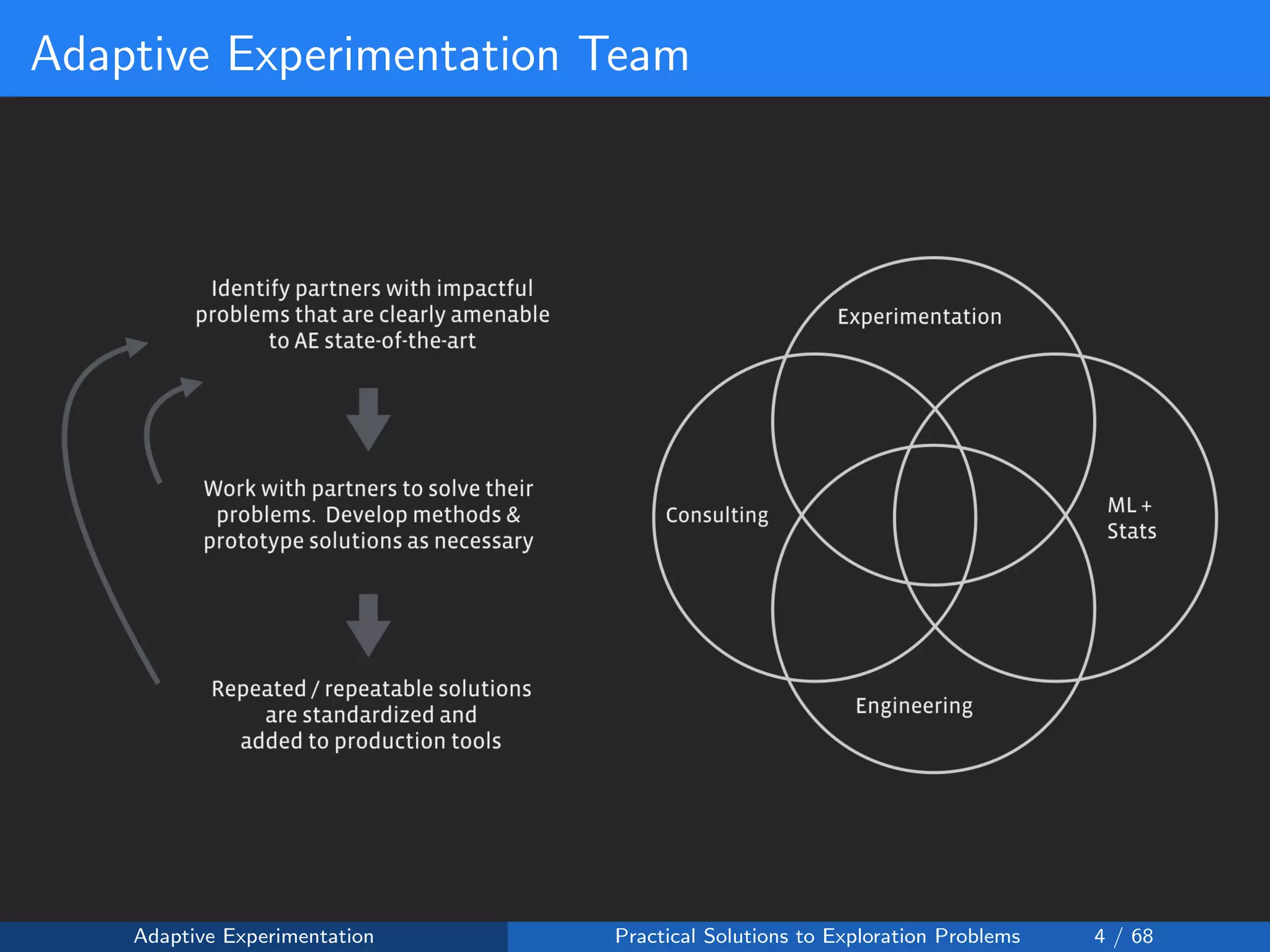
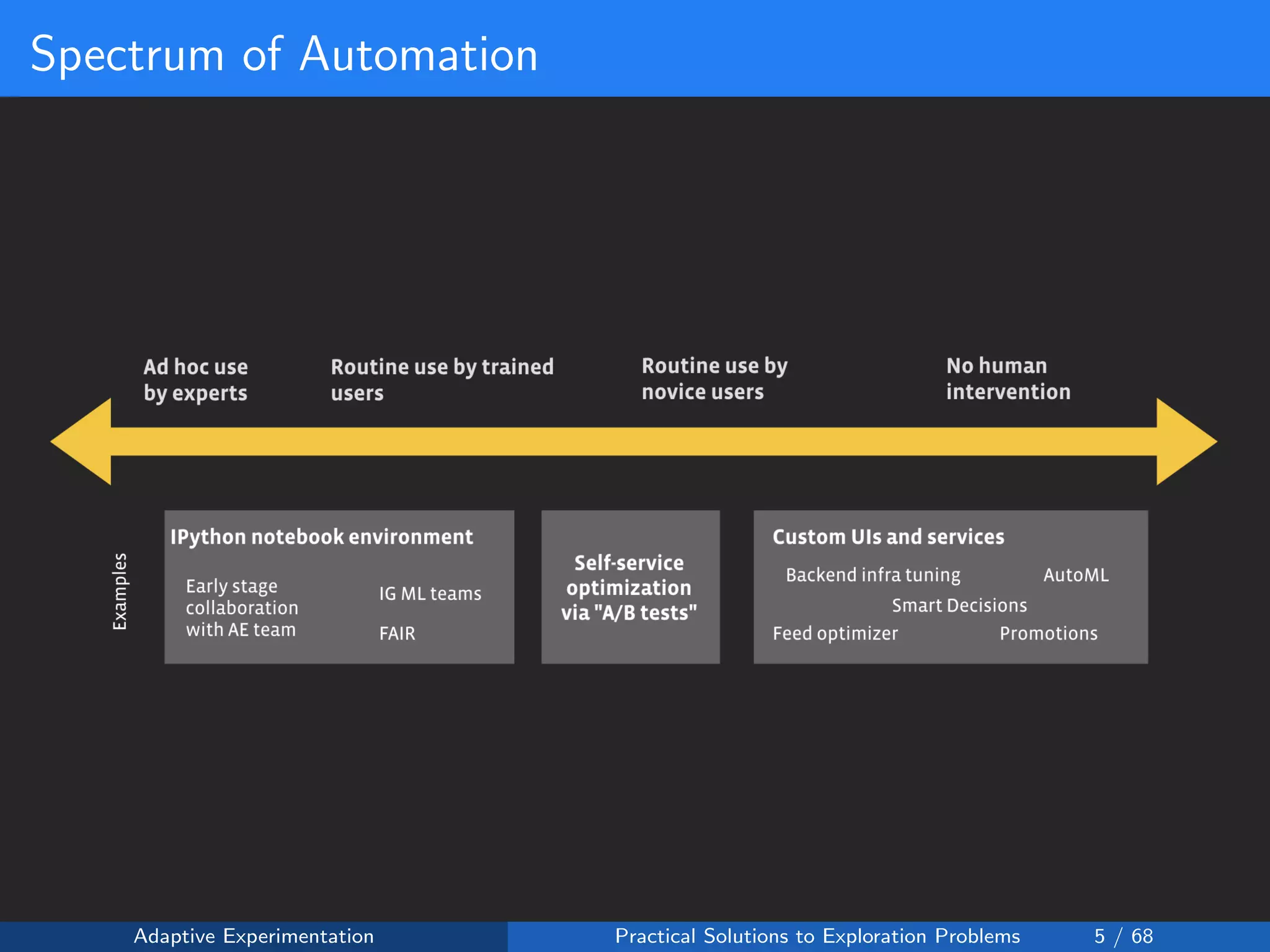
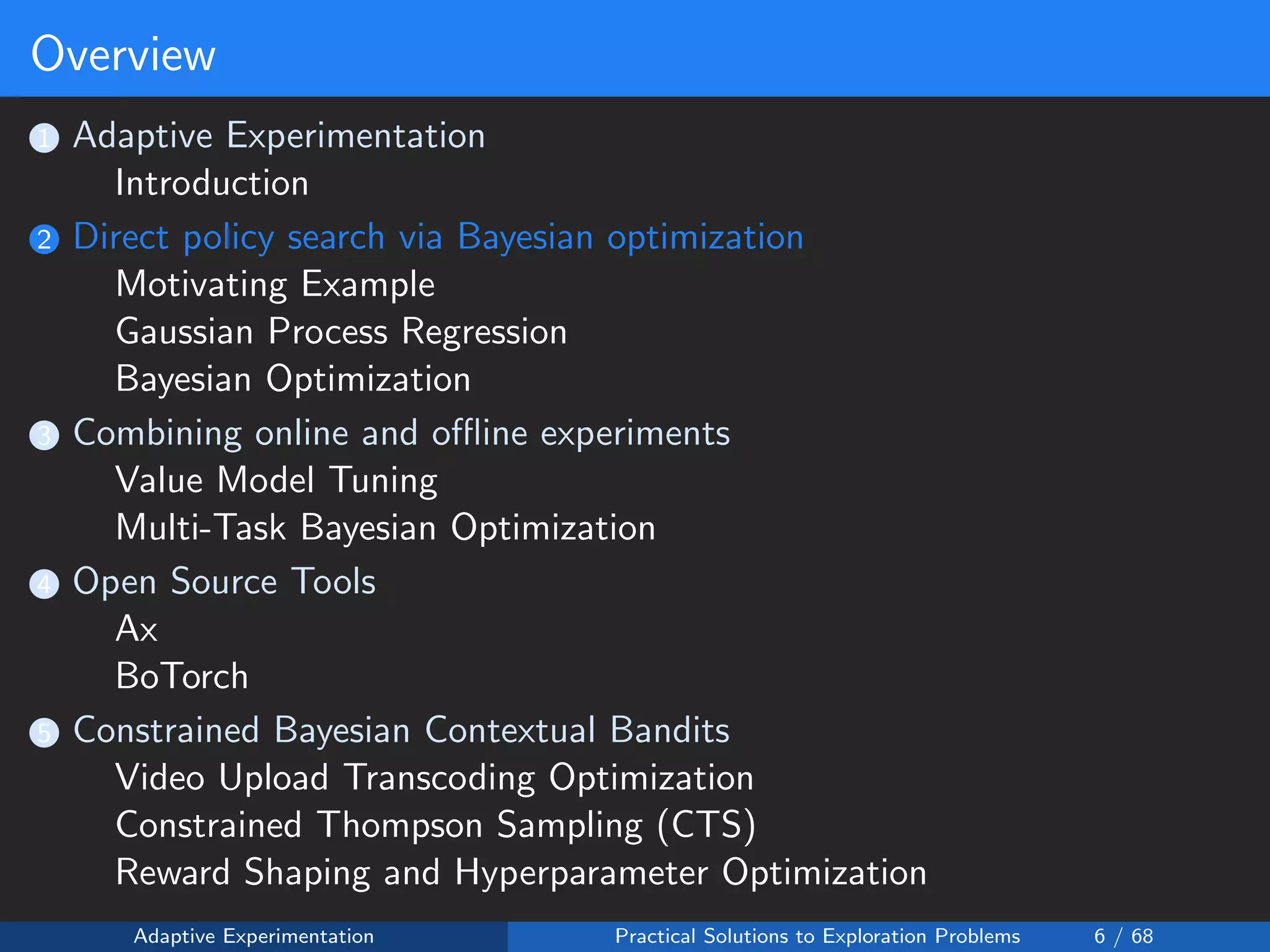
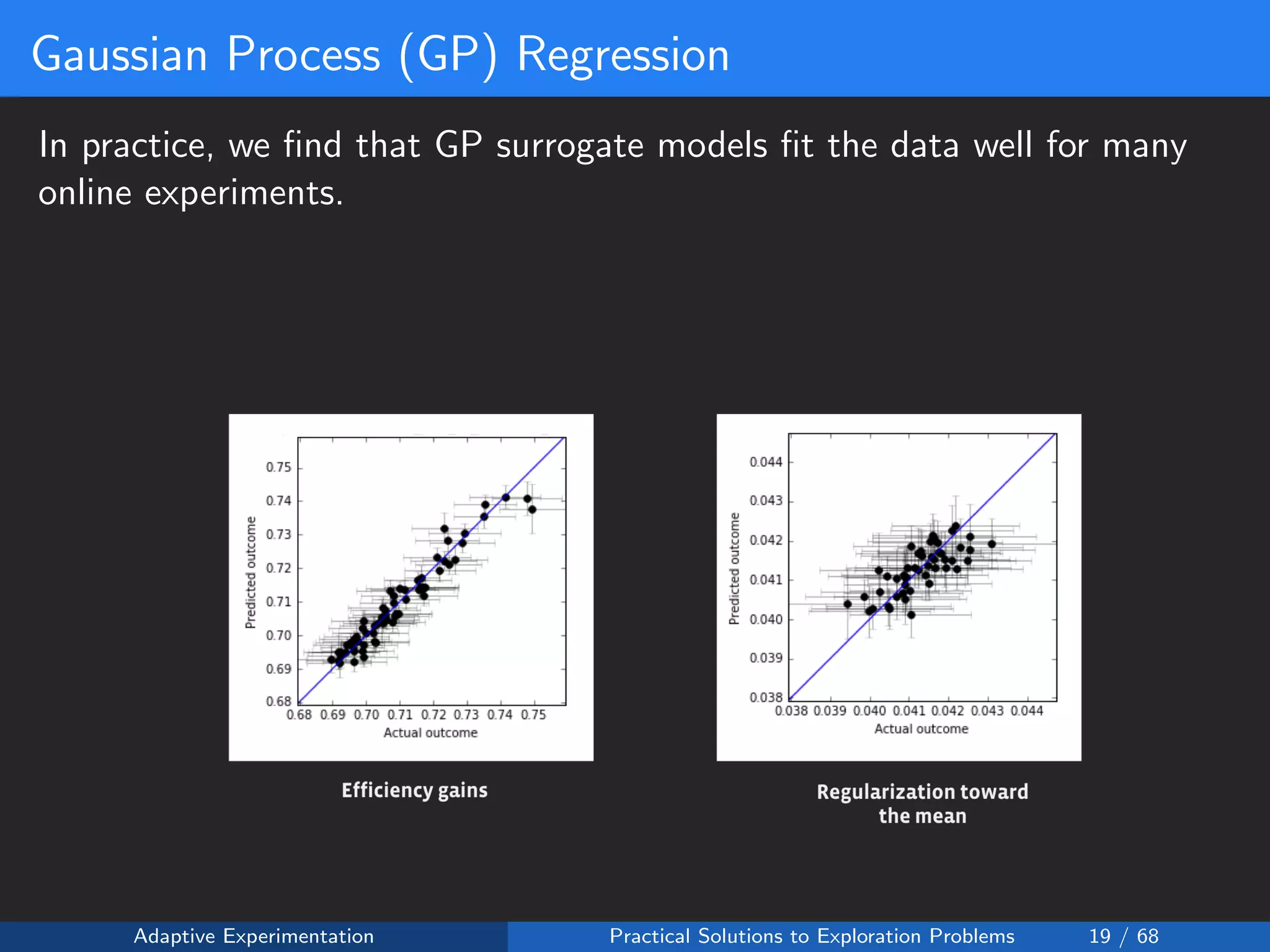
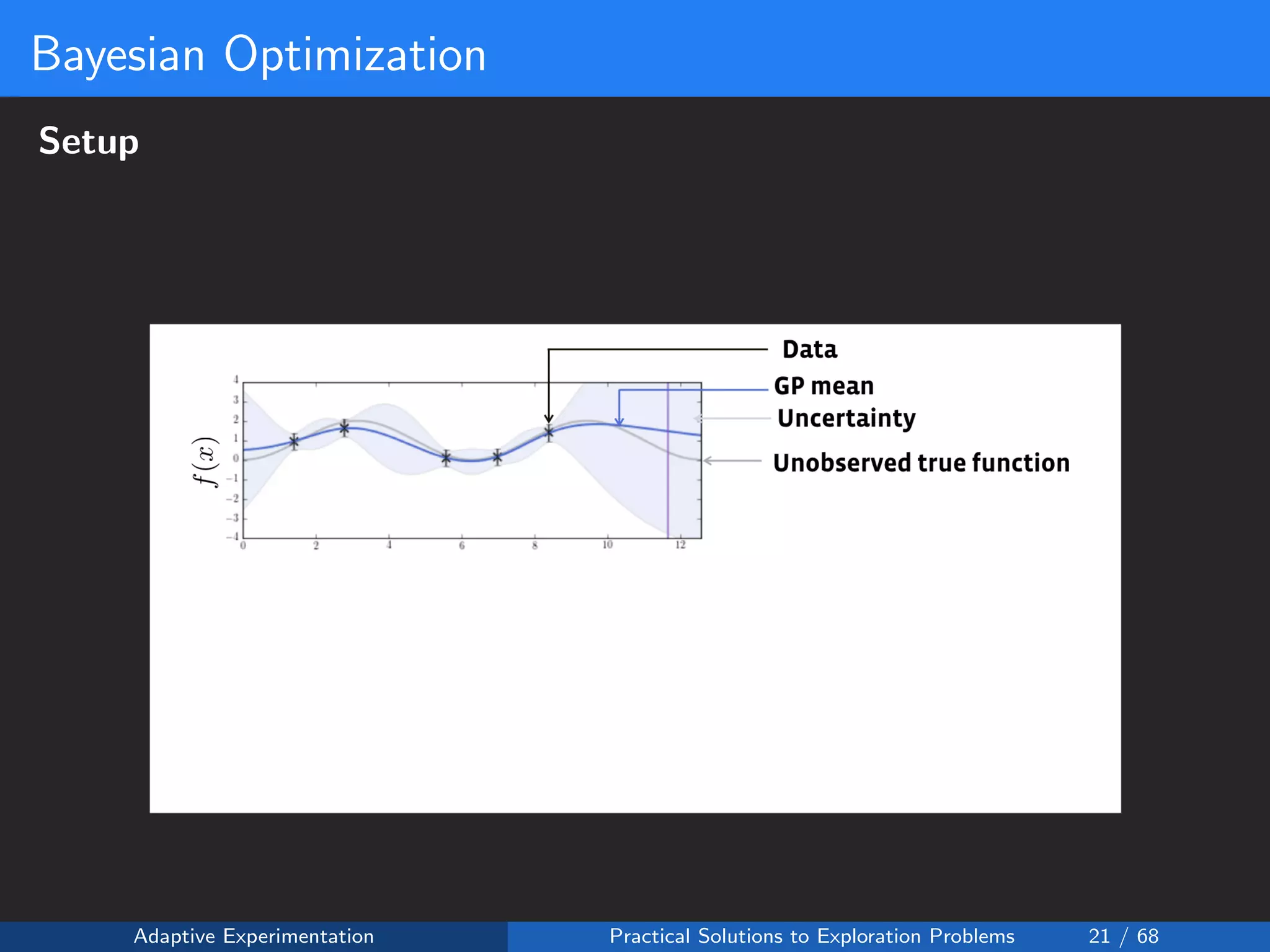
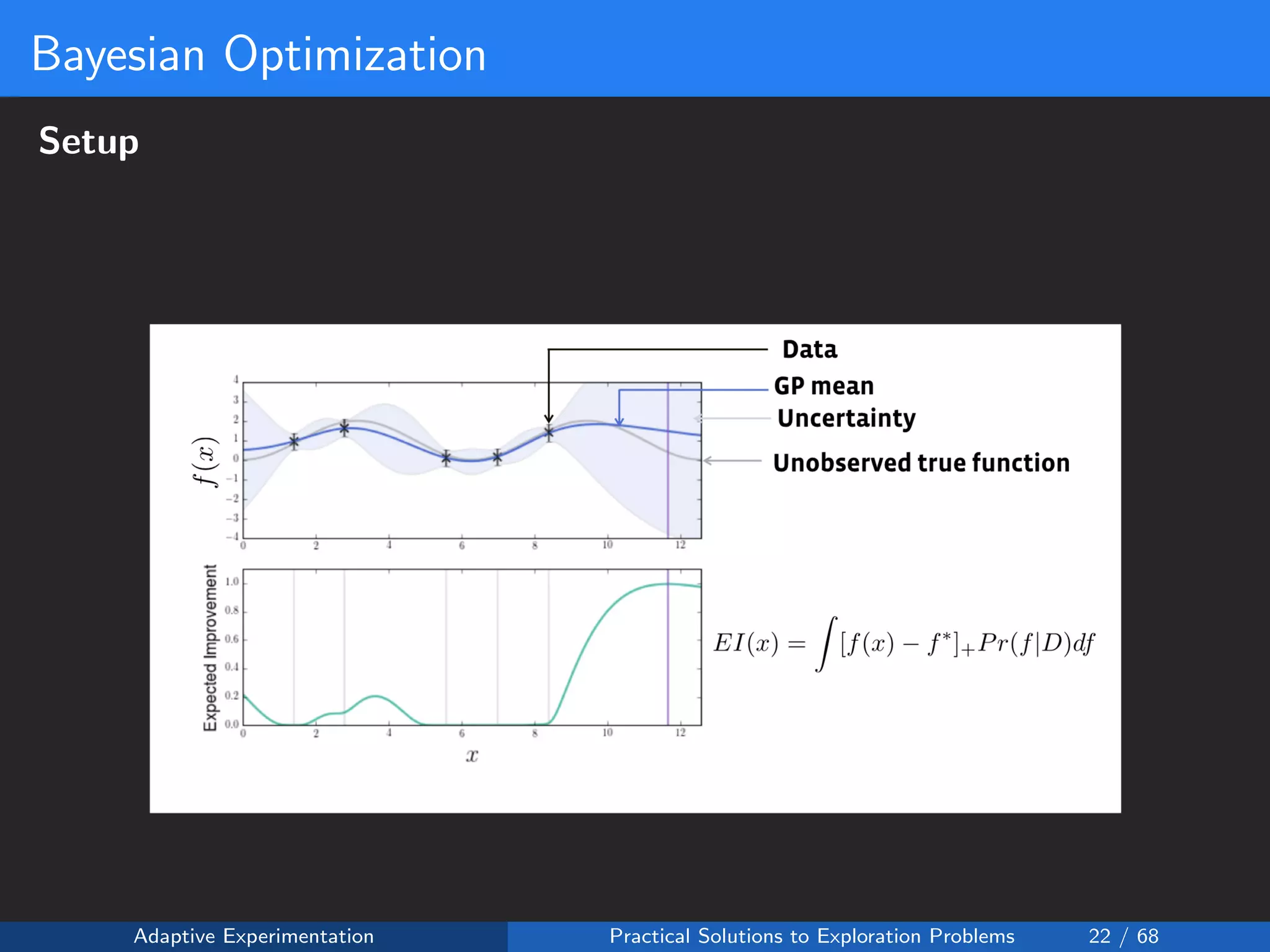
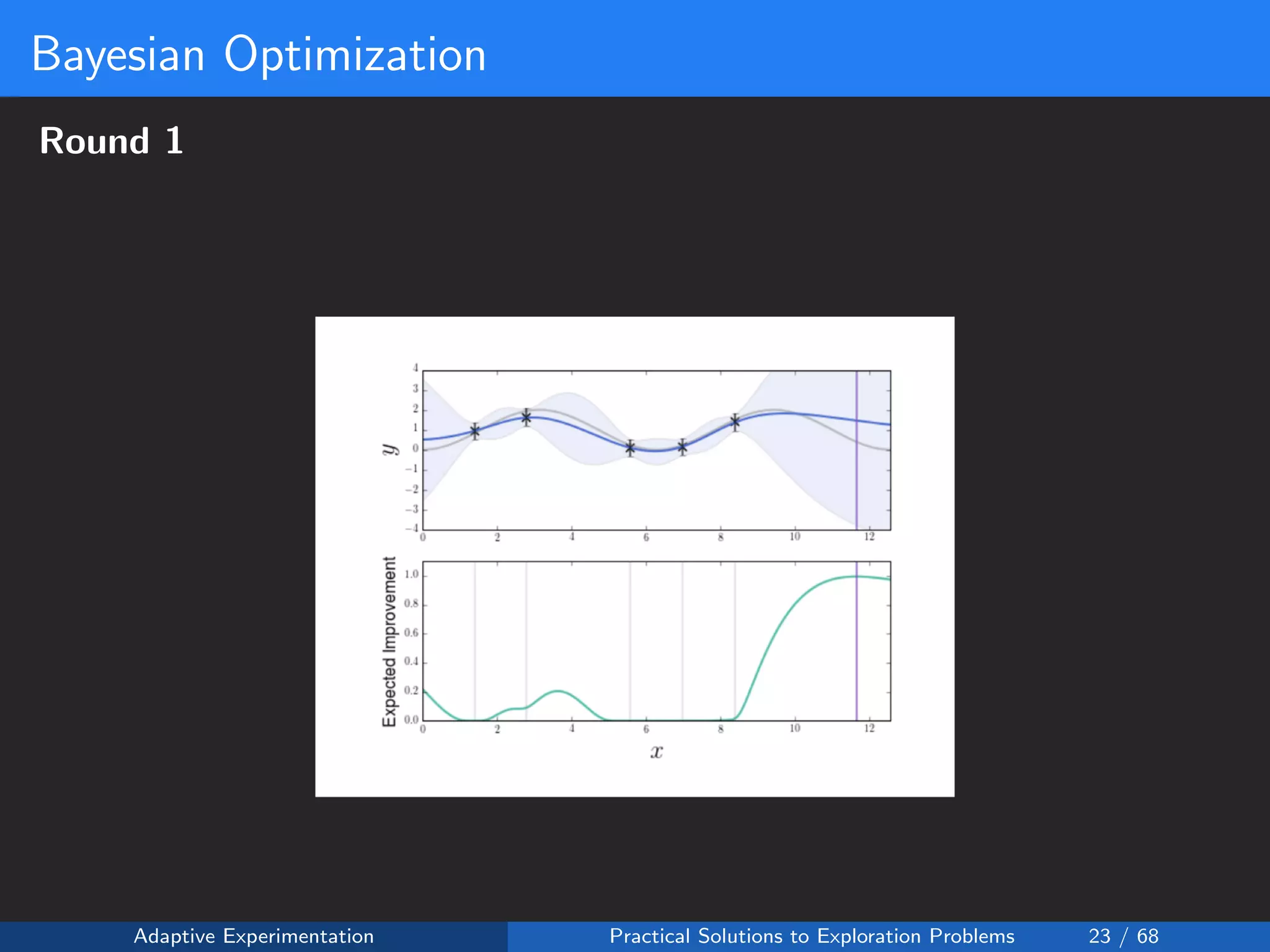
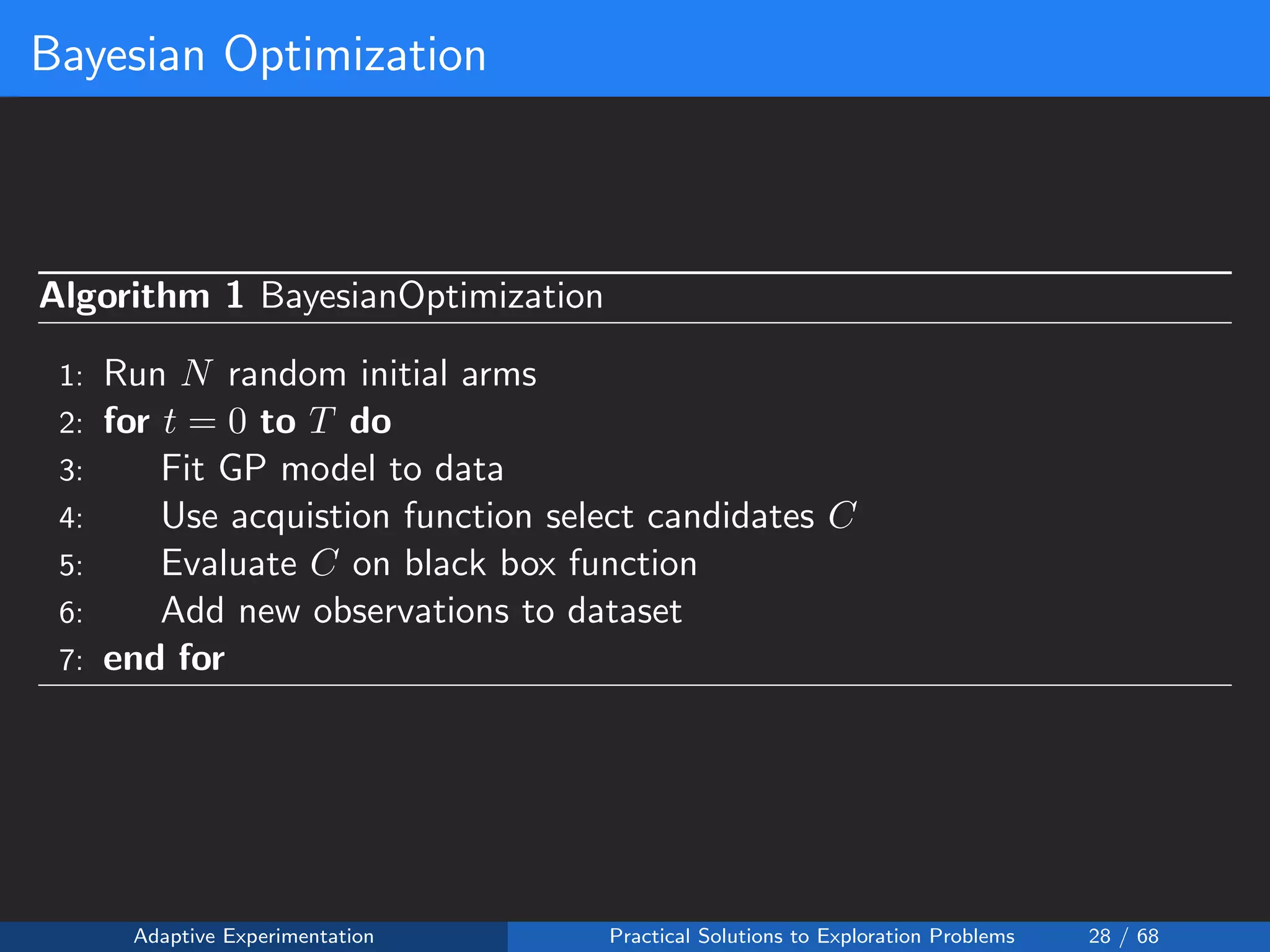
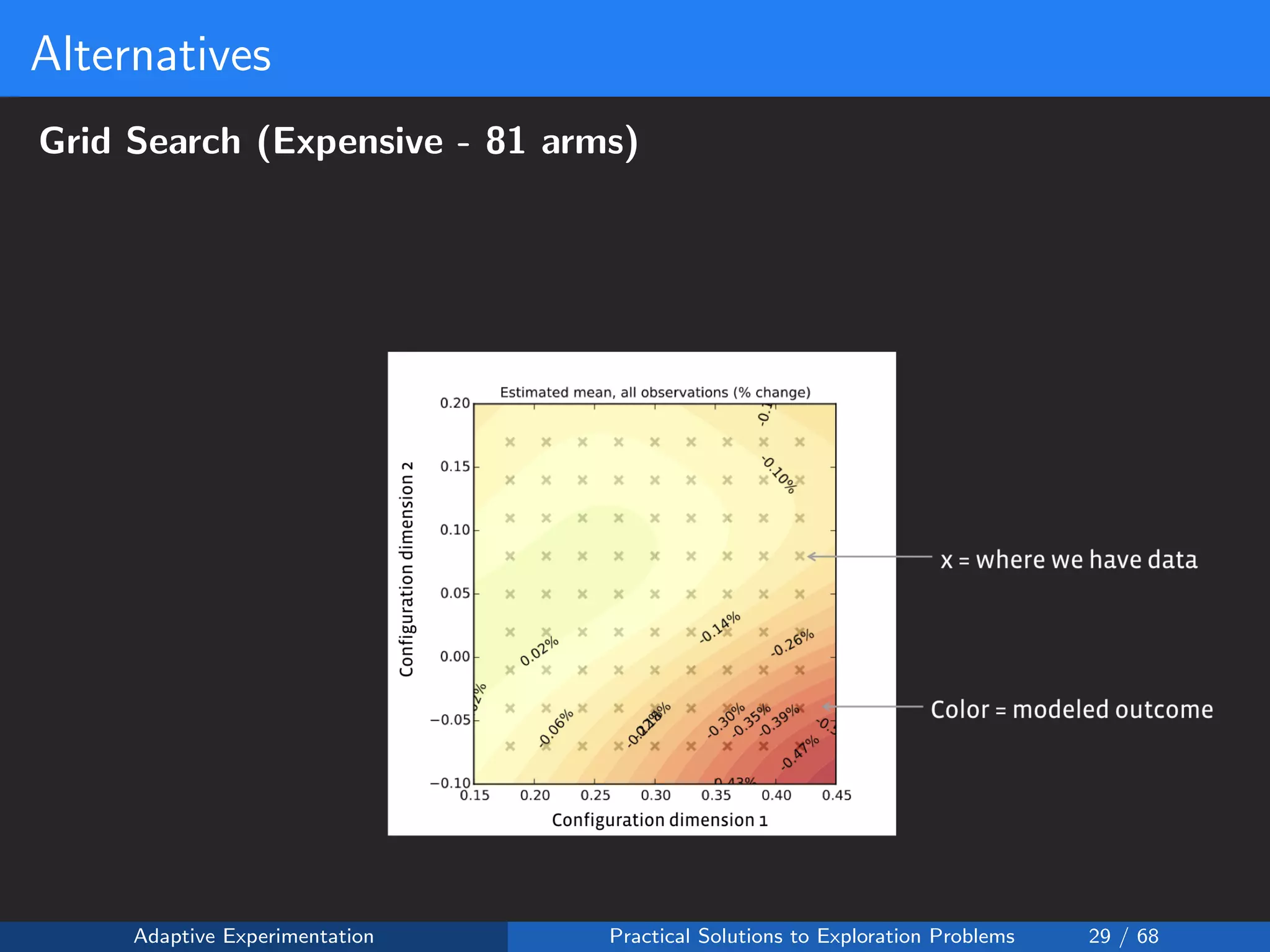
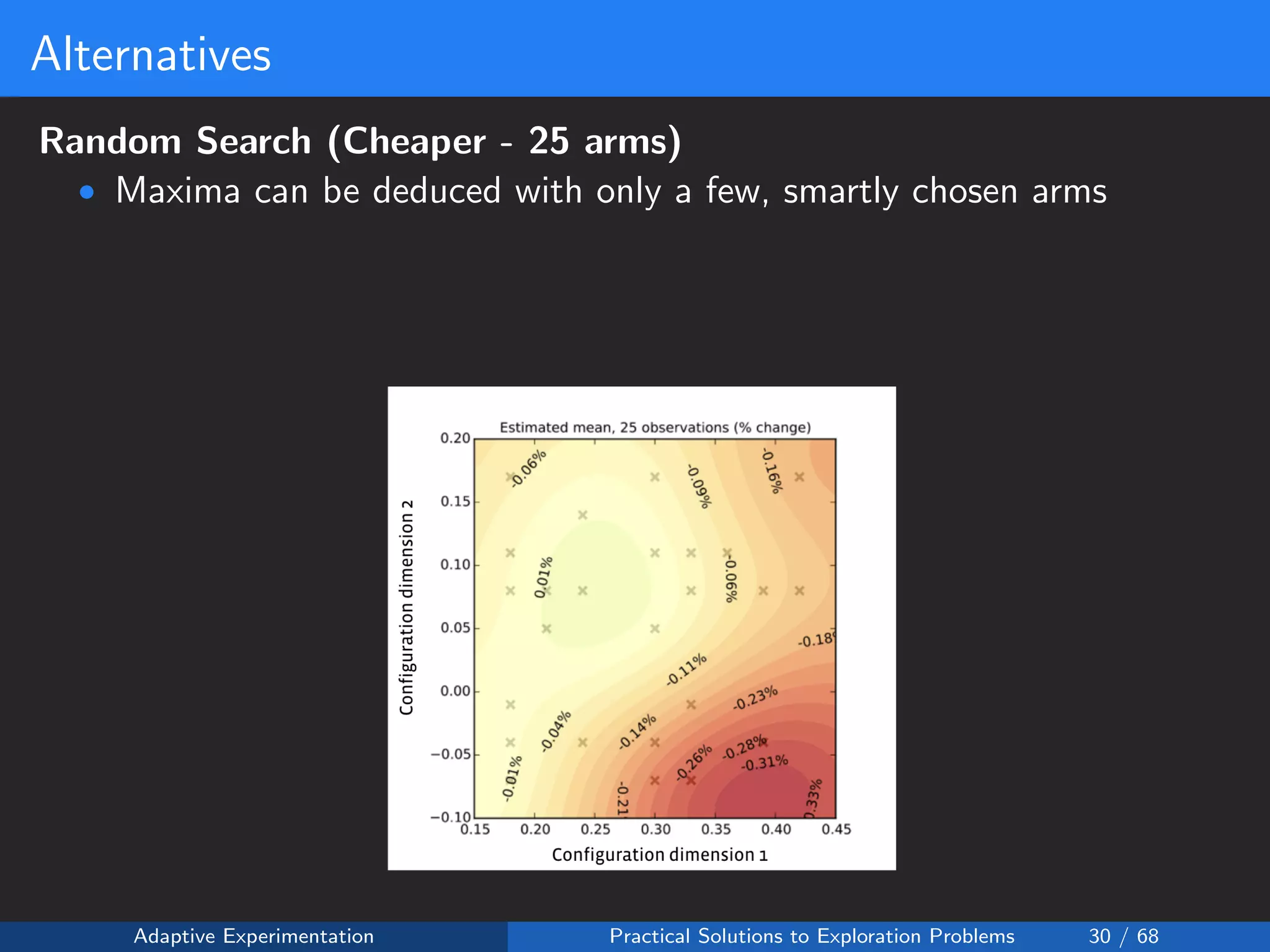
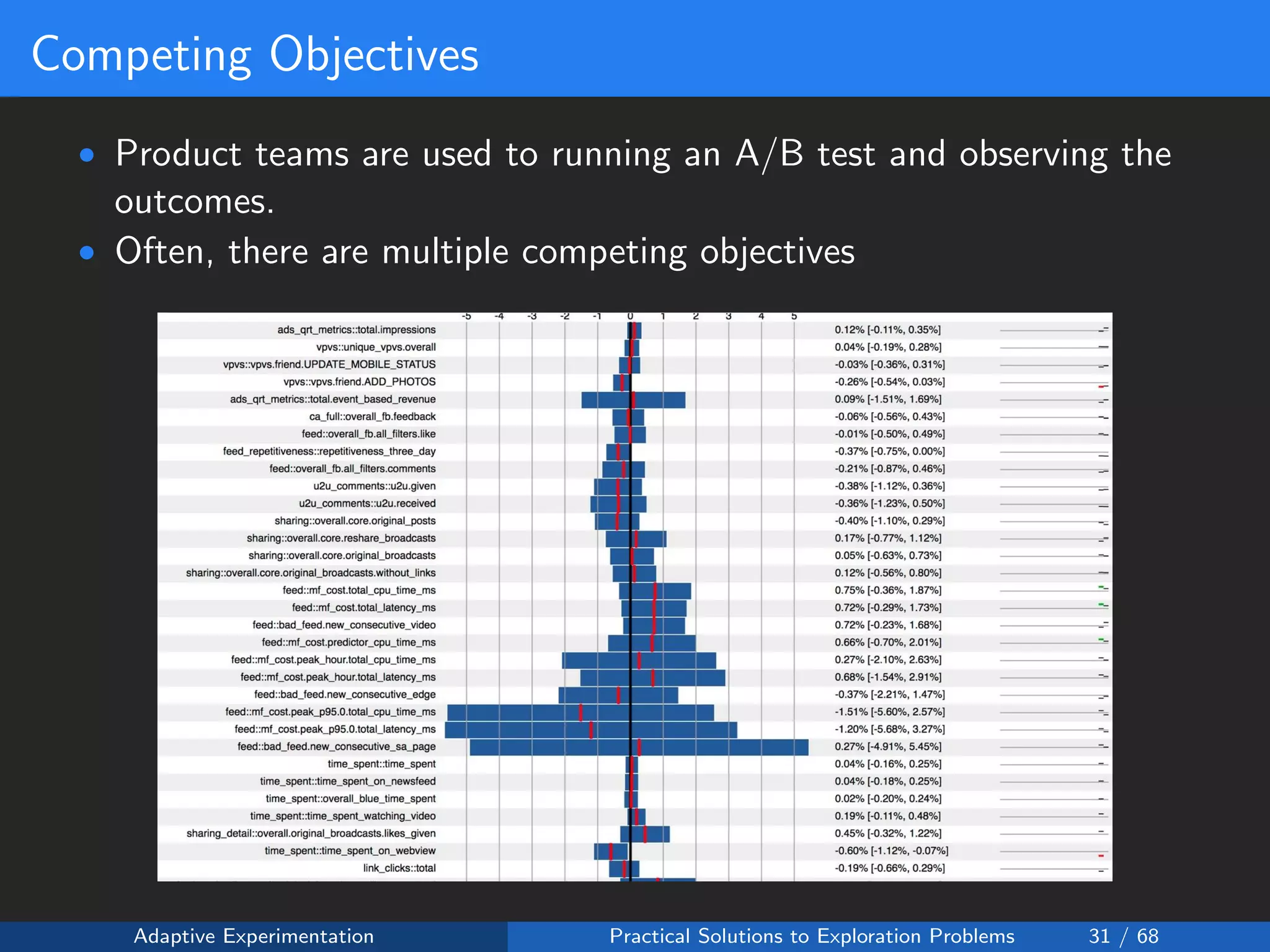
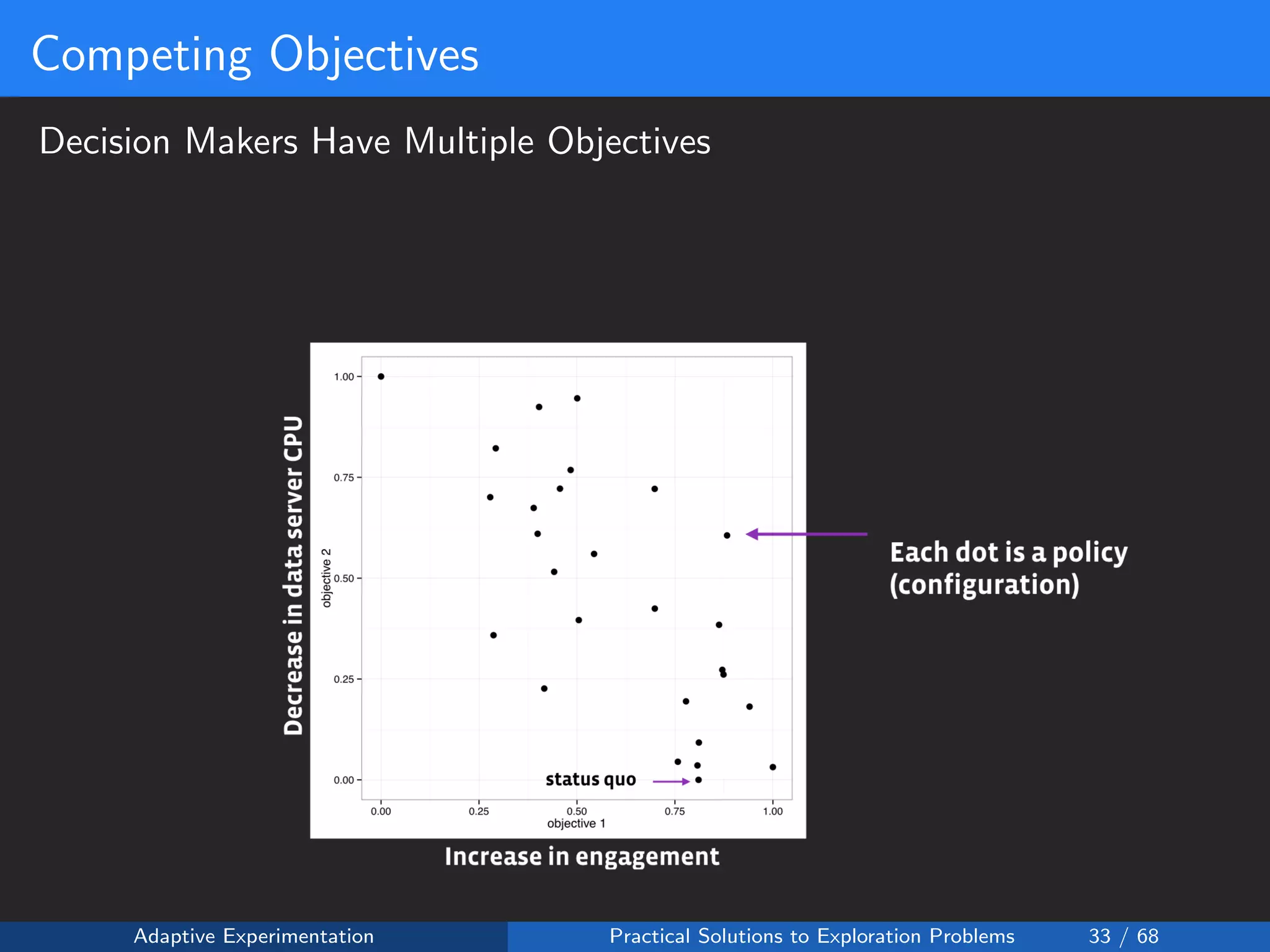
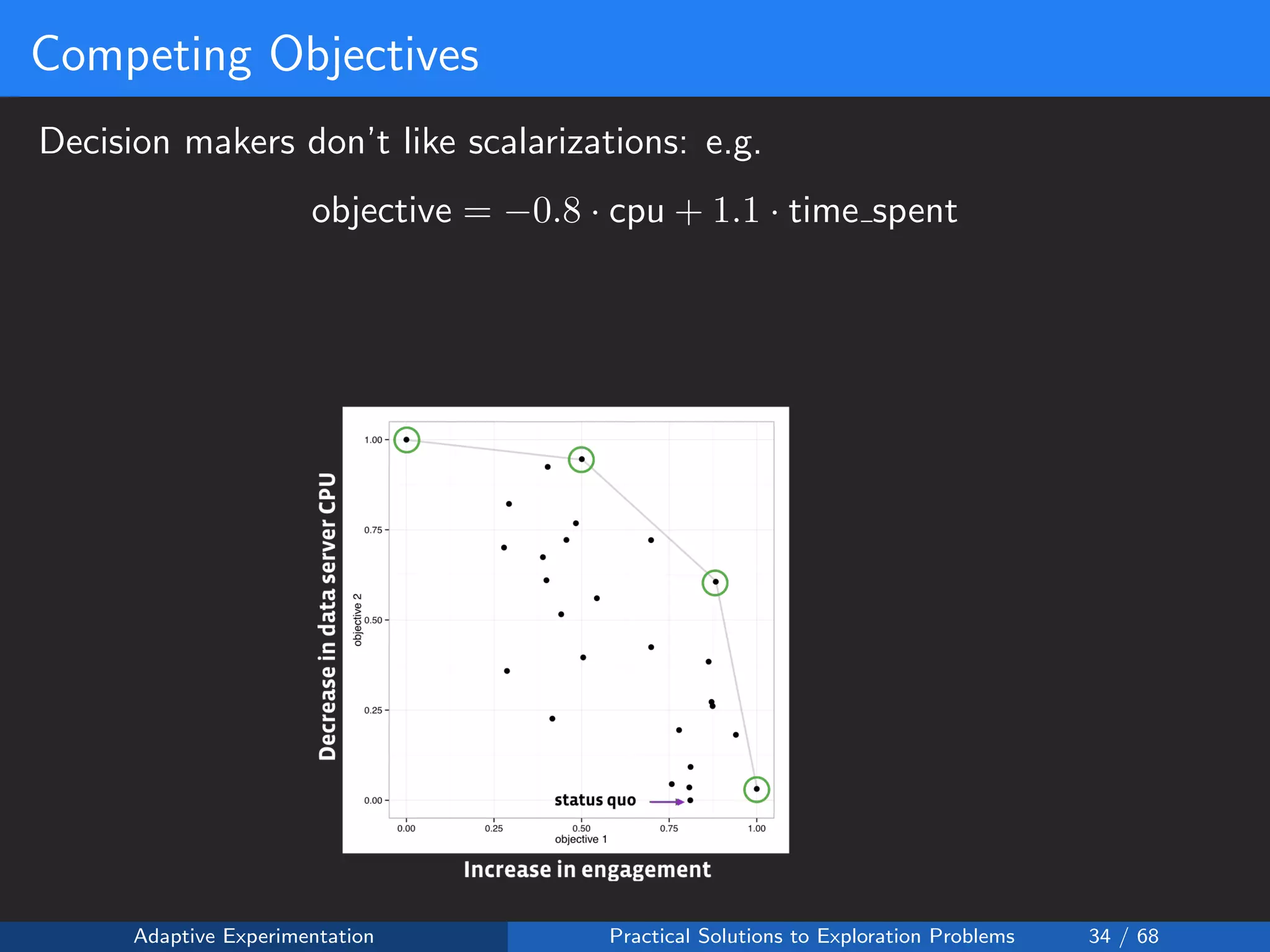
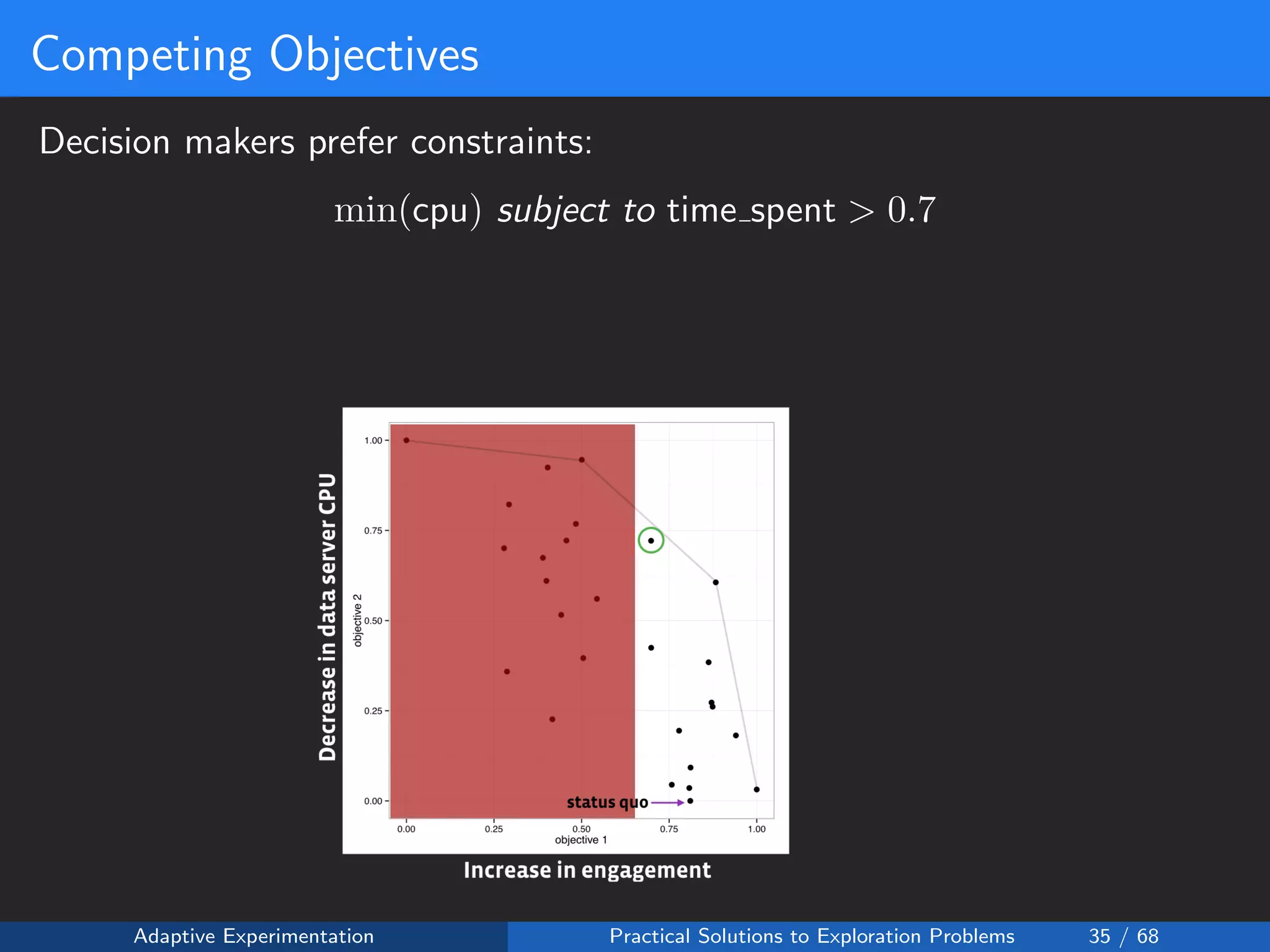
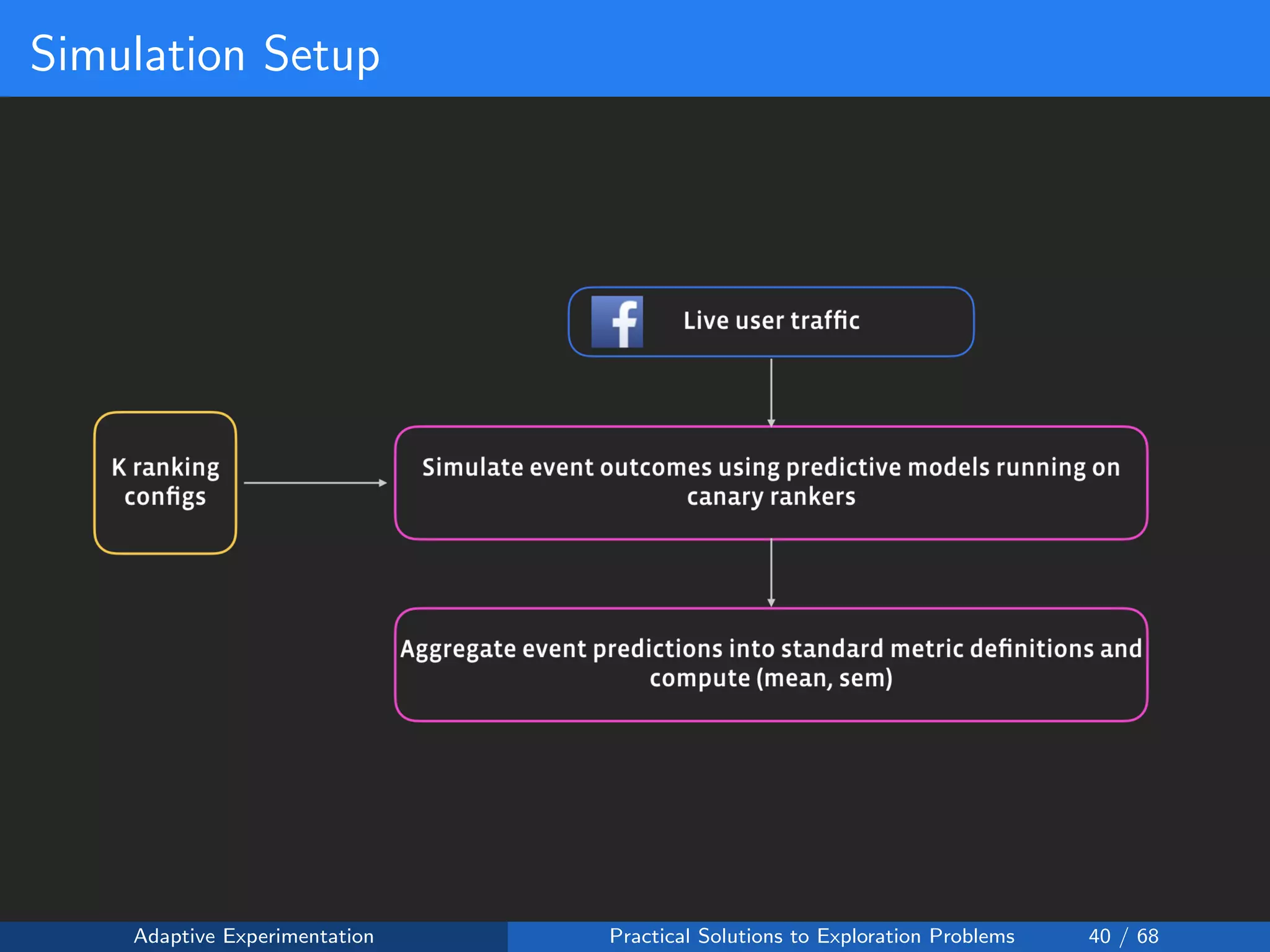
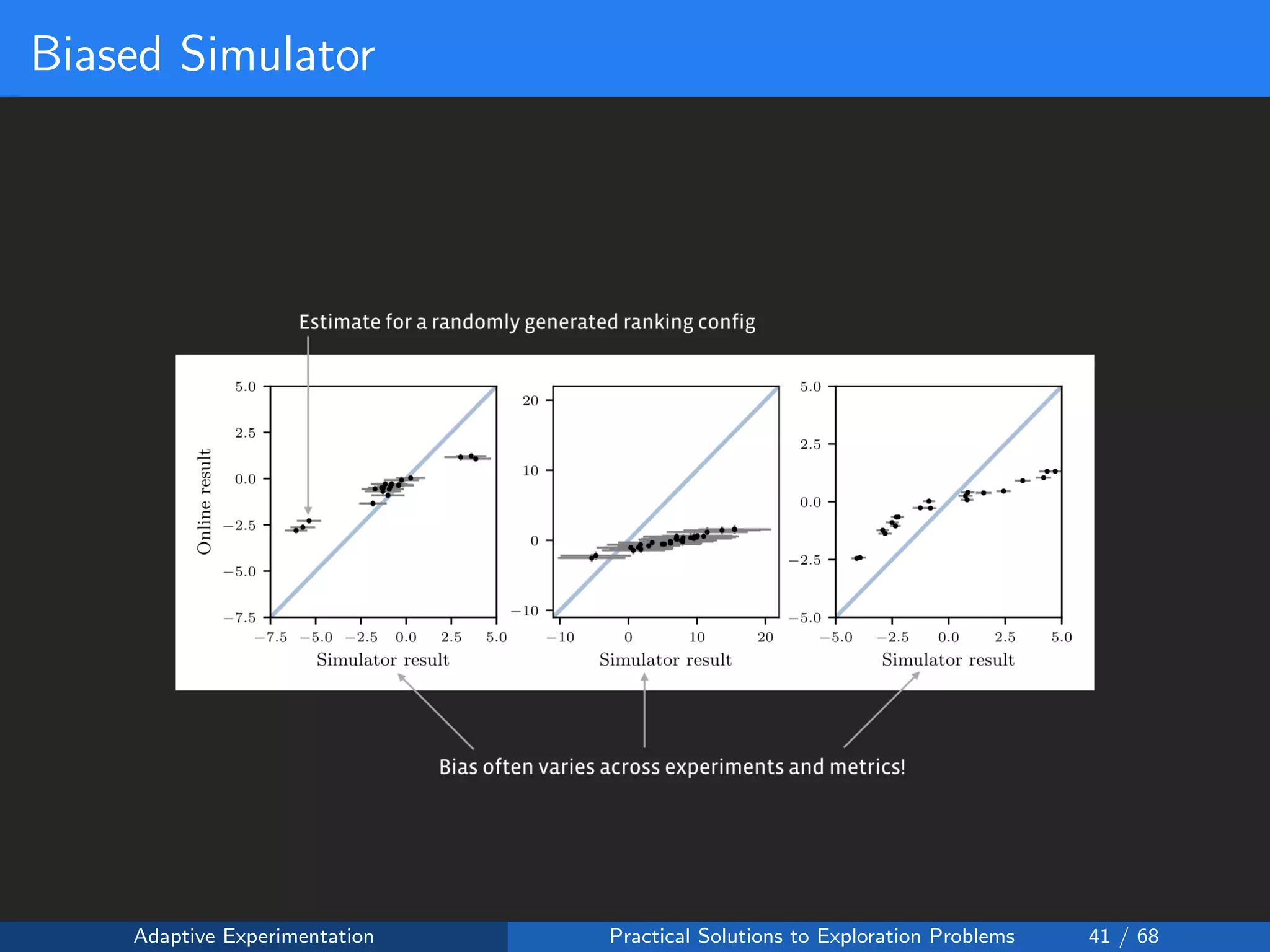
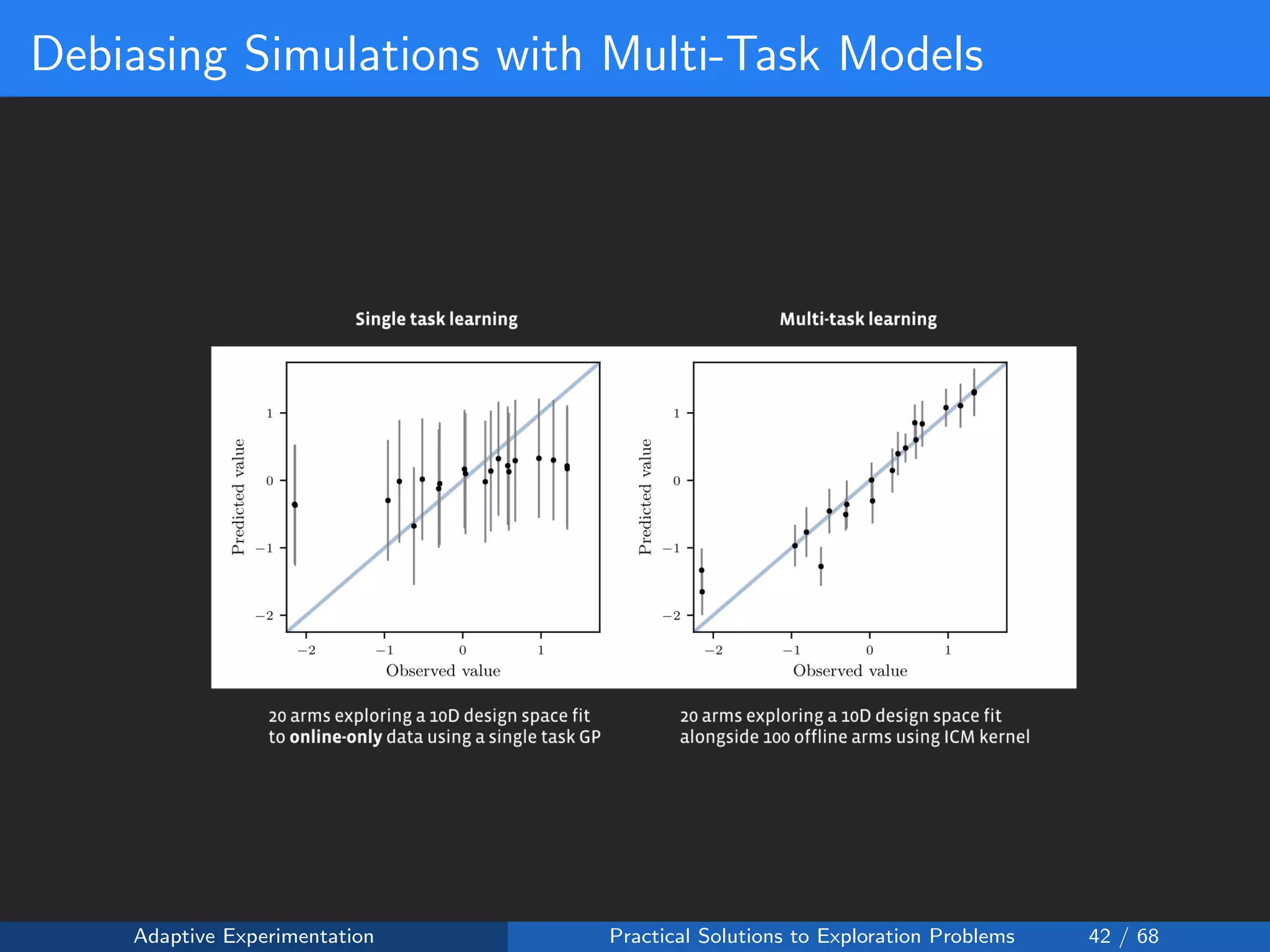
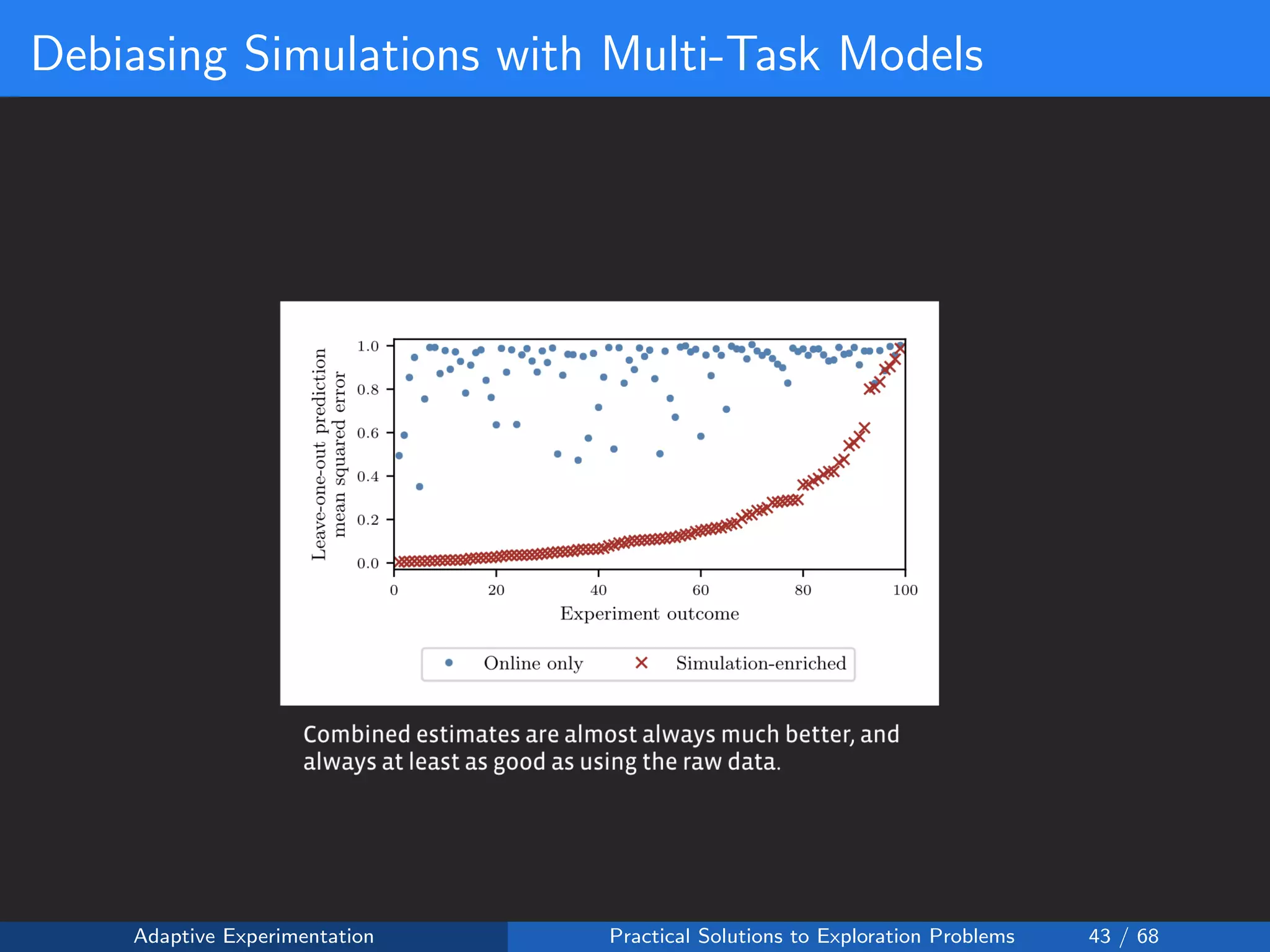
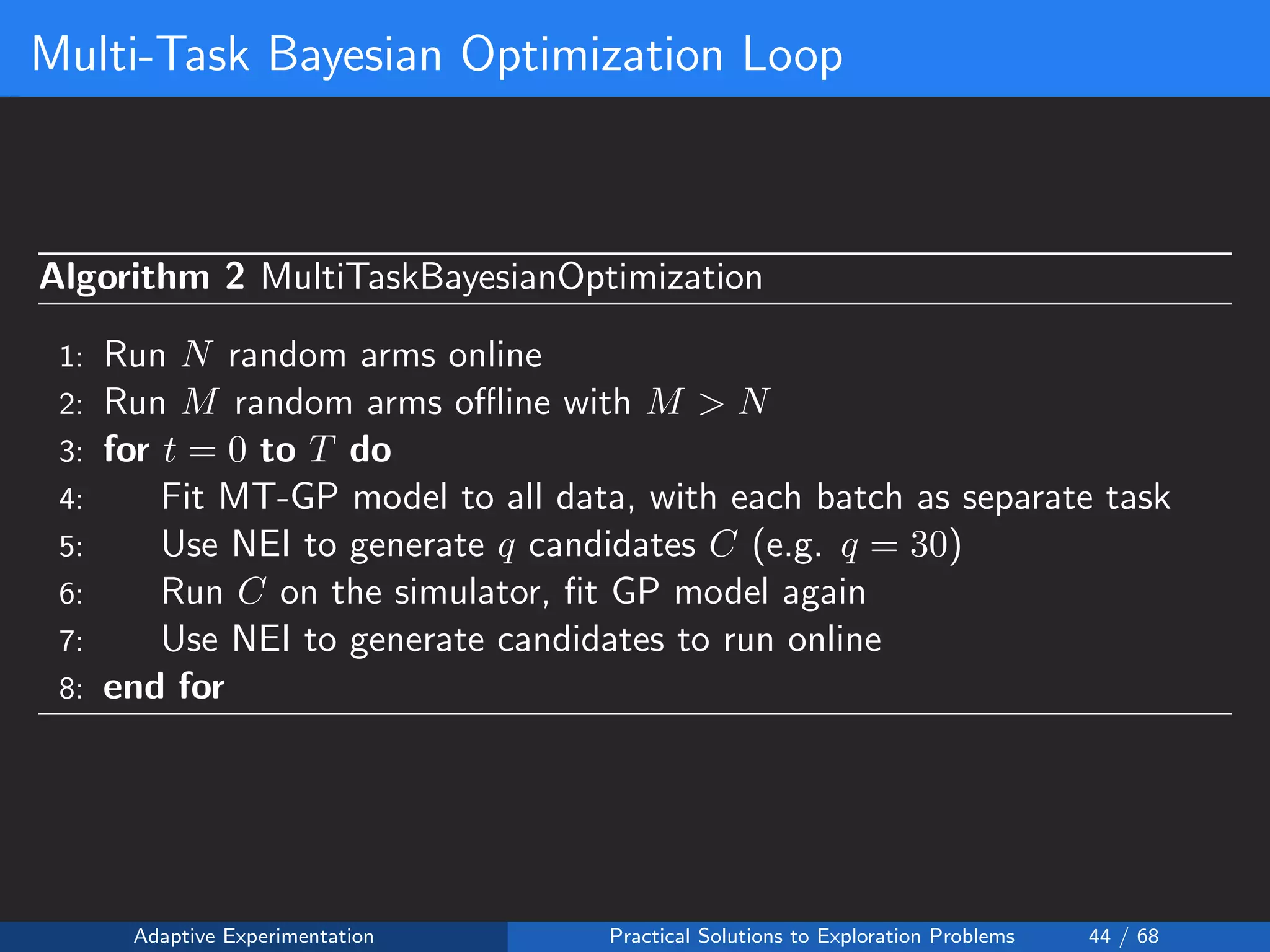
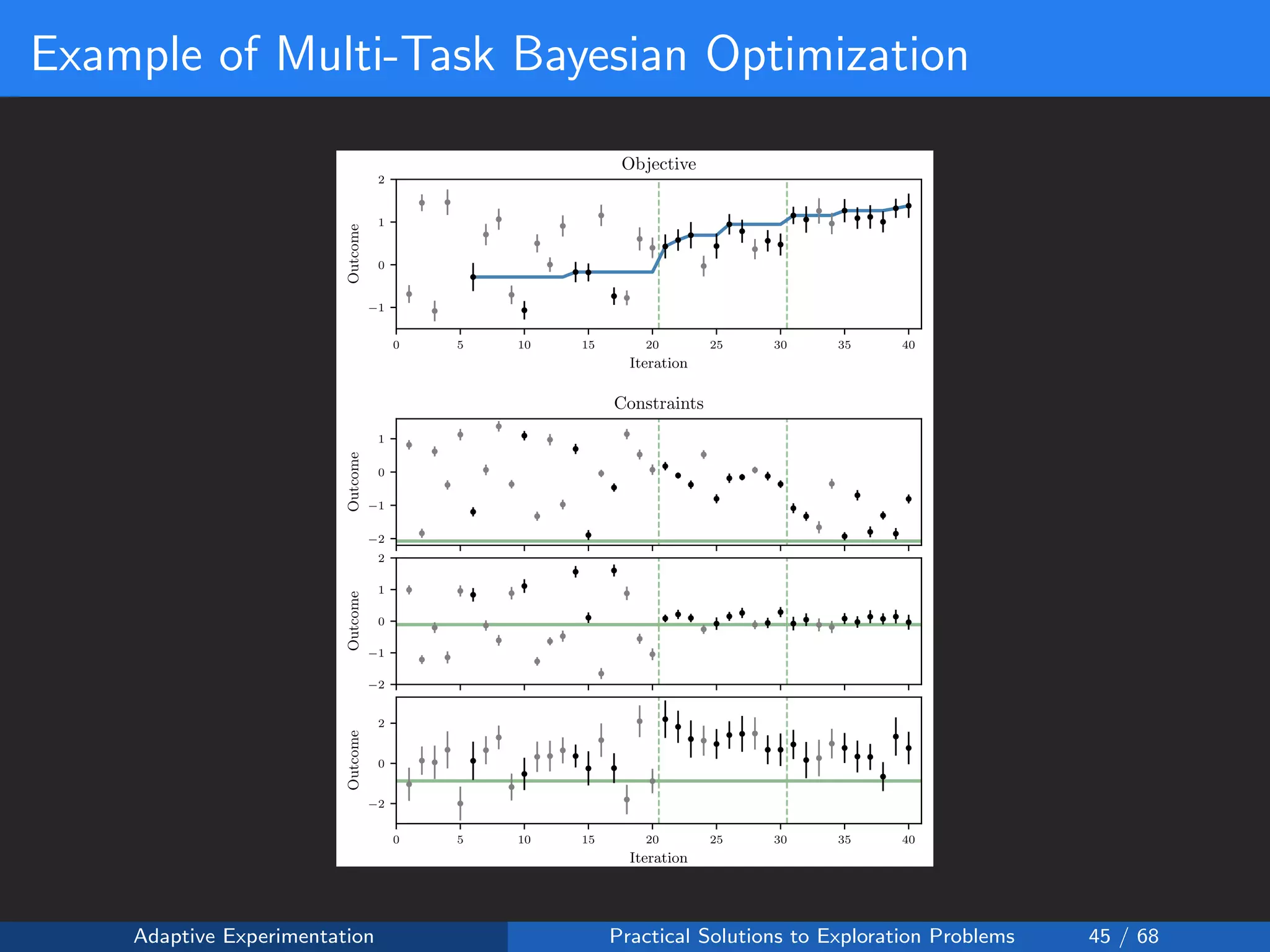
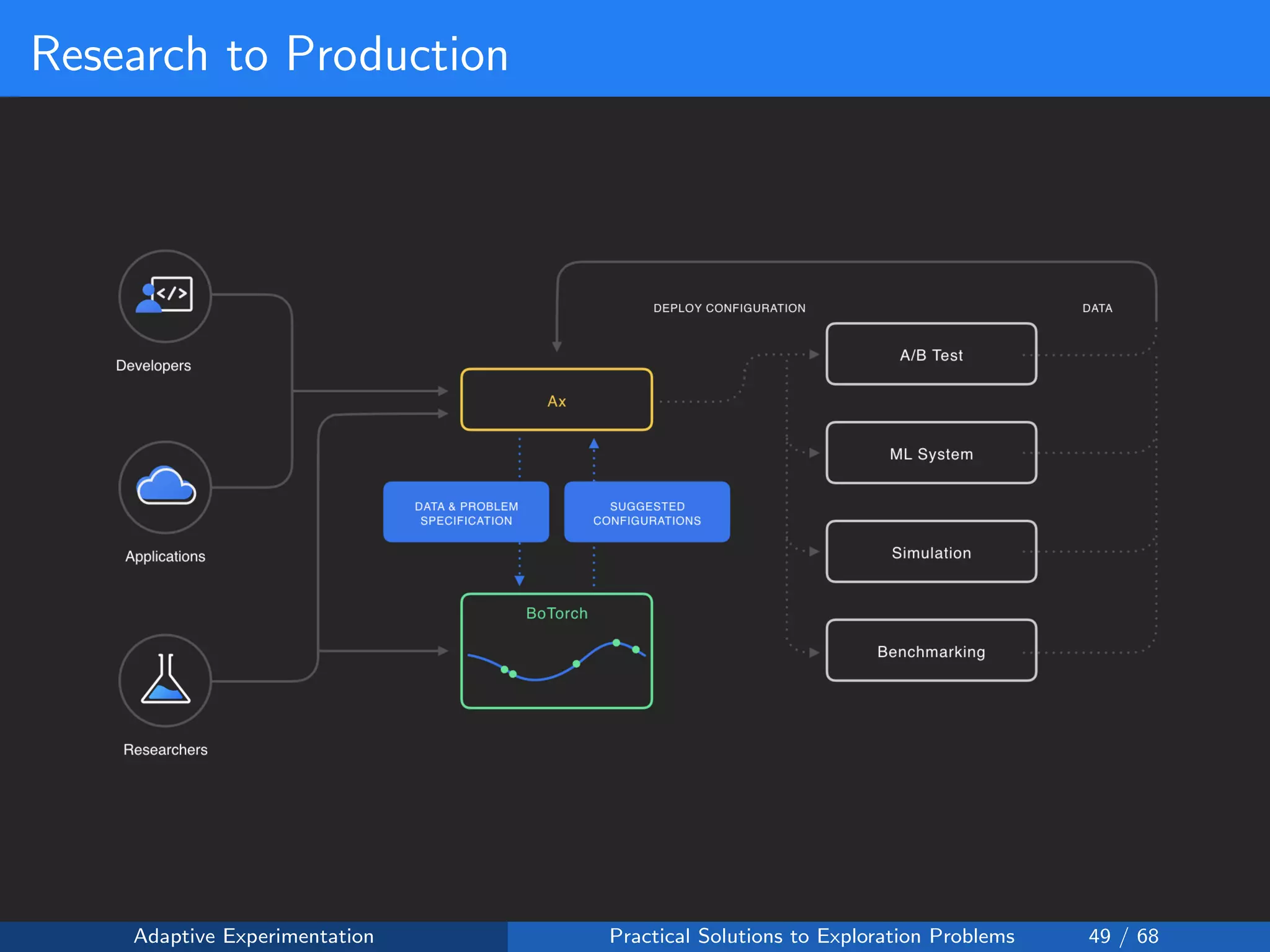
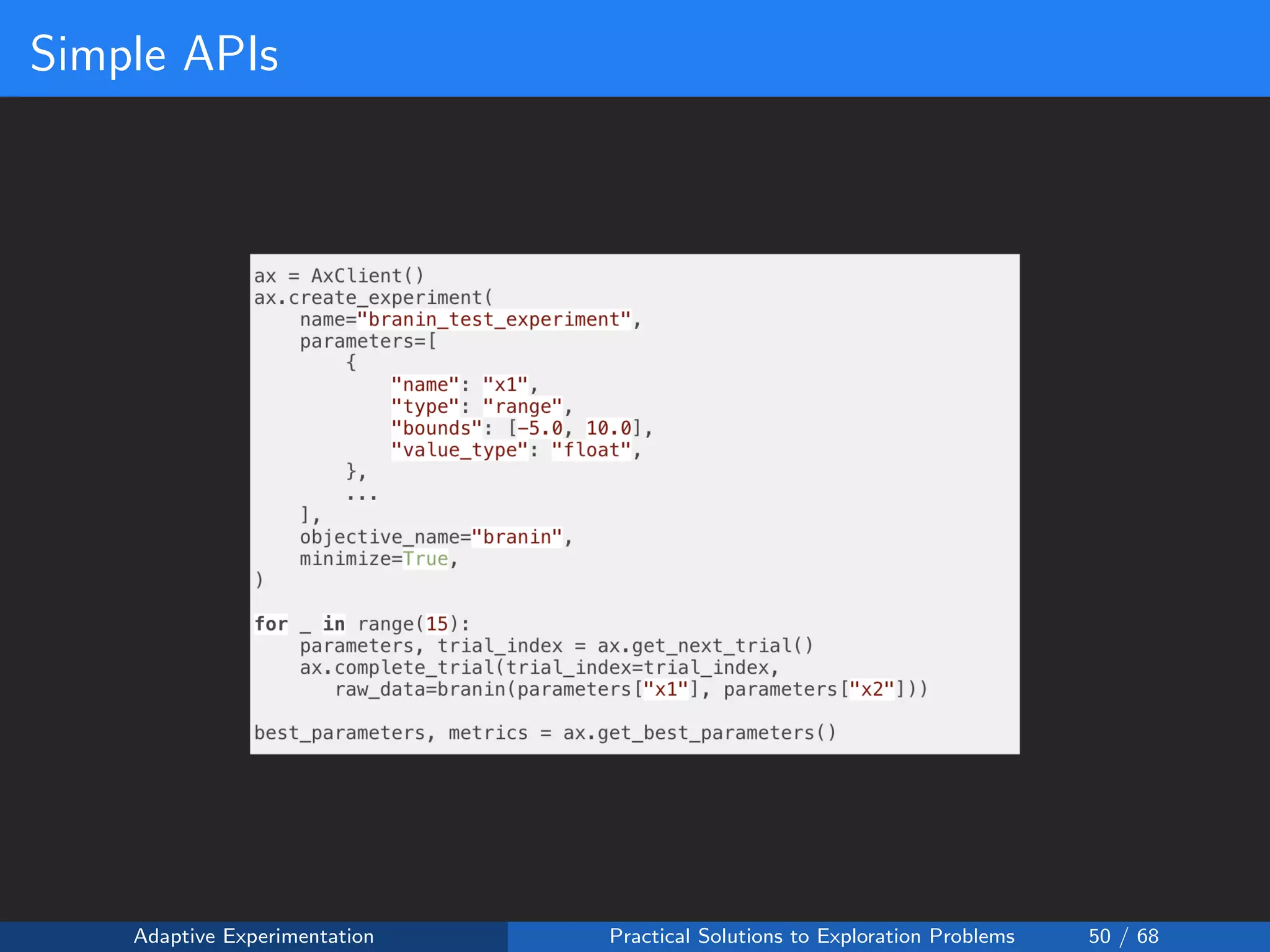
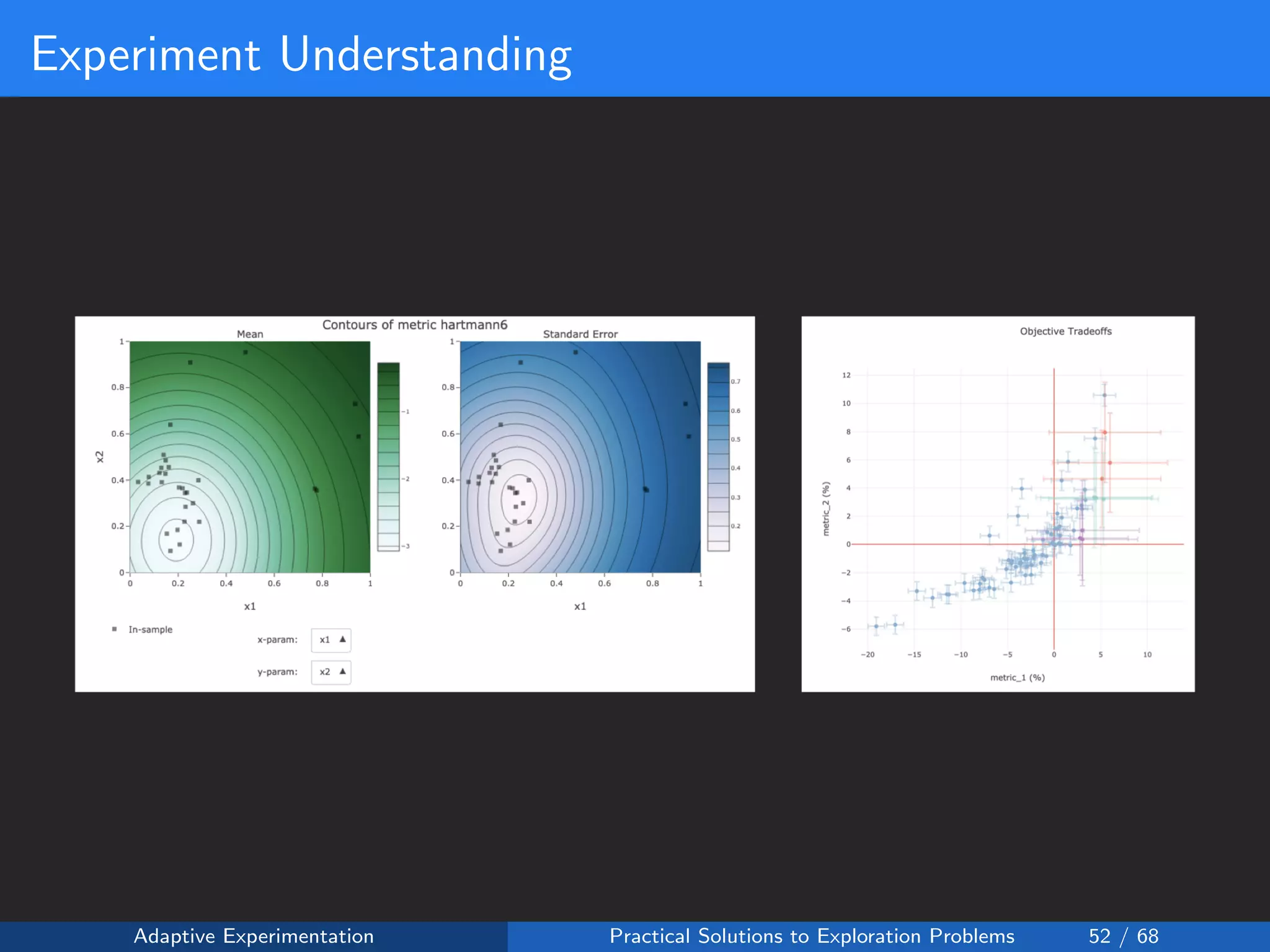
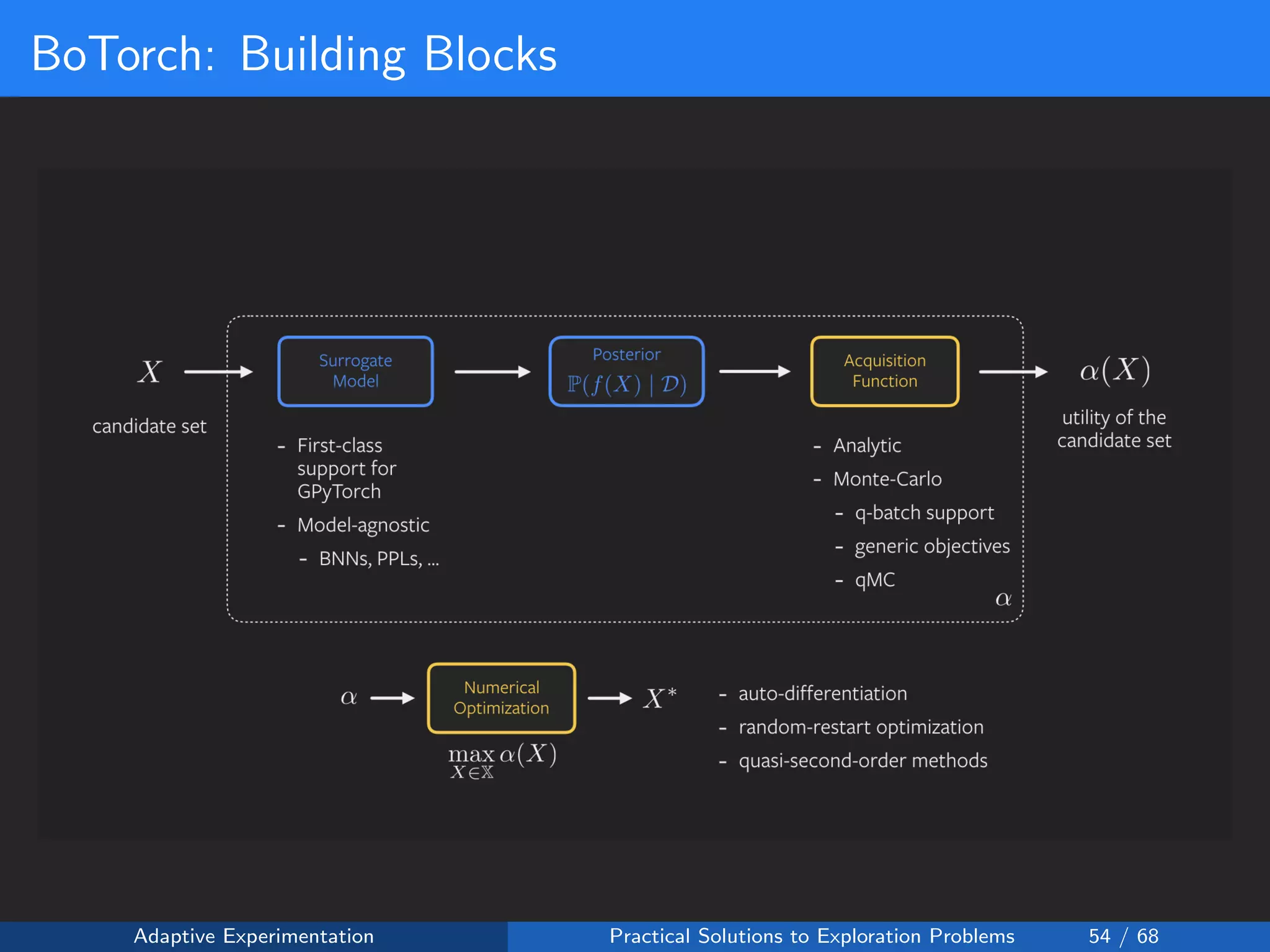
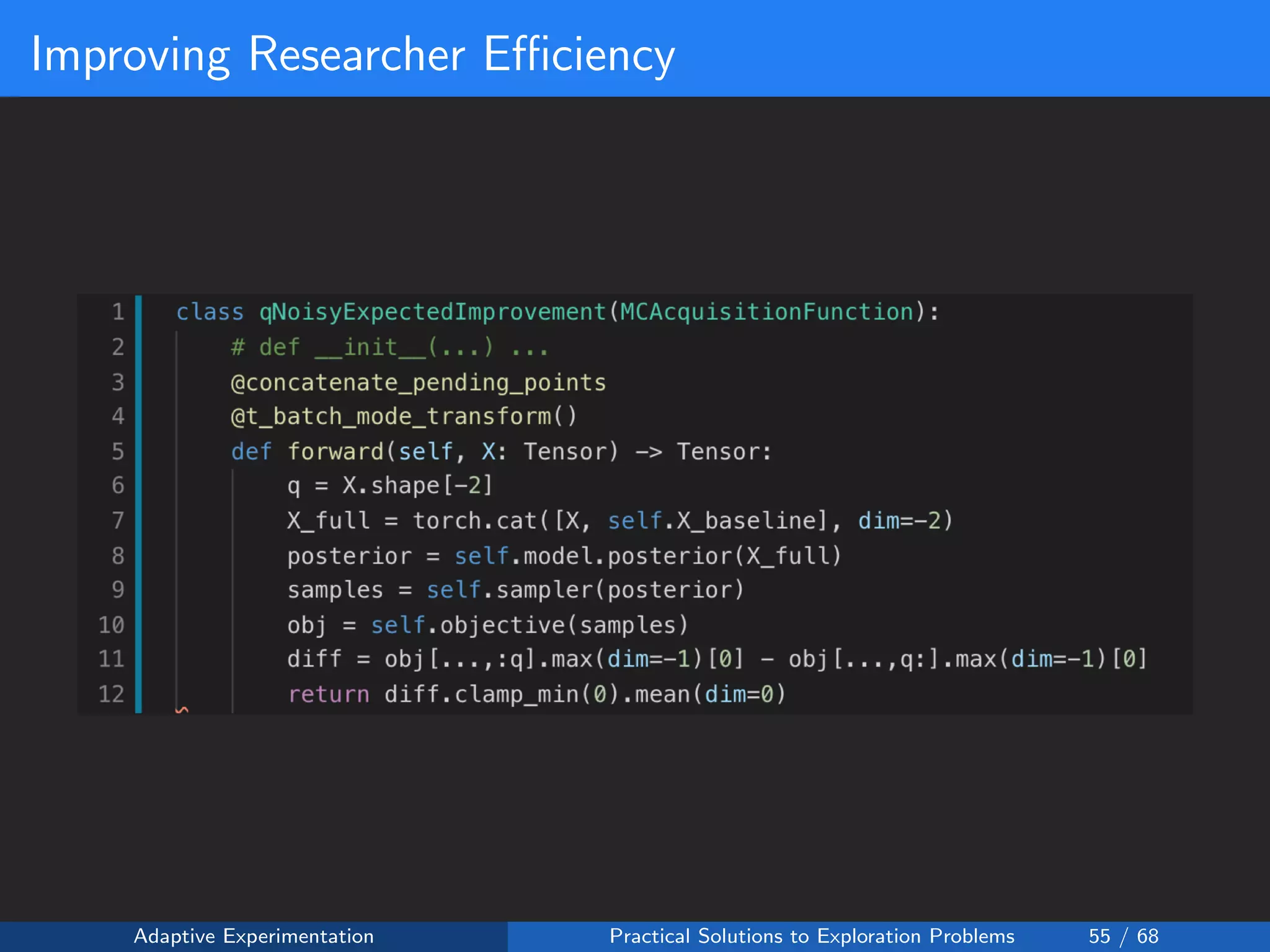
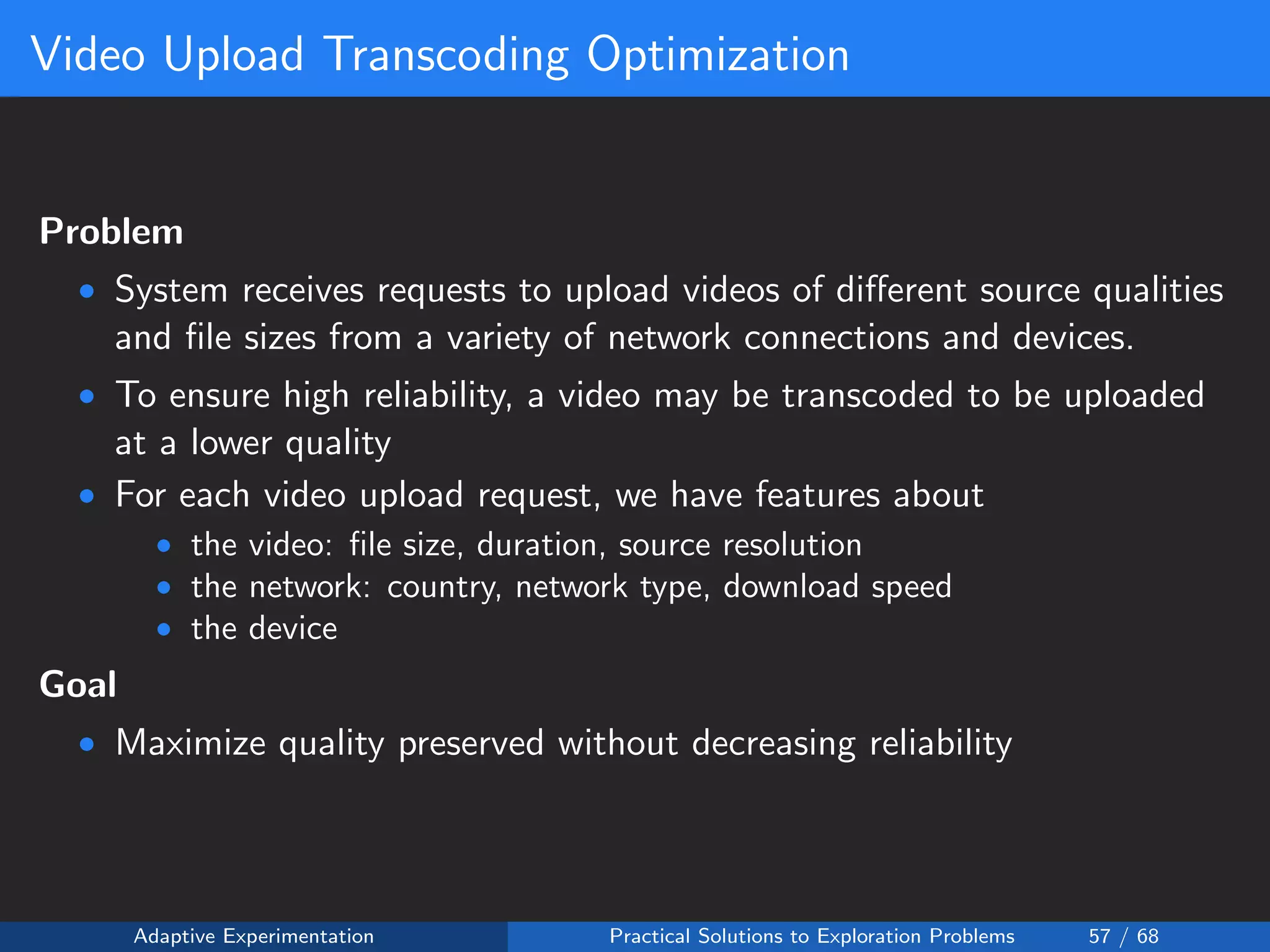
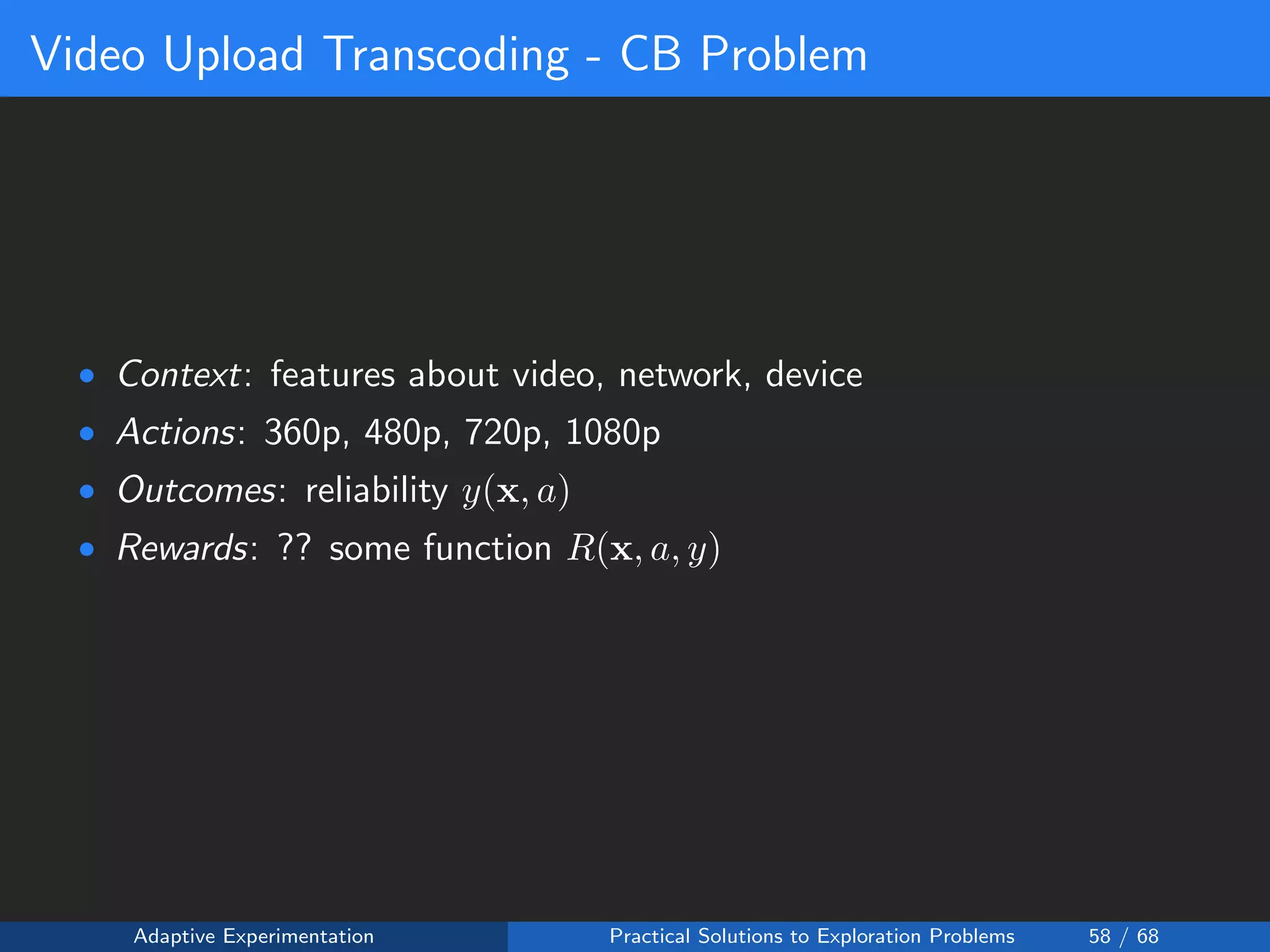
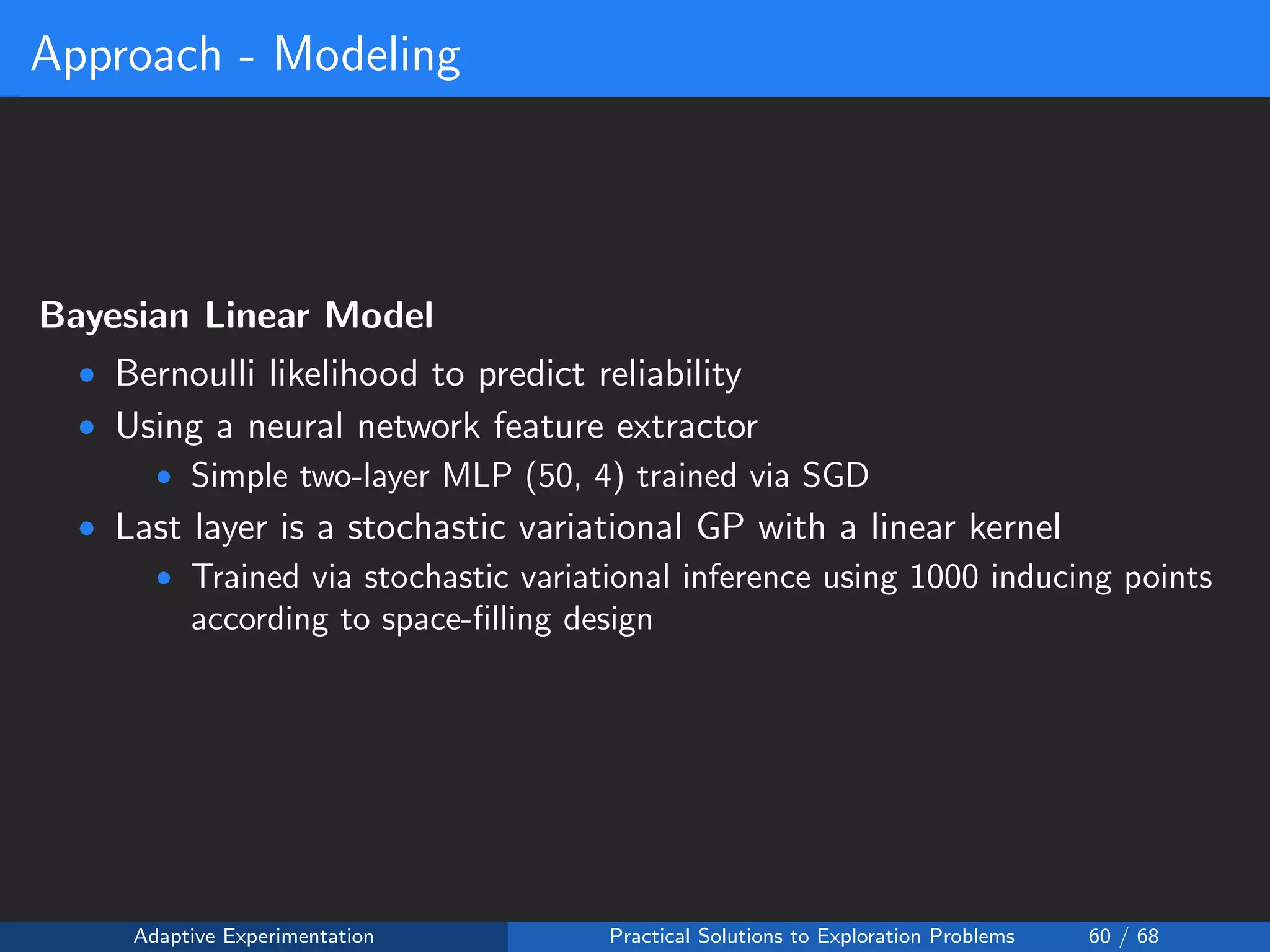
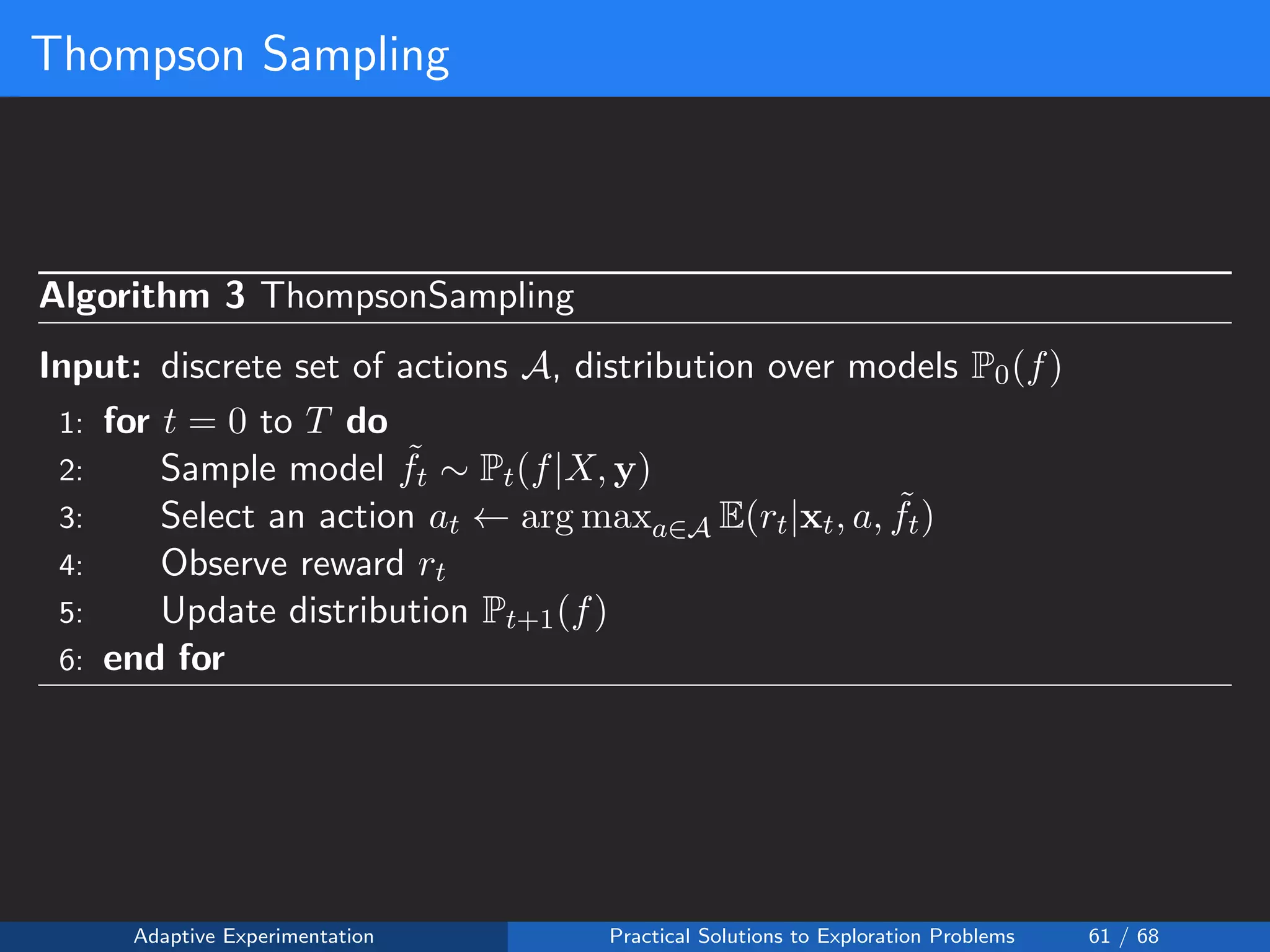
The document discusses adaptive experimentation at Facebook, focusing on practical solutions for exploration problems in decision-making through methods such as Bayesian optimization and contextual bandits. It outlines the methodology for implementing automated experimentation to balance performance and constraints, with applications including video upload transcoding optimization. Various tools and techniques, such as Ax and BoTorch, are introduced to improve and automate the experimentation process.




![Potential Contextualized Policies
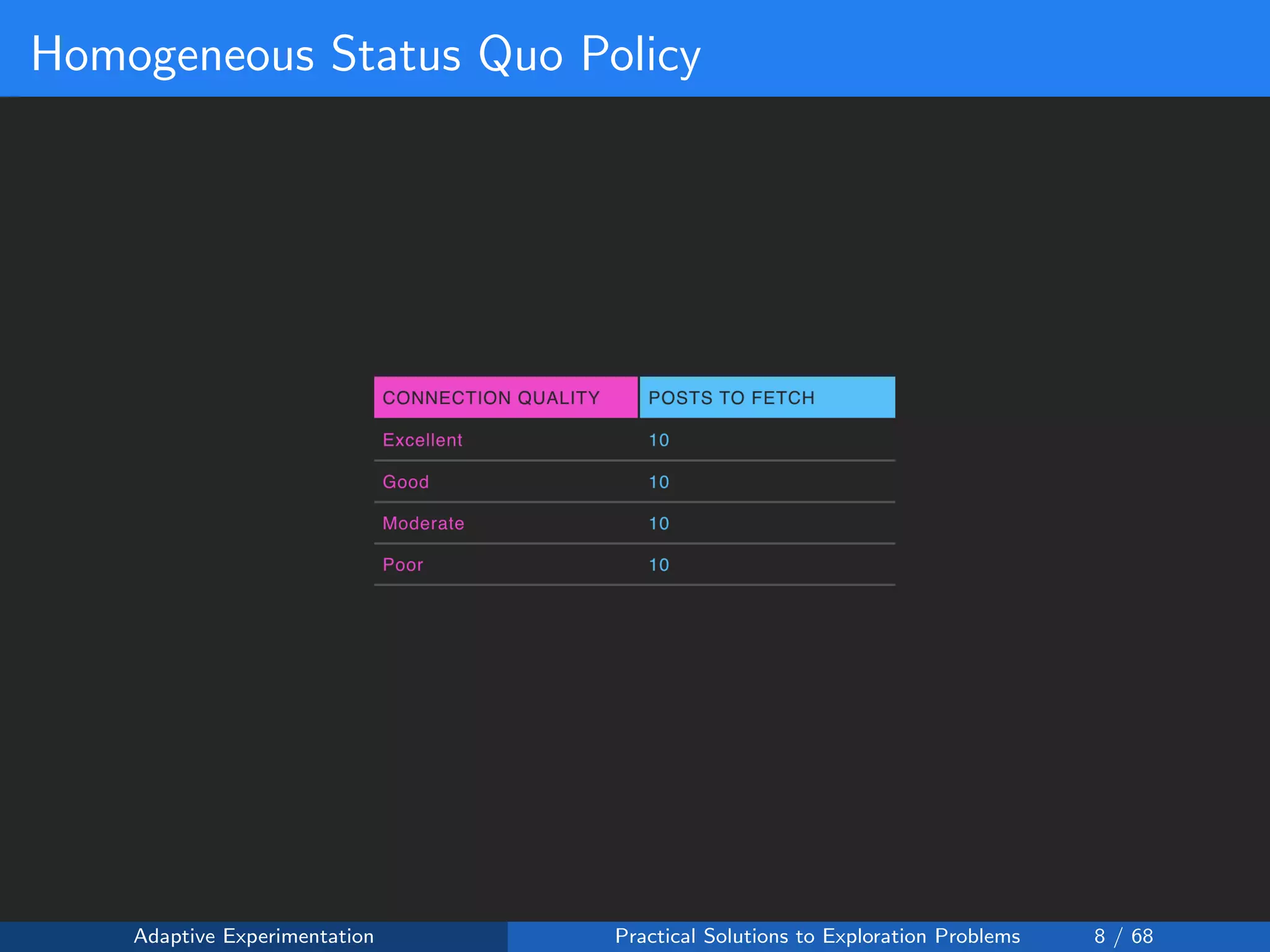
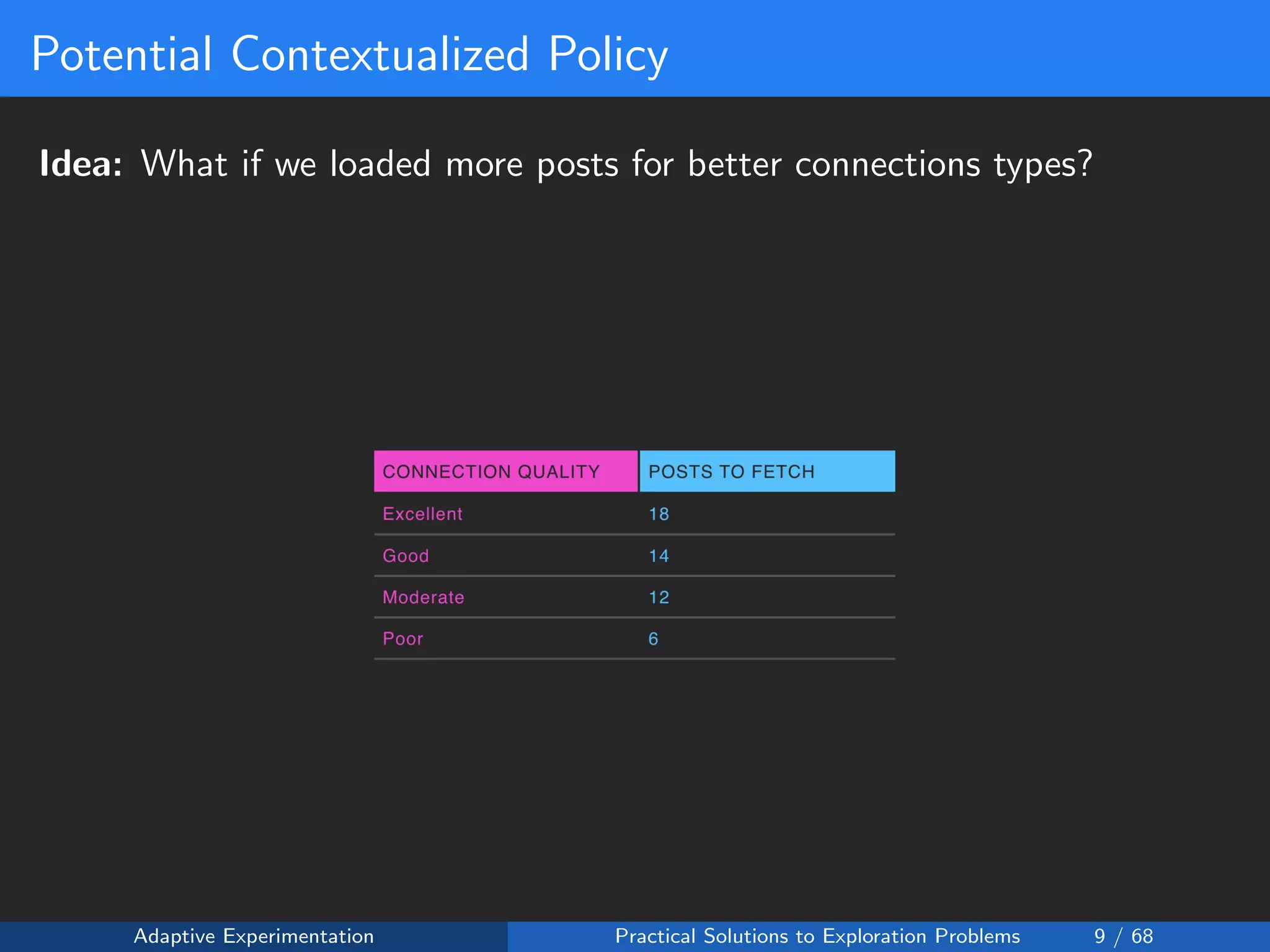
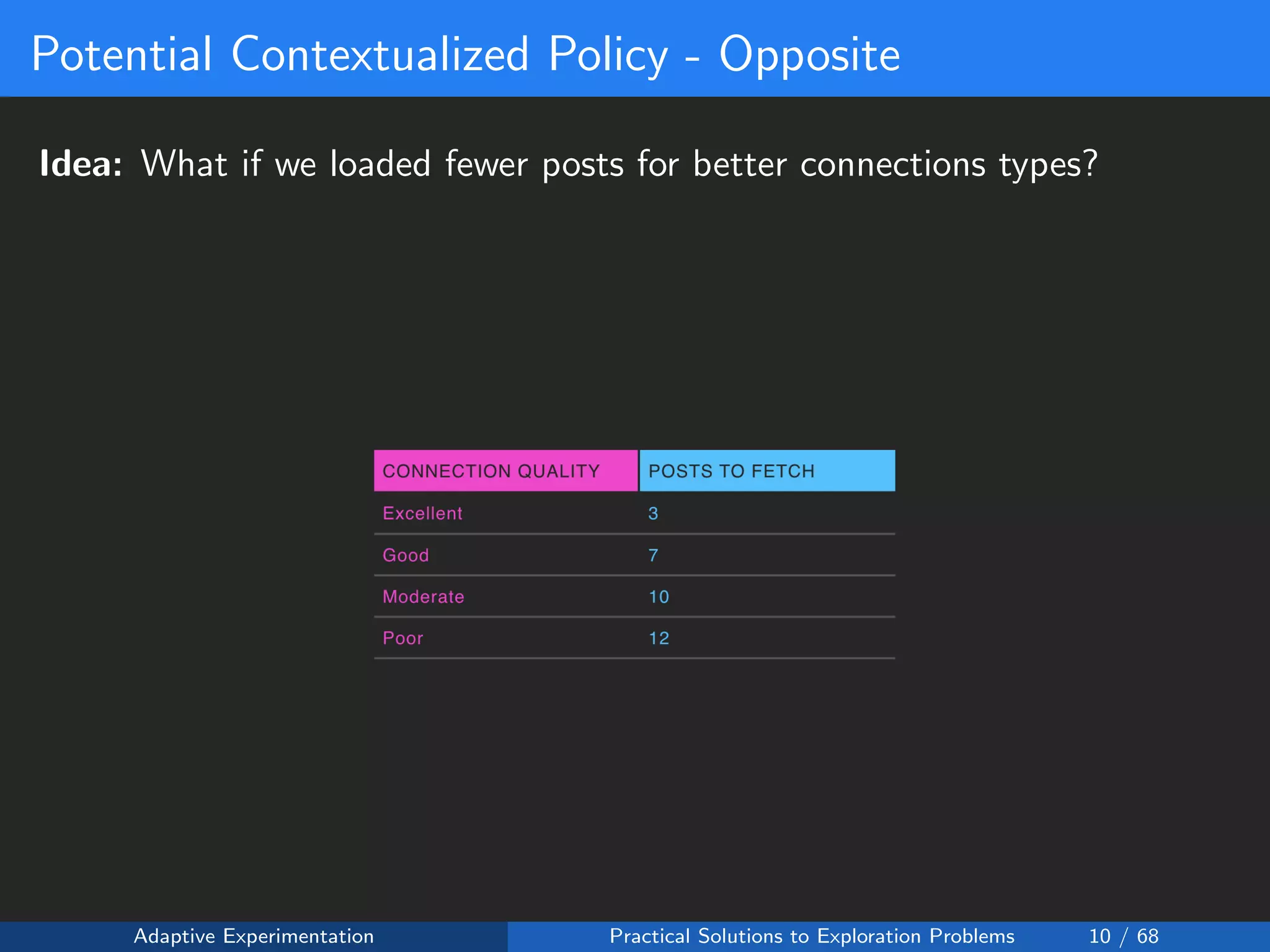
Suppose that for each connection type c:
• We could fetch any number of posts xc ∈ [2, 24]
• Then there are 224 = 234, 256 possible configurations to test!
Adaptive Experimentation Practical Solutions to Exploration Problems 11 / 68](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/daultonnetflixpracticalexploreexploit1-191017042254/75/Facebook-Talk-at-Netflix-ML-Platform-meetup-Sep-2019-12-2048.jpg)
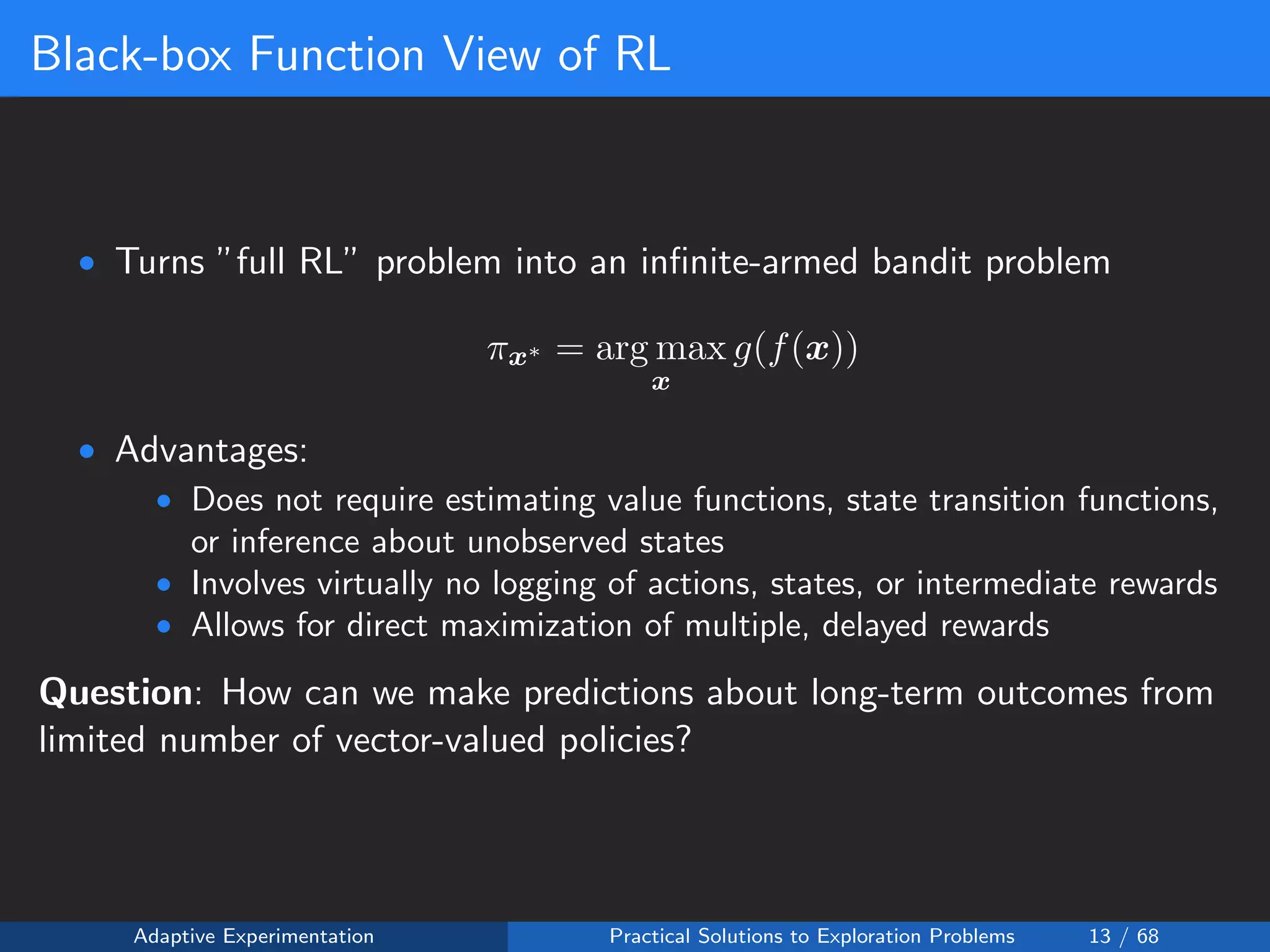
![Policies as Black-box Functions
The average treatment effect over all individuals can be expected to be
some smooth function of the policy table x = [x1, ..., xk]:
f(x) : Rk
→ R
Adaptive Experimentation Practical Solutions to Exploration Problems 12 / 68](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/daultonnetflixpracticalexploreexploit1-191017042254/75/Facebook-Talk-at-Netflix-ML-Platform-meetup-Sep-2019-13-2048.jpg)








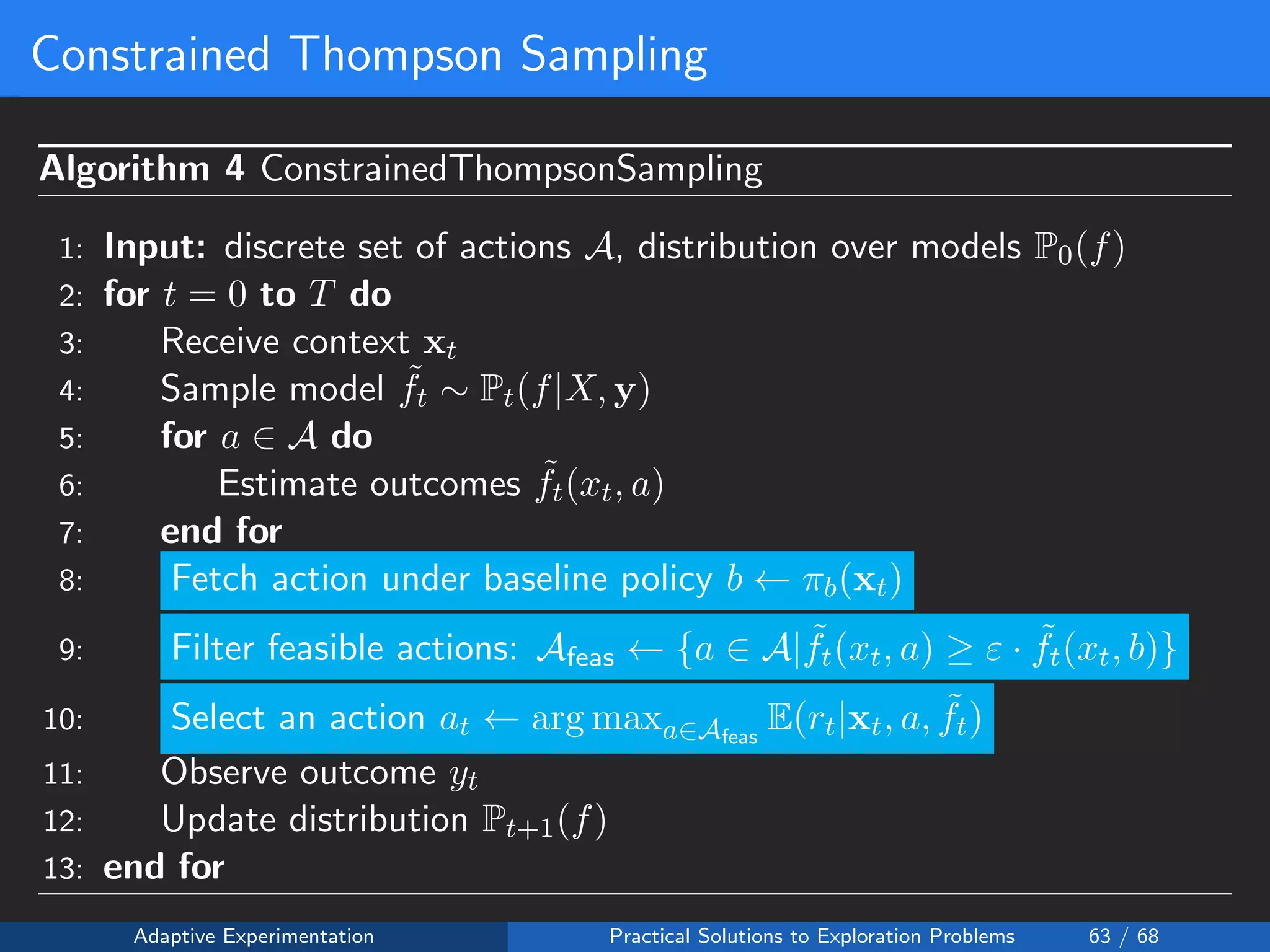
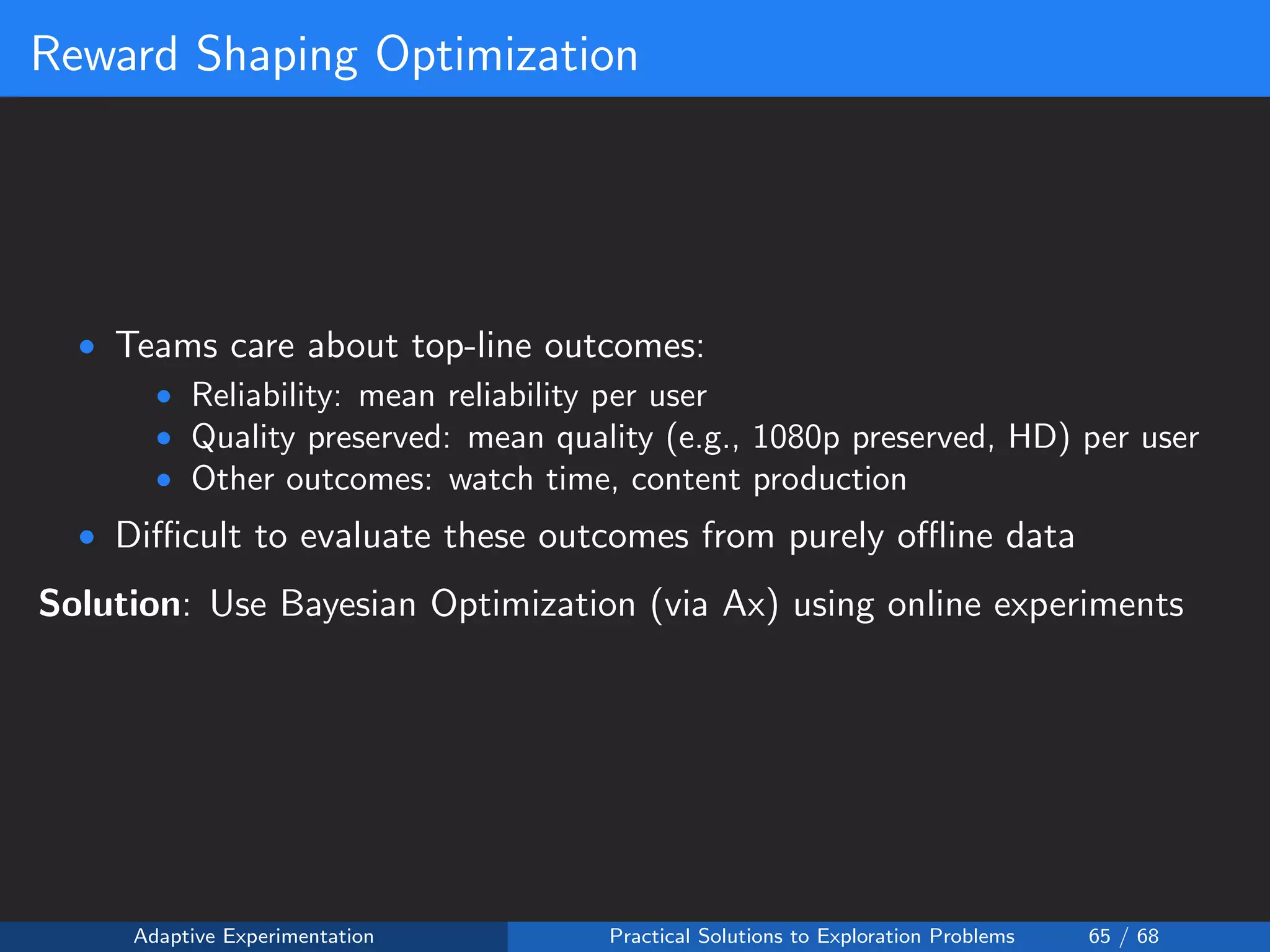
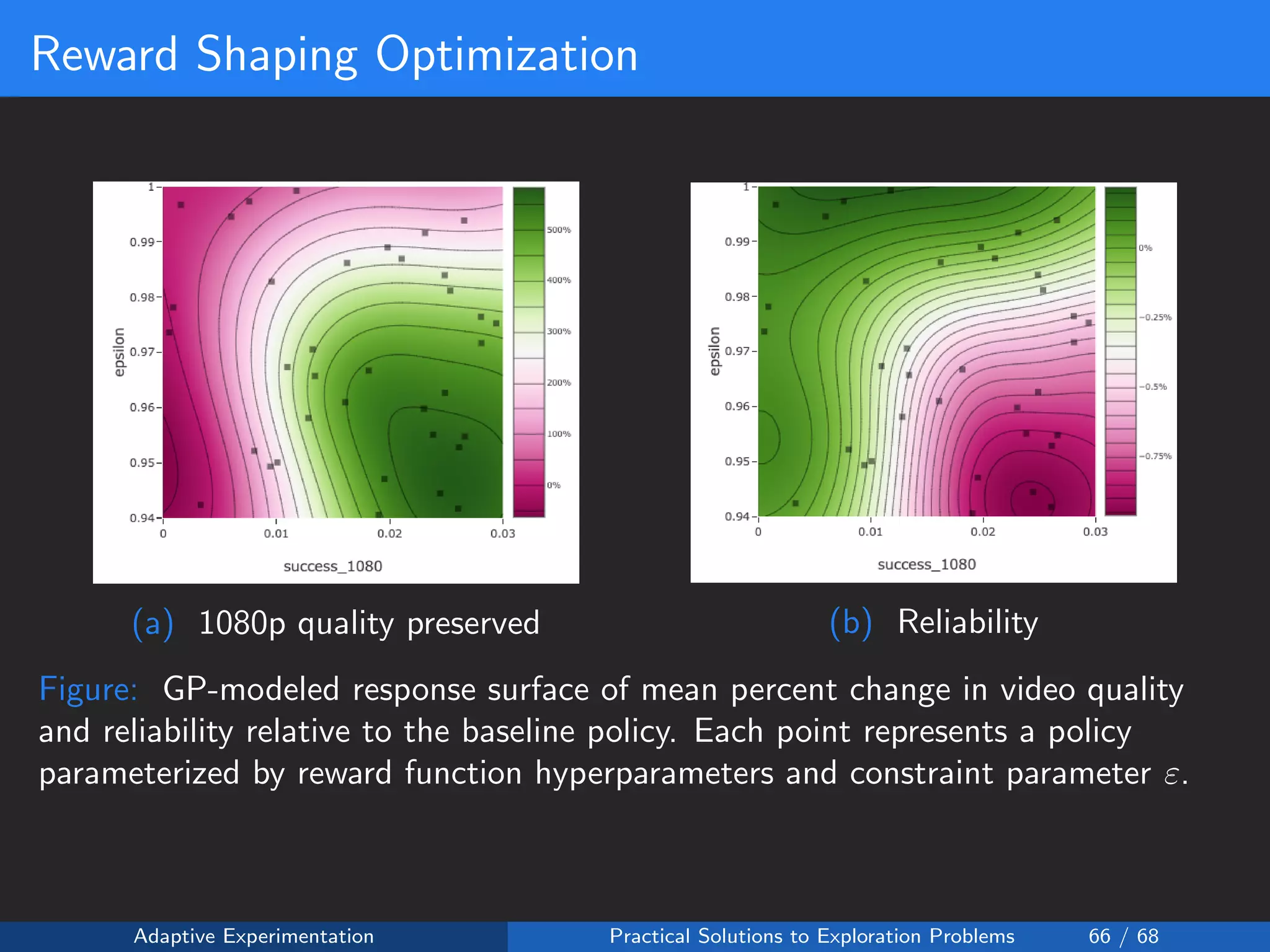
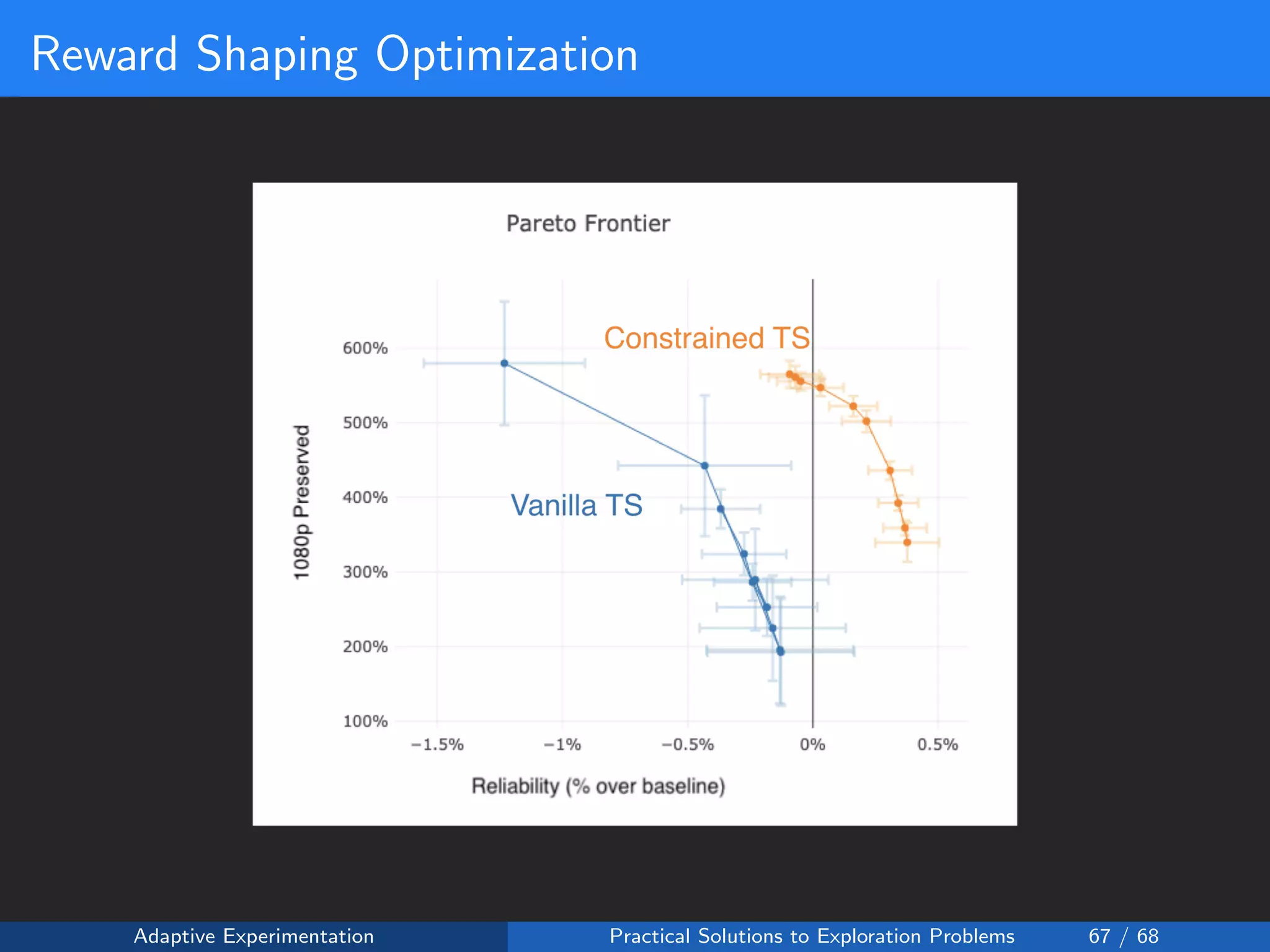
![Reward Shaping Setup
Reward Shaping:
• Reward is 0 if the upload is a failure
• Reward is fixed at 1 for a 360p upload success:
• Reward is monotonically increasing with quality:
R(y = 1, a) = 1 +
a ≤a
wa
where
wi ∈ (0.0, 0.2]
Safety Constraint: ε ∈ [0.95, 1.0]
Adaptive Experimentation Practical Solutions to Exploration Problems 64 / 68](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/daultonnetflixpracticalexploreexploit1-191017042254/75/Facebook-Talk-at-Netflix-ML-Platform-meetup-Sep-2019-65-2048.jpg)